Jiaxi Gu
Repeating Words for Video-Language Retrieval with Coarse-to-Fine Objectives
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:The explosive growth of video streaming presents challenges in achieving high accuracy and low training costs for video-language retrieval. However, existing methods rely on large-scale pre-training to improve video retrieval performance, resulting in significant computational demands. Additionally, the fine-grained information in videos and texts remains underexplored. To alleviate these problems, we propose a novel framework to learn fine-grained features for better alignment and introduce an inference pipeline to improve performance without additional training. Specifically, we employ coarse-to-fine objectives to understand the semantic information of video-text pairs, including contrastive and matching learning. The fine-grained data used for training is obtained through the Granularity-Aware Representation module, which is designed based on similarity analysis between video frames and words in captions. Furthermore, we observe that the repetition of keywords in the original captions, referred to as "Repetition", can enhance retrieval performance and improve alignment between video and text. Based on this insight, we propose a novel and effective inference pipeline that incorporates a voting mechanism and a new Matching Entropy metric to achieve better retrieval performance without requiring additional pre-training. Experimental results on four benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms previous approaches. Additionally, our inference pipeline achieves significant performance improvements, with a 2.1% increase in Recall@1 on the MSR-VTT dataset and a 1.6% increase on the DiDeMo dataset.
ShoulderShot: Generating Over-the-Shoulder Dialogue Videos
Aug 11, 2025



Abstract:Over-the-shoulder dialogue videos are essential in films, short dramas, and advertisements, providing visual variety and enhancing viewers' emotional connection. Despite their importance, such dialogue scenes remain largely underexplored in video generation research. The main challenges include maintaining character consistency across different shots, creating a sense of spatial continuity, and generating long, multi-turn dialogues within limited computational budgets. Here, we present ShoulderShot, a framework that combines dual-shot generation with looping video, enabling extended dialogues while preserving character consistency. Our results demonstrate capabilities that surpass existing methods in terms of shot-reverse-shot layout, spatial continuity, and flexibility in dialogue length, thereby opening up new possibilities for practical dialogue video generation. Videos and comparisons are available at https://shouldershot.github.io.
Conservative approximation-based feedforward neural network for WENO schemes
Jul 08, 2025Abstract:In this work, we present the feedforward neural network based on the conservative approximation to the derivative from point values, for the weighted essentially non-oscillatory (WENO) schemes in solving hyperbolic conservation laws. The feedforward neural network, whose inputs are point values from the three-point stencil and outputs are two nonlinear weights, takes the place of the classical WENO weighting procedure. For the training phase, we employ the supervised learning and create a new labeled dataset for one-dimensional conservative approximation, where we construct a numerical flux function from the given point values such that the flux difference approximates the derivative to high-order accuracy. The symmetric-balancing term is introduced for the loss function so that it propels the neural network to match the conservative approximation to the derivative and satisfy the symmetric property that WENO3-JS and WENO3-Z have in common. The consequent WENO schemes, WENO3-CADNNs, demonstrate robust generalization across various benchmark scenarios and resolutions, where they outperform WENO3-Z and achieve accuracy comparable to WENO5-JS.
EasyControl: Transfer ControlNet to Video Diffusion for Controllable Generation and Interpolation
Aug 23, 2024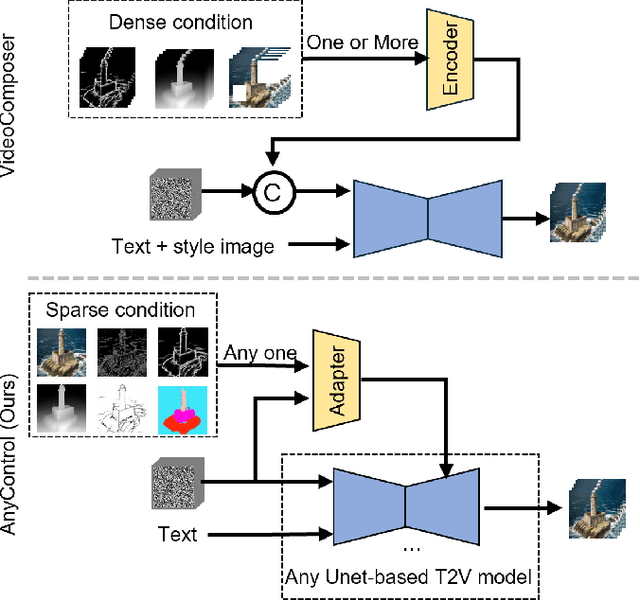
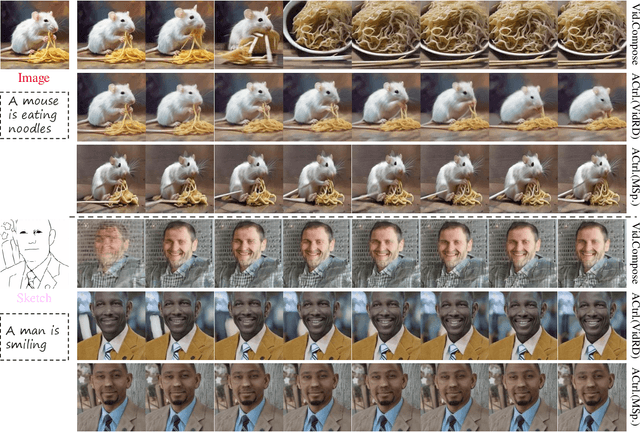

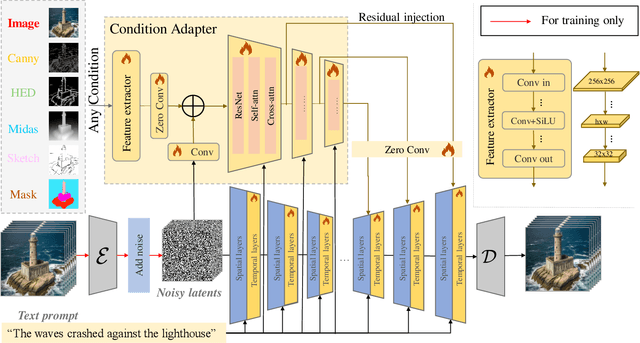

Abstract:Following the advancements in text-guided image generation technology exemplified by Stable Diffusion, video generation is gaining increased attention in the academic community. However, relying solely on text guidance for video generation has serious limitations, as videos contain much richer content than images, especially in terms of motion. This information can hardly be adequately described with plain text. Fortunately, in computer vision, various visual representations can serve as additional control signals to guide generation. With the help of these signals, video generation can be controlled in finer detail, allowing for greater flexibility for different applications. Integrating various controls, however, is nontrivial. In this paper, we propose a universal framework called EasyControl. By propagating and injecting condition features through condition adapters, our method enables users to control video generation with a single condition map. With our framework, various conditions including raw pixels, depth, HED, etc., can be integrated into different Unet-based pre-trained video diffusion models at a low practical cost. We conduct comprehensive experiments on public datasets, and both quantitative and qualitative results indicate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods. EasyControl significantly improves various evaluation metrics across multiple validation datasets compared to previous works. Specifically, for the sketch-to-video generation task, EasyControl achieves an improvement of 152.0 on FVD and 19.9 on IS, respectively, in UCF101 compared with VideoComposer. For fidelity, our model demonstrates powerful image retention ability, resulting in high FVD and IS in UCF101 and MSR-VTT compared to other image-to-video models.
A third-order finite difference weighted essentially non-oscillatory scheme with shallow neural network
Jul 10, 2024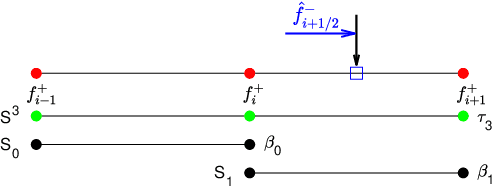
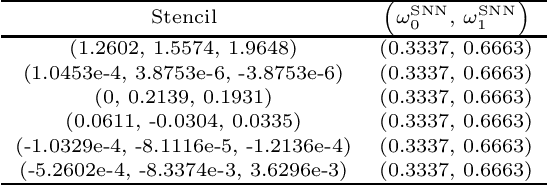
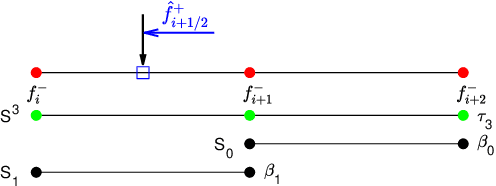
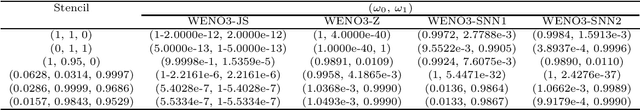
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce the finite difference weighted essentially non-oscillatory (WENO) scheme based on the neural network for hyperbolic conservation laws. We employ the supervised learning and design two loss functions, one with the mean squared error and the other with the mean squared logarithmic error, where the WENO3-JS weights are computed as the labels. Each loss function consists of two components where the first component compares the difference between the weights from the neural network and WENO3-JS weights, while the second component matches the output weights of the neural network and the linear weights. The former of the loss function enforces the neural network to follow the WENO properties, implying that there is no need for the post-processing layer. Additionally the latter leads to better performance around discontinuities. As a neural network structure, we choose the shallow neural network (SNN) for computational efficiency with the Delta layer consisting of the normalized undivided differences. These constructed WENO3-SNN schemes show the outperformed results in one-dimensional examples and improved behavior in two-dimensional examples, compared with the simulations from WENO3-JS and WENO3-Z.
MimicMotion: High-Quality Human Motion Video Generation with Confidence-aware Pose Guidance
Jun 28, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, generative artificial intelligence has achieved significant advancements in the field of image generation, spawning a variety of applications. However, video generation still faces considerable challenges in various aspects, such as controllability, video length, and richness of details, which hinder the application and popularization of this technology. In this work, we propose a controllable video generation framework, dubbed MimicMotion, which can generate high-quality videos of arbitrary length mimicking specific motion guidance. Compared with previous methods, our approach has several highlights. Firstly, we introduce confidence-aware pose guidance that ensures high frame quality and temporal smoothness. Secondly, we introduce regional loss amplification based on pose confidence, which significantly reduces image distortion. Lastly, for generating long and smooth videos, we propose a progressive latent fusion strategy. By this means, we can produce videos of arbitrary length with acceptable resource consumption. With extensive experiments and user studies, MimicMotion demonstrates significant improvements over previous approaches in various aspects. Detailed results and comparisons are available on our project page: https://tencent.github.io/MimicMotion .
AutoTVG: A New Vision-language Pre-training Paradigm for Temporal Video Grounding
Jun 11, 2024



Abstract:Temporal Video Grounding (TVG) aims to localize a moment from an untrimmed video given the language description. Since the annotation of TVG is labor-intensive, TVG under limited supervision has accepted attention in recent years. The great success of vision-language pre-training guides TVG to follow the traditional "pre-training + fine-tuning" paradigm, however, the pre-training process would suffer from a lack of temporal modeling and fine-grained alignment due to the difference of data nature between pre-train and test. Besides, the large gap between pretext and downstream tasks makes zero-shot testing impossible for the pre-trained model. To avoid the drawbacks of the traditional paradigm, we propose AutoTVG, a new vision-language pre-training paradigm for TVG that enables the model to learn semantic alignment and boundary regression from automatically annotated untrimmed videos. To be specific, AutoTVG consists of a novel Captioned Moment Generation (CMG) module to generate captioned moments from untrimmed videos, and TVGNet with a regression head to predict localization results. Experimental results on Charades-STA and ActivityNet Captions show that, regarding zero-shot temporal video grounding, AutoTVG achieves highly competitive performance with in-distribution methods under out-of-distribution testing, and is superior to existing pre-training frameworks with much less training data.
DreamVideo: High-Fidelity Image-to-Video Generation with Image Retention and Text Guidance
Dec 05, 2023Abstract:Image-to-video generation, which aims to generate a video starting from a given reference image, has drawn great attention. Existing methods try to extend pre-trained text-guided image diffusion models to image-guided video generation models. Nevertheless, these methods often result in either low fidelity or flickering over time due to their limitation to shallow image guidance and poor temporal consistency. To tackle these problems, we propose a high-fidelity image-to-video generation method by devising a frame retention branch on the basis of a pre-trained video diffusion model, named DreamVideo. Instead of integrating the reference image into the diffusion process in a semantic level, our DreamVideo perceives the reference image via convolution layers and concatenate the features with the noisy latents as model input. By this means, the details of the reference image can be preserved to the greatest extent. In addition, by incorporating double-condition classifier-free guidance, a single image can be directed to videos of different actions by providing varying prompt texts. This has significant implications for controllable video generation and holds broad application prospects. We conduct comprehensive experiments on the public dataset, both quantitative and qualitative results indicate that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art method. Especially for fidelity, our model has powerful image retention ability and result in high FVD in UCF101 compared to other image-to-video models. Also, precise control can be achieved by giving different text prompts. Further details and comprehensive results of our model will be presented in https://anonymous0769.github.io/DreamVideo/.
BIVDiff: A Training-Free Framework for General-Purpose Video Synthesis via Bridging Image and Video Diffusion Models
Dec 05, 2023Abstract:Diffusion models have made tremendous progress in text-driven image and video generation. Now text-to-image foundation models are widely applied to various downstream image synthesis tasks, such as controllable image generation and image editing, while downstream video synthesis tasks are less explored for several reasons. First, it requires huge memory and compute overhead to train a video generation foundation model. Even with video foundation models, additional costly training is still required for downstream video synthesis tasks. Second, although some works extend image diffusion models into videos in a training-free manner, temporal consistency cannot be well kept. Finally, these adaption methods are specifically designed for one task and fail to generalize to different downstream video synthesis tasks. To mitigate these issues, we propose a training-free general-purpose video synthesis framework, coined as BIVDiff, via bridging specific image diffusion models and general text-to-video foundation diffusion models. Specifically, we first use an image diffusion model (like ControlNet, Instruct Pix2Pix) for frame-wise video generation, then perform Mixed Inversion on the generated video, and finally input the inverted latents into the video diffusion model for temporal smoothing. Decoupling image and video models enables flexible image model selection for different purposes, which endows the framework with strong task generalization and high efficiency. To validate the effectiveness and general use of BIVDiff, we perform a wide range of video generation tasks, including controllable video generation video editing, video inpainting and outpainting. Our project page is available at https://bivdiff.github.io.
VideoAssembler: Identity-Consistent Video Generation with Reference Entities using Diffusion Model
Dec 01, 2023Abstract:Identity-consistent video generation seeks to synthesize videos that are guided by both textual prompts and reference images of entities. Current approaches typically utilize cross-attention layers to integrate the appearance of the entity, which predominantly captures semantic attributes, resulting in compromised fidelity of entities. Moreover, these methods necessitate iterative fine-tuning for each new entity encountered, thereby limiting their applicability. To address these challenges, we introduce VideoAssembler, a novel end-to-end framework for identity-consistent video generation that can conduct inference directly when encountering new entities. VideoAssembler is adept at producing videos that are not only flexible with respect to the input reference entities but also responsive to textual conditions. Additionally, by modulating the quantity of input images for the entity, VideoAssembler enables the execution of tasks ranging from image-to-video generation to sophisticated video editing. VideoAssembler comprises two principal components: the Reference Entity Pyramid (REP) encoder and the Entity-Prompt Attention Fusion (EPAF) module. The REP encoder is designed to infuse comprehensive appearance details into the denoising stages of the stable diffusion model. Concurrently, the EPAF module is utilized to integrate text-aligned features effectively. Furthermore, to mitigate the challenge of scarce data, we present a methodology for the preprocessing of training data. Our evaluation of the VideoAssembler framework on the UCF-101, MSR-VTT, and DAVIS datasets indicates that it achieves good performances in both quantitative and qualitative analyses (346.84 in FVD and 48.01 in IS on UCF-101). Our project page is at https://gulucaptain.github.io/videoassembler/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge