Haoran Tang
From Logits to Latents: Contrastive Representation Shaping for LLM Unlearning
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Most LLM unlearning methods aim to approximate retrain-from-scratch behaviors with minimal distribution shift, often via alignment-style objectives defined in the prediction space. While effective at reducing forgotten content generation, such approaches may act as suppression: forgotten concepts can persist in representations and remain entangled with retained knowledge. We introduce CLReg, a contrastive representation regularizer that identifies forget features while pushing them away from retain features, explicitly reducing forget-retain interference with minimal shifts on retain features. We provide first theoretical insights that relate representation shaping to entanglement reduction. Across unlearning benchmarks and LLMs of different sizes, CLReg decreases forget-retain representation entanglement that facilitates mainstream unlearning methods without positing extra privacy risks, inspiring future work that reshapes the representation space to remove forget concepts.
Order from Chaos: Physical World Understanding from Glitchy Gameplay Videos
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Understanding the physical world, including object dynamics, material properties, and causal interactions, remains a core challenge in artificial intelligence. Although recent multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated impressive general reasoning capabilities, they still fall short of achieving human-level understanding of physical principles. Existing datasets for physical reasoning either rely on real-world videos, which incur high annotation costs, or on synthetic simulations, which suffer from limited realism and diversity. In this paper, we propose a novel paradigm that leverages glitches in gameplay videos, referring to visual anomalies that violate predefined physical laws, as a rich and scalable supervision source for physical world understanding. We introduce PhysGame, an meta information guided instruction-tuning dataset containing 140,057 glitch-centric question-answer pairs across five physical domains and sixteen fine-grained categories. To ensure data accuracy, we design a prompting strategy that utilizes gameplay metadata such as titles and descriptions to guide high-quality QA generation. Complementing PhysGame, we construct GameBench, an expert-annotated benchmark with 880 glitch-identified gameplay videos designed to evaluate physical reasoning capabilities. Extensive experiments show that PhysGame significantly enhances both Game2Real transferability, improving the real world physical reasoning performance of Qwen2.5VL by 2.5% on PhysBench, and Game2General transferability, yielding a 1.9% gain on the MVBench benchmark. Moreover, PhysGame-tuned models achieve a 3.7% absolute improvement on GameBench, demonstrating enhanced robustness in detecting physical implausibilities. These results indicate that learning from gameplay anomalies offers a scalable and effective pathway toward advancing physical world understanding in multimodal intelligence.
Open-Vocabulary 3D Instruction Ambiguity Detection
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:In safety-critical domains, linguistic ambiguity can have severe consequences; a vague command like "Pass me the vial" in a surgical setting could lead to catastrophic errors. Yet, most embodied AI research overlooks this, assuming instructions are clear and focusing on execution rather than confirmation. To address this critical safety gap, we are the first to define Open-Vocabulary 3D Instruction Ambiguity Detection, a fundamental new task where a model must determine if a command has a single, unambiguous meaning within a given 3D scene. To support this research, we build Ambi3D, the large-scale benchmark for this task, featuring over 700 diverse 3D scenes and around 22k instructions. Our analysis reveals a surprising limitation: state-of-the-art 3D Large Language Models (LLMs) struggle to reliably determine if an instruction is ambiguous. To address this challenge, we propose AmbiVer, a two-stage framework that collects explicit visual evidence from multiple views and uses it to guide an vision-language model (VLM) in judging instruction ambiguity. Extensive experiments demonstrate the challenge of our task and the effectiveness of AmbiVer, paving the way for safer and more trustworthy embodied AI. Code and dataset available at https://jiayuding031020.github.io/ambi3d/.
Video Spatial Reasoning with Object-Centric 3D Rollout
Nov 17, 2025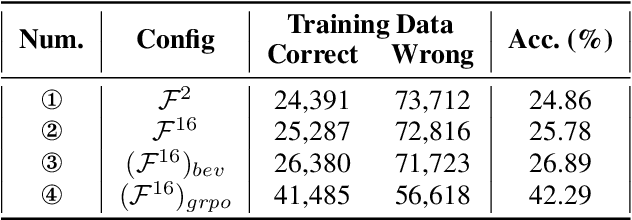
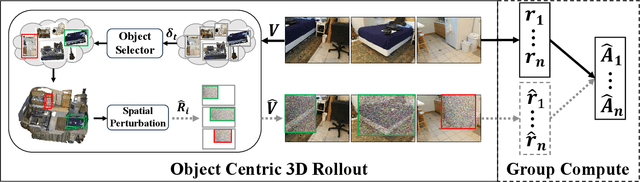
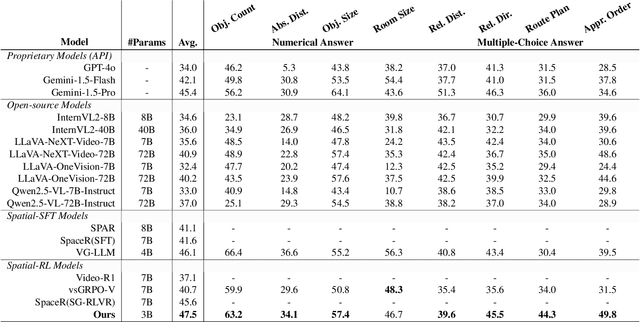
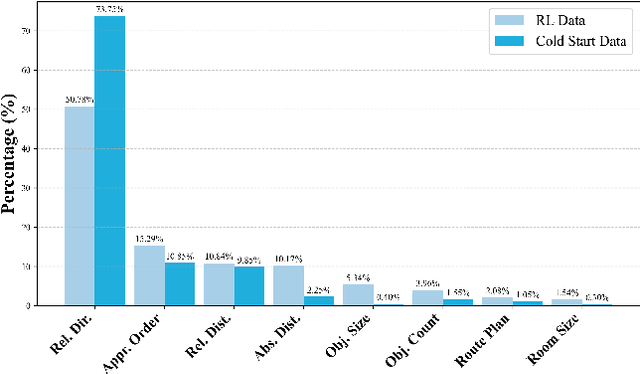
Abstract:Recent advances in Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have showcased remarkable capabilities in vision-language understanding. However, enabling robust video spatial reasoning-the ability to comprehend object locations, orientations, and inter-object relationships in dynamic 3D scenes-remains a key unsolved challenge. Existing approaches primarily rely on spatially grounded supervised fine-tuning or reinforcement learning, yet we observe that such models often exhibit query-locked reasoning, focusing narrowly on objects explicitly mentioned in the prompt while ignoring critical contextual cues. To address this limitation, we propose Object-Centric 3D Rollout (OCR), a novel strategy that introduces structured perturbations to the 3D geometry of selected objects during training. By degrading object-specific visual cues and projecting the altered geometry into 2D space, OCR compels the model to reason holistically across the entire scene. We further design a rollout-based training pipeline that jointly leverages vanilla and region-noisy videos to optimize spatial reasoning trajectories. Experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art performance: our 3B-parameter model achieves 47.5% accuracy on VSI-Bench, outperforming several 7B baselines. Ablations confirm OCR's superiority over prior rollout strategies (e.g., T-GRPO, NoisyRollout).
Sharpness-Aware Machine Unlearning
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:We characterize the effectiveness of Sharpness-aware minimization (SAM) under machine unlearning scheme, where unlearning forget signals interferes with learning retain signals. While previous work prove that SAM improves generalization with noise memorization prevention, we show that SAM abandons such denoising property when fitting the forget set, leading to various test error bounds depending on signal strength. We further characterize the signal surplus of SAM in the order of signal strength, which enables learning from less retain signals to maintain model performance and putting more weight on unlearning the forget set. Empirical studies show that SAM outperforms SGD with relaxed requirement for retain signals and can enhance various unlearning methods either as pretrain or unlearn algorithm. Observing that overfitting can benefit more stringent sample-specific unlearning, we propose Sharp MinMax, which splits the model into two to learn retain signals with SAM and unlearn forget signals with sharpness maximization, achieving best performance. Extensive experiments show that SAM enhances unlearning across varying difficulties measured by data memorization, yielding decreased feature entanglement between retain and forget sets, stronger resistance to membership inference attacks, and a flatter loss landscape.
Video SimpleQA: Towards Factuality Evaluation in Large Video Language Models
Mar 24, 2025


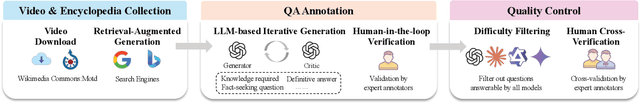
Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Video Language Models (LVLMs) have highlighted their potential for multi-modal understanding, yet evaluating their factual grounding in video contexts remains a critical unsolved challenge. To address this gap, we introduce Video SimpleQA, the first comprehensive benchmark tailored for factuality evaluation of LVLMs. Our work distinguishes from existing video benchmarks through the following key features: 1) Knowledge required: demanding integration of external knowledge beyond the explicit narrative; 2) Fact-seeking question: targeting objective, undisputed events or relationships, avoiding subjective interpretation; 3) Definitive & short-form answer: Answers are crafted as unambiguous and definitively correct in a short format, enabling automated evaluation through LLM-as-a-judge frameworks with minimal scoring variance; 4) External-source verified: All annotations undergo rigorous validation against authoritative external references to ensure the reliability; 5) Temporal reasoning required: The annotated question types encompass both static single-frame understanding and dynamic temporal reasoning, explicitly evaluating LVLMs factuality under the long-context dependencies. We extensively evaluate 41 state-of-the-art LVLMs and summarize key findings as follows: 1) Current LVLMs exhibit notable deficiencies in factual adherence, particularly for open-source models. The best-performing model Gemini-1.5-Pro achieves merely an F-score of 54.4%; 2) Test-time compute paradigms show insignificant performance gains, revealing fundamental constraints for enhancing factuality through post-hoc computation; 3) Retrieval-Augmented Generation demonstrates consistent improvements at the cost of additional inference time overhead, presenting a critical efficiency-performance trade-off.
Dual Mutual Learning Network with Global-local Awareness for RGB-D Salient Object Detection
Jan 03, 2025



Abstract:RGB-D salient object detection (SOD), aiming to highlight prominent regions of a given scene by jointly modeling RGB and depth information, is one of the challenging pixel-level prediction tasks. Recently, the dual-attention mechanism has been devoted to this area due to its ability to strengthen the detection process. However, most existing methods directly fuse attentional cross-modality features under a manual-mandatory fusion paradigm without considering the inherent discrepancy between the RGB and depth, which may lead to a reduction in performance. Moreover, the long-range dependencies derived from global and local information make it difficult to leverage a unified efficient fusion strategy. Hence, in this paper, we propose the GL-DMNet, a novel dual mutual learning network with global-local awareness. Specifically, we present a position mutual fusion module and a channel mutual fusion module to exploit the interdependencies among different modalities in spatial and channel dimensions. Besides, we adopt an efficient decoder based on cascade transformer-infused reconstruction to integrate multi-level fusion features jointly. Extensive experiments on six benchmark datasets demonstrate that our proposed GL-DMNet performs better than 24 RGB-D SOD methods, achieving an average improvement of ~3% across four evaluation metrics compared to the second-best model (S3Net). Codes and results are available at https://github.com/kingkung2016/GL-DMNet.
PhysGame: Uncovering Physical Commonsense Violations in Gameplay Videos
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in video-based large language models (Video LLMs) have witnessed the emergence of diverse capabilities to reason and interpret dynamic visual content. Among them, gameplay videos stand out as a distinctive data source, often containing glitches that defy physics commonsense. This characteristic renders them an effective benchmark for assessing the under-explored capability of physical commonsense understanding in video LLMs. In this paper, we propose PhysGame as a pioneering benchmark to evaluate physical commonsense violations in gameplay videos. PhysGame comprises 880 videos associated with glitches spanning four fundamental domains (i.e., mechanics, kinematics, optics, and material properties) and across 12 distinct physical commonsense. Through extensively evaluating various state-ofthe-art video LLMs, our findings reveal that the performance of current open-source video LLMs significantly lags behind that of proprietary counterparts. To bridge this gap, we curate an instruction tuning dataset PhysInstruct with 140,057 question-answering pairs to facilitate physical commonsense learning. In addition, we also propose a preference optimization dataset PhysDPO with 34,358 training pairs, where the dis-preferred responses are generated conditioned on misleading titles (i.e., meta information hacking), fewer frames (i.e., temporal hacking) and lower spatial resolutions (i.e., spatial hacking). Based on the suite of datasets, we propose PhysVLM as a physical knowledge-enhanced video LLM. Extensive experiments on both physical-oriented benchmark PhysGame and general video understanding benchmarks demonstrate the state-ofthe-art performance of PhysVLM.
PPLLaVA: Varied Video Sequence Understanding With Prompt Guidance
Nov 05, 2024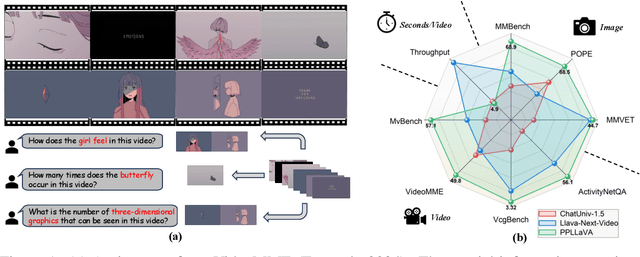
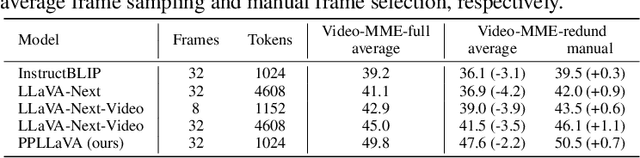
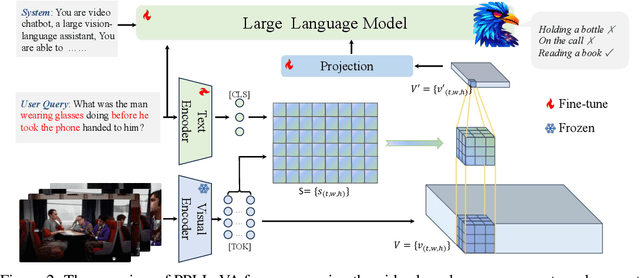
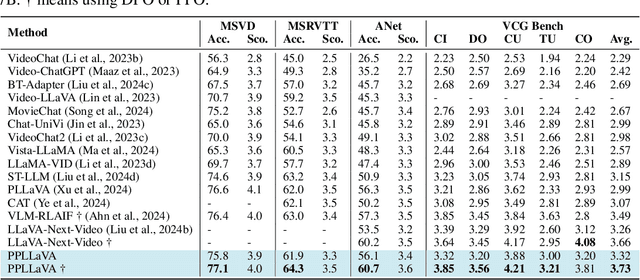
Abstract:The past year has witnessed the significant advancement of video-based large language models. However, the challenge of developing a unified model for both short and long video understanding remains unresolved. Most existing video LLMs cannot handle hour-long videos, while methods custom for long videos tend to be ineffective for shorter videos and images. In this paper, we identify the key issue as the redundant content in videos. To address this, we propose a novel pooling strategy that simultaneously achieves token compression and instruction-aware visual feature aggregation. Our model is termed Prompt-guided Pooling LLaVA, or PPLLaVA for short. Specifically, PPLLaVA consists of three core components: the CLIP-based visual-prompt alignment that extracts visual information relevant to the user's instructions, the prompt-guided pooling that compresses the visual sequence to arbitrary scales using convolution-style pooling, and the clip context extension designed for lengthy prompt common in visual dialogue. Moreover, our codebase also integrates the most advanced video Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) and visual interleave training. Extensive experiments have validated the performance of our model. With superior throughput and only 1024 visual context, PPLLaVA achieves better results on image benchmarks as a video LLM, while achieving state-of-the-art performance across various video benchmarks, excelling in tasks ranging from caption generation to multiple-choice questions, and handling video lengths from seconds to hours. Codes have been available at https://github.com/farewellthree/PPLLaVA.
A Peaceman-Rachford Splitting Approach with Deep Equilibrium Network for Channel Estimation
Oct 31, 2024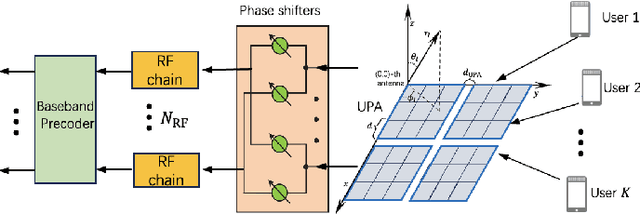
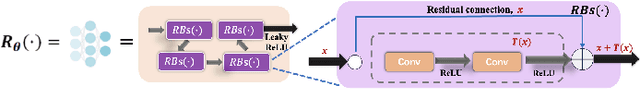
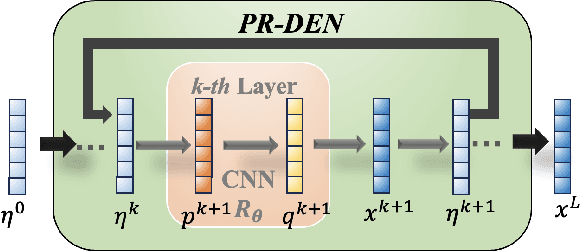
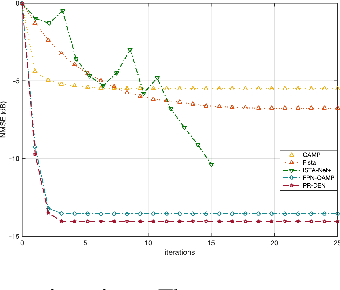
Abstract:Multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) is pivotal for wireless systems, yet its high-dimensional, stochastic channel poses significant challenges for accurate estimation, highlighting the critical need for robust estimation techniques. In this paper, we introduce a novel channel estimation method for the MIMO system. The main idea is to construct a fixed-point equation for channel estimation, which can be implemented into the deep equilibrium (DEQ) model with a fixed network. Specifically, the Peaceman-Rachford (PR) splitting method is applied to the dual form of the regularized minimization problem to construct fixed-point equation with non-expansive property. Then, the fixed-point equation is implemented into the DEQ model with a fixed layer, leveraging its advantage of the low training complexity. Moreover, we provide a rigorous theoretical analysis, demonstrating the convergence and optimality of our approach. Additionally, simulations of hybrid far- and near-field channels demonstrate that our approach yields favorable results, indicating its ability to advance channel estimation in MIMO system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge