Haoran Liu
From Chains to Graphs: Self-Structured Reasoning for General-Domain LLMs
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) show strong reasoning ability in open-domain question answering, yet their reasoning processes are typically linear and often logically inconsistent. In contrast, real-world reasoning requires integrating multiple premises and solving subproblems in parallel. Existing methods, such as Chain-of-Thought (CoT), express reasoning in a linear textual form, which may appear coherent but frequently leads to inconsistent conclusions. Recent approaches rely on externally provided graphs and do not explore how LLMs can construct and use their own graph-structured reasoning, particularly in open-domain QA. To fill this gap, we novelly explore graph-structured reasoning of LLMs in general-domain question answering. We propose Self-Graph Reasoning (SGR), a framework that enables LLMs to explicitly represent their reasoning process as a structured graph before producing the final answer. We further construct a graph-structured reasoning dataset that merges multiple candidate reasoning graphs into refined graph structures for model training. Experiments on five QA benchmarks across both general and specialized domains show that SGR consistently improves reasoning consistency and yields a 17.74% gain over the base model. The LLaMA-3.3-70B model fine-tuned with SGR performs comparably to GPT-4o and surpasses Claude-3.5-Haiku, demonstrating the effectiveness of graph-structured reasoning.
U-Net-Like Spiking Neural Networks for Single Image Dehazing
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Image dehazing is a critical challenge in computer vision, essential for enhancing image clarity in hazy conditions. Traditional methods often rely on atmospheric scattering models, while recent deep learning techniques, specifically Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Transformers, have improved performance by effectively analyzing image features. However, CNNs struggle with long-range dependencies, and Transformers demand significant computational resources. To address these limitations, we propose DehazeSNN, an innovative architecture that integrates a U-Net-like design with Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs). DehazeSNN captures multi-scale image features while efficiently managing local and long-range dependencies. The introduction of the Orthogonal Leaky-Integrate-and-Fire Block (OLIFBlock) enhances cross-channel communication, resulting in superior dehazing performance with reduced computational burden. Our extensive experiments show that DehazeSNN is highly competitive to state-of-the-art methods on benchmark datasets, delivering high-quality haze-free images with a smaller model size and less multiply-accumulate operations. The proposed dehazing method is publicly available at https://github.com/HaoranLiu507/DehazeSNN.
* 9 pages, 4 figures. Accepted at IJCNN 2025 (Rome, Italy). To appear in IEEE/IJCNN 2025 proceedings
Simultaneous Secrecy and Covert Communications (SSACC) in Mobility-Aware RIS-Aided Networks
Dec 18, 2025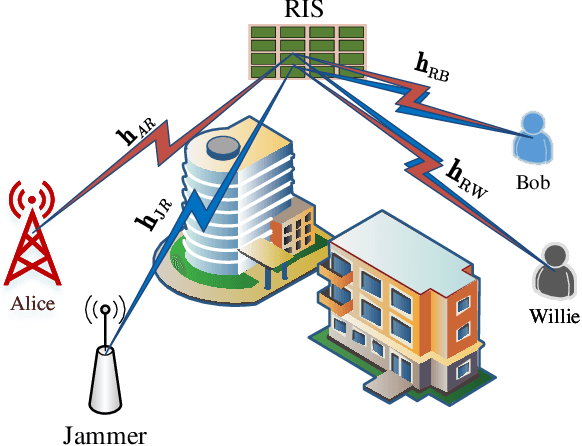
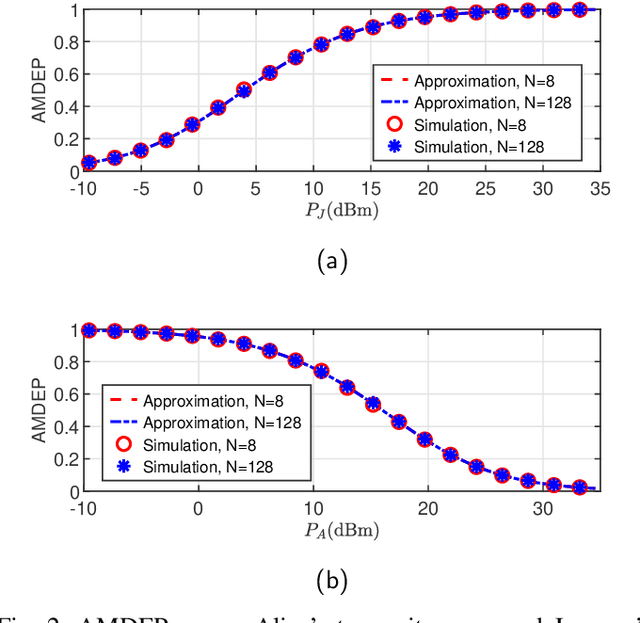
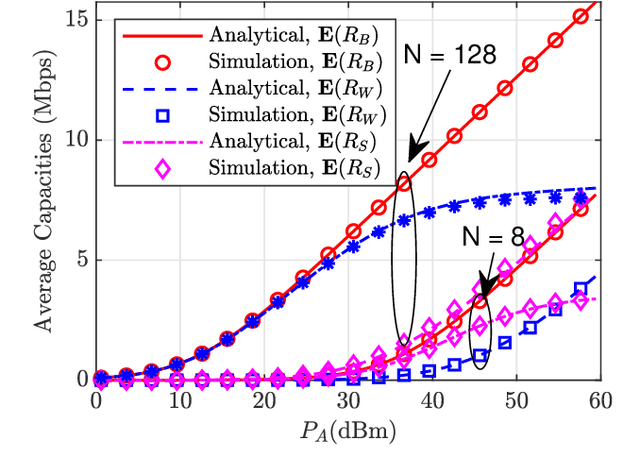
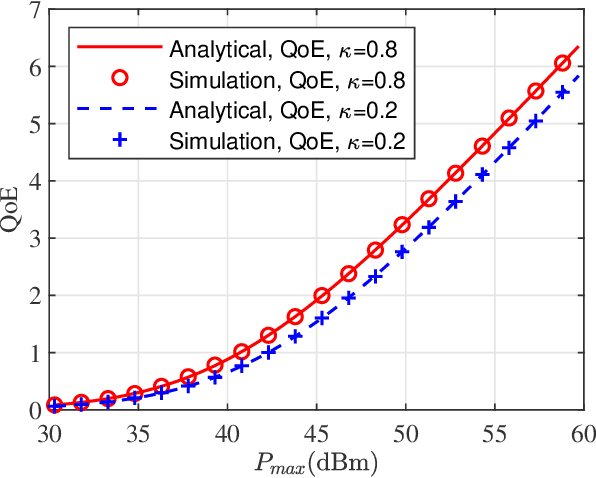
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a simultaneous secrecy and covert communications (SSACC) scheme in a reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided network with a cooperative jammer. The scheme enhances communication security by maximizing the secrecy capacity and the detection error probability (DEP). Under a worst-case scenario for covert communications, we consider that the eavesdropper can optimally adjust the detection threshold to minimize the DEP. Accordingly, we derive closedform expressions for both average minimum DEP (AMDEP) and average secrecy capacity (ASC). To balance AMDEP and ASC, we propose a new performance metric and design an algorithm based on generative diffusion models (GDM) and deep reinforcement learning (DRL). The algorithm maximizes data rates under user mobility while ensuring high AMDEP and ASC by optimizing power allocation. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm achieves faster convergence and superior performance compared to conventional deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) methods, thereby validating its effectiveness in balancing security and capacity performance.
PMMD: A pose-guided multi-view multi-modal diffusion for person generation
Dec 17, 2025



Abstract:Generating consistent human images with controllable pose and appearance is essential for applications in virtual try on, image editing, and digital human creation. Current methods often suffer from occlusions, garment style drift, and pose misalignment. We propose Pose-guided Multi-view Multimodal Diffusion (PMMD), a diffusion framework that synthesizes photorealistic person images conditioned on multi-view references, pose maps, and text prompts. A multimodal encoder jointly models visual views, pose features, and semantic descriptions, which reduces cross modal discrepancy and improves identity fidelity. We further design a ResCVA module to enhance local detail while preserving global structure, and a cross modal fusion module that integrates image semantics with text throughout the denoising pipeline. Experiments on the DeepFashion MultiModal dataset show that PMMD outperforms representative baselines in consistency, detail preservation, and controllability. Project page and code are available at https://github.com/ZANMANGLOOPYE/PMMD.
Masculine Defaults via Gendered Discourse in Podcasts and Large Language Models
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Masculine defaults are widely recognized as a significant type of gender bias, but they are often unseen as they are under-researched. Masculine defaults involve three key parts: (i) the cultural context, (ii) the masculine characteristics or behaviors, and (iii) the reward for, or simply acceptance of, those masculine characteristics or behaviors. In this work, we study discourse-based masculine defaults, and propose a twofold framework for (i) the large-scale discovery and analysis of gendered discourse words in spoken content via our Gendered Discourse Correlation Framework (GDCF); and (ii) the measurement of the gender bias associated with these gendered discourse words in LLMs via our Discourse Word-Embedding Association Test (D-WEAT). We focus our study on podcasts, a popular and growing form of social media, analyzing 15,117 podcast episodes. We analyze correlations between gender and discourse words -- discovered via LDA and BERTopic -- to automatically form gendered discourse word lists. We then study the prevalence of these gendered discourse words in domain-specific contexts, and find that gendered discourse-based masculine defaults exist in the domains of business, technology/politics, and video games. Next, we study the representation of these gendered discourse words from a state-of-the-art LLM embedding model from OpenAI, and find that the masculine discourse words have a more stable and robust representation than the feminine discourse words, which may result in better system performance on downstream tasks for men. Hence, men are rewarded for their discourse patterns with better system performance by one of the state-of-the-art language models -- and this embedding disparity is a representational harm and a masculine default.
MKG-Rank: Enhancing Large Language Models with Knowledge Graph for Multilingual Medical Question Answering
Mar 21, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable progress in medical question answering (QA), yet their effectiveness remains predominantly limited to English due to imbalanced multilingual training data and scarce medical resources for low-resource languages. To address this critical language gap in medical QA, we propose Multilingual Knowledge Graph-based Retrieval Ranking (MKG-Rank), a knowledge graph-enhanced framework that enables English-centric LLMs to perform multilingual medical QA. Through a word-level translation mechanism, our framework efficiently integrates comprehensive English-centric medical knowledge graphs into LLM reasoning at a low cost, mitigating cross-lingual semantic distortion and achieving precise medical QA across language barriers. To enhance efficiency, we introduce caching and multi-angle ranking strategies to optimize the retrieval process, significantly reducing response times and prioritizing relevant medical knowledge. Extensive evaluations on multilingual medical QA benchmarks across Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and Swahili demonstrate that MKG-Rank consistently outperforms zero-shot LLMs, achieving maximum 35.03% increase in accuracy, while maintaining an average retrieval time of only 0.0009 seconds.
GraphCheck: Breaking Long-Term Text Barriers with Extracted Knowledge Graph-Powered Fact-Checking
Feb 23, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are widely used, but they often generate subtle factual errors, especially in long-form text. These errors are fatal in some specialized domains such as medicine. Existing fact-checking with grounding documents methods face two main challenges: (1) they struggle to understand complex multihop relations in long documents, often overlooking subtle factual errors; (2) most specialized methods rely on pairwise comparisons, requiring multiple model calls, leading to high resource and computational costs. To address these challenges, we propose \textbf{\textit{GraphCheck}}, a fact-checking framework that uses extracted knowledge graphs to enhance text representation. Graph Neural Networks further process these graphs as a soft prompt, enabling LLMs to incorporate structured knowledge more effectively. Enhanced with graph-based reasoning, GraphCheck captures multihop reasoning chains which are often overlooked by existing methods, enabling precise and efficient fact-checking in a single inference call. Experimental results on seven benchmarks spanning both general and medical domains demonstrate a 6.1\% overall improvement over baseline models. Notably, GraphCheck outperforms existing specialized fact-checkers and achieves comparable performance with state-of-the-art LLMs, such as DeepSeek-V3 and OpenAI-o1, with significantly fewer parameters.
Hierarchical Contextual Manifold Alignment for Structuring Latent Representations in Large Language Models
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:The organization of latent token representations plays a crucial role in determining the stability, generalization, and contextual consistency of language models, yet conventional approaches to embedding refinement often rely on parameter modifications that introduce additional computational overhead. A hierarchical alignment method was introduced to restructure token embeddings without altering core model weights, ensuring that representational distributions maintained coherence across different linguistic contexts. Experimental evaluations demonstrated improvements in rare token retrieval, adversarial robustness, and long-range dependency tracking, highlighting the advantages of hierarchical structuring in mitigating inconsistencies in latent space organization. The comparative analysis against conventional fine-tuning and embedding perturbation methods revealed that hierarchical restructuring maintained computational efficiency while achieving measurable gains in representation quality. Structural refinements introduced through the alignment process resulted in improved contextual stability across varied linguistic tasks, reducing inconsistencies in token proximity relationships and enhancing interpretability in language generation. A detailed computational assessment confirmed that the realignment process introduced minimal inference overhead, ensuring that representational improvements did not compromise model efficiency. The findings reinforced the broader significance of structured representation learning, illustrating that hierarchical embedding modifications could serve as an effective strategy for refining latent space distributions while preserving pre-learned semantic associations.
Issues with Neural Tangent Kernel Approach to Neural Networks
Jan 19, 2025


Abstract:Neural tangent kernels (NTKs) have been proposed to study the behavior of trained neural networks from the perspective of Gaussian processes. An important result in this body of work is the theorem of equivalence between a trained neural network and kernel regression with the corresponding NTK. This theorem allows for an interpretation of neural networks as special cases of kernel regression. However, does this theorem of equivalence hold in practice? In this paper, we revisit the derivation of the NTK rigorously and conduct numerical experiments to evaluate this equivalence theorem. We observe that adding a layer to a neural network and the corresponding updated NTK do not yield matching changes in the predictor error. Furthermore, we observe that kernel regression with a Gaussian process kernel in the literature that does not account for neural network training produces prediction errors very close to that of kernel regression with NTKs. These observations suggest the equivalence theorem does not hold well in practice and puts into question whether neural tangent kernels adequately address the training process of neural networks.
Learning Disentangled Equivariant Representation for Explicitly Controllable 3D Molecule Generation
Dec 19, 2024Abstract:We consider the conditional generation of 3D drug-like molecules with \textit{explicit control} over molecular properties such as drug-like properties (e.g., Quantitative Estimate of Druglikeness or Synthetic Accessibility score) and effectively binding to specific protein sites. To tackle this problem, we propose an E(3)-equivariant Wasserstein autoencoder and factorize the latent space of our generative model into two disentangled aspects: molecular properties and the remaining structural context of 3D molecules. Our model ensures explicit control over these molecular attributes while maintaining equivariance of coordinate representation and invariance of data likelihood. Furthermore, we introduce a novel alignment-based coordinate loss to adapt equivariant networks for auto-regressive de-novo 3D molecule generation from scratch. Extensive experiments validate our model's effectiveness on property-guided and context-guided molecule generation, both for de-novo 3D molecule design and structure-based drug discovery against protein targets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge