Rajiv Khanna
Why Some Models Resist Unlearning: A Linear Stability Perspective
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Machine unlearning, the ability to erase the effect of specific training samples without retraining from scratch, is critical for privacy, regulation, and efficiency. However, most progress in unlearning has been empirical, with little theoretical understanding of when and why unlearning works. We tackle this gap by framing unlearning through the lens of asymptotic linear stability to capture the interaction between optimization dynamics and data geometry. The key quantity in our analysis is data coherence which is the cross sample alignment of loss surface directions near the optimum. We decompose coherence along three axes: within the retain set, within the forget set, and between them, and prove tight stability thresholds that separate convergence from divergence. To further link data properties to forgettability, we study a two layer ReLU CNN under a signal plus noise model and show that stronger memorization makes forgetting easier: when the signal to noise ratio (SNR) is lower, cross sample alignment is weaker, reducing coherence and making unlearning easier; conversely, high SNR, highly aligned models resist unlearning. For empirical verification, we show that Hessian tests and CNN heatmaps align closely with the predicted boundary, mapping the stability frontier of gradient based unlearning as a function of batching, mixing, and data/model alignment. Our analysis is grounded in random matrix theory tools and provides the first principled account of the trade offs between memorization, coherence, and unlearning.
From Logits to Latents: Contrastive Representation Shaping for LLM Unlearning
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Most LLM unlearning methods aim to approximate retrain-from-scratch behaviors with minimal distribution shift, often via alignment-style objectives defined in the prediction space. While effective at reducing forgotten content generation, such approaches may act as suppression: forgotten concepts can persist in representations and remain entangled with retained knowledge. We introduce CLReg, a contrastive representation regularizer that identifies forget features while pushing them away from retain features, explicitly reducing forget-retain interference with minimal shifts on retain features. We provide first theoretical insights that relate representation shaping to entanglement reduction. Across unlearning benchmarks and LLMs of different sizes, CLReg decreases forget-retain representation entanglement that facilitates mainstream unlearning methods without positing extra privacy risks, inspiring future work that reshapes the representation space to remove forget concepts.
Structure-Aware Spectral Sparsification via Uniform Edge Sampling
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:Spectral clustering is a fundamental method for graph partitioning, but its reliance on eigenvector computation limits scalability to massive graphs. Classical sparsification methods preserve spectral properties by sampling edges proportionally to their effective resistances, but require expensive preprocessing to estimate these resistances. We study whether uniform edge sampling-a simple, structure-agnostic strategy-can suffice for spectral clustering. Our main result shows that for graphs admitting a well-separated $k$-clustering, characterized by a large structure ratio $\Upsilon(k) = \lambda_{k+1} / \rho_G(k)$, uniform sampling preserves the spectral subspace used for clustering. Specifically, we prove that uniformly sampling $O(\gamma^2 n \log n / \epsilon^2)$ edges, where $\gamma$ is the Laplacian condition number, yields a sparsifier whose top $(n-k)$-dimensional eigenspace is approximately orthogonal to the cluster indicators. This ensures that the spectral embedding remains faithful, and clustering quality is preserved. Our analysis introduces new resistance bounds for intra-cluster edges, a rank-$(n-k)$ effective resistance formulation, and a matrix Chernoff bound adapted to the dominant eigenspace. These tools allow us to bypass importance sampling entirely. Conceptually, our result connects recent coreset-based clustering theory to spectral sparsification, showing that under strong clusterability, even uniform sampling is structure-aware. This provides the first provable guarantee that uniform edge sampling suffices for structure-preserving spectral clustering.
Sharpness-Aware Machine Unlearning
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:We characterize the effectiveness of Sharpness-aware minimization (SAM) under machine unlearning scheme, where unlearning forget signals interferes with learning retain signals. While previous work prove that SAM improves generalization with noise memorization prevention, we show that SAM abandons such denoising property when fitting the forget set, leading to various test error bounds depending on signal strength. We further characterize the signal surplus of SAM in the order of signal strength, which enables learning from less retain signals to maintain model performance and putting more weight on unlearning the forget set. Empirical studies show that SAM outperforms SGD with relaxed requirement for retain signals and can enhance various unlearning methods either as pretrain or unlearn algorithm. Observing that overfitting can benefit more stringent sample-specific unlearning, we propose Sharp MinMax, which splits the model into two to learn retain signals with SAM and unlearn forget signals with sharpness maximization, achieving best performance. Extensive experiments show that SAM enhances unlearning across varying difficulties measured by data memorization, yielding decreased feature entanglement between retain and forget sets, stronger resistance to membership inference attacks, and a flatter loss landscape.
The Space Complexity of Approximating Logistic Loss
Dec 03, 2024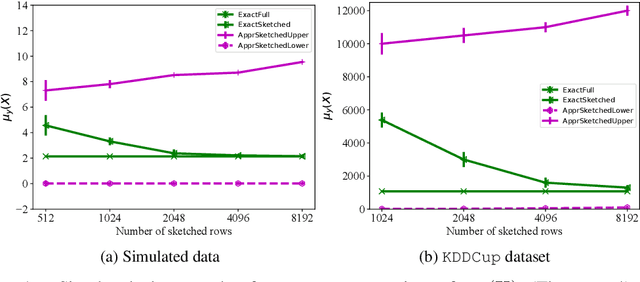
Abstract:We provide space complexity lower bounds for data structures that approximate logistic loss up to $\epsilon$-relative error on a logistic regression problem with data $\mathbf{X} \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times d}$ and labels $\mathbf{y} \in \{-1,1\}^d$. The space complexity of existing coreset constructions depend on a natural complexity measure $\mu_\mathbf{y}(\mathbf{X})$, first defined in (Munteanu, 2018). We give an $\tilde{\Omega}(\frac{d}{\epsilon^2})$ space complexity lower bound in the regime $\mu_\mathbf{y}(\mathbf{X}) = O(1)$ that shows existing coresets are optimal in this regime up to lower order factors. We also prove a general $\tilde{\Omega}(d\cdot \mu_\mathbf{y}(\mathbf{X}))$ space lower bound when $\epsilon$ is constant, showing that the dependency on $\mu_\mathbf{y}(\mathbf{X})$ is not an artifact of mergeable coresets. Finally, we refute a prior conjecture that $\mu_\mathbf{y}(\mathbf{X})$ is hard to compute by providing an efficient linear programming formulation, and we empirically compare our algorithm to prior approximate methods.
A Precise Characterization of SGD Stability Using Loss Surface Geometry
Jan 22, 2024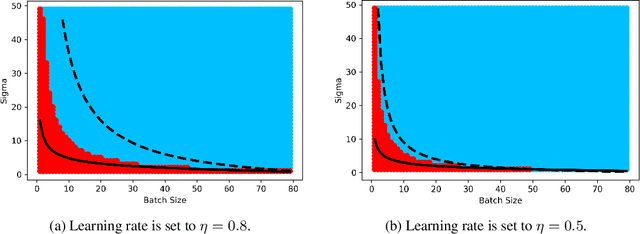
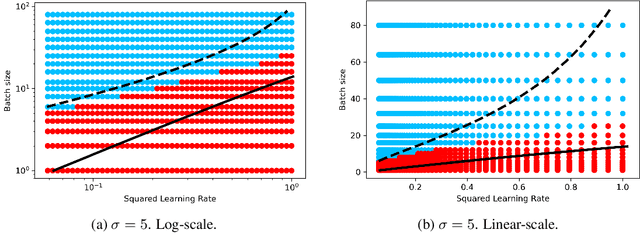
Abstract:Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) stands as a cornerstone optimization algorithm with proven real-world empirical successes but relatively limited theoretical understanding. Recent research has illuminated a key factor contributing to its practical efficacy: the implicit regularization it instigates. Several studies have investigated the linear stability property of SGD in the vicinity of a stationary point as a predictive proxy for sharpness and generalization error in overparameterized neural networks (Wu et al., 2022; Jastrzebski et al., 2019; Cohen et al., 2021). In this paper, we delve deeper into the relationship between linear stability and sharpness. More specifically, we meticulously delineate the necessary and sufficient conditions for linear stability, contingent on hyperparameters of SGD and the sharpness at the optimum. Towards this end, we introduce a novel coherence measure of the loss Hessian that encapsulates pertinent geometric properties of the loss function that are relevant to the linear stability of SGD. It enables us to provide a simplified sufficient condition for identifying linear instability at an optimum. Notably, compared to previous works, our analysis relies on significantly milder assumptions and is applicable for a broader class of loss functions than known before, encompassing not only mean-squared error but also cross-entropy loss.
On Memorization and Privacy risks of Sharpness Aware Minimization
Sep 30, 2023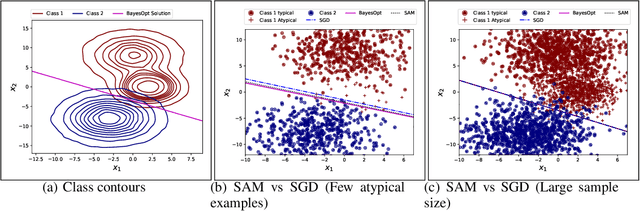
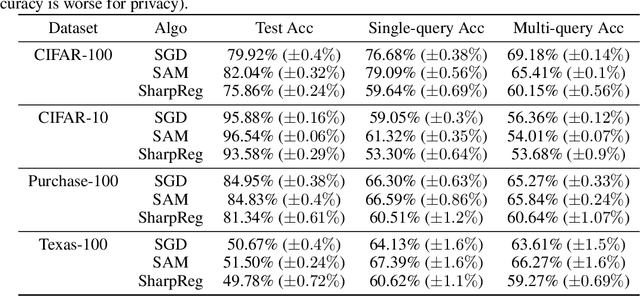
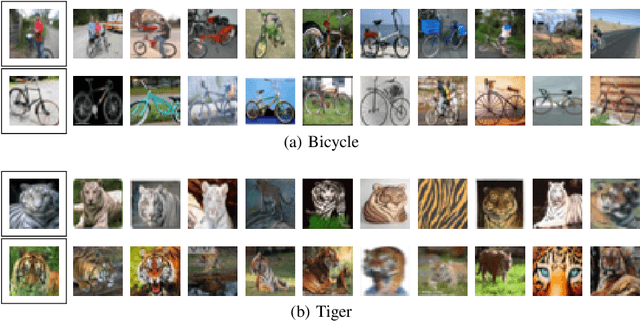
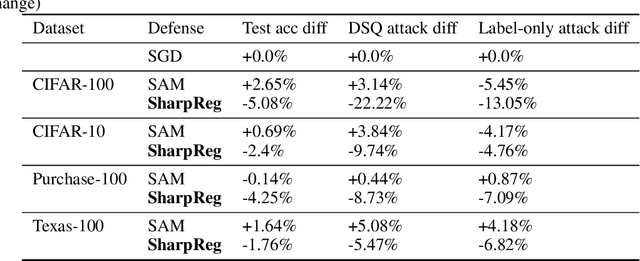
Abstract:In many recent works, there is an increased focus on designing algorithms that seek flatter optima for neural network loss optimization as there is empirical evidence that it leads to better generalization performance in many datasets. In this work, we dissect these performance gains through the lens of data memorization in overparameterized models. We define a new metric that helps us identify which data points specifically do algorithms seeking flatter optima do better when compared to vanilla SGD. We find that the generalization gains achieved by Sharpness Aware Minimization (SAM) are particularly pronounced for atypical data points, which necessitate memorization. This insight helps us unearth higher privacy risks associated with SAM, which we verify through exhaustive empirical evaluations. Finally, we propose mitigation strategies to achieve a more desirable accuracy vs privacy tradeoff.
Generalization Guarantees via Algorithm-dependent Rademacher Complexity
Jul 04, 2023Abstract:Algorithm- and data-dependent generalization bounds are required to explain the generalization behavior of modern machine learning algorithms. In this context, there exists information theoretic generalization bounds that involve (various forms of) mutual information, as well as bounds based on hypothesis set stability. We propose a conceptually related, but technically distinct complexity measure to control generalization error, which is the empirical Rademacher complexity of an algorithm- and data-dependent hypothesis class. Combining standard properties of Rademacher complexity with the convenient structure of this class, we are able to (i) obtain novel bounds based on the finite fractal dimension, which (a) extend previous fractal dimension-type bounds from continuous to finite hypothesis classes, and (b) avoid a mutual information term that was required in prior work; (ii) we greatly simplify the proof of a recent dimension-independent generalization bound for stochastic gradient descent; and (iii) we easily recover results for VC classes and compression schemes, similar to approaches based on conditional mutual information.
Feature Space Sketching for Logistic Regression
Mar 24, 2023Abstract:We present novel bounds for coreset construction, feature selection, and dimensionality reduction for logistic regression. All three approaches can be thought of as sketching the logistic regression inputs. On the coreset construction front, we resolve open problems from prior work and present novel bounds for the complexity of coreset construction methods. On the feature selection and dimensionality reduction front, we initiate the study of forward error bounds for logistic regression. Our bounds are tight up to constant factors and our forward error bounds can be extended to Generalized Linear Models.
Fast Feature Selection with Fairness Constraints
Feb 28, 2022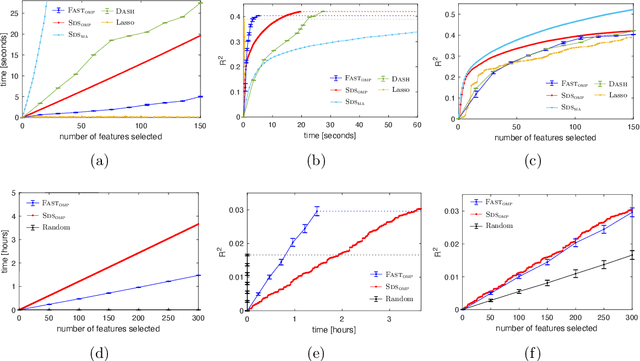
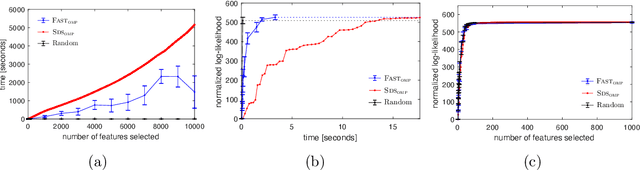
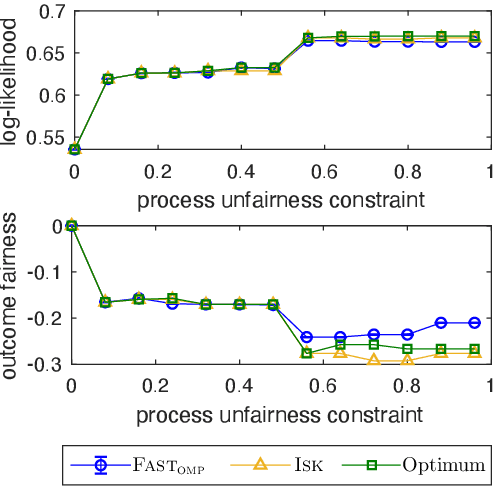
Abstract:We study the fundamental problem of selecting optimal features for model construction. This problem is computationally challenging on large datasets, even with the use of greedy algorithm variants. To address this challenge, we extend the adaptive query model, recently proposed for the greedy forward selection for submodular functions, to the faster paradigm of Orthogonal Matching Pursuit for non-submodular functions. Our extension also allows the use of downward-closed constraints, which can be used to encode certain fairness criteria into the feature selection process. The proposed algorithm achieves exponentially fast parallel run time in the adaptive query model, scaling much better than prior work. The proposed algorithm also handles certain fairness constraints by design. We prove strong approximation guarantees for the algorithm based on standard assumptions. These guarantees are applicable to many parametric models, including Generalized Linear Models. Finally, we demonstrate empirically that the proposed algorithm competes favorably with state-of-the-art techniques for feature selection, on real-world and synthetic datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge