Xiangyu Zhu
One Ring to Rule Them All: Unifying Group-Based RL via Dynamic Power-Mean Geometry
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Group-based reinforcement learning has evolved from the arithmetic mean of GRPO to the geometric mean of GMPO. While GMPO improves stability by constraining a conservative objective, it shares a fundamental limitation with GRPO: reliance on a fixed aggregation geometry that ignores the evolving and heterogeneous nature of each trajectory. In this work, we unify these approaches under Power-Mean Policy Optimization (PMPO), a generalized framework that parameterizes the aggregation geometry via the power-mean geometry exponent p. Within this framework, GRPO and GMPO are recovered as special cases. Theoretically, we demonstrate that adjusting p modulates the concentration of gradient updates, effectively reweighting tokens based on their advantage contribution. To determine p adaptively, we introduce a Clip-aware Effective Sample Size (ESS) mechanism. Specifically, we propose a deterministic rule that maps a trajectory clipping fraction to a target ESS. Then, we solve for the specific p to align the trajectory induced ESS with this target one. This allows PMPO to dynamically transition between the aggressive arithmetic mean for reliable trajectories and the conservative geometric mean for unstable ones. Experiments on multiple mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that PMPO outperforms strong baselines.
UPA: Unsupervised Prompt Agent via Tree-Based Search and Selection
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Prompt agents have recently emerged as a promising paradigm for automated prompt optimization, framing refinement as a sequential decision-making problem over a structured prompt space. While this formulation enables the use of advanced planning algorithms, these methods typically assume access to supervised reward signals, which are often unavailable in practical scenarios. In this work, we propose UPA, an Unsupervised Prompt Agent that realizes structured search and selection without relying on supervised feedback. Specifically, during search, UPA iteratively constructs an evolving tree structure to navigate the prompt space, guided by fine-grained and order-invariant pairwise comparisons from Large Language Models (LLMs). Crucially, as these local comparisons do not inherently yield a consistent global scale, we decouple systematic prompt exploration from final selection, introducing a two-stage framework grounded in the Bradley-Terry-Luce (BTL) model. This framework first performs path-wise Bayesian aggregation of local comparisons to filter candidates under uncertainty, followed by global tournament-style comparisons to infer latent prompt quality and identify the optimal prompt. Experiments across multiple tasks demonstrate that UPA consistently outperforms existing prompt optimization methods, showing that agent-style optimization remains highly effective even in fully unsupervised settings.
Pose-RFT: Enhancing MLLMs for 3D Pose Generation via Hybrid Action Reinforcement Fine-Tuning
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Generating 3D human poses from multimodal inputs such as images or text requires models to capture both rich spatial and semantic correspondences. While pose-specific multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have shown promise in this task, they are typically trained with supervised objectives such as SMPL parameter regression or token-level prediction, which struggle to model the inherent ambiguity and achieve task-specific alignment required for accurate 3D pose generation. To address these limitations, we propose Pose-RFT, a reinforcement fine-tuning framework tailored for 3D human pose generation in MLLMs. We formulate the task as a hybrid action reinforcement learning problem that jointly optimizes discrete language prediction and continuous pose generation. To this end, we introduce HyGRPO, a hybrid reinforcement learning algorithm that performs group-wise reward normalization over sampled responses to guide joint optimization of discrete and continuous actions. Pose-RFT further incorporates task-specific reward functions to guide optimization towards spatial alignment in image-to-pose generation and semantic consistency in text-to-pose generation. Extensive experiments on multiple pose generation benchmarks demonstrate that Pose-RFT significantly improves performance over existing pose-specific MLLMs, validating the effectiveness of hybrid action reinforcement fine-tuning for 3D pose generation.
SyncTalk++: High-Fidelity and Efficient Synchronized Talking Heads Synthesis Using Gaussian Splatting
Jun 17, 2025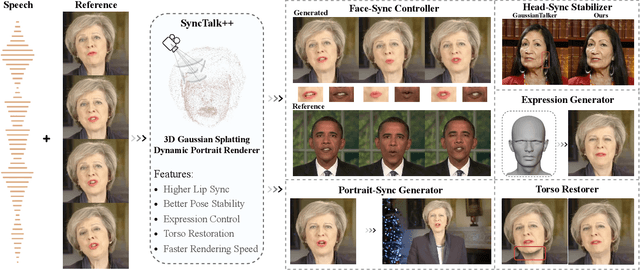
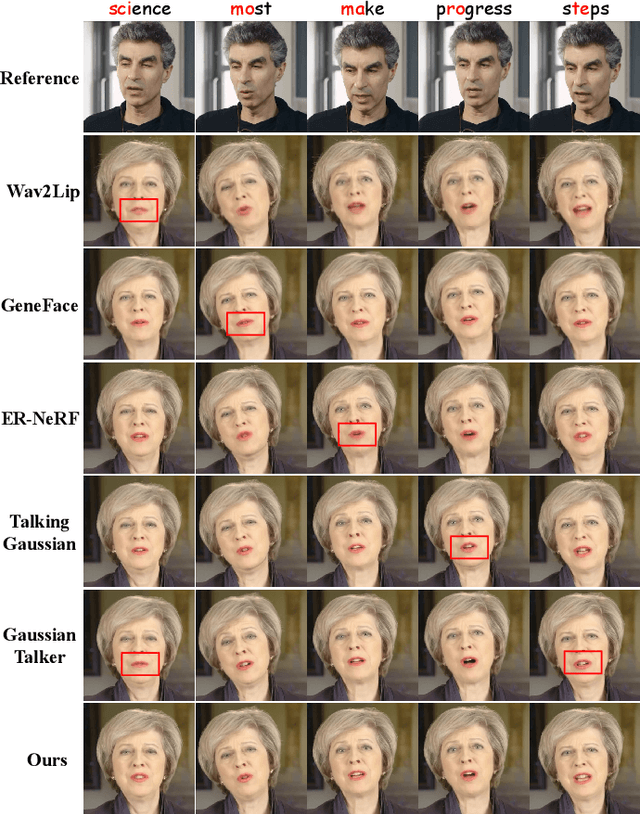


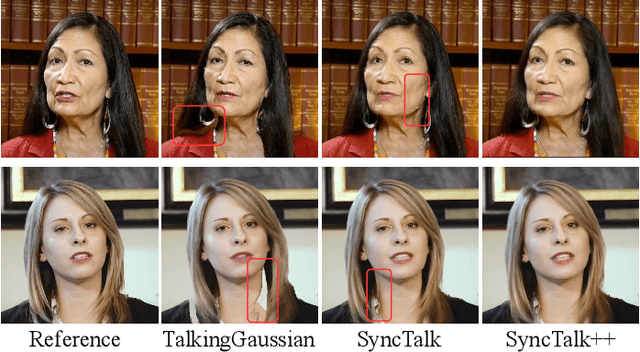
Abstract:Achieving high synchronization in the synthesis of realistic, speech-driven talking head videos presents a significant challenge. A lifelike talking head requires synchronized coordination of subject identity, lip movements, facial expressions, and head poses. The absence of these synchronizations is a fundamental flaw, leading to unrealistic results. To address the critical issue of synchronization, identified as the ''devil'' in creating realistic talking heads, we introduce SyncTalk++, which features a Dynamic Portrait Renderer with Gaussian Splatting to ensure consistent subject identity preservation and a Face-Sync Controller that aligns lip movements with speech while innovatively using a 3D facial blendshape model to reconstruct accurate facial expressions. To ensure natural head movements, we propose a Head-Sync Stabilizer, which optimizes head poses for greater stability. Additionally, SyncTalk++ enhances robustness to out-of-distribution (OOD) audio by incorporating an Expression Generator and a Torso Restorer, which generate speech-matched facial expressions and seamless torso regions. Our approach maintains consistency and continuity in visual details across frames and significantly improves rendering speed and quality, achieving up to 101 frames per second. Extensive experiments and user studies demonstrate that SyncTalk++ outperforms state-of-the-art methods in synchronization and realism. We recommend watching the supplementary video: https://ziqiaopeng.github.io/synctalk++.
MLLM-Enhanced Face Forgery Detection: A Vision-Language Fusion Solution
May 04, 2025Abstract:Reliable face forgery detection algorithms are crucial for countering the growing threat of deepfake-driven disinformation. Previous research has demonstrated the potential of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in identifying manipulated faces. However, existing methods typically depend on either the Large Language Model (LLM) alone or an external detector to generate classification results, which often leads to sub-optimal integration of visual and textual modalities. In this paper, we propose VLF-FFD, a novel Vision-Language Fusion solution for MLLM-enhanced Face Forgery Detection. Our key contributions are twofold. First, we present EFF++, a frame-level, explainability-driven extension of the widely used FaceForensics++ (FF++) dataset. In EFF++, each manipulated video frame is paired with a textual annotation that describes both the forgery artifacts and the specific manipulation technique applied, enabling more effective and informative MLLM training. Second, we design a Vision-Language Fusion Network (VLF-Net) that promotes bidirectional interaction between visual and textual features, supported by a three-stage training pipeline to fully leverage its potential. VLF-FFD achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in both cross-dataset and intra-dataset evaluations, underscoring its exceptional effectiveness in face forgery detection.
Progressive Rendering Distillation: Adapting Stable Diffusion for Instant Text-to-Mesh Generation without 3D Data
Mar 27, 2025



Abstract:It is highly desirable to obtain a model that can generate high-quality 3D meshes from text prompts in just seconds. While recent attempts have adapted pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models, such as Stable Diffusion (SD), into generators of 3D representations (e.g., Triplane), they often suffer from poor quality due to the lack of sufficient high-quality 3D training data. Aiming at overcoming the data shortage, we propose a novel training scheme, termed as Progressive Rendering Distillation (PRD), eliminating the need for 3D ground-truths by distilling multi-view diffusion models and adapting SD into a native 3D generator. In each iteration of training, PRD uses the U-Net to progressively denoise the latent from random noise for a few steps, and in each step it decodes the denoised latent into 3D output. Multi-view diffusion models, including MVDream and RichDreamer, are used in joint with SD to distill text-consistent textures and geometries into the 3D outputs through score distillation. Since PRD supports training without 3D ground-truths, we can easily scale up the training data and improve generation quality for challenging text prompts with creative concepts. Meanwhile, PRD can accelerate the inference speed of the generation model in just a few steps. With PRD, we train a Triplane generator, namely TriplaneTurbo, which adds only $2.5\%$ trainable parameters to adapt SD for Triplane generation. TriplaneTurbo outperforms previous text-to-3D generators in both efficiency and quality. Specifically, it can produce high-quality 3D meshes in 1.2 seconds and generalize well for challenging text input. The code is available at https://github.com/theEricMa/TriplaneTurbo.
PC-Talk: Precise Facial Animation Control for Audio-Driven Talking Face Generation
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in audio-driven talking face generation have made great progress in lip synchronization. However, current methods often lack sufficient control over facial animation such as speaking style and emotional expression, resulting in uniform outputs. In this paper, we focus on improving two key factors: lip-audio alignment and emotion control, to enhance the diversity and user-friendliness of talking videos. Lip-audio alignment control focuses on elements like speaking style and the scale of lip movements, whereas emotion control is centered on generating realistic emotional expressions, allowing for modifications in multiple attributes such as intensity. To achieve precise control of facial animation, we propose a novel framework, PC-Talk, which enables lip-audio alignment and emotion control through implicit keypoint deformations. First, our lip-audio alignment control module facilitates precise editing of speaking styles at the word level and adjusts lip movement scales to simulate varying vocal loudness levels, maintaining lip synchronization with the audio. Second, our emotion control module generates vivid emotional facial features with pure emotional deformation. This module also enables the fine modification of intensity and the combination of multiple emotions across different facial regions. Our method demonstrates outstanding control capabilities and achieves state-of-the-art performance on both HDTF and MEAD datasets in extensive experiments.
SRM-Hair: Single Image Head Mesh Reconstruction via 3D Morphable Hair
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:3D Morphable Models (3DMMs) have played a pivotal role as a fundamental representation or initialization for 3D avatar animation and reconstruction. However, extending 3DMMs to hair remains challenging due to the difficulty of enforcing vertex-level consistent semantic meaning across hair shapes. This paper introduces a novel method, Semantic-consistent Ray Modeling of Hair (SRM-Hair), for making 3D hair morphable and controlled by coefficients. The key contribution lies in semantic-consistent ray modeling, which extracts ordered hair surface vertices and exhibits notable properties such as additivity for hairstyle fusion, adaptability, flipping, and thickness modification. We collect a dataset of over 250 high-fidelity real hair scans paired with 3D face data to serve as a prior for the 3D morphable hair. Based on this, SRM-Hair can reconstruct a hair mesh combined with a 3D head from a single image. Note that SRM-Hair produces an independent hair mesh, facilitating applications in virtual avatar creation, realistic animation, and high-fidelity hair rendering. Both quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate that SRM-Hair achieves state-of-the-art performance in 3D mesh reconstruction. Our project is available at https://github.com/wang-zidu/SRM-Hair
DynamicGSG: Dynamic 3D Gaussian Scene Graphs for Environment Adaptation
Feb 21, 2025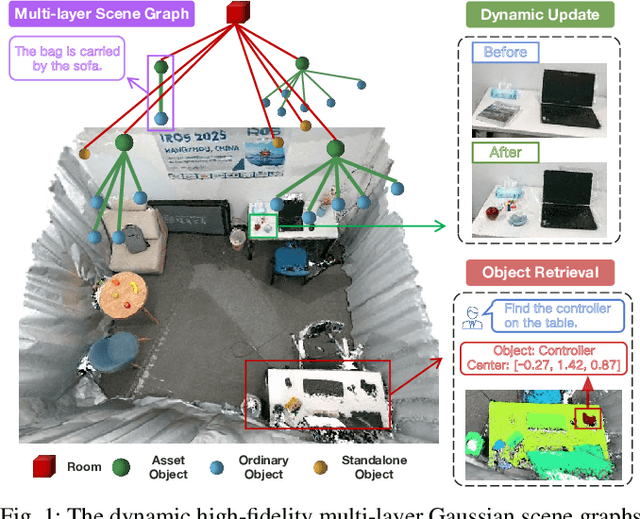
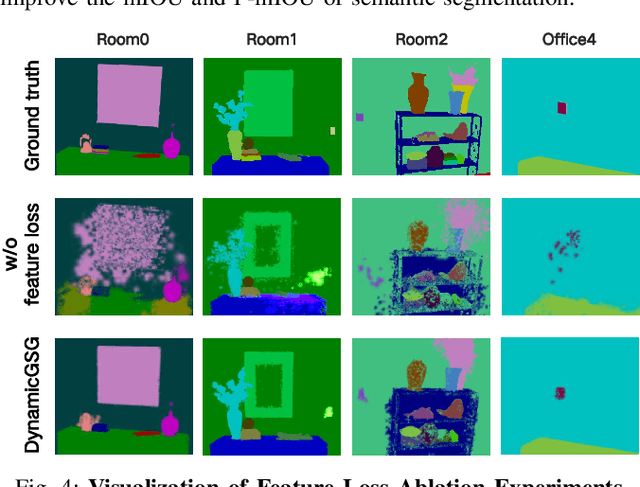
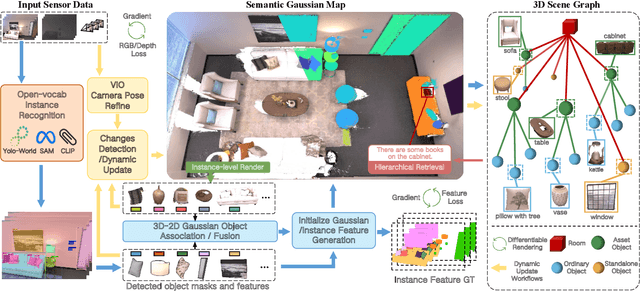
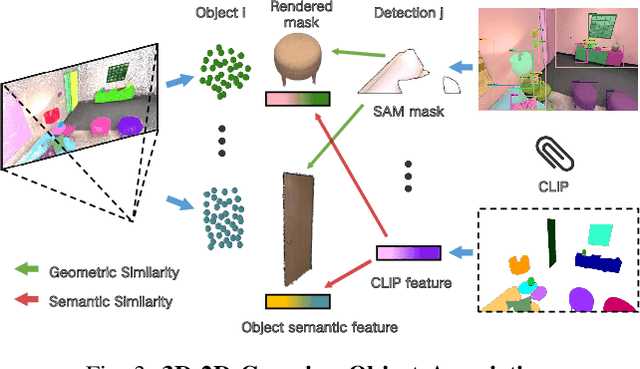

Abstract:In real-world scenarios, the environment changes caused by agents or human activities make it extremely challenging for robots to perform various long-term tasks. To effectively understand and adapt to dynamic environments, the perception system of a robot needs to extract instance-level semantic information, reconstruct the environment in a fine-grained manner, and update its environment representation in memory according to environment changes. To address these challenges, We propose \textbf{DynamicGSG}, a dynamic, high-fidelity, open-vocabulary scene graph generation system leveraging Gaussian splatting. Our system comprises three key components: (1) constructing hierarchical scene graphs using advanced vision foundation models to represent the spatial and semantic relationships of objects in the environment, (2) designing a joint feature loss to optimize the Gaussian map for incremental high-fidelity reconstruction, and (3) updating the Gaussian map and scene graph according to real environment changes for long-term environment adaptation. Experiments and ablation studies demonstrate the performance and efficacy of the proposed method in terms of semantic segmentation, language-guided object retrieval, and reconstruction quality. Furthermore, we have validated the dynamic updating capabilities of our system in real laboratory environments. The source code will be released at:~\href{https://github.com/GeLuzhou/Dynamic-GSG}{https://github.com/GeLuzhou/DynamicGSG}.
Data Center Cooling System Optimization Using Offline Reinforcement Learning
Jan 25, 2025



Abstract:The recent advances in information technology and artificial intelligence have fueled a rapid expansion of the data center (DC) industry worldwide, accompanied by an immense appetite for electricity to power the DCs. In a typical DC, around 30~40% of the energy is spent on the cooling system rather than on computer servers, posing a pressing need for developing new energy-saving optimization technologies for DC cooling systems. However, optimizing such real-world industrial systems faces numerous challenges, including but not limited to a lack of reliable simulation environments, limited historical data, and stringent safety and control robustness requirements. In this work, we present a novel physics-informed offline reinforcement learning (RL) framework for energy efficiency optimization of DC cooling systems. The proposed framework models the complex dynamical patterns and physical dependencies inside a server room using a purposely designed graph neural network architecture that is compliant with the fundamental time-reversal symmetry. Because of its well-behaved and generalizable state-action representations, the model enables sample-efficient and robust latent space offline policy learning using limited real-world operational data. Our framework has been successfully deployed and verified in a large-scale production DC for closed-loop control of its air-cooling units (ACUs). We conducted a total of 2000 hours of short and long-term experiments in the production DC environment. The results show that our method achieves 14~21% energy savings in the DC cooling system, without any violation of the safety or operational constraints. Our results have demonstrated the significant potential of offline RL in solving a broad range of data-limited, safety-critical real-world industrial control problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge