Fangyuan Zou
InpaintDPO: Mitigating Spatial Relationship Hallucinations in Foreground-conditioned Inpainting via Diverse Preference Optimization
Dec 16, 2025



Abstract:Foreground-conditioned inpainting, which aims at generating a harmonious background for a given foreground subject based on the text prompt, is an important subfield in controllable image generation. A common challenge in current methods, however, is the occurrence of Spatial Relationship Hallucinations between the foreground subject and the generated background, including inappropriate scale, positional relationships, and viewpoints. Critically, the subjective nature of spatial rationality makes it challenging to quantify, hindering the use of traditional reward-based RLHF methods. To address this issue, we propose InpaintDPO, the first Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) based framework dedicated to spatial rationality in foreground-conditioned inpainting, ensuring plausible spatial relationships between foreground and background elements. To resolve the gradient conflicts in standard DPO caused by identical foreground in win-lose pairs, we propose MaskDPO, which confines preference optimization exclusively to the background to enhance background spatial relationships, while retaining the inpainting loss in the foreground region for robust foreground preservation. To enhance coherence at the foreground-background boundary, we propose Conditional Asymmetric Preference Optimization, which samples pairs with differentiated cropping operations and applies global preference optimization to promote contextual awareness and enhance boundary coherence. Finally, based on the observation that winning samples share a commonality in plausible spatial relationships, we propose Shared Commonality Preference Optimization to enhance the model's understanding of spatial commonality across high-quality winning samples, further promoting shared spatial rationality.
ShoulderShot: Generating Over-the-Shoulder Dialogue Videos
Aug 11, 2025



Abstract:Over-the-shoulder dialogue videos are essential in films, short dramas, and advertisements, providing visual variety and enhancing viewers' emotional connection. Despite their importance, such dialogue scenes remain largely underexplored in video generation research. The main challenges include maintaining character consistency across different shots, creating a sense of spatial continuity, and generating long, multi-turn dialogues within limited computational budgets. Here, we present ShoulderShot, a framework that combines dual-shot generation with looping video, enabling extended dialogues while preserving character consistency. Our results demonstrate capabilities that surpass existing methods in terms of shot-reverse-shot layout, spatial continuity, and flexibility in dialogue length, thereby opening up new possibilities for practical dialogue video generation. Videos and comparisons are available at https://shouldershot.github.io.
A$^\text{T}$A: Adaptive Transformation Agent for Text-Guided Subject-Position Variable Background Inpainting
Apr 02, 2025



Abstract:Image inpainting aims to fill the missing region of an image. Recently, there has been a surge of interest in foreground-conditioned background inpainting, a sub-task that fills the background of an image while the foreground subject and associated text prompt are provided. Existing background inpainting methods typically strictly preserve the subject's original position from the source image, resulting in inconsistencies between the subject and the generated background. To address this challenge, we propose a new task, the "Text-Guided Subject-Position Variable Background Inpainting", which aims to dynamically adjust the subject position to achieve a harmonious relationship between the subject and the inpainted background, and propose the Adaptive Transformation Agent (A$^\text{T}$A) for this task. Firstly, we design a PosAgent Block that adaptively predicts an appropriate displacement based on given features to achieve variable subject-position. Secondly, we design the Reverse Displacement Transform (RDT) module, which arranges multiple PosAgent blocks in a reverse structure, to transform hierarchical feature maps from deep to shallow based on semantic information. Thirdly, we equip A$^\text{T}$A with a Position Switch Embedding to control whether the subject's position in the generated image is adaptively predicted or fixed. Extensive comparative experiments validate the effectiveness of our A$^\text{T}$A approach, which not only demonstrates superior inpainting capabilities in subject-position variable inpainting, but also ensures good performance on subject-position fixed inpainting.
Pinco: Position-induced Consistent Adapter for Diffusion Transformer in Foreground-conditioned Inpainting
Dec 05, 2024Abstract:Foreground-conditioned inpainting aims to seamlessly fill the background region of an image by utilizing the provided foreground subject and a text description. While existing T2I-based image inpainting methods can be applied to this task, they suffer from issues of subject shape expansion, distortion, or impaired ability to align with the text description, resulting in inconsistencies between the visual elements and the text description. To address these challenges, we propose Pinco, a plug-and-play foreground-conditioned inpainting adapter that generates high-quality backgrounds with good text alignment while effectively preserving the shape of the foreground subject. Firstly, we design a Self-Consistent Adapter that integrates the foreground subject features into the layout-related self-attention layer, which helps to alleviate conflicts between the text and subject features by ensuring that the model can effectively consider the foreground subject's characteristics while processing the overall image layout. Secondly, we design a Decoupled Image Feature Extraction method that employs distinct architectures to extract semantic and shape features separately, significantly improving subject feature extraction and ensuring high-quality preservation of the subject's shape. Thirdly, to ensure precise utilization of the extracted features and to focus attention on the subject region, we introduce a Shared Positional Embedding Anchor, greatly improving the model's understanding of subject features and boosting training efficiency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance and efficiency in foreground-conditioned inpainting.
MimicMotion: High-Quality Human Motion Video Generation with Confidence-aware Pose Guidance
Jun 28, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, generative artificial intelligence has achieved significant advancements in the field of image generation, spawning a variety of applications. However, video generation still faces considerable challenges in various aspects, such as controllability, video length, and richness of details, which hinder the application and popularization of this technology. In this work, we propose a controllable video generation framework, dubbed MimicMotion, which can generate high-quality videos of arbitrary length mimicking specific motion guidance. Compared with previous methods, our approach has several highlights. Firstly, we introduce confidence-aware pose guidance that ensures high frame quality and temporal smoothness. Secondly, we introduce regional loss amplification based on pose confidence, which significantly reduces image distortion. Lastly, for generating long and smooth videos, we propose a progressive latent fusion strategy. By this means, we can produce videos of arbitrary length with acceptable resource consumption. With extensive experiments and user studies, MimicMotion demonstrates significant improvements over previous approaches in various aspects. Detailed results and comparisons are available on our project page: https://tencent.github.io/MimicMotion .
Revisiting Out-of-distribution Robustness in NLP: Benchmark, Analysis, and LLMs Evaluations
Jun 07, 2023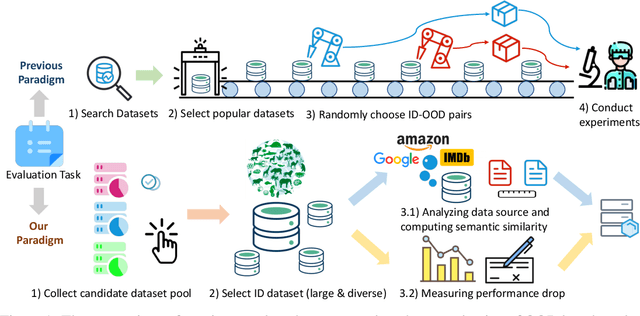
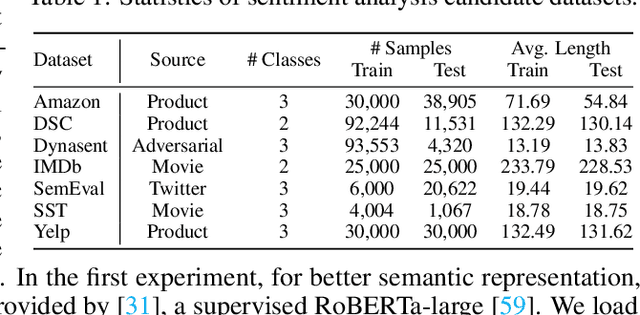
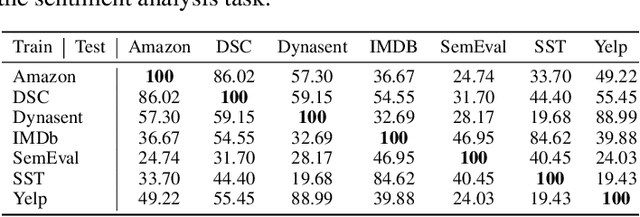
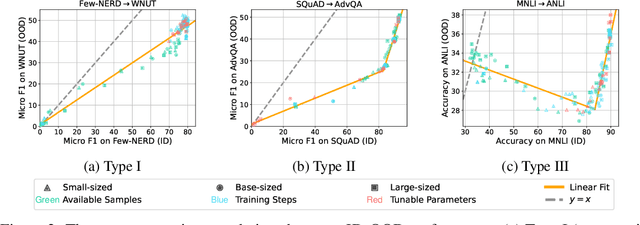
Abstract:This paper reexamines the research on out-of-distribution (OOD) robustness in the field of NLP. We find that the distribution shift settings in previous studies commonly lack adequate challenges, hindering the accurate evaluation of OOD robustness. To address these issues, we propose a benchmark construction protocol that ensures clear differentiation and challenging distribution shifts. Then we introduce BOSS, a Benchmark suite for Out-of-distribution robustneSS evaluation covering 5 tasks and 20 datasets. Based on BOSS, we conduct a series of experiments on pre-trained language models for analysis and evaluation of OOD robustness. First, for vanilla fine-tuning, we examine the relationship between in-distribution (ID) and OOD performance. We identify three typical types that unveil the inner learning mechanism, which could potentially facilitate the forecasting of OOD robustness, correlating with the advancements on ID datasets. Then, we evaluate 5 classic methods on BOSS and find that, despite exhibiting some effectiveness in specific cases, they do not offer significant improvement compared to vanilla fine-tuning. Further, we evaluate 5 LLMs with various adaptation paradigms and find that when sufficient ID data is available, fine-tuning domain-specific models outperform LLMs on ID examples significantly. However, in the case of OOD instances, prioritizing LLMs with in-context learning yields better results. We identify that both fine-tuned small models and LLMs face challenges in effectively addressing downstream tasks. The code is public at \url{https://github.com/lifan-yuan/OOD_NLP}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge