Cong Wang
Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Who Transfers Safety? Identifying and Targeting Cross-Lingual Shared Safety Neurons
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Multilingual safety remains significantly imbalanced, leaving non-high-resource (NHR) languages vulnerable compared to robust high-resource (HR) ones. Moreover, the neural mechanisms driving safety alignment remain unclear despite observed cross-lingual representation transfer. In this paper, we find that LLMs contain a set of cross-lingual shared safety neurons (SS-Neurons), a remarkably small yet critical neuronal subset that jointly regulates safety behavior across languages. We first identify monolingual safety neurons (MS-Neurons) and validate their causal role in safety refusal behavior through targeted activation and suppression. Our cross-lingual analyses then identify SS-Neurons as the subset of MS-Neurons shared between HR and NHR languages, serving as a bridge to transfer safety capabilities from HR to NHR domains. We observe that suppressing these neurons causes concurrent safety drops across NHR languages, whereas reinforcing them improves cross-lingual defensive consistency. Building on these insights, we propose a simple neuron-oriented training strategy that targets SS-Neurons based on language resource distribution and model architecture. Experiments demonstrate that fine-tuning this tiny neuronal subset outperforms state-of-the-art methods, significantly enhancing NHR safety while maintaining the model's general capabilities. The code and dataset will be available athttps://github.com/1518630367/SS-Neuron-Expansion.
Just Ask: Curious Code Agents Reveal System Prompts in Frontier LLMs
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Autonomous code agents built on large language models are reshaping software and AI development through tool use, long-horizon reasoning, and self-directed interaction. However, this autonomy introduces a previously unrecognized security risk: agentic interaction fundamentally expands the LLM attack surface, enabling systematic probing and recovery of hidden system prompts that guide model behavior. We identify system prompt extraction as an emergent vulnerability intrinsic to code agents and present \textbf{\textsc{JustAsk}}, a self-evolving framework that autonomously discovers effective extraction strategies through interaction alone. Unlike prior prompt-engineering or dataset-based attacks, \textsc{JustAsk} requires no handcrafted prompts, labeled supervision, or privileged access beyond standard user interaction. It formulates extraction as an online exploration problem, using Upper Confidence Bound-based strategy selection and a hierarchical skill space spanning atomic probes and high-level orchestration. These skills exploit imperfect system-instruction generalization and inherent tensions between helpfulness and safety. Evaluated on \textbf{41} black-box commercial models across multiple providers, \textsc{JustAsk} consistently achieves full or near-complete system prompt recovery, revealing recurring design- and architecture-level vulnerabilities. Our results expose system prompts as a critical yet largely unprotected attack surface in modern agent systems.
TraceRouter: Robust Safety for Large Foundation Models via Path-Level Intervention
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Despite their capabilities, large foundation models (LFMs) remain susceptible to adversarial manipulation. Current defenses predominantly rely on the "locality hypothesis", suppressing isolated neurons or features. However, harmful semantics act as distributed, cross-layer circuits, rendering such localized interventions brittle and detrimental to utility. To bridge this gap, we propose \textbf{TraceRouter}, a path-level framework that traces and disconnects the causal propagation circuits of illicit semantics. TraceRouter operates in three stages: (1) it pinpoints a sensitive onset layer by analyzing attention divergence; (2) it leverages sparse autoencoders (SAEs) and differential activation analysis to disentangle and isolate malicious features; and (3) it maps these features to downstream causal pathways via feature influence scores (FIS) derived from zero-out interventions. By selectively suppressing these causal chains, TraceRouter physically severs the flow of harmful information while leaving orthogonal computation routes intact. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TraceRouter significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, achieving a superior trade-off between adversarial robustness and general utility. Our code will be publicly released. WARNING: This paper contains unsafe model responses.
Innovator-VL: A Multimodal Large Language Model for Scientific Discovery
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:We present Innovator-VL, a scientific multimodal large language model designed to advance understanding and reasoning across diverse scientific domains while maintaining excellent performance on general vision tasks. Contrary to the trend of relying on massive domain-specific pretraining and opaque pipelines, our work demonstrates that principled training design and transparent methodology can yield strong scientific intelligence with substantially reduced data requirements. (i) First, we provide a fully transparent, end-to-end reproducible training pipeline, covering data collection, cleaning, preprocessing, supervised fine-tuning, reinforcement learning, and evaluation, along with detailed optimization recipes. This facilitates systematic extension by the community. (ii) Second, Innovator-VL exhibits remarkable data efficiency, achieving competitive performance on various scientific tasks using fewer than five million curated samples without large-scale pretraining. These results highlight that effective reasoning can be achieved through principled data selection rather than indiscriminate scaling. (iii) Third, Innovator-VL demonstrates strong generalization, achieving competitive performance on general vision, multimodal reasoning, and scientific benchmarks. This indicates that scientific alignment can be integrated into a unified model without compromising general-purpose capabilities. Our practices suggest that efficient, reproducible, and high-performing scientific multimodal models can be built even without large-scale data, providing a practical foundation for future research.
FUSE-RSVLM: Feature Fusion Vision-Language Model for Remote Sensing
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Large vision-language models (VLMs) exhibit strong performance across various tasks. However, these VLMs encounter significant challenges when applied to the remote sensing domain due to the inherent differences between remote sensing images and natural images. Existing remote sensing VLMs often fail to extract fine-grained visual features and suffer from visual forgetting during deep language processing. To address this, we introduce MF-RSVLM, a Multi-Feature Fusion Remote Sensing Vision--Language Model that effectively extracts and fuses visual features for RS understanding. MF-RSVLM learns multi-scale visual representations and combines global context with local details, improving the capture of small and complex structures in RS scenes. A recurrent visual feature injection scheme ensures the language model remains grounded in visual evidence and reduces visual forgetting during generation. Extensive experiments on diverse RS benchmarks show that MF-RSVLM achieves state-of-the-art or highly competitive performance across remote sensing classification, image captioning, and VQA tasks. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/Yunkaidang/RSVLM.
PrivTune: Efficient and Privacy-Preserving Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models via Device-Cloud Collaboration
Dec 09, 2025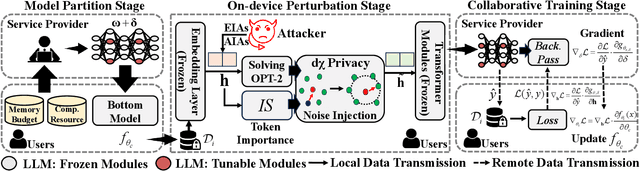
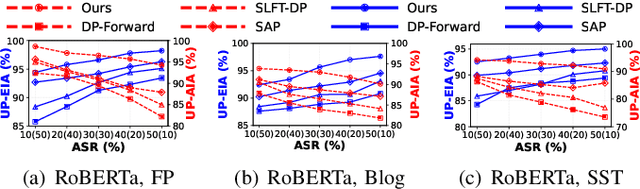
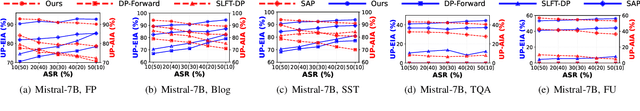
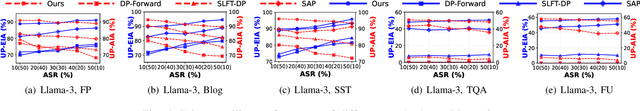
Abstract:With the rise of large language models, service providers offer language models as a service, enabling users to fine-tune customized models via uploaded private datasets. However, this raises concerns about sensitive data leakage. Prior methods, relying on differential privacy within device-cloud collaboration frameworks, struggle to balance privacy and utility, exposing users to inference attacks or degrading fine-tuning performance. To address this, we propose PrivTune, an efficient and privacy-preserving fine-tuning framework via Split Learning (SL). The key idea of PrivTune is to inject crafted noise into token representations from the SL bottom model, making each token resemble the $n$-hop indirect neighbors. PrivTune formulates this as an optimization problem to compute the optimal noise vector, aligning with defense-utility goals. On this basis, it then adjusts the parameters (i.e., mean) of the $d_χ$-Privacy noise distribution to align with the optimization direction and scales the noise according to token importance to minimize distortion. Experiments on five datasets (covering both classification and generation tasks) against three embedding inversion and three attribute inference attacks show that, using RoBERTa on the Stanford Sentiment Treebank dataset, PrivTune reduces the attack success rate to 10% with only a 3.33% drop in utility performance, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines.
RegionMarker: A Region-Triggered Semantic Watermarking Framework for Embedding-as-a-Service Copyright Protection
Nov 17, 2025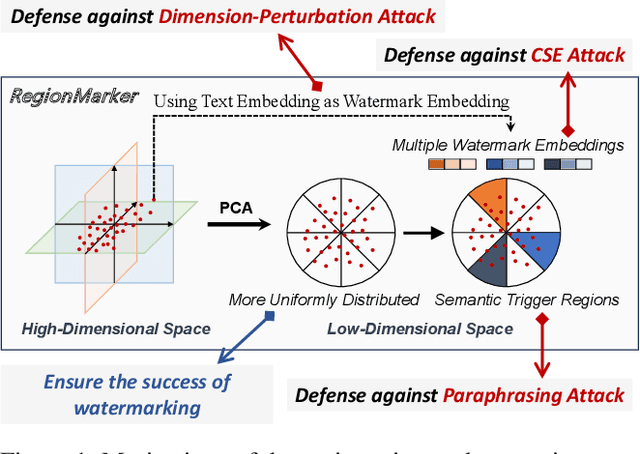
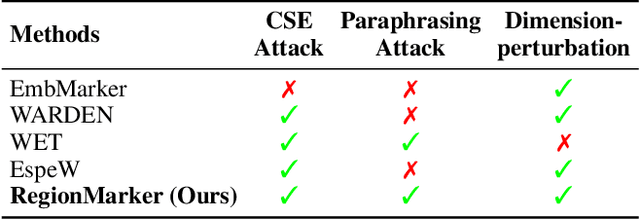
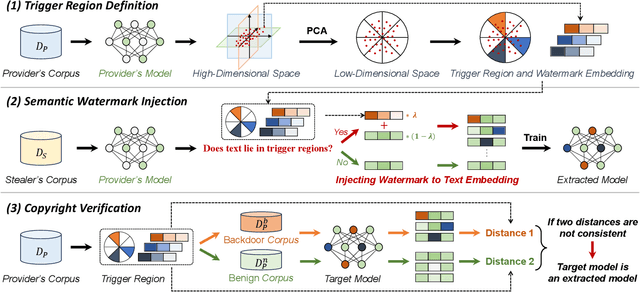
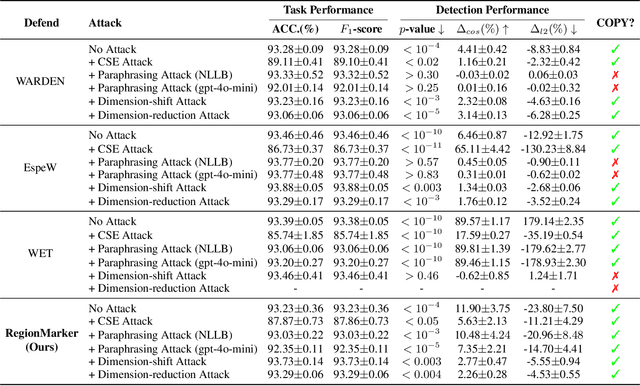
Abstract:Embedding-as-a-Service (EaaS) is an effective and convenient deployment solution for addressing various NLP tasks. Nevertheless, recent research has shown that EaaS is vulnerable to model extraction attacks, which could lead to significant economic losses for model providers. For copyright protection, existing methods inject watermark embeddings into text embeddings and use them to detect copyright infringement. However, current watermarking methods often resist only a subset of attacks and fail to provide \textit{comprehensive} protection. To this end, we present the region-triggered semantic watermarking framework called RegionMarker, which defines trigger regions within a low-dimensional space and injects watermarks into text embeddings associated with these regions. By utilizing a secret dimensionality reduction matrix to project onto this subspace and randomly selecting trigger regions, RegionMarker makes it difficult for watermark removal attacks to evade detection. Furthermore, by embedding watermarks across the entire trigger region and using the text embedding as the watermark, RegionMarker is resilient to both paraphrasing and dimension-perturbation attacks. Extensive experiments on various datasets show that RegionMarker is effective in resisting different attack methods, thereby protecting the copyright of EaaS.
HQ-SVC: Towards High-Quality Zero-Shot Singing Voice Conversion in Low-Resource Scenarios
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Zero-shot singing voice conversion (SVC) transforms a source singer's timbre to an unseen target speaker's voice while preserving melodic content without fine-tuning. Existing methods model speaker timbre and vocal content separately, losing essential acoustic information that degrades output quality while requiring significant computational resources. To overcome these limitations, we propose HQ-SVC, an efficient framework for high-quality zero-shot SVC. HQ-SVC first extracts jointly content and speaker features using a decoupled codec. It then enhances fidelity through pitch and volume modeling, preserving critical acoustic information typically lost in separate modeling approaches, and progressively refines outputs via differentiable signal processing and diffusion techniques. Evaluations confirm HQ-SVC significantly outperforms state-of-the-art zero-shot SVC methods in conversion quality and efficiency. Beyond voice conversion, HQ-SVC achieves superior voice naturalness compared to specialized audio super-resolution methods while natively supporting voice super-resolution tasks.
Black-Box Guardrail Reverse-engineering Attack
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) increasingly employ guardrails to enforce ethical, legal, and application-specific constraints on their outputs. While effective at mitigating harmful responses, these guardrails introduce a new class of vulnerabilities by exposing observable decision patterns. In this work, we present the first study of black-box LLM guardrail reverse-engineering attacks. We propose Guardrail Reverse-engineering Attack (GRA), a reinforcement learning-based framework that leverages genetic algorithm-driven data augmentation to approximate the decision-making policy of victim guardrails. By iteratively collecting input-output pairs, prioritizing divergence cases, and applying targeted mutations and crossovers, our method incrementally converges toward a high-fidelity surrogate of the victim guardrail. We evaluate GRA on three widely deployed commercial systems, namely ChatGPT, DeepSeek, and Qwen3, and demonstrate that it achieves an rule matching rate exceeding 0.92 while requiring less than $85 in API costs. These findings underscore the practical feasibility of guardrail extraction and highlight significant security risks for current LLM safety mechanisms. Our findings expose critical vulnerabilities in current guardrail designs and highlight the urgent need for more robust defense mechanisms in LLM deployment.
CHOIR: Collaborative Harmonization fOr Inference Robustness
Oct 26, 2025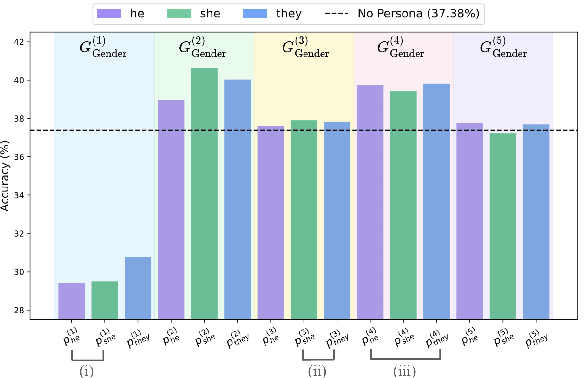

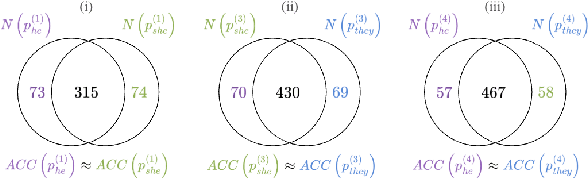

Abstract:Persona-assigned Large Language Models (LLMs) can adopt diverse roles, enabling personalized and context-aware reasoning. However, even minor demographic perturbations in personas, such as simple pronoun changes, can alter reasoning trajectories, leading to divergent sets of correct answers. Instead of treating these variations as biases to be mitigated, we explore their potential as a constructive resource to improve reasoning robustness. We propose CHOIR (Collaborative Harmonization fOr Inference Robustness), a test-time framework that harmonizes multiple persona-conditioned reasoning signals into a unified prediction. CHOIR orchestrates a collaborative decoding process among counterfactual personas, dynamically balancing agreement and divergence in their reasoning paths. Experiments on various reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that CHOIR consistently enhances performance across demographics, model architectures, scales, and tasks - without additional training. Improvements reach up to 26.4% for individual demographic groups and 19.2% on average across five demographics. It remains effective even when base personas are suboptimal. By reframing persona variation as a constructive signal, CHOIR provides a scalable and generalizable approach to more reliable LLM reasoning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge