Lanqing Hong
AEQ-Bench: Measuring Empathy of Omni-Modal Large Models
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:While the automatic evaluation of omni-modal large models (OLMs) is essential, assessing empathy remains a significant challenge due to its inherent affectivity. To investigate this challenge, we introduce AEQ-Bench (Audio Empathy Quotient Benchmark), a novel benchmark to systematically assess two core empathetic capabilities of OLMs: (i) generating empathetic responses by comprehending affective cues from multi-modal inputs (audio + text), and (ii) judging the empathy of audio responses without relying on text transcription. Compared to existing benchmarks, AEQ-Bench incorporates two novel settings that vary in context specificity and speech tone. Comprehensive assessment across linguistic and paralinguistic metrics reveals that (1) OLMs trained with audio output capabilities generally outperformed models with text-only outputs, and (2) while OLMs align with human judgments for coarse-grained quality assessment, they remain unreliable for evaluating fine-grained paralinguistic expressiveness.
InSight-o3: Empowering Multimodal Foundation Models with Generalized Visual Search
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:The ability for AI agents to "think with images" requires a sophisticated blend of reasoning and perception. However, current open multimodal agents still largely fall short on the reasoning aspect crucial for real-world tasks like analyzing documents with dense charts/diagrams and navigating maps. To address this gap, we introduce O3-Bench, a new benchmark designed to evaluate multimodal reasoning with interleaved attention to visual details. O3-Bench features challenging problems that require agents to piece together subtle visual information from distinct image areas through multi-step reasoning. The problems are highly challenging even for frontier systems like OpenAI o3, which only obtains 40.8% accuracy on O3-Bench. To make progress, we propose InSight-o3, a multi-agent framework consisting of a visual reasoning agent (vReasoner) and a visual search agent (vSearcher) for which we introduce the task of generalized visual search -- locating relational, fuzzy, or conceptual regions described in free-form language, beyond just simple objects or figures in natural images. We then present a multimodal LLM purpose-trained for this task via reinforcement learning. As a plug-and-play agent, our vSearcher empowers frontier multimodal models (as vReasoners), significantly improving their performance on a wide range of benchmarks. This marks a concrete step towards powerful o3-like open systems. Our code and dataset can be found at https://github.com/m-Just/InSight-o3 .
Developing a Grounded View of AI
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:As a capability coming from computation, how does AI differ fundamentally from the capabilities delivered by rule-based software program? The paper examines the behavior of artificial intelligence (AI) from engineering points of view to clarify its nature and limits. The paper argues that the rationality underlying humanity's impulse to pursue, articulate, and adhere to rules deserves to be valued and preserved. Identifying where rule-based practical rationality ends is the beginning of making it aware until action. Although the rules of AI behaviors are still hidden or only weakly observable, the paper has proposed a methodology to make a sense of discrimination possible and practical to identify the distinctions of the behavior of AI models with three types of decisions. It is a prerequisite for human responsibilities with alternative possibilities, considering how and when to use AI. It would be a solid start for people to ensure AI system soundness for the well-being of humans, society, and the environment.
ECCV 2024 W-CODA: 1st Workshop on Multimodal Perception and Comprehension of Corner Cases in Autonomous Driving
Jul 02, 2025
Abstract:In this paper, we present details of the 1st W-CODA workshop, held in conjunction with the ECCV 2024. W-CODA aims to explore next-generation solutions for autonomous driving corner cases, empowered by state-of-the-art multimodal perception and comprehension techniques. 5 Speakers from both academia and industry are invited to share their latest progress and opinions. We collect research papers and hold a dual-track challenge, including both corner case scene understanding and generation. As the pioneering effort, we will continuously bridge the gap between frontier autonomous driving techniques and fully intelligent, reliable self-driving agents robust towards corner cases.
Perceptual Decoupling for Scalable Multi-modal Reasoning via Reward-Optimized Captioning
Jun 05, 2025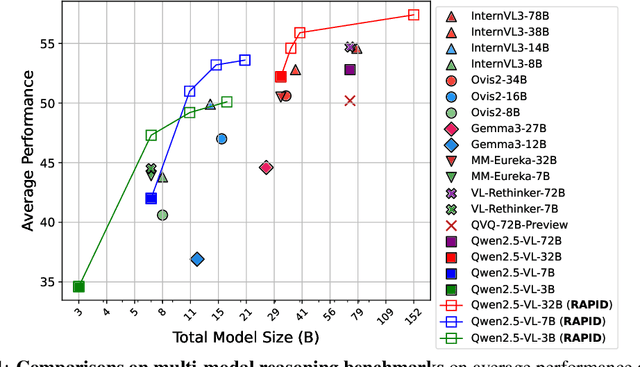
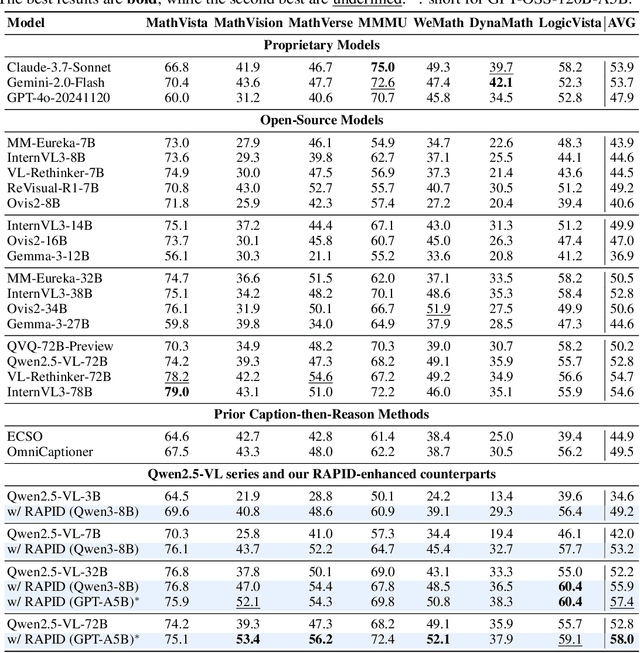
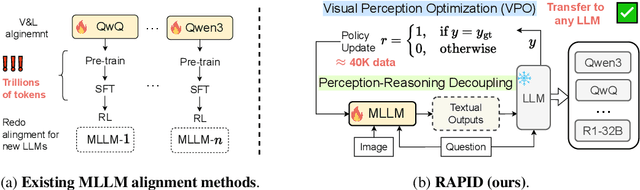
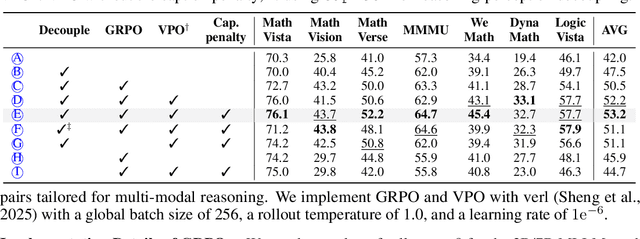
Abstract:Recent advances in slow-thinking language models (e.g., OpenAI-o1 and DeepSeek-R1) have demonstrated remarkable abilities in complex reasoning tasks by emulating human-like reflective cognition. However, extending such capabilities to multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) remains challenging due to the high cost of retraining vision-language alignments when upgrading the underlying reasoner LLMs. A straightforward solution is to decouple perception from reasoning, i.e., converting visual inputs into language representations (e.g., captions) that are then passed to a powerful text-only reasoner. However, this decoupling introduces a critical challenge: the visual extractor must generate descriptions that are both faithful to the image and informative enough to support accurate downstream reasoning. To address this, we propose Reasoning-Aligned Perceptual Decoupling via Caption Reward Optimization (RACRO) - a reasoning-guided reinforcement learning strategy that aligns the extractor's captioning behavior with the reasoning objective. By closing the perception-reasoning loop via reward-based optimization, RACRO significantly enhances visual grounding and extracts reasoning-optimized representations. Experiments on multi-modal math and science benchmarks show that the proposed RACRO method achieves state-of-the-art average performance while enabling superior scalability and plug-and-play adaptation to more advanced reasoning LLMs without the necessity for costly multi-modal re-alignment.
Self-Error-Instruct: Generalizing from Errors for LLMs Mathematical Reasoning
May 28, 2025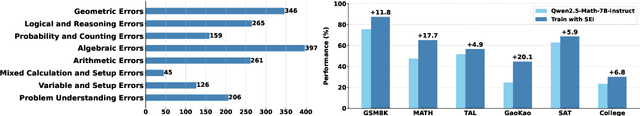
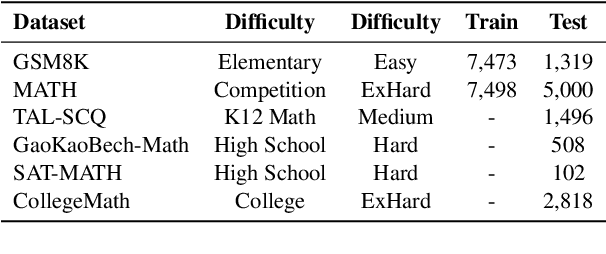

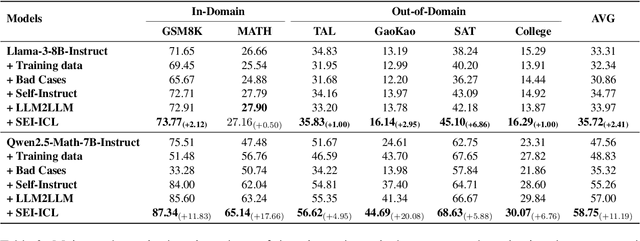
Abstract:Although large language models demonstrate strong performance across various domains, they still struggle with numerous bad cases in mathematical reasoning. Previous approaches to learning from errors synthesize training data by solely extrapolating from isolated bad cases, thereby failing to generalize the extensive patterns inherent within these cases. This paper presents Self-Error-Instruct (SEI), a framework that addresses these model weaknesses and synthesizes more generalized targeted training data. Specifically, we explore a target model on two mathematical datasets, GSM8K and MATH, to pinpoint bad cases. Then, we generate error keyphrases for these cases based on the instructor model's (GPT-4o) analysis and identify error types by clustering these keyphrases. Next, we sample a few bad cases during each generation for each identified error type and input them into the instructor model, which synthesizes additional training data using a self-instruct approach. This new data is refined through a one-shot learning process to ensure that only the most effective examples are kept. Finally, we use these curated data to fine-tune the target model, iteratively repeating the process to enhance performance. We apply our framework to various models and observe improvements in their reasoning abilities across both in-domain and out-of-domain mathematics datasets. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of self-error instruction in improving LLMs' mathematical reasoning through error generalization.
Perception, Reason, Think, and Plan: A Survey on Large Multimodal Reasoning Models
May 08, 2025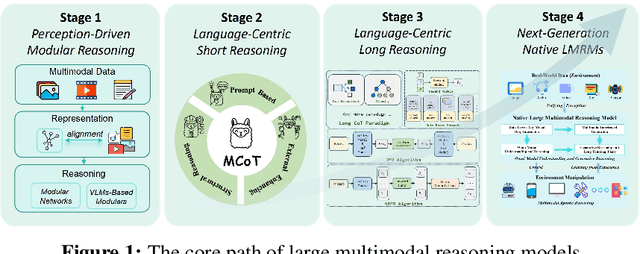
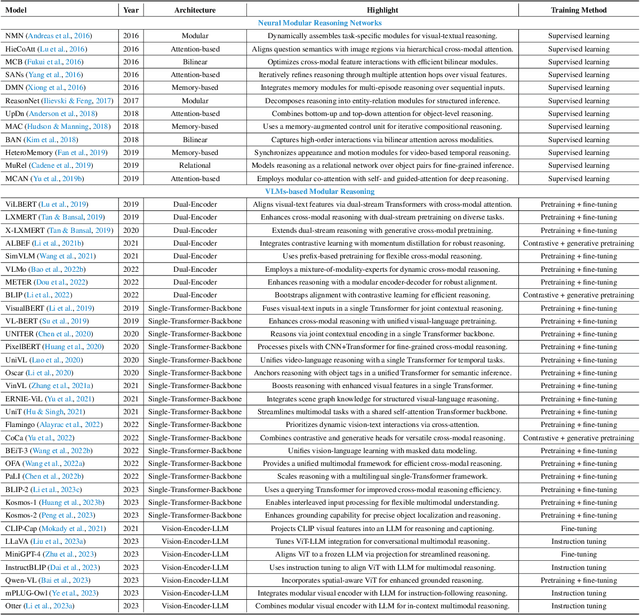
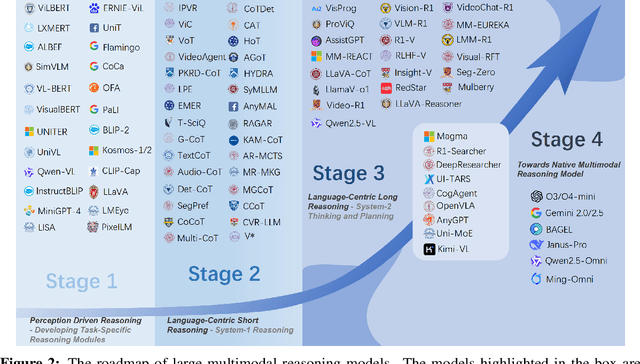
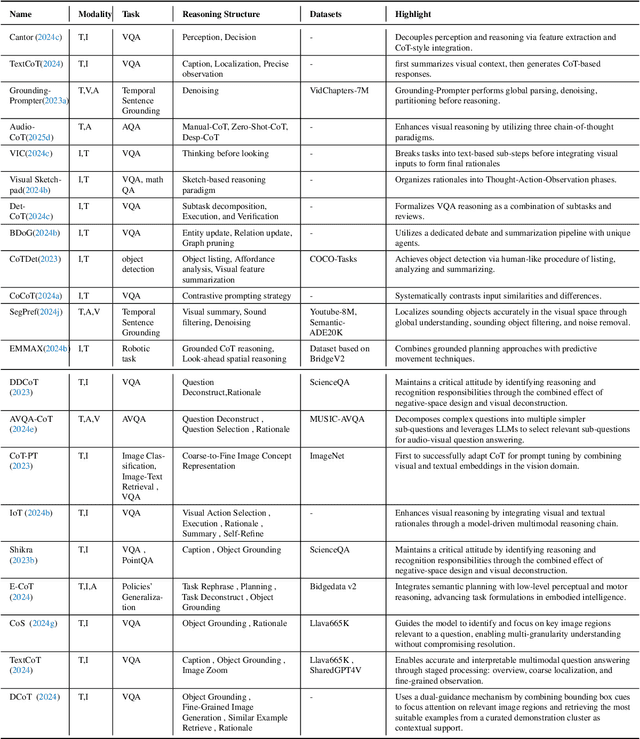
Abstract:Reasoning lies at the heart of intelligence, shaping the ability to make decisions, draw conclusions, and generalize across domains. In artificial intelligence, as systems increasingly operate in open, uncertain, and multimodal environments, reasoning becomes essential for enabling robust and adaptive behavior. Large Multimodal Reasoning Models (LMRMs) have emerged as a promising paradigm, integrating modalities such as text, images, audio, and video to support complex reasoning capabilities and aiming to achieve comprehensive perception, precise understanding, and deep reasoning. As research advances, multimodal reasoning has rapidly evolved from modular, perception-driven pipelines to unified, language-centric frameworks that offer more coherent cross-modal understanding. While instruction tuning and reinforcement learning have improved model reasoning, significant challenges remain in omni-modal generalization, reasoning depth, and agentic behavior. To address these issues, we present a comprehensive and structured survey of multimodal reasoning research, organized around a four-stage developmental roadmap that reflects the field's shifting design philosophies and emerging capabilities. First, we review early efforts based on task-specific modules, where reasoning was implicitly embedded across stages of representation, alignment, and fusion. Next, we examine recent approaches that unify reasoning into multimodal LLMs, with advances such as Multimodal Chain-of-Thought (MCoT) and multimodal reinforcement learning enabling richer and more structured reasoning chains. Finally, drawing on empirical insights from challenging benchmarks and experimental cases of OpenAI O3 and O4-mini, we discuss the conceptual direction of native large multimodal reasoning models (N-LMRMs), which aim to support scalable, agentic, and adaptive reasoning and planning in complex, real-world environments.
PaMi-VDPO: Mitigating Video Hallucinations by Prompt-Aware Multi-Instance Video Preference Learning
Apr 08, 2025



Abstract:Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) helps reduce hallucinations in Video Multimodal Large Language Models (VLLMs), but its reliance on offline preference data limits adaptability and fails to capture true video-response misalignment. We propose Video Direct Preference Optimization (VDPO), an online preference learning framework that eliminates the need for preference annotation by leveraging video augmentations to generate rejected samples while keeping responses fixed. However, selecting effective augmentations is non-trivial, as some clips may be semantically identical to the original under specific prompts, leading to false rejections and disrupting alignment. To address this, we introduce Prompt-aware Multi-instance Learning VDPO (PaMi-VDPO), which selects augmentations based on prompt context. Instead of a single rejection, we construct a candidate set of augmented clips and apply a close-to-far selection strategy, initially ensuring all clips are semantically relevant while then prioritizing the most prompt-aware distinct clip. This allows the model to better capture meaningful visual differences, mitigating hallucinations, while avoiding false rejections, and improving alignment. PaMi-VDPOseamlessly integrates into existing VLLMs without additional parameters, GPT-4/human supervision. With only 10k SFT data, it improves the base model by 5.3% on VideoHallucer, surpassing GPT-4o, while maintaining stable performance on general video benchmarks.
ILLUME+: Illuminating Unified MLLM with Dual Visual Tokenization and Diffusion Refinement
Apr 03, 2025



Abstract:We present ILLUME+ that leverages dual visual tokenization and a diffusion decoder to improve both deep semantic understanding and high-fidelity image generation. Existing unified models have struggled to simultaneously handle the three fundamental capabilities in a unified model: understanding, generation, and editing. Models like Chameleon and EMU3 utilize VQGAN for image discretization, due to the lack of deep semantic interaction, they lag behind specialist models like LLaVA in visual understanding tasks. To mitigate this, LaViT and ILLUME employ semantic encoders for tokenization, but they struggle with image editing due to poor texture preservation. Meanwhile, Janus series decouples the input and output image representation, limiting their abilities to seamlessly handle interleaved image-text understanding and generation. In contrast, ILLUME+ introduces a unified dual visual tokenizer, DualViTok, which preserves both fine-grained textures and text-aligned semantics while enabling a coarse-to-fine image representation strategy for multimodal understanding and generation. Additionally, we employ a diffusion model as the image detokenizer for enhanced generation quality and efficient super-resolution. ILLUME+ follows a continuous-input, discrete-output scheme within the unified MLLM and adopts a progressive training procedure that supports dynamic resolution across the vision tokenizer, MLLM, and diffusion decoder. This design allows for flexible and efficient context-aware image editing and generation across diverse tasks. ILLUME+ (3B) exhibits competitive performance against existing unified MLLMs and specialized models across multimodal understanding, generation, and editing benchmarks. With its strong performance, ILLUME+ provides a scalable and versatile foundation for future multimodal applications. Project Page: https://illume-unified-mllm.github.io/.
Can Atomic Step Decomposition Enhance the Self-structured Reasoning of Multimodal Large Models?
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we address the challenging task of multimodal mathematical reasoning by incorporating the ability of "slow thinking" into multimodal large language models (MLLMs). Our core idea is that different levels of reasoning abilities can be combined dynamically to tackle questions with different complexity. To this end, we propose a paradigm of Self-structured Chain of Thought (SCoT), which is composed of minimal semantic atomic steps. Different from existing methods that rely on structured templates or free-form paradigms, our method can not only generate cognitive CoT structures for various complex tasks but also mitigates the phenomenon of overthinking. To introduce structured reasoning capabilities into visual understanding models, we further design a novel AtomThink framework with four key modules, including (i) a data engine to generate high-quality multimodal reasoning paths; (ii) a supervised fine-tuning process with serialized inference data; (iii) a policy-guided multi-turn inference method; and (iv) an atomic capability metric to evaluate the single step utilization rate. We conduct extensive experiments to show that the proposed AtomThink significantly improves the performance of baseline MLLMs, achieving more than 10\% average accuracy gains on MathVista and MathVerse. Compared to state-of-the-art structured CoT approaches, our method not only achieves higher accuracy but also improves data utilization by 5 times and boosts inference efficiency by 85.3\%. Our code is now public available in https://github.com/Quinn777/AtomThink.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge