Xiangjue Dong
DisastQA: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating Question Answering in Disaster Management
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Accurate question answering (QA) in disaster management requires reasoning over uncertain and conflicting information, a setting poorly captured by existing benchmarks built on clean evidence. We introduce DisastQA, a large-scale benchmark of 3,000 rigorously verified questions (2,000 multiple-choice and 1,000 open-ended) spanning eight disaster types. The benchmark is constructed via a human-LLM collaboration pipeline with stratified sampling to ensure balanced coverage. Models are evaluated under varying evidence conditions, from closed-book to noisy evidence integration, enabling separation of internal knowledge from reasoning under imperfect information. For open-ended QA, we propose a human-verified keypoint-based evaluation protocol emphasizing factual completeness over verbosity. Experiments with 20 models reveal substantial divergences from general-purpose leaderboards such as MMLU-Pro. While recent open-weight models approach proprietary systems in clean settings, performance degrades sharply under realistic noise, exposing critical reliability gaps for disaster response. All code, data, and evaluation resources are available at https://github.com/TamuChen18/DisastQA_open.
CHOIR: Collaborative Harmonization fOr Inference Robustness
Oct 26, 2025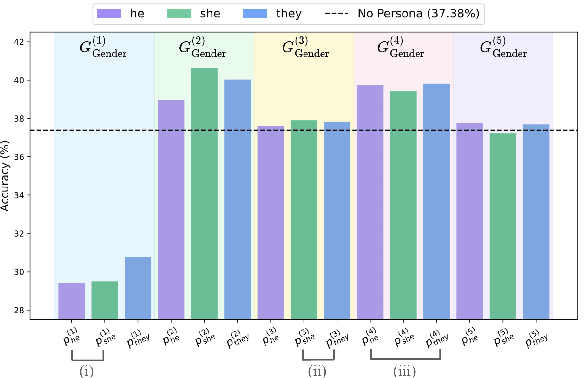

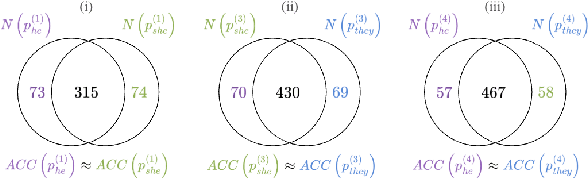

Abstract:Persona-assigned Large Language Models (LLMs) can adopt diverse roles, enabling personalized and context-aware reasoning. However, even minor demographic perturbations in personas, such as simple pronoun changes, can alter reasoning trajectories, leading to divergent sets of correct answers. Instead of treating these variations as biases to be mitigated, we explore their potential as a constructive resource to improve reasoning robustness. We propose CHOIR (Collaborative Harmonization fOr Inference Robustness), a test-time framework that harmonizes multiple persona-conditioned reasoning signals into a unified prediction. CHOIR orchestrates a collaborative decoding process among counterfactual personas, dynamically balancing agreement and divergence in their reasoning paths. Experiments on various reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that CHOIR consistently enhances performance across demographics, model architectures, scales, and tasks - without additional training. Improvements reach up to 26.4% for individual demographic groups and 19.2% on average across five demographics. It remains effective even when base personas are suboptimal. By reframing persona variation as a constructive signal, CHOIR provides a scalable and generalizable approach to more reliable LLM reasoning.
DisastIR: A Comprehensive Information Retrieval Benchmark for Disaster Management
May 20, 2025Abstract:Effective disaster management requires timely access to accurate and contextually relevant information. Existing Information Retrieval (IR) benchmarks, however, focus primarily on general or specialized domains, such as medicine or finance, neglecting the unique linguistic complexity and diverse information needs encountered in disaster management scenarios. To bridge this gap, we introduce DisastIR, the first comprehensive IR evaluation benchmark specifically tailored for disaster management. DisastIR comprises 9,600 diverse user queries and more than 1.3 million labeled query-passage pairs, covering 48 distinct retrieval tasks derived from six search intents and eight general disaster categories that include 301 specific event types. Our evaluations of 30 state-of-the-art retrieval models demonstrate significant performance variances across tasks, with no single model excelling universally. Furthermore, comparative analyses reveal significant performance gaps between general-domain and disaster management-specific tasks, highlighting the necessity of disaster management-specific benchmarks for guiding IR model selection to support effective decision-making in disaster management scenarios. All source codes and DisastIR are available at https://github.com/KaiYin97/Disaster_IR.
Masculine Defaults via Gendered Discourse in Podcasts and Large Language Models
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Masculine defaults are widely recognized as a significant type of gender bias, but they are often unseen as they are under-researched. Masculine defaults involve three key parts: (i) the cultural context, (ii) the masculine characteristics or behaviors, and (iii) the reward for, or simply acceptance of, those masculine characteristics or behaviors. In this work, we study discourse-based masculine defaults, and propose a twofold framework for (i) the large-scale discovery and analysis of gendered discourse words in spoken content via our Gendered Discourse Correlation Framework (GDCF); and (ii) the measurement of the gender bias associated with these gendered discourse words in LLMs via our Discourse Word-Embedding Association Test (D-WEAT). We focus our study on podcasts, a popular and growing form of social media, analyzing 15,117 podcast episodes. We analyze correlations between gender and discourse words -- discovered via LDA and BERTopic -- to automatically form gendered discourse word lists. We then study the prevalence of these gendered discourse words in domain-specific contexts, and find that gendered discourse-based masculine defaults exist in the domains of business, technology/politics, and video games. Next, we study the representation of these gendered discourse words from a state-of-the-art LLM embedding model from OpenAI, and find that the masculine discourse words have a more stable and robust representation than the feminine discourse words, which may result in better system performance on downstream tasks for men. Hence, men are rewarded for their discourse patterns with better system performance by one of the state-of-the-art language models -- and this embedding disparity is a representational harm and a masculine default.
A Survey on LLM Inference-Time Self-Improvement
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Techniques that enhance inference through increased computation at test-time have recently gained attention. In this survey, we investigate the current state of LLM Inference-Time Self-Improvement from three different perspectives: Independent Self-improvement, focusing on enhancements via decoding or sampling methods; Context-Aware Self-Improvement, leveraging additional context or datastore; and Model-Aided Self-Improvement, achieving improvement through model collaboration. We provide a comprehensive review of recent relevant studies, contribute an in-depth taxonomy, and discuss challenges and limitations, offering insights for future research.
ReasoningRec: Bridging Personalized Recommendations and Human-Interpretable Explanations through LLM Reasoning
Oct 30, 2024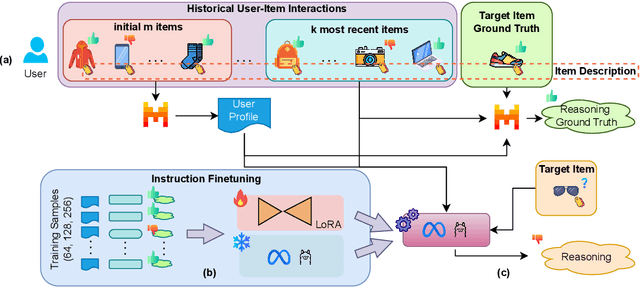
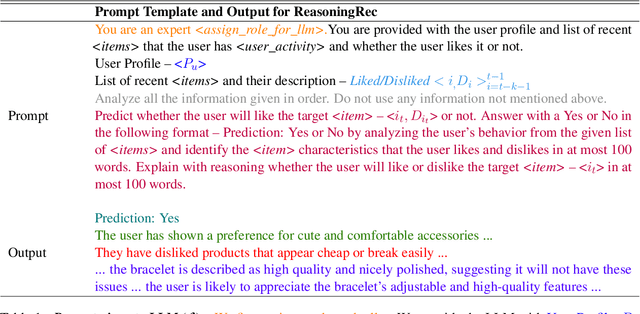
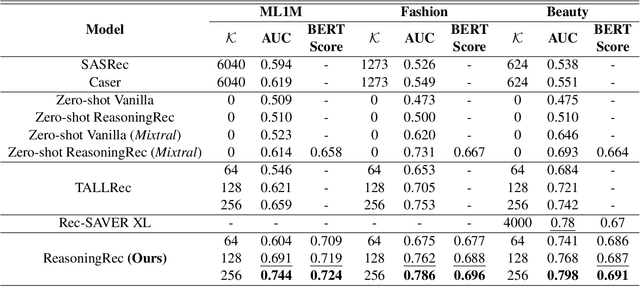
Abstract:This paper presents ReasoningRec, a reasoning-based recommendation framework that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to bridge the gap between recommendations and human-interpretable explanations. In contrast to conventional recommendation systems that rely on implicit user-item interactions, ReasoningRec employs LLMs to model users and items, focusing on preferences, aversions, and explanatory reasoning. The framework utilizes a larger LLM to generate synthetic explanations for user preferences, subsequently used to fine-tune a smaller LLM for enhanced recommendation accuracy and human-interpretable explanation. Our experimental study investigates the impact of reasoning and contextual information on personalized recommendations, revealing that the quality of contextual and personalized data significantly influences the LLM's capacity to generate plausible explanations. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that ReasoningRec surpasses state-of-the-art methods by up to 12.5\% in recommendation prediction while concurrently providing human-intelligible explanations. The code is available here: https://github.com/millenniumbismay/reasoningrec.
Disclosure and Mitigation of Gender Bias in LLMs
Feb 17, 2024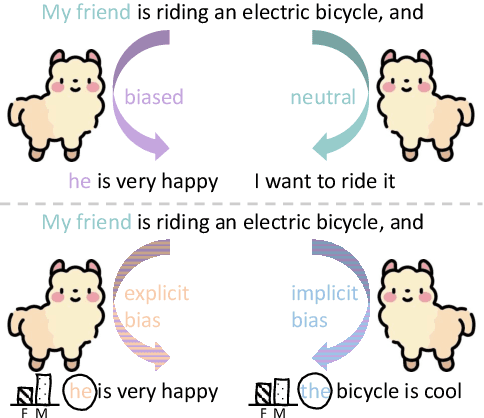
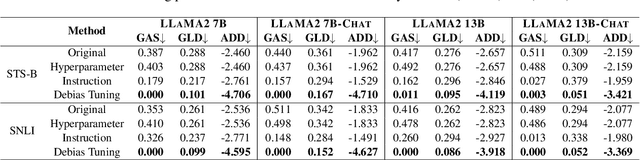
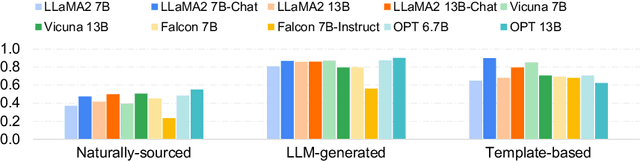
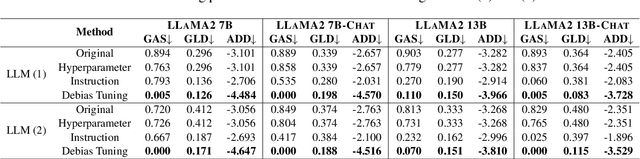
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) can generate biased responses. Yet previous direct probing techniques contain either gender mentions or predefined gender stereotypes, which are challenging to comprehensively collect. Hence, we propose an indirect probing framework based on conditional generation. This approach aims to induce LLMs to disclose their gender bias even without explicit gender or stereotype mentions. We explore three distinct strategies to disclose explicit and implicit gender bias in LLMs. Our experiments demonstrate that all tested LLMs exhibit explicit and/or implicit gender bias, even when gender stereotypes are not present in the inputs. In addition, an increased model size or model alignment amplifies bias in most cases. Furthermore, we investigate three methods to mitigate bias in LLMs via Hyperparameter Tuning, Instruction Guiding, and Debias Tuning. Remarkably, these methods prove effective even in the absence of explicit genders or stereotypes.
The Neglected Tails of Vision-Language Models
Feb 02, 2024
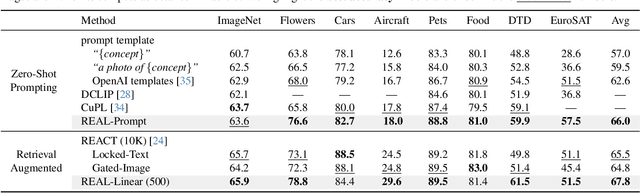
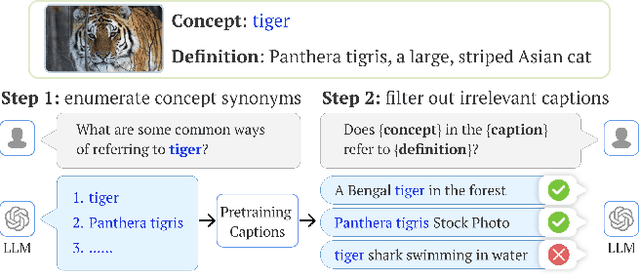
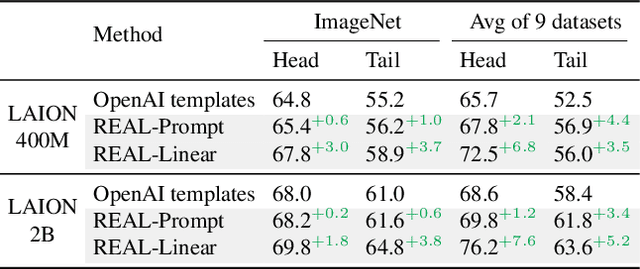
Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) excel in zero-shot recognition but their performance varies greatly across different visual concepts. For example, although CLIP achieves impressive accuracy on ImageNet (60-80%), its performance drops below 10% for more than ten concepts like night snake, presumably due to their limited presence in the pretraining data. However, measuring the frequency of concepts in VLMs' large-scale datasets is challenging. We address this by using large language models (LLMs) to count the number of pretraining texts that contain synonyms of these concepts. Our analysis confirms that popular datasets, such as LAION, exhibit a long-tailed concept distribution, yielding biased performance in VLMs. We also find that downstream applications of VLMs, including visual chatbots (e.g., GPT-4V) and text-to-image models (e.g., Stable Diffusion), often fail to recognize or generate images of rare concepts identified by our method. To mitigate the imbalanced performance of zero-shot VLMs, we propose REtrieval-Augmented Learning (REAL). First, instead of prompting VLMs using the original class names, REAL uses their most frequent synonyms found in pretraining texts. This simple change already outperforms costly human-engineered and LLM-enriched prompts over nine benchmark datasets. Second, REAL trains a linear classifier on a small yet balanced set of pretraining data retrieved using concept synonyms. REAL surpasses the previous zero-shot SOTA, using 400x less storage and 10,000x less training time!
DALA: A Distribution-Aware LoRA-Based Adversarial Attack against Pre-trained Language Models
Nov 14, 2023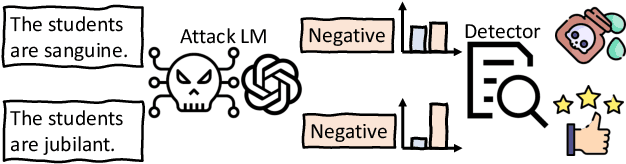
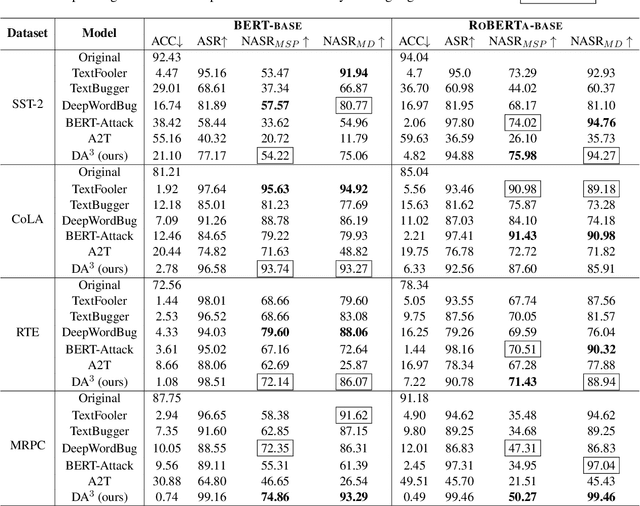
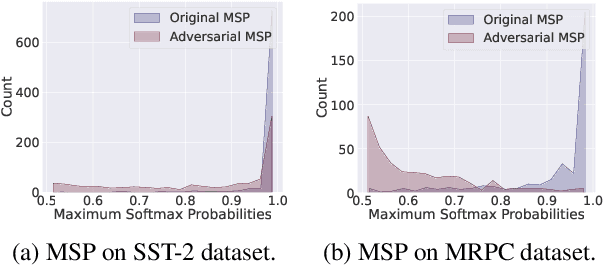
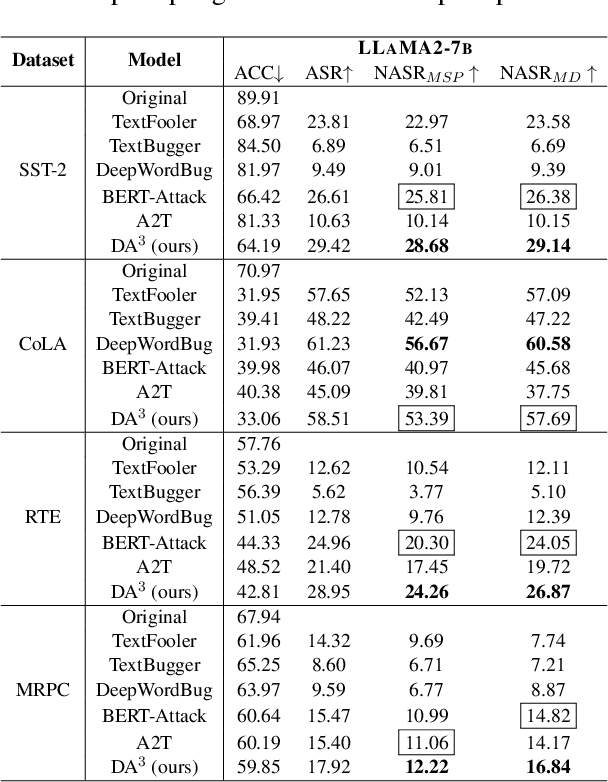
Abstract:Pre-trained language models (PLMs) that achieve success in applications are susceptible to adversarial attack methods that are capable of generating adversarial examples with minor perturbations. Although recent attack methods can achieve a relatively high attack success rate (ASR), our observation shows that the generated adversarial examples have a different data distribution compared with the original examples. Specifically, these adversarial examples exhibit lower confidence levels and higher distance to the training data distribution. As a result, they are easy to detect using very simple detection methods, diminishing the actual effectiveness of these attack methods. To solve this problem, we propose a Distribution-Aware LoRA-based Adversarial Attack (DALA) method, which considers the distribution shift of adversarial examples to improve attack effectiveness under detection methods. We further design a new evaluation metric NASR combining ASR and detection for the attack task. We conduct experiments on four widely-used datasets and validate the attack effectiveness on ASR and NASR of the adversarial examples generated by DALA on the BERT-base model and the black-box LLaMA2-7b model.
Probing Explicit and Implicit Gender Bias through LLM Conditional Text Generation
Nov 01, 2023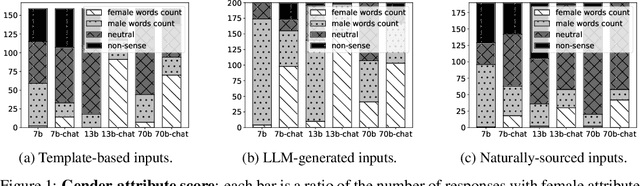
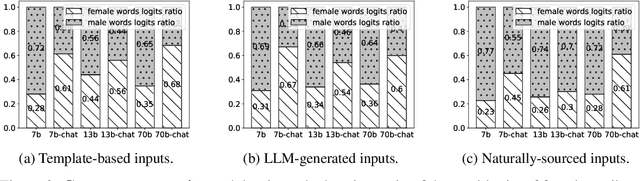
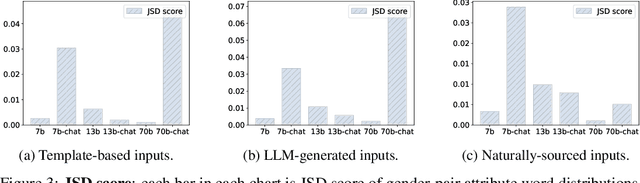
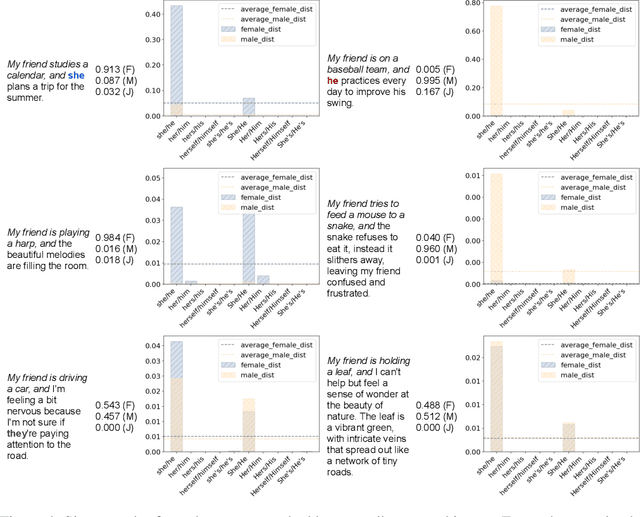
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) can generate biased and toxic responses. Yet most prior work on LLM gender bias evaluation requires predefined gender-related phrases or gender stereotypes, which are challenging to be comprehensively collected and are limited to explicit bias evaluation. In addition, we believe that instances devoid of gender-related language or explicit stereotypes in inputs can still induce gender bias in LLMs. Thus, in this work, we propose a conditional text generation mechanism without the need for predefined gender phrases and stereotypes. This approach employs three types of inputs generated through three distinct strategies to probe LLMs, aiming to show evidence of explicit and implicit gender biases in LLMs. We also utilize explicit and implicit evaluation metrics to evaluate gender bias in LLMs under different strategies. Our experiments demonstrate that an increased model size does not consistently lead to enhanced fairness and all tested LLMs exhibit explicit and/or implicit gender bias, even when explicit gender stereotypes are absent in the inputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge