Qun Liu
ARTIS: Agentic Risk-Aware Test-Time Scaling via Iterative Simulation
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Current test-time scaling (TTS) techniques enhance large language model (LLM) performance by allocating additional computation at inference time, yet they remain insufficient for agentic settings, where actions directly interact with external environments and their effects can be irreversible and costly. We propose ARTIS, Agentic Risk-Aware Test-Time Scaling via Iterative Simulation, a framework that decouples exploration from commitment by enabling test-time exploration through simulated interactions prior to real-world execution. This design allows extending inference-time computation to improve action-level reliability and robustness without incurring environmental risk. We further show that naive LLM-based simulators struggle to capture rare but high-impact failure modes, substantially limiting their effectiveness for agentic decision making. To address this limitation, we introduce a risk-aware tool simulator that emphasizes fidelity on failure-inducing actions via targeted data generation and rebalanced training. Experiments on multi-turn and multi-step agentic benchmarks demonstrate that iterative simulation substantially improves agent reliability, and that risk-aware simulation is essential for consistently realizing these gains across models and tasks.
The Synergy Dilemma of Long-CoT SFT and RL: Investigating Post-Training Techniques for Reasoning VLMs
Jul 10, 2025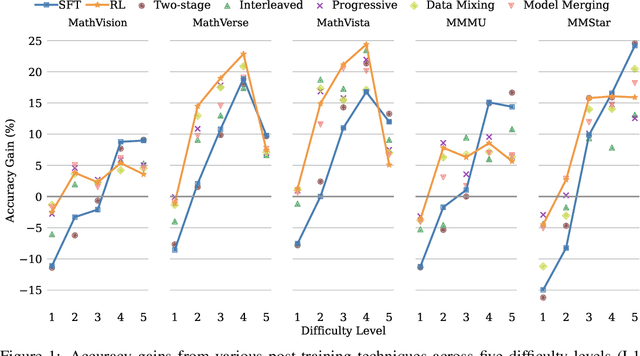
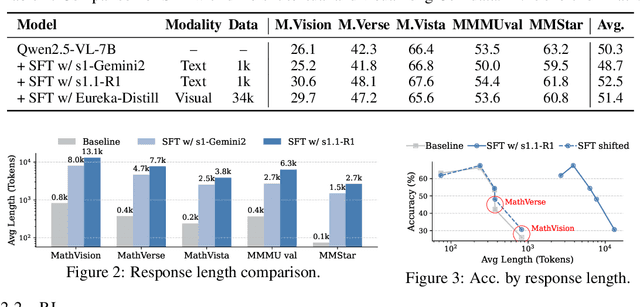
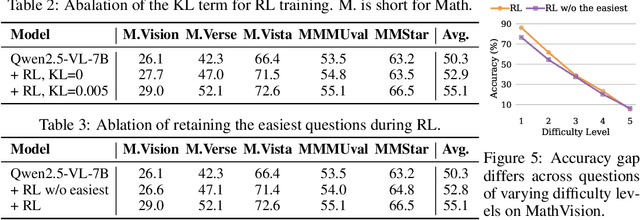
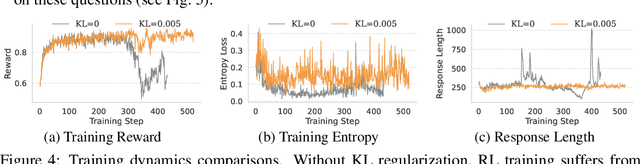
Abstract:Large vision-language models (VLMs) increasingly adopt post-training techniques such as long chain-of-thought (CoT) supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL) to elicit sophisticated reasoning. While these methods exhibit synergy in language-only models, their joint effectiveness in VLMs remains uncertain. We present a systematic investigation into the distinct roles and interplay of long-CoT SFT and RL across multiple multimodal reasoning benchmarks. We find that SFT improves performance on difficult questions by in-depth, structured reasoning, but introduces verbosity and degrades performance on simpler ones. In contrast, RL promotes generalization and brevity, yielding consistent improvements across all difficulty levels, though the improvements on the hardest questions are less prominent compared to SFT. Surprisingly, combining them through two-staged, interleaved, or progressive training strategies, as well as data mixing and model merging, all fails to produce additive benefits, instead leading to trade-offs in accuracy, reasoning style, and response length. This ``synergy dilemma'' highlights the need for more seamless and adaptive approaches to unlock the full potential of combined post-training techniques for reasoning VLMs.
Spectra-to-Structure and Structure-to-Spectra Inference Across the Periodic Table
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy (XAS) is a powerful technique for probing local atomic environments, yet its interpretation remains limited by the need for expert-driven analysis, computationally expensive simulations, and element-specific heuristics. Recent advances in machine learning have shown promise for accelerating XAS interpretation, but many existing models are narrowly focused on specific elements, edge types, or spectral regimes. In this work, we present XAStruct, a learning framework capable of both predicting XAS spectra from crystal structures and inferring local structural descriptors from XAS input. XAStruct is trained on a large-scale dataset spanning over 70 elements across the periodic table, enabling generalization to a wide variety of chemistries and bonding environments. The model includes the first machine learning approach for predicting neighbor atom types directly from XAS spectra, as well as a unified regression model for mean nearest-neighbor distance that requires no element-specific tuning. While we explored integrating the two pipelines into a single end-to-end model, empirical results showed performance degradation. As a result, the two tasks were trained independently to ensure optimal accuracy and task-specific performance. By combining deep neural networks for complex structure-property mappings with efficient baseline models for simpler tasks, XAStruct offers a scalable and extensible solution for data-driven XAS analysis and local structure inference. The source code will be released upon paper acceptance.
Beyond Homogeneous Attention: Memory-Efficient LLMs via Fourier-Approximated KV Cache
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models struggle with memory demands from the growing Key-Value (KV) cache as context lengths increase. Existing compression methods homogenize head dimensions or rely on attention-guided token pruning, often sacrificing accuracy or introducing computational overhead. We propose FourierAttention, a training-free framework that exploits the heterogeneous roles of transformer head dimensions: lower dimensions prioritize local context, while upper ones capture long-range dependencies. By projecting the long-context-insensitive dimensions onto orthogonal Fourier bases, FourierAttention approximates their temporal evolution with fixed-length spectral coefficients. Evaluations on LLaMA models show that FourierAttention achieves the best long-context accuracy on LongBench and Needle-In-A-Haystack (NIAH). Besides, a custom Triton kernel, FlashFourierAttention, is designed to optimize memory via streamlined read-write operations, enabling efficient deployment without performance compromise.
Safe: Enhancing Mathematical Reasoning in Large Language Models via Retrospective Step-aware Formal Verification
Jun 05, 2025



Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting has become the de facto method to elicit reasoning capabilities from large language models (LLMs). However, to mitigate hallucinations in CoT that are notoriously difficult to detect, current methods such as process reward models (PRMs) or self-consistency operate as opaque boxes and do not provide checkable evidence for their judgments, possibly limiting their effectiveness. To address this issue, we draw inspiration from the idea that "the gold standard for supporting a mathematical claim is to provide a proof". We propose a retrospective, step-aware formal verification framework $Safe$. Rather than assigning arbitrary scores, we strive to articulate mathematical claims in formal mathematical language Lean 4 at each reasoning step and provide formal proofs to identify hallucinations. We evaluate our framework $Safe$ across multiple language models and various mathematical datasets, demonstrating a significant performance improvement while offering interpretable and verifiable evidence. We also propose $FormalStep$ as a benchmark for step correctness theorem proving with $30,809$ formal statements. To the best of our knowledge, our work represents the first endeavor to utilize formal mathematical language Lean 4 for verifying natural language content generated by LLMs, aligning with the reason why formal mathematical languages were created in the first place: to provide a robust foundation for hallucination-prone human-written proofs.
Stepwise Reasoning Checkpoint Analysis: A Test Time Scaling Method to Enhance LLMs' Reasoning
May 23, 2025Abstract:Mathematical reasoning through Chain-of-Thought (CoT) has emerged as a powerful capability of Large Language Models (LLMs), which can be further enhanced through Test-Time Scaling (TTS) methods like Beam Search and DVTS. However, these methods, despite improving accuracy by allocating more computational resources during inference, often suffer from path homogenization and inefficient use of intermediate results. To address these limitations, we propose Stepwise Reasoning Checkpoint Analysis (SRCA), a framework that introduces checkpoints between reasoning steps. It incorporates two key strategies: (1) Answer-Clustered Search, which groups reasoning paths by their intermediate checkpoint answers to maintain diversity while ensuring quality, and (2) Checkpoint Candidate Augmentation, which leverages all intermediate answers for final decision-making. Our approach effectively reduces path homogenization and creates a fault-tolerant mechanism by utilizing high-quality intermediate results. Experimental results show that SRCA improves reasoning accuracy compared to existing TTS methods across various mathematical datasets.
ToolACE-R: Tool Learning with Adaptive Self-Refinement
Apr 02, 2025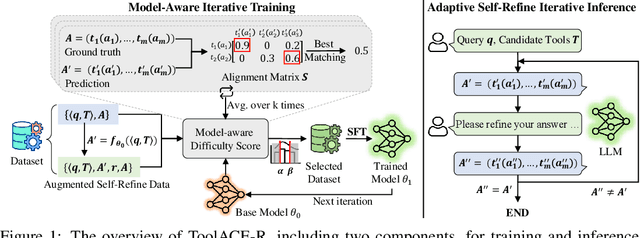
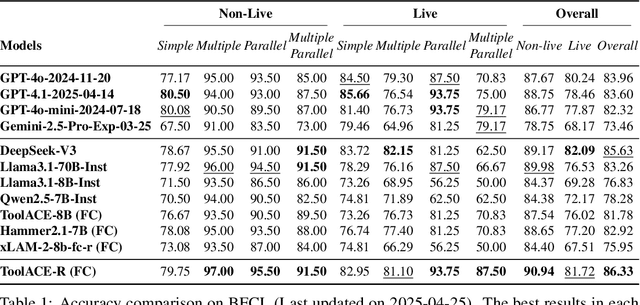
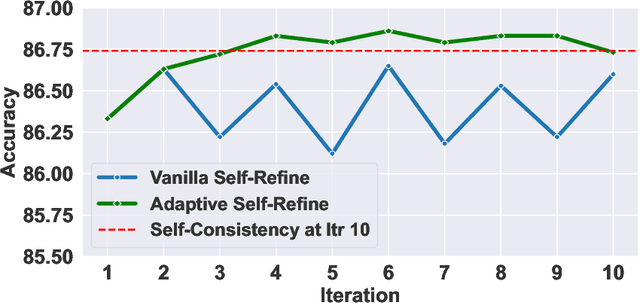
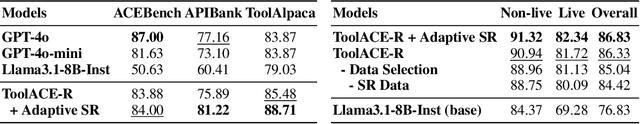
Abstract:Tool learning, which allows Large Language Models (LLMs) to leverage external tools for solving complex user tasks, has emerged as a promising avenue for extending model capabilities. However, current approaches primarily focus on data synthesis for fine-tuning LLMs to invoke tools effectively, largely ignoring how to fully stimulate the potential of the model. In this paper, we propose ToolACE-R, a novel method that introduces adaptive self-refinement for tool invocations. Our approach features a model-aware iterative training procedure that progressively incorporates more training samples based on the model's evolving capabilities. Additionally, it allows LLMs to iteratively refine their tool calls, optimizing performance without requiring external feedback. To further enhance computational efficiency, we integrate an adaptive mechanism when scaling the inference time, enabling the model to autonomously determine when to stop the refinement process. We conduct extensive experiments across several benchmark datasets, showing that ToolACE-R achieves competitive performance compared to advanced API-based models, even without any refinement. Furthermore, its performance can be further improved efficiently through adaptive self-refinement. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, which is compatible with base models of various sizes, offering a promising direction for more efficient tool learning.
DAST: Difficulty-Aware Self-Training on Large Language Models
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:Present Large Language Models (LLM) self-training methods always under-sample on challenging queries, leading to inadequate learning on difficult problems which limits LLMs' ability. Therefore, this work proposes a difficulty-aware self-training (DAST) framework that focuses on improving both the quantity and quality of self-generated responses on challenging queries during self-training. DAST is specified in three components: 1) sampling-based difficulty level estimation, 2) difficulty-aware data augmentation, and 3) the self-training algorithm using SFT and DPO respectively. Experiments on mathematical tasks demonstrate the effectiveness and generalization of DAST, highlighting the critical role of difficulty-aware strategies in advancing LLM self-training.
KnowLogic: A Benchmark for Commonsense Reasoning via Knowledge-Driven Data Synthesis
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:Current evaluations of commonsense reasoning in LLMs are hindered by the scarcity of natural language corpora with structured annotations for reasoning tasks. To address this, we introduce KnowLogic, a benchmark generated through a knowledge-driven synthetic data strategy. KnowLogic integrates diverse commonsense knowledge, plausible scenarios, and various types of logical reasoning. One of the key advantages of KnowLogic is its adjustable difficulty levels, allowing for flexible control over question complexity. It also includes fine-grained labels for in-depth evaluation of LLMs' reasoning abilities across multiple dimensions. Our benchmark consists of 3,000 bilingual (Chinese and English) questions across various domains, and presents significant challenges for current LLMs, with the highest-performing model achieving only 69.57\%. Our analysis highlights common errors, such as misunderstandings of low-frequency commonsense, logical inconsistencies, and overthinking. This approach, along with our benchmark, provides a valuable tool for assessing and enhancing LLMs' commonsense reasoning capabilities and can be applied to a wide range of knowledge domains.
Tgea: An error-annotated dataset and benchmark tasks for text generation from pretrained language models
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:In order to deeply understand the capability of pretrained language models in text generation and conduct a diagnostic evaluation, we propose TGEA, an error-annotated dataset with multiple benchmark tasks for text generation from pretrained language models (PLMs). We use carefully selected prompt words to guide GPT-2 to generate candidate sentences, from which we select 47K for error annotation. Crowdsourced workers manually check each of these sentences and detect 12k erroneous sentences. We create an error taxonomy to cover 24 types of errors occurring in these erroneous sentences according to the nature of errors with respect to linguistics and knowledge (eg, common sense). For each erroneous span in PLM-generated sentences, we also detect another span that is closely associated with it. Each error is hence manually labeled with comprehensive annotations, including the span of the error, the associated span, minimal correction to the error, the type of the error, and rationale behind the error. Apart from the fully annotated dataset, we also present a detailed description of the data collection procedure, statistics and analysis of the dataset. This is the first dataset with comprehensive annotations for PLM-generated texts, which facilitates the diagnostic evaluation of PLM-based text generation. Furthermore, we use TGEA as a benchmark dataset and propose a series of automatic diagnosis tasks, including error detection, error type classification, associated span detection, error rationale generation, to further promote future study on the automatic error detection and correction on texts generated by pretrained language models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge