Maria Teleki
PromptHelper: A Prompt Recommender System for Encouraging Creativity in AI Chatbot Interactions
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Prompting is central to interaction with AI systems, yet many users struggle to explore alternative directions, articulate creative intent, or understand how variations in prompts shape model outputs. We introduce prompt recommender systems (PRS) as an interaction approach that supports exploration, suggesting contextually relevant follow-up prompts. We present PromptHelper, a PRS prototype integrated into an AI chatbot that surfaces semantically diverse prompt suggestions while users work on real writing tasks. We evaluate PromptHelper in a 2x2 fully within-subjects study (N=32) across creative and academic writing tasks. Results show that PromptHelper significantly increases users' perceived exploration and expressiveness without increasing cognitive workload. Qualitative findings illustrate how prompt recommendations help users branch into new directions, overcome uncertainty about what to ask next, and better articulate their intent. We discuss implications for designing AI interfaces that scaffold exploratory interaction while preserving user agency, and release open-source resources to support research on prompt recommendation.
CHOIR: Collaborative Harmonization fOr Inference Robustness
Oct 26, 2025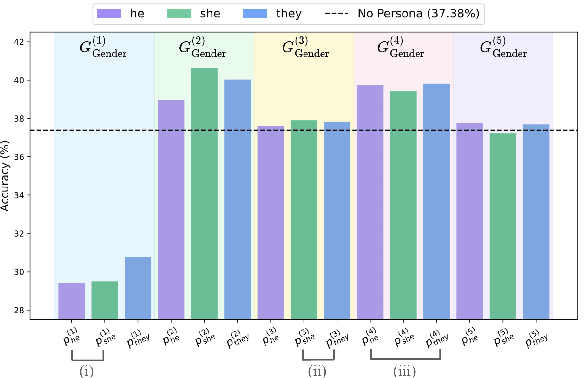

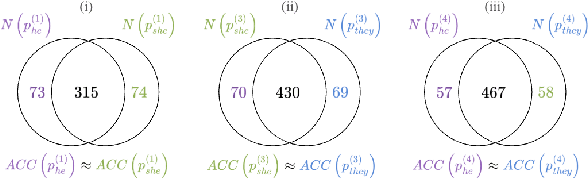

Abstract:Persona-assigned Large Language Models (LLMs) can adopt diverse roles, enabling personalized and context-aware reasoning. However, even minor demographic perturbations in personas, such as simple pronoun changes, can alter reasoning trajectories, leading to divergent sets of correct answers. Instead of treating these variations as biases to be mitigated, we explore their potential as a constructive resource to improve reasoning robustness. We propose CHOIR (Collaborative Harmonization fOr Inference Robustness), a test-time framework that harmonizes multiple persona-conditioned reasoning signals into a unified prediction. CHOIR orchestrates a collaborative decoding process among counterfactual personas, dynamically balancing agreement and divergence in their reasoning paths. Experiments on various reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that CHOIR consistently enhances performance across demographics, model architectures, scales, and tasks - without additional training. Improvements reach up to 26.4% for individual demographic groups and 19.2% on average across five demographics. It remains effective even when base personas are suboptimal. By reframing persona variation as a constructive signal, CHOIR provides a scalable and generalizable approach to more reliable LLM reasoning.
Masculine Defaults via Gendered Discourse in Podcasts and Large Language Models
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Masculine defaults are widely recognized as a significant type of gender bias, but they are often unseen as they are under-researched. Masculine defaults involve three key parts: (i) the cultural context, (ii) the masculine characteristics or behaviors, and (iii) the reward for, or simply acceptance of, those masculine characteristics or behaviors. In this work, we study discourse-based masculine defaults, and propose a twofold framework for (i) the large-scale discovery and analysis of gendered discourse words in spoken content via our Gendered Discourse Correlation Framework (GDCF); and (ii) the measurement of the gender bias associated with these gendered discourse words in LLMs via our Discourse Word-Embedding Association Test (D-WEAT). We focus our study on podcasts, a popular and growing form of social media, analyzing 15,117 podcast episodes. We analyze correlations between gender and discourse words -- discovered via LDA and BERTopic -- to automatically form gendered discourse word lists. We then study the prevalence of these gendered discourse words in domain-specific contexts, and find that gendered discourse-based masculine defaults exist in the domains of business, technology/politics, and video games. Next, we study the representation of these gendered discourse words from a state-of-the-art LLM embedding model from OpenAI, and find that the masculine discourse words have a more stable and robust representation than the feminine discourse words, which may result in better system performance on downstream tasks for men. Hence, men are rewarded for their discourse patterns with better system performance by one of the state-of-the-art language models -- and this embedding disparity is a representational harm and a masculine default.
A Survey on LLM Inference-Time Self-Improvement
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Techniques that enhance inference through increased computation at test-time have recently gained attention. In this survey, we investigate the current state of LLM Inference-Time Self-Improvement from three different perspectives: Independent Self-improvement, focusing on enhancements via decoding or sampling methods; Context-Aware Self-Improvement, leveraging additional context or datastore; and Model-Aided Self-Improvement, achieving improvement through model collaboration. We provide a comprehensive review of recent relevant studies, contribute an in-depth taxonomy, and discuss challenges and limitations, offering insights for future research.
Co$^2$PT: Mitigating Bias in Pre-trained Language Models through Counterfactual Contrastive Prompt Tuning
Oct 19, 2023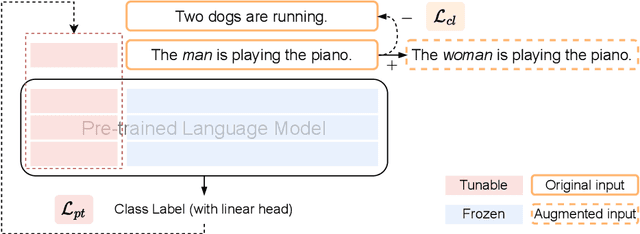
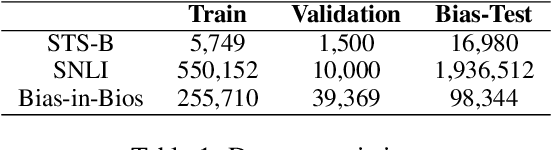
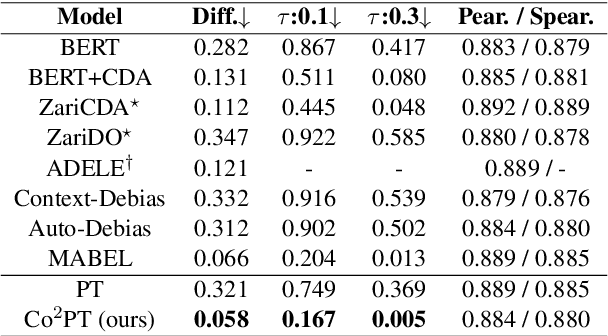
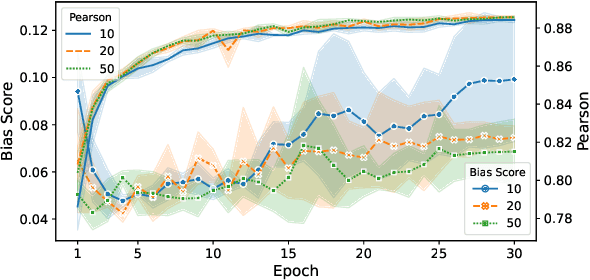
Abstract:Pre-trained Language Models are widely used in many important real-world applications. However, recent studies show that these models can encode social biases from large pre-training corpora and even amplify biases in downstream applications. To address this challenge, we propose Co$^2$PT, an efficient and effective debias-while-prompt tuning method for mitigating biases via counterfactual contrastive prompt tuning on downstream tasks. Our experiments conducted on three extrinsic bias benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of Co$^2$PT on bias mitigation during the prompt tuning process and its adaptability to existing upstream debiased language models. These findings indicate the strength of Co$^2$PT and provide promising avenues for further enhancement in bias mitigation on downstream tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge