Tianshuo Zhang
One Ring to Rule Them All: Unifying Group-Based RL via Dynamic Power-Mean Geometry
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Group-based reinforcement learning has evolved from the arithmetic mean of GRPO to the geometric mean of GMPO. While GMPO improves stability by constraining a conservative objective, it shares a fundamental limitation with GRPO: reliance on a fixed aggregation geometry that ignores the evolving and heterogeneous nature of each trajectory. In this work, we unify these approaches under Power-Mean Policy Optimization (PMPO), a generalized framework that parameterizes the aggregation geometry via the power-mean geometry exponent p. Within this framework, GRPO and GMPO are recovered as special cases. Theoretically, we demonstrate that adjusting p modulates the concentration of gradient updates, effectively reweighting tokens based on their advantage contribution. To determine p adaptively, we introduce a Clip-aware Effective Sample Size (ESS) mechanism. Specifically, we propose a deterministic rule that maps a trajectory clipping fraction to a target ESS. Then, we solve for the specific p to align the trajectory induced ESS with this target one. This allows PMPO to dynamically transition between the aggressive arithmetic mean for reliable trajectories and the conservative geometric mean for unstable ones. Experiments on multiple mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that PMPO outperforms strong baselines.
UPA: Unsupervised Prompt Agent via Tree-Based Search and Selection
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Prompt agents have recently emerged as a promising paradigm for automated prompt optimization, framing refinement as a sequential decision-making problem over a structured prompt space. While this formulation enables the use of advanced planning algorithms, these methods typically assume access to supervised reward signals, which are often unavailable in practical scenarios. In this work, we propose UPA, an Unsupervised Prompt Agent that realizes structured search and selection without relying on supervised feedback. Specifically, during search, UPA iteratively constructs an evolving tree structure to navigate the prompt space, guided by fine-grained and order-invariant pairwise comparisons from Large Language Models (LLMs). Crucially, as these local comparisons do not inherently yield a consistent global scale, we decouple systematic prompt exploration from final selection, introducing a two-stage framework grounded in the Bradley-Terry-Luce (BTL) model. This framework first performs path-wise Bayesian aggregation of local comparisons to filter candidates under uncertainty, followed by global tournament-style comparisons to infer latent prompt quality and identify the optimal prompt. Experiments across multiple tasks demonstrate that UPA consistently outperforms existing prompt optimization methods, showing that agent-style optimization remains highly effective even in fully unsupervised settings.
Shackled Dancing: A Bit-Locked Diffusion Algorithm for Lossless and Controllable Image Steganography
May 16, 2025Abstract:Data steganography aims to conceal information within visual content, yet existing spatial- and frequency-domain approaches suffer from trade-offs between security, capacity, and perceptual quality. Recent advances in generative models, particularly diffusion models, offer new avenues for adaptive image synthesis, but integrating precise information embedding into the generative process remains challenging. We introduce Shackled Dancing Diffusion, or SD$^2$, a plug-and-play generative steganography method that combines bit-position locking with diffusion sampling injection to enable controllable information embedding within the generative trajectory. SD$^2$ leverages the expressive power of diffusion models to synthesize diverse carrier images while maintaining full message recovery with $100\%$ accuracy. Our method achieves a favorable balance between randomness and constraint, enhancing robustness against steganalysis without compromising image fidelity. Extensive experiments show that SD$^2$ substantially outperforms prior methods in security, embedding capacity, and stability. This algorithm offers new insights into controllable generation and opens promising directions for secure visual communication.
MLLM-Enhanced Face Forgery Detection: A Vision-Language Fusion Solution
May 04, 2025Abstract:Reliable face forgery detection algorithms are crucial for countering the growing threat of deepfake-driven disinformation. Previous research has demonstrated the potential of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in identifying manipulated faces. However, existing methods typically depend on either the Large Language Model (LLM) alone or an external detector to generate classification results, which often leads to sub-optimal integration of visual and textual modalities. In this paper, we propose VLF-FFD, a novel Vision-Language Fusion solution for MLLM-enhanced Face Forgery Detection. Our key contributions are twofold. First, we present EFF++, a frame-level, explainability-driven extension of the widely used FaceForensics++ (FF++) dataset. In EFF++, each manipulated video frame is paired with a textual annotation that describes both the forgery artifacts and the specific manipulation technique applied, enabling more effective and informative MLLM training. Second, we design a Vision-Language Fusion Network (VLF-Net) that promotes bidirectional interaction between visual and textual features, supported by a three-stage training pipeline to fully leverage its potential. VLF-FFD achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in both cross-dataset and intra-dataset evaluations, underscoring its exceptional effectiveness in face forgery detection.
WMamba: Wavelet-based Mamba for Face Forgery Detection
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:With the rapid advancement of deepfake generation technologies, the demand for robust and accurate face forgery detection algorithms has become increasingly critical. Recent studies have demonstrated that wavelet analysis can uncover subtle forgery artifacts that remain imperceptible in the spatial domain. Wavelets effectively capture important facial contours, which are often slender, fine-grained, and global in nature. However, existing wavelet-based approaches fail to fully leverage these unique characteristics, resulting in sub-optimal feature extraction and limited generalizability. To address this challenge, we introduce WMamba, a novel wavelet-based feature extractor built upon the Mamba architecture. WMamba maximizes the utility of wavelet information through two key innovations. First, we propose Dynamic Contour Convolution (DCConv), which employs specially crafted deformable kernels to adaptively model slender facial contours. Second, by leveraging the Mamba architecture, our method captures long-range spatial relationships with linear computational complexity. This efficiency allows for the extraction of fine-grained, global forgery artifacts from small image patches. Extensive experimental results show that WMamba achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance, highlighting its effectiveness and superiority in face forgery detection.
S2TD-Face: Reconstruct a Detailed 3D Face with Controllable Texture from a Single Sketch
Aug 02, 2024



Abstract:3D textured face reconstruction from sketches applicable in many scenarios such as animation, 3D avatars, artistic design, missing people search, etc., is a highly promising but underdeveloped research topic. On the one hand, the stylistic diversity of sketches leads to existing sketch-to-3D-face methods only being able to handle pose-limited and realistically shaded sketches. On the other hand, texture plays a vital role in representing facial appearance, yet sketches lack this information, necessitating additional texture control in the reconstruction process. This paper proposes a novel method for reconstructing controllable textured and detailed 3D faces from sketches, named S2TD-Face. S2TD-Face introduces a two-stage geometry reconstruction framework that directly reconstructs detailed geometry from the input sketch. To keep geometry consistent with the delicate strokes of the sketch, we propose a novel sketch-to-geometry loss that ensures the reconstruction accurately fits the input features like dimples and wrinkles. Our training strategies do not rely on hard-to-obtain 3D face scanning data or labor-intensive hand-drawn sketches. Furthermore, S2TD-Face introduces a texture control module utilizing text prompts to select the most suitable textures from a library and seamlessly integrate them into the geometry, resulting in a 3D detailed face with controllable texture. S2TD-Face surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods in extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments. Our project is available at https://github.com/wang-zidu/S2TD-Face .
3D Face Reconstruction with the Geometric Guidance of Facial Part Segmentation
Dec 04, 2023



Abstract:3D Morphable Models (3DMMs) provide promising 3D face reconstructions in various applications. However, existing methods struggle to reconstruct faces with extreme expressions due to deficiencies in supervisory signals, such as sparse or inaccurate landmarks. Segmentation information contains effective geometric contexts for face reconstruction. Certain attempts intuitively depend on differentiable renderers to compare the rendered silhouettes of reconstruction with segmentation, which is prone to issues like local optima and gradient instability. In this paper, we fully utilize the facial part segmentation geometry by introducing Part Re-projection Distance Loss (PRDL). Specifically, PRDL transforms facial part segmentation into 2D points and re-projects the reconstruction onto the image plane. Subsequently, by introducing grid anchors and computing different statistical distances from these anchors to the point sets, PRDL establishes geometry descriptors to optimize the distribution of the point sets for face reconstruction. PRDL exhibits a clear gradient compared to the renderer-based methods and presents state-of-the-art reconstruction performance in extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments. The project will be publicly available.
Safe Self-Refinement for Transformer-based Domain Adaptation
Apr 16, 2022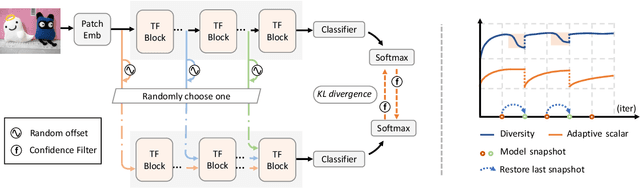



Abstract:Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) aims to leverage a label-rich source domain to solve tasks on a related unlabeled target domain. It is a challenging problem especially when a large domain gap lies between the source and target domains. In this paper we propose a novel solution named SSRT (Safe Self-Refinement for Transformer-based domain adaptation), which brings improvement from two aspects. First, encouraged by the success of vision transformers in various vision tasks, we arm SSRT with a transformer backbone. We find that the combination of vision transformer with simple adversarial adaptation surpasses best reported Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)-based results on the challenging DomainNet benchmark, showing its strong transferable feature representation. Second, to reduce the risk of model collapse and improve the effectiveness of knowledge transfer between domains with large gaps, we propose a Safe Self-Refinement strategy. Specifically, SSRT utilizes predictions of perturbed target domain data to refine the model. Since the model capacity of vision transformer is large and predictions in such challenging tasks can be noisy, a safe training mechanism is designed to adaptively adjust learning configuration. Extensive evaluations are conducted on several widely tested UDA benchmarks and SSRT achieves consistently the best performances, including 85.43% on Office-Home, 88.76% on VisDA-2017 and 45.2% on DomainNet.
Shuffle Augmentation of Features from Unlabeled Data for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Jan 28, 2022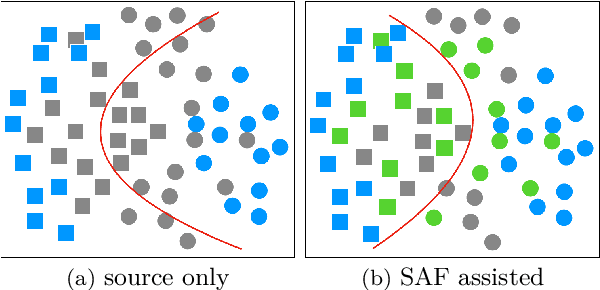



Abstract:Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA), a branch of transfer learning where labels for target samples are unavailable, has been widely researched and developed in recent years with the help of adversarially trained models. Although existing UDA algorithms are able to guide neural networks to extract transferable and discriminative features, classifiers are merely trained under the supervision of labeled source data. Given the inevitable discrepancy between source and target domains, the classifiers can hardly be aware of the target classification boundaries. In this paper, Shuffle Augmentation of Features (SAF), a novel UDA framework, is proposed to address the problem by providing the classifier with supervisory signals from target feature representations. SAF learns from the target samples, adaptively distills class-aware target features, and implicitly guides the classifier to find comprehensive class borders. Demonstrated by extensive experiments, the SAF module can be integrated into any existing adversarial UDA models to achieve performance improvements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge