Jianhua Han
Thinking with Geometry: Active Geometry Integration for Spatial Reasoning
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Recent progress in spatial reasoning with Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) increasingly leverages geometric priors from 3D encoders. However, most existing integration strategies remain passive: geometry is exposed as a global stream and fused in an indiscriminate manner, which often induces semantic-geometry misalignment and redundant signals. We propose GeoThinker, a framework that shifts the paradigm from passive fusion to active perception. Instead of feature mixing, GeoThinker enables the model to selectively retrieve geometric evidence conditioned on its internal reasoning demands. GeoThinker achieves this through Spatial-Grounded Fusion applied at carefully selected VLM layers, where semantic visual priors selectively query and integrate task-relevant geometry via frame-strict cross-attention, further calibrated by Importance Gating that biases per-frame attention toward task-relevant structures. Comprehensive evaluation results show that GeoThinker sets a new state-of-the-art in spatial intelligence, achieving a peak score of 72.6 on the VSI-Bench. Furthermore, GeoThinker demonstrates robust generalization and significantly improved spatial perception across complex downstream scenarios, including embodied referring and autonomous driving. Our results indicate that the ability to actively integrate spatial structures is essential for next-generation spatial intelligence. Code can be found at https://github.com/Li-Hao-yuan/GeoThinker.
SlowFocus: Enhancing Fine-grained Temporal Understanding in Video LLM
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated exceptional capabilities in text understanding, which has paved the way for their expansion into video LLMs (Vid-LLMs) to analyze video data. However, current Vid-LLMs struggle to simultaneously retain high-quality frame-level semantic information (i.e., a sufficient number of tokens per frame) and comprehensive video-level temporal information (i.e., an adequate number of sampled frames per video). This limitation hinders the advancement of Vid-LLMs towards fine-grained video understanding. To address this issue, we introduce the SlowFocus mechanism, which significantly enhances the equivalent sampling frequency without compromising the quality of frame-level visual tokens. SlowFocus begins by identifying the query-related temporal segment based on the posed question, then performs dense sampling on this segment to extract local high-frequency features. A multi-frequency mixing attention module is further leveraged to aggregate these local high-frequency details with global low-frequency contexts for enhanced temporal comprehension. Additionally, to tailor Vid-LLMs to this innovative mechanism, we introduce a set of training strategies aimed at bolstering both temporal grounding and detailed temporal reasoning capabilities. Furthermore, we establish FineAction-CGR, a benchmark specifically devised to assess the ability of Vid-LLMs to process fine-grained temporal understanding tasks. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our mechanism across both existing public video understanding benchmarks and our proposed FineAction-CGR.
Aligning Perception, Reasoning, Modeling and Interaction: A Survey on Physical AI
Oct 06, 2025
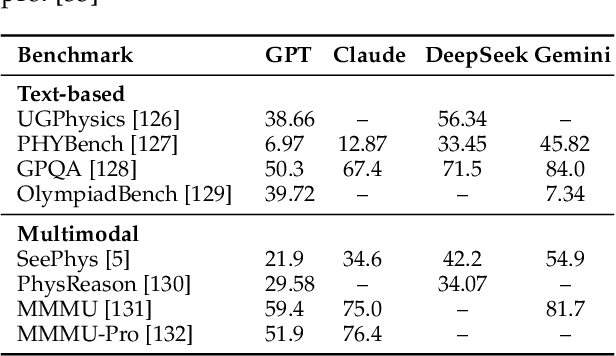

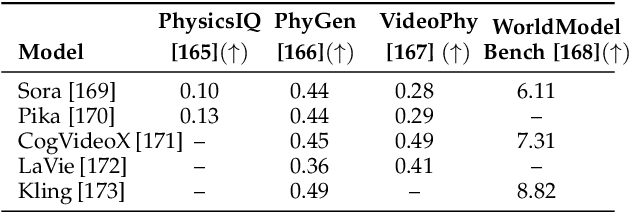
Abstract:The rapid advancement of embodied intelligence and world models has intensified efforts to integrate physical laws into AI systems, yet physical perception and symbolic physics reasoning have developed along separate trajectories without a unified bridging framework. This work provides a comprehensive overview of physical AI, establishing clear distinctions between theoretical physics reasoning and applied physical understanding while systematically examining how physics-grounded methods enhance AI's real-world comprehension across structured symbolic reasoning, embodied systems, and generative models. Through rigorous analysis of recent advances, we advocate for intelligent systems that ground learning in both physical principles and embodied reasoning processes, transcending pattern recognition toward genuine understanding of physical laws. Our synthesis envisions next-generation world models capable of explaining physical phenomena and predicting future states, advancing safe, generalizable, and interpretable AI systems. We maintain a continuously updated resource at https://github.com/AI4Phys/Awesome-AI-for-Physics.
C2-Evo: Co-Evolving Multimodal Data and Model for Self-Improving Reasoning
Jul 22, 2025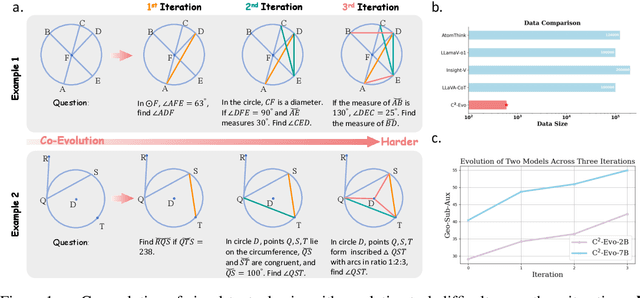

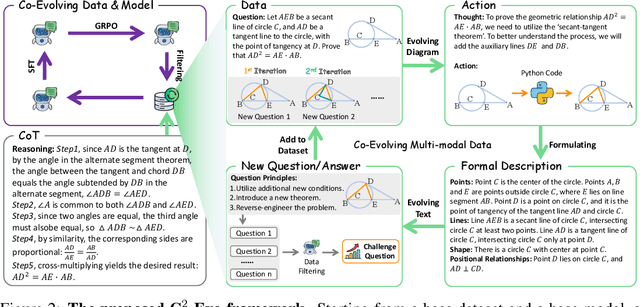
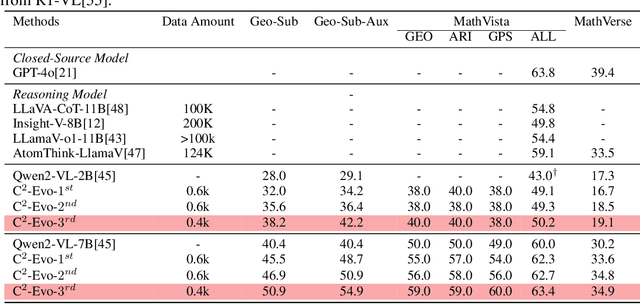
Abstract:Recent advances in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have shown impressive reasoning capabilities. However, further enhancing existing MLLMs necessitates high-quality vision-language datasets with carefully curated task complexities, which are both costly and challenging to scale. Although recent self-improving models that iteratively refine themselves offer a feasible solution, they still suffer from two core challenges: (i) most existing methods augment visual or textual data separately, resulting in discrepancies in data complexity (e.g., over-simplified diagrams paired with redundant textual descriptions); and (ii) the evolution of data and models is also separated, leading to scenarios where models are exposed to tasks with mismatched difficulty levels. To address these issues, we propose C2-Evo, an automatic, closed-loop self-improving framework that jointly evolves both training data and model capabilities. Specifically, given a base dataset and a base model, C2-Evo enhances them by a cross-modal data evolution loop and a data-model evolution loop. The former loop expands the base dataset by generating complex multimodal problems that combine structured textual sub-problems with iteratively specified geometric diagrams, while the latter loop adaptively selects the generated problems based on the performance of the base model, to conduct supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning alternately. Consequently, our method continuously refines its model and training data, and consistently obtains considerable performance gains across multiple mathematical reasoning benchmarks. Our code, models, and datasets will be released.
Does Your 3D Encoder Really Work? When Pretrain-SFT from 2D VLMs Meets 3D VLMs
Jun 06, 2025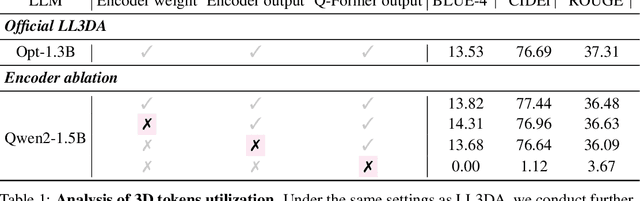
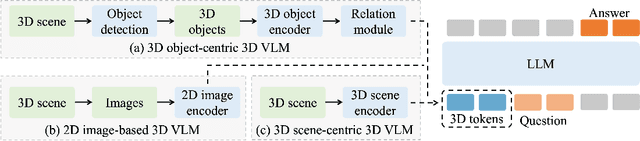

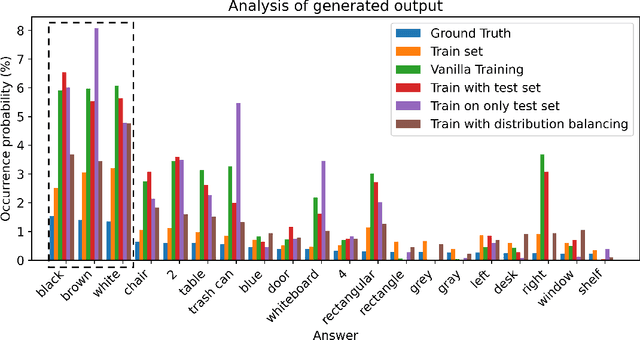
Abstract:Remarkable progress in 2D Vision-Language Models (VLMs) has spurred interest in extending them to 3D settings for tasks like 3D Question Answering, Dense Captioning, and Visual Grounding. Unlike 2D VLMs that typically process images through an image encoder, 3D scenes, with their intricate spatial structures, allow for diverse model architectures. Based on their encoder design, this paper categorizes recent 3D VLMs into 3D object-centric, 2D image-based, and 3D scene-centric approaches. Despite the architectural similarity of 3D scene-centric VLMs to their 2D counterparts, they have exhibited comparatively lower performance compared with the latest 3D object-centric and 2D image-based approaches. To understand this gap, we conduct an in-depth analysis, revealing that 3D scene-centric VLMs show limited reliance on the 3D scene encoder, and the pre-train stage appears less effective than in 2D VLMs. Furthermore, we observe that data scaling benefits are less pronounced on larger datasets. Our investigation suggests that while these models possess cross-modal alignment capabilities, they tend to over-rely on linguistic cues and overfit to frequent answer distributions, thereby diminishing the effective utilization of the 3D encoder. To address these limitations and encourage genuine 3D scene understanding, we introduce a novel 3D Relevance Discrimination QA dataset designed to disrupt shortcut learning and improve 3D understanding. Our findings highlight the need for advanced evaluation and improved strategies for better 3D understanding in 3D VLMs.
SeePhys: Does Seeing Help Thinking? -- Benchmarking Vision-Based Physics Reasoning
May 25, 2025Abstract:We present SeePhys, a large-scale multimodal benchmark for LLM reasoning grounded in physics questions ranging from middle school to PhD qualifying exams. The benchmark covers 7 fundamental domains spanning the physics discipline, incorporating 21 categories of highly heterogeneous diagrams. In contrast to prior works where visual elements mainly serve auxiliary purposes, our benchmark features a substantial proportion of vision-essential problems (75\%) that mandate visual information extraction for correct solutions. Through extensive evaluation, we observe that even the most advanced visual reasoning models (e.g., Gemini-2.5-pro and o4-mini) achieve sub-60\% accuracy on our benchmark. These results reveal fundamental challenges in current large language models' visual understanding capabilities, particularly in: (i) establishing rigorous coupling between diagram interpretation and physics reasoning, and (ii) overcoming their persistent reliance on textual cues as cognitive shortcuts.
ILLUME+: Illuminating Unified MLLM with Dual Visual Tokenization and Diffusion Refinement
Apr 03, 2025



Abstract:We present ILLUME+ that leverages dual visual tokenization and a diffusion decoder to improve both deep semantic understanding and high-fidelity image generation. Existing unified models have struggled to simultaneously handle the three fundamental capabilities in a unified model: understanding, generation, and editing. Models like Chameleon and EMU3 utilize VQGAN for image discretization, due to the lack of deep semantic interaction, they lag behind specialist models like LLaVA in visual understanding tasks. To mitigate this, LaViT and ILLUME employ semantic encoders for tokenization, but they struggle with image editing due to poor texture preservation. Meanwhile, Janus series decouples the input and output image representation, limiting their abilities to seamlessly handle interleaved image-text understanding and generation. In contrast, ILLUME+ introduces a unified dual visual tokenizer, DualViTok, which preserves both fine-grained textures and text-aligned semantics while enabling a coarse-to-fine image representation strategy for multimodal understanding and generation. Additionally, we employ a diffusion model as the image detokenizer for enhanced generation quality and efficient super-resolution. ILLUME+ follows a continuous-input, discrete-output scheme within the unified MLLM and adopts a progressive training procedure that supports dynamic resolution across the vision tokenizer, MLLM, and diffusion decoder. This design allows for flexible and efficient context-aware image editing and generation across diverse tasks. ILLUME+ (3B) exhibits competitive performance against existing unified MLLMs and specialized models across multimodal understanding, generation, and editing benchmarks. With its strong performance, ILLUME+ provides a scalable and versatile foundation for future multimodal applications. Project Page: https://illume-unified-mllm.github.io/.
SemHiTok: A Unified Image Tokenizer via Semantic-Guided Hierarchical Codebook for Multimodal Understanding and Generation
Mar 09, 2025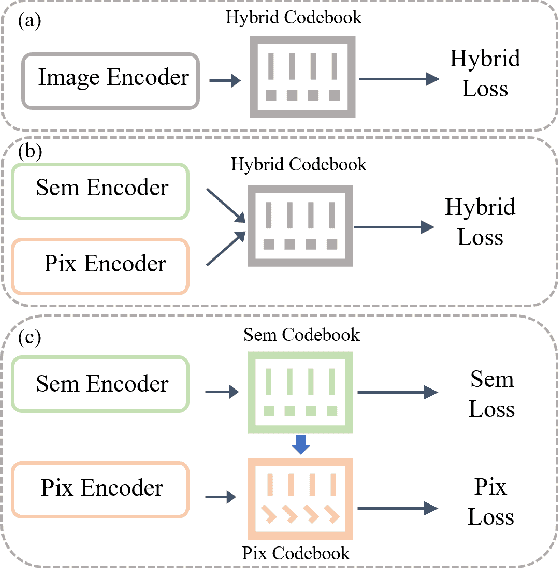
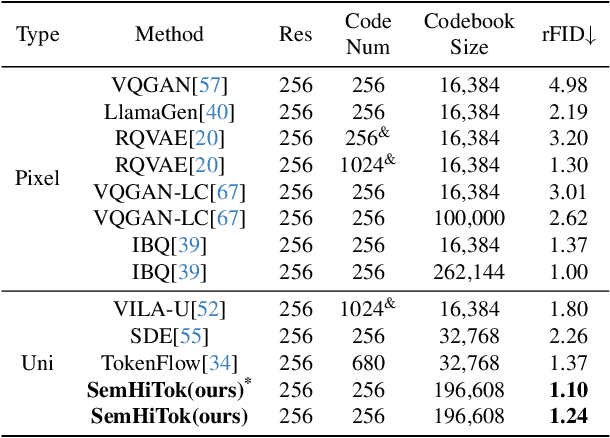
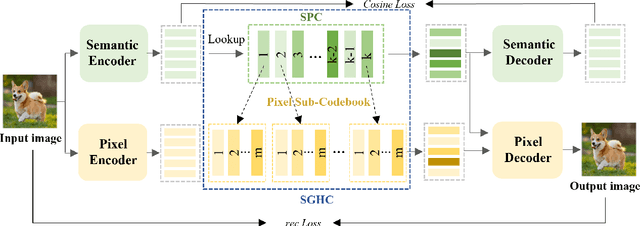
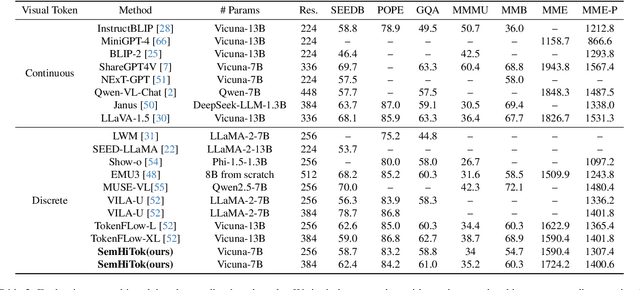
Abstract:We present SemHiTok, a unified image Tokenizer via Semantic-Guided Hierarchical codebook that provides consistent discrete feature representations for multimodal understanding and generation tasks. Recently, unified multimodal large models (MLLMs) for understanding and generation have sparked exploration within research community. Previous works attempt to train a unified image tokenizer by combining loss functions for semantic feature reconstruction and pixel reconstruction. However, due to the differing levels of features prioritized by multimodal understanding and generation tasks, joint training methods face significant challenges in achieving a good trade-off. SemHiTok addresses this challenge through Semantic-Guided Hierarchical codebook which builds texture sub-codebooks on pre-trained semantic codebook. This design decouples the training of semantic reconstruction and pixel reconstruction and equips the tokenizer with low-level texture feature extraction capability without degradation of high-level semantic feature extraction ability. Our experiments demonstrate that SemHiTok achieves state-of-the-art rFID score at 256X256resolution compared to other unified tokenizers, and exhibits competitive performance on multimodal understanding and generation tasks.
Can Atomic Step Decomposition Enhance the Self-structured Reasoning of Multimodal Large Models?
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we address the challenging task of multimodal mathematical reasoning by incorporating the ability of "slow thinking" into multimodal large language models (MLLMs). Our core idea is that different levels of reasoning abilities can be combined dynamically to tackle questions with different complexity. To this end, we propose a paradigm of Self-structured Chain of Thought (SCoT), which is composed of minimal semantic atomic steps. Different from existing methods that rely on structured templates or free-form paradigms, our method can not only generate cognitive CoT structures for various complex tasks but also mitigates the phenomenon of overthinking. To introduce structured reasoning capabilities into visual understanding models, we further design a novel AtomThink framework with four key modules, including (i) a data engine to generate high-quality multimodal reasoning paths; (ii) a supervised fine-tuning process with serialized inference data; (iii) a policy-guided multi-turn inference method; and (iv) an atomic capability metric to evaluate the single step utilization rate. We conduct extensive experiments to show that the proposed AtomThink significantly improves the performance of baseline MLLMs, achieving more than 10\% average accuracy gains on MathVista and MathVerse. Compared to state-of-the-art structured CoT approaches, our method not only achieves higher accuracy but also improves data utilization by 5 times and boosts inference efficiency by 85.3\%. Our code is now public available in https://github.com/Quinn777/AtomThink.
TransMamba: Fast Universal Architecture Adaption from Transformers to Mamba
Feb 21, 2025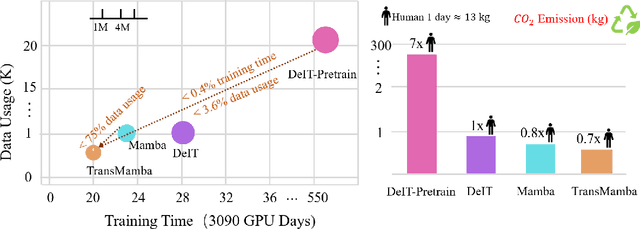
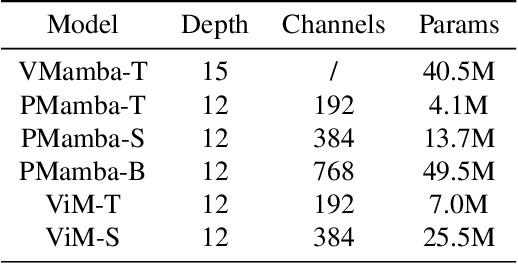
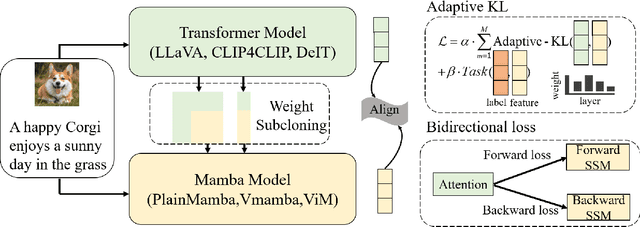
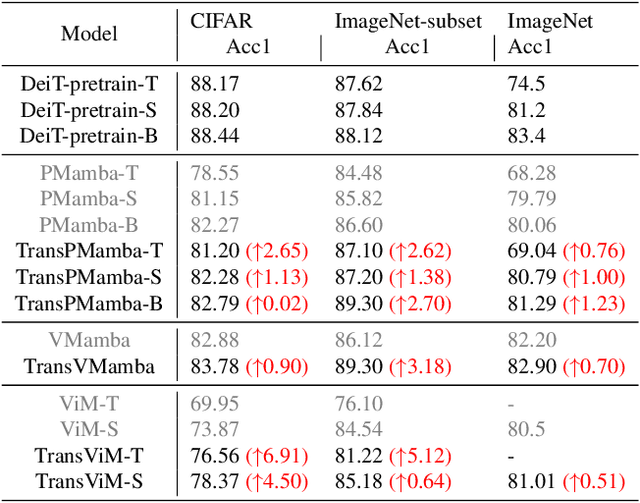
Abstract:Transformers have been favored in both uni-modal and multi-modal foundation models for their flexible scalability in attention modules. Consequently, a number of pre-trained Transformer models, e.g., LLaVA, CLIP, and DEIT, are publicly available. Recent research has introduced subquadratic architectures like Mamba, which enables global awareness with linear complexity. Nevertheless, training specialized subquadratic architectures from scratch for certain tasks is both resource-intensive and time-consuming. As a motivator, we explore cross-architecture training to transfer the ready knowledge in existing Transformer models to alternative architecture Mamba, termed TransMamba. Our approach employs a two-stage strategy to expedite training new Mamba models, ensuring effectiveness in across uni-modal and cross-modal tasks. Concerning architecture disparities, we project the intermediate features into an aligned latent space before transferring knowledge. On top of that, a Weight Subcloning and Adaptive Bidirectional distillation method (WSAB) is introduced for knowledge transfer without limitations on varying layer counts. For cross-modal learning, we propose a cross-Mamba module that integrates language awareness into Mamba's visual features, enhancing the cross-modal interaction capabilities of Mamba architecture. Despite using less than 75% of the training data typically required for training from scratch, TransMamba boasts substantially stronger performance across various network architectures and downstream tasks, including image classification, visual question answering, and text-video retrieval. The code will be publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge