Bingqi Liu
Random-coupled Neural Network
Mar 26, 2024Abstract:Improving the efficiency of current neural networks and modeling them in biological neural systems have become popular research directions in recent years. Pulse-coupled neural network (PCNN) is a well applicated model for imitating the computation characteristics of the human brain in computer vision and neural network fields. However, differences between the PCNN and biological neural systems remain: limited neural connection, high computational cost, and lack of stochastic property. In this study, random-coupled neural network (RCNN) is proposed. It overcomes these difficulties in PCNN's neuromorphic computing via a random inactivation process. This process randomly closes some neural connections in the RCNN model, realized by the random inactivation weight matrix of link input. This releases the computational burden of PCNN, making it affordable to achieve vast neural connections. Furthermore, the image and video processing mechanisms of RCNN are researched. It encodes constant stimuli as periodic spike trains and periodic stimuli as chaotic spike trains, the same as biological neural information encoding characteristics. Finally, the RCNN is applicated to image segmentation, fusion, and pulse shape discrimination subtasks. It is demonstrated to be robust, efficient, and highly anti-noised, with outstanding performance in all applications mentioned above.
H2O+: An Improved Framework for Hybrid Offline-and-Online RL with Dynamics Gaps
Sep 22, 2023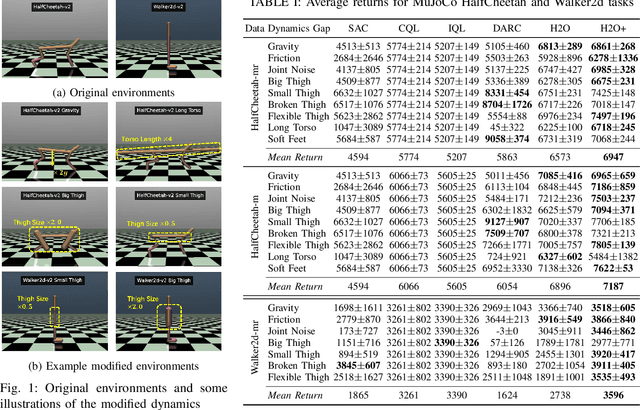
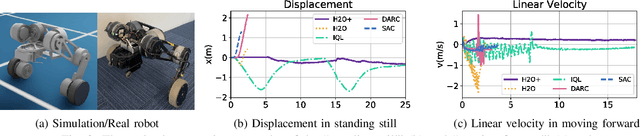
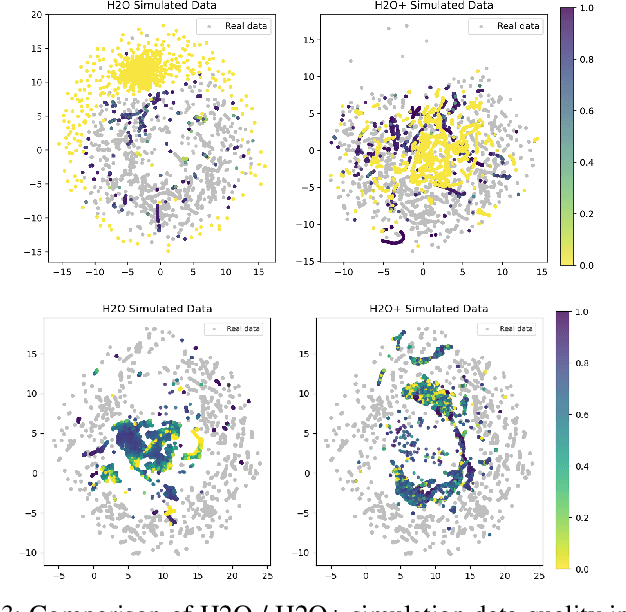
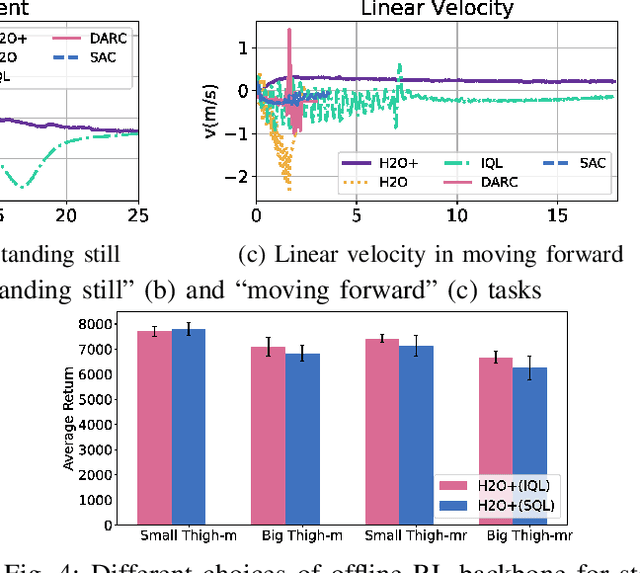
Abstract:Solving real-world complex tasks using reinforcement learning (RL) without high-fidelity simulation environments or large amounts of offline data can be quite challenging. Online RL agents trained in imperfect simulation environments can suffer from severe sim-to-real issues. Offline RL approaches although bypass the need for simulators, often pose demanding requirements on the size and quality of the offline datasets. The recently emerged hybrid offline-and-online RL provides an attractive framework that enables joint use of limited offline data and imperfect simulator for transferable policy learning. In this paper, we develop a new algorithm, called H2O+, which offers great flexibility to bridge various choices of offline and online learning methods, while also accounting for dynamics gaps between the real and simulation environment. Through extensive simulation and real-world robotics experiments, we demonstrate superior performance and flexibility over advanced cross-domain online and offline RL algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge