Guandong Xu
University of Technology Sydney
CASTLE: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating Student-Tailored Personalized Safety in Large Language Models
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have advanced the development of personalized learning in education. However, their inherent generation mechanisms often produce homogeneous responses to identical prompts. This one-size-fits-all mechanism overlooks the substantial heterogeneity in students cognitive and psychological, thereby posing potential safety risks to vulnerable groups. Existing safety evaluations primarily rely on context-independent metrics such as factual accuracy, bias, or toxicity, which fail to capture the divergent harms that the same response might cause across different student attributes. To address this gap, we propose the concept of Student-Tailored Personalized Safety and construct CASTLE based on educational theories. This benchmark covers 15 educational safety risks and 14 student attributes, comprising 92,908 bilingual scenarios. We further design three evaluation metrics: Risk Sensitivity, measuring the model ability to detect risks; Emotional Empathy, evaluating the model capacity to recognize student states; and Student Alignment, assessing the match between model responses and student attributes. Experiments on 18 SOTA LLMs demonstrate that CASTLE poses a significant challenge: all models scored below an average safety rating of 2.3 out of 5, indicating substantial deficiencies in personalized safety assurance.
Towards Comprehensive Stage-wise Benchmarking of Large Language Models in Fact-Checking
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in real-world fact-checking systems, yet existing evaluations focus predominantly on claim verification and overlook the broader fact-checking workflow, including claim extraction and evidence retrieval. This narrow focus prevents current benchmarks from revealing systematic reasoning failures, factual blind spots, and robustness limitations of modern LLMs. To bridge this gap, we present FactArena, a fully automated arena-style evaluation framework that conducts comprehensive, stage-wise benchmarking of LLMs across the complete fact-checking pipeline. FactArena integrates three key components: (i) an LLM-driven fact-checking process that standardizes claim decomposition, evidence retrieval via tool-augmented interactions, and justification-based verdict prediction; (ii) an arena-styled judgment mechanism guided by consolidated reference guidelines to ensure unbiased and consistent pairwise comparisons across heterogeneous judge agents; and (iii) an arena-driven claim-evolution module that adaptively generates more challenging and semantically controlled claims to probe LLMs' factual robustness beyond fixed seed data. Across 16 state-of-the-art LLMs spanning seven model families, FactArena produces stable and interpretable rankings. Our analyses further reveal significant discrepancies between static claim-verification accuracy and end-to-end fact-checking competence, highlighting the necessity of holistic evaluation. The proposed framework offers a scalable and trustworthy paradigm for diagnosing LLMs' factual reasoning, guiding future model development, and advancing the reliable deployment of LLMs in safety-critical fact-checking applications.
Listwise Preference Alignment Optimization for Tail Item Recommendation
Jul 03, 2025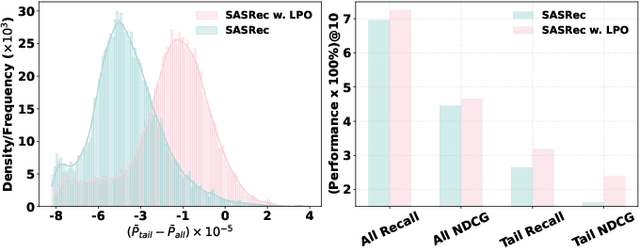
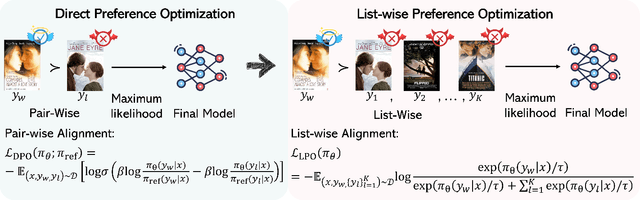
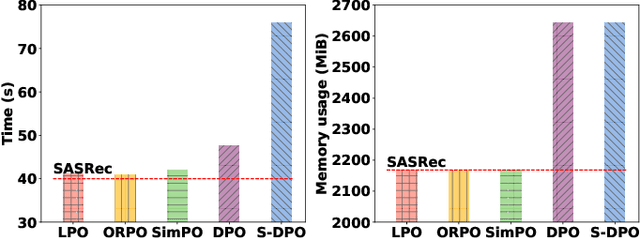
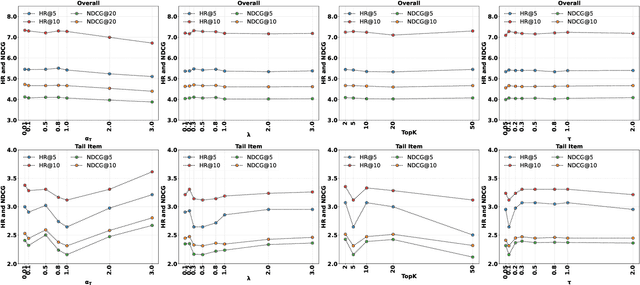
Abstract:Preference alignment has achieved greater success on Large Language Models (LLMs) and drawn broad interest in recommendation research. Existing preference alignment methods for recommendation either require explicit reward modeling or only support pairwise preference comparison. The former directly increases substantial computational costs, while the latter hinders training efficiency on negative samples. Moreover, no existing effort has explored preference alignment solutions for tail-item recommendation. To bridge the above gaps, we propose LPO4Rec, which extends the Bradley-Terry model from pairwise comparison to listwise comparison, to improve the efficiency of model training. Specifically, we derive a closed form optimal policy to enable more efficient and effective training without explicit reward modeling. We also present an adaptive negative sampling and reweighting strategy to prioritize tail items during optimization and enhance performance in tail-item recommendations. Besides, we theoretically prove that optimizing the listwise preference optimization (LPO) loss is equivalent to maximizing the upper bound of the optimal reward. Our experiments on three public datasets show that our method outperforms 10 baselines by a large margin, achieving up to 50% performance improvement while reducing 17.9% GPU memory usage when compared with direct preference optimization (DPO) in tail-item recommendation. Our code is available at https://github.com/Yuhanleeee/LPO4Rec.
A Comprehensive Survey of Knowledge-Based Vision Question Answering Systems: The Lifecycle of Knowledge in Visual Reasoning Task
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Knowledge-based Vision Question Answering (KB-VQA) extends general Vision Question Answering (VQA) by not only requiring the understanding of visual and textual inputs but also extensive range of knowledge, enabling significant advancements across various real-world applications. KB-VQA introduces unique challenges, including the alignment of heterogeneous information from diverse modalities and sources, the retrieval of relevant knowledge from noisy or large-scale repositories, and the execution of complex reasoning to infer answers from the combined context. With the advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs), KB-VQA systems have also undergone a notable transformation, where LLMs serve as powerful knowledge repositories, retrieval-augmented generators and strong reasoners. Despite substantial progress, no comprehensive survey currently exists that systematically organizes and reviews the existing KB-VQA methods. This survey aims to fill this gap by establishing a structured taxonomy of KB-VQA approaches, and categorizing the systems into main stages: knowledge representation, knowledge retrieval, and knowledge reasoning. By exploring various knowledge integration techniques and identifying persistent challenges, this work also outlines promising future research directions, providing a foundation for advancing KB-VQA models and their applications.
UniRVQA: A Unified Framework for Retrieval-Augmented Vision Question Answering via Self-Reflective Joint Training
Apr 05, 2025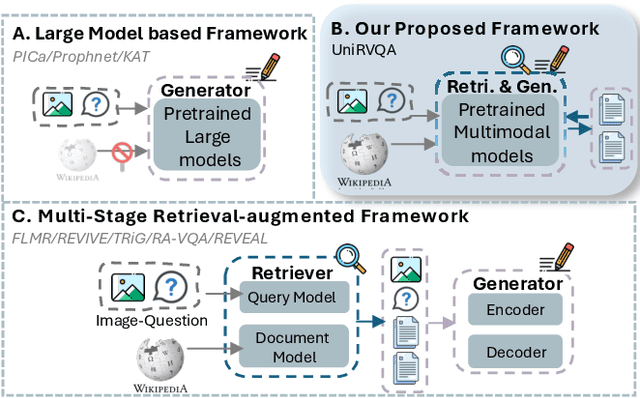
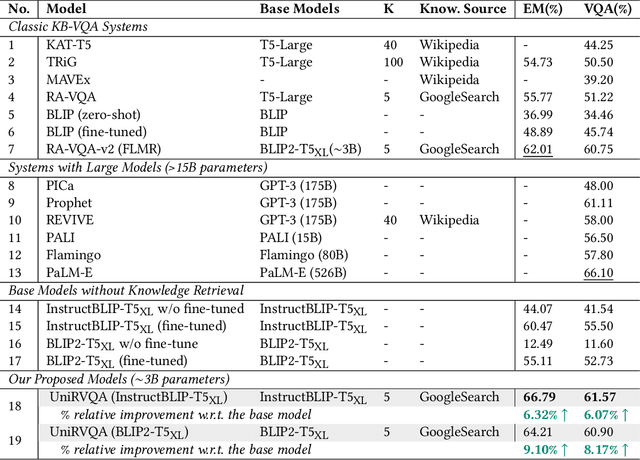
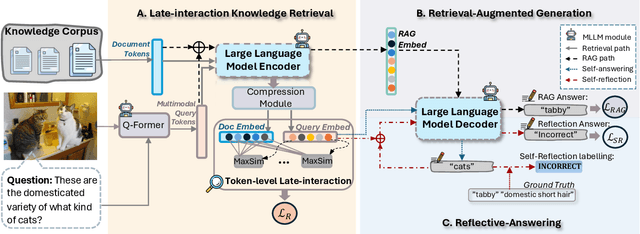
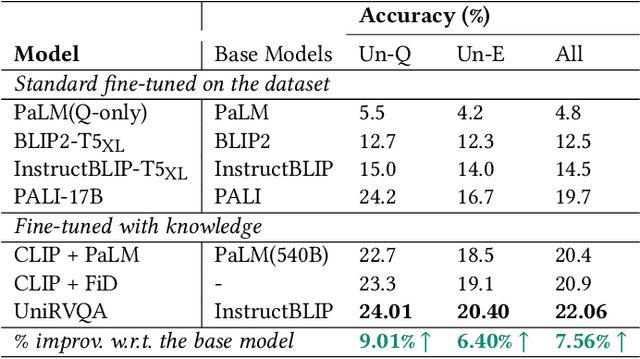
Abstract:Knowledge-based Vision Question Answering (KB-VQA) systems address complex visual-grounded questions requiring external knowledge, such as web-sourced encyclopedia articles. Existing methods often use sequential and separate frameworks for the retriever and the generator with limited parametric knowledge sharing. However, since both retrieval and generation tasks require accurate understanding of contextual and external information, such separation can potentially lead to suboptimal system performance. Another key challenge is the integration of multimodal information. General-purpose multimodal pre-trained models, while adept at multimodal representation learning, struggle with fine-grained retrieval required for knowledge-intensive visual questions. Recent specialized pre-trained models mitigate the issue, but are computationally expensive. To bridge the gap, we propose a Unified Retrieval-Augmented VQA framework (UniRVQA). UniRVQA adapts general multimodal pre-trained models for fine-grained knowledge-intensive tasks within a unified framework, enabling cross-task parametric knowledge sharing and the extension of existing multimodal representation learning capability. We further introduce a reflective-answering mechanism that allows the model to explicitly evaluate and refine its knowledge boundary. Additionally, we integrate late interaction into the retrieval-augmented generation joint training process to enhance fine-grained understanding of queries and documents. Our approach achieves competitive performance against state-of-the-art models, delivering a significant 4.7% improvement in answering accuracy, and brings an average 7.5% boost in base MLLMs' VQA performance.
Is LLMs Hallucination Usable? LLM-based Negative Reasoning for Fake News Detection
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:The questionable responses caused by knowledge hallucination may lead to LLMs' unstable ability in decision-making. However, it has never been investigated whether the LLMs' hallucination is possibly usable to generate negative reasoning for facilitating the detection of fake news. This study proposes a novel supervised self-reinforced reasoning rectification approach - SR$^3$ that yields both common reasonable reasoning and wrong understandings (negative reasoning) for news via LLMs reflection for semantic consistency learning. Upon that, we construct a negative reasoning-based news learning model called - \emph{NRFE}, which leverages positive or negative news-reasoning pairs for learning the semantic consistency between them. To avoid the impact of label-implicated reasoning, we deploy a student model - \emph{NRFE-D} that only takes news content as input to inspect the performance of our method by distilling the knowledge from \emph{NRFE}. The experimental results verified on three popular fake news datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method compared with three kinds of baselines including prompting on LLMs, fine-tuning on pre-trained SLMs, and other representative fake news detection methods.
HyperG: Hypergraph-Enhanced LLMs for Structured Knowledge
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Given that substantial amounts of domain-specific knowledge are stored in structured formats, such as web data organized through HTML, Large Language Models (LLMs) are expected to fully comprehend this structured information to broaden their applications in various real-world downstream tasks. Current approaches for applying LLMs to structured data fall into two main categories: serialization-based and operation-based methods. Both approaches, whether relying on serialization or using SQL-like operations as an intermediary, encounter difficulties in fully capturing structural relationships and effectively handling sparse data. To address these unique characteristics of structured data, we propose HyperG, a hypergraph-based generation framework aimed at enhancing LLMs' ability to process structured knowledge. Specifically, HyperG first augment sparse data with contextual information, leveraging the generative power of LLMs, and incorporate a prompt-attentive hypergraph learning (PHL) network to encode both the augmented information and the intricate structural relationships within the data. To validate the effectiveness and generalization of HyperG, we conduct extensive experiments across two different downstream tasks requiring structured knowledge.
STAR: Stepwise Task Augmentation and Relation Learning for Aspect Sentiment Quad Prediction
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:Aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA) aims to identify four sentiment elements, including aspect term, aspect category, opinion term, and sentiment polarity. These elements construct the complete picture of sentiments. The most challenging task, aspect sentiment quad prediction (ASQP), predicts these elements simultaneously, hindered by difficulties in accurately coupling different sentiment elements. A key challenge is insufficient annotated data that limits the capability of models in semantic understanding and reasoning about quad prediction. To address this, we propose stepwise task augmentation and relation learning (STAR), a strategy inspired by human reasoning. STAR constructs auxiliary data to learn quadruple relationships incrementally by augmenting with pairwise and overall relation tasks derived from training data. By encouraging the model to infer causal relationships among sentiment elements without requiring additional annotations, STAR effectively enhances quad prediction. Extensive experiments demonstrate the proposed STAR exhibits superior performance on four benchmark datasets.
How to Select Pre-Trained Code Models for Reuse? A Learning Perspective
Jan 07, 2025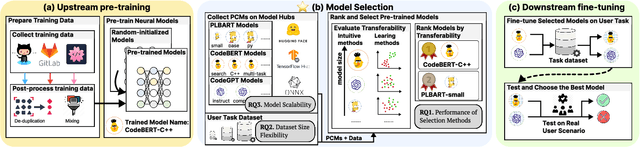
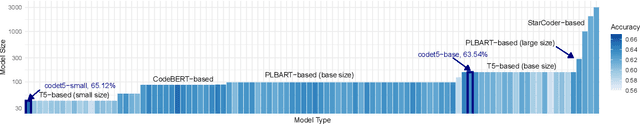
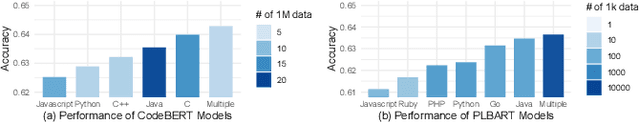
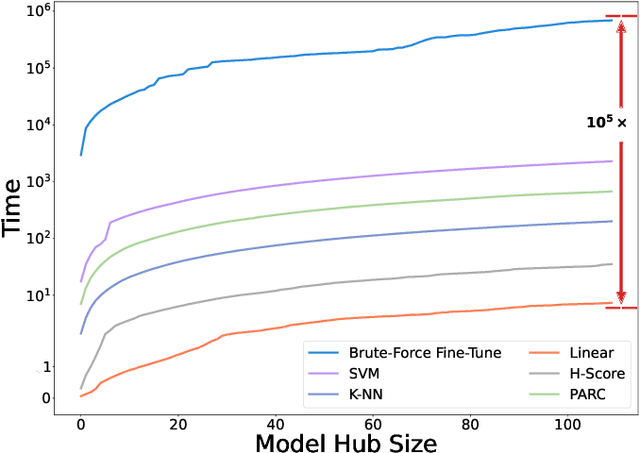
Abstract:Pre-training a language model and then fine-tuning it has shown to be an efficient and effective technique for a wide range of code intelligence tasks, such as code generation, code summarization, and vulnerability detection. However, pretraining language models on a large-scale code corpus is computationally expensive. Fortunately, many off-the-shelf Pre-trained Code Models (PCMs), such as CodeBERT, CodeT5, CodeGen, and Code Llama, have been released publicly. These models acquire general code understanding and generation capability during pretraining, which enhances their performance on downstream code intelligence tasks. With an increasing number of these public pre-trained models, selecting the most suitable one to reuse for a specific task is essential. In this paper, we systematically investigate the reusability of PCMs. We first explore three intuitive model selection methods that select by size, training data, or brute-force fine-tuning. Experimental results show that these straightforward techniques either perform poorly or suffer high costs. Motivated by these findings, we explore learning-based model selection strategies that utilize pre-trained models without altering their parameters. Specifically, we train proxy models to gauge the performance of pre-trained models, and measure the distribution deviation between a model's latent features and the task's labels, using their closeness as an indicator of model transferability. We conduct experiments on 100 widely-used opensource PCMs for code intelligence tasks, with sizes ranging from 42.5 million to 3 billion parameters. The results demonstrate that learning-based selection methods reduce selection time to 100 seconds, compared to 2,700 hours with brute-force fine-tuning, with less than 6% performance degradation across related tasks.
Multi-Task Learning with LLMs for Implicit Sentiment Analysis: Data-level and Task-level Automatic Weight Learning
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:Implicit sentiment analysis (ISA) presents significant challenges due to the absence of salient cue words. Previous methods have struggled with insufficient data and limited reasoning capabilities to infer underlying opinions. Integrating multi-task learning (MTL) with large language models (LLMs) offers the potential to enable models of varying sizes to reliably perceive and recognize genuine opinions in ISA. However, existing MTL approaches are constrained by two sources of uncertainty: data-level uncertainty, arising from hallucination problems in LLM-generated contextual information, and task-level uncertainty, stemming from the varying capacities of models to process contextual information. To handle these uncertainties, we introduce MT-ISA, a novel MTL framework that enhances ISA by leveraging the generation and reasoning capabilities of LLMs through automatic MTL. Specifically, MT-ISA constructs auxiliary tasks using generative LLMs to supplement sentiment elements and incorporates automatic MTL to fully exploit auxiliary data. We introduce data-level and task-level automatic weight learning (AWL), which dynamically identifies relationships and prioritizes more reliable data and critical tasks, enabling models of varying sizes to adaptively learn fine-grained weights based on their reasoning capabilities. We investigate three strategies for data-level AWL, while also introducing homoscedastic uncertainty for task-level AWL. Extensive experiments reveal that models of varying sizes achieve an optimal balance between primary prediction and auxiliary tasks in MT-ISA. This underscores the effectiveness and adaptability of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge