Jun Tang
Neural personal sound zones with flexible bright zone control
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Personal sound zone (PSZ) reproduction system, which attempts to create distinct virtual acoustic scenes for different listeners at their respective positions within the same spatial area using one loudspeaker array, is a fundamental technology in the application of virtual reality. For practical applications, the reconstruction targets must be measured on the same fixed receiver array used to record the local room impulse responses (RIRs) from the loudspeaker array to the control points in each PSZ, which makes the system inconvenient and costly for real-world use. In this paper, a 3D convolutional neural network (CNN) designed for PSZ reproduction with flexible control microphone grid and alternative reproduction target is presented, utilizing the virtual target scene as inputs and the PSZ pre-filters as output. Experimental results of the proposed method are compared with the traditional method, demonstrating that the proposed method is able to handle varied reproduction targets on flexible control point grid using only one training session. Furthermore, the proposed method also demonstrates the capability to learn global spatial information from sparse sampling points distributed in PSZs.
A Two-Stage ISAC Framework for Low-Altitude Economy Based on 5G NR Signals
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:The evolution of next-generation wireless networks has spurred the vigorous development of the low-altitude economy (LAE). To support this emerging field while remaining compatible with existing network architectures, integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) based on 5G New Radio (NR) signals is regarded as a promising solution. However, merely leveraging standard 5G NR signals, such as the Synchronization Signal Block (SSB), presents fundamental limitations in sensing resolution. To address the issue, this paper proposes a two-stage coarse-to-fine sensing framework that utilizes standard 5G NR initial access signals augmented by a custom-designed sparse pilot structure (SPS) for high-precision unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) sensing. In Stage I, we first fuse information from the SSB, Type\#0-PDCCH, and system information block 1 (SIB1) to ensure the initial target detection. In Stage II, a refined estimation algorithm is introduced to overcome the resolution limitations of these signals. Inspired by the sparse array theory, this stage employs a novel SPS, which is inserted into resource blocks (RBs) within the CORSET\#0 bandwidth. To accurately extract the off-grid range and velocity parameters from these sparse pilots, we develop a corresponding high-resolution algorithm based on the weighted unwrapped phase (WUP) technique and the RELAX-based iterative method. Finally, the density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN) algorithm is adopted to prune the redundant detections arising from beam overlap. Comprehensive simulation results demonstrate the superior estimation accuracy and computational efficiency of the proposed framework in comparison to other techniques.
OmniParser V2: Structured-Points-of-Thought for Unified Visual Text Parsing and Its Generality to Multimodal Large Language Models
Feb 22, 2025Abstract:Visually-situated text parsing (VsTP) has recently seen notable advancements, driven by the growing demand for automated document understanding and the emergence of large language models capable of processing document-based questions. While various methods have been proposed to tackle the complexities of VsTP, existing solutions often rely on task-specific architectures and objectives for individual tasks. This leads to modal isolation and complex workflows due to the diversified targets and heterogeneous schemas. In this paper, we introduce OmniParser V2, a universal model that unifies VsTP typical tasks, including text spotting, key information extraction, table recognition, and layout analysis, into a unified framework. Central to our approach is the proposed Structured-Points-of-Thought (SPOT) prompting schemas, which improves model performance across diverse scenarios by leveraging a unified encoder-decoder architecture, objective, and input\&output representation. SPOT eliminates the need for task-specific architectures and loss functions, significantly simplifying the processing pipeline. Our extensive evaluations across four tasks on eight different datasets show that OmniParser V2 achieves state-of-the-art or competitive results in VsTP. Additionally, we explore the integration of SPOT within a multimodal large language model structure, further enhancing text localization and recognition capabilities, thereby confirming the generality of SPOT prompting technique. The code is available at \href{https://github.com/AlibabaResearch/AdvancedLiterateMachinery}{AdvancedLiterateMachinery}.
Qwen2.5-VL Technical Report
Feb 19, 2025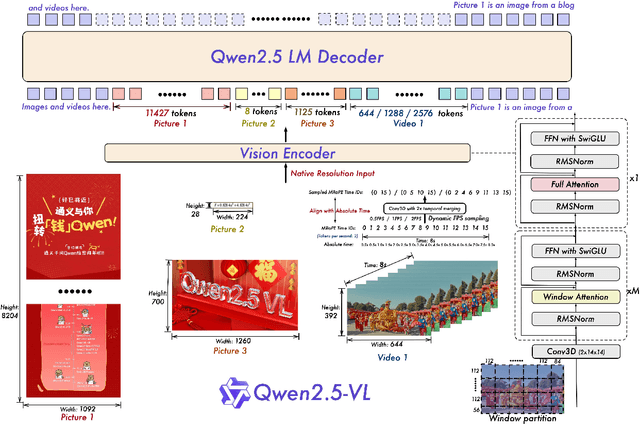
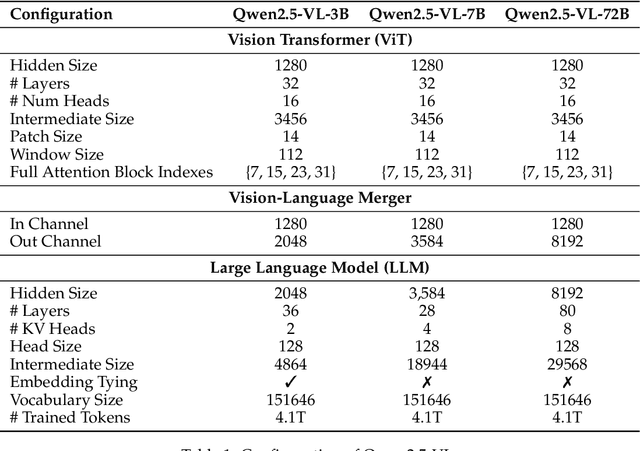
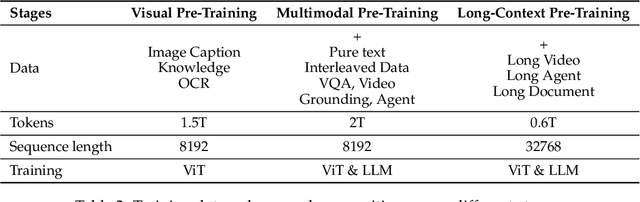
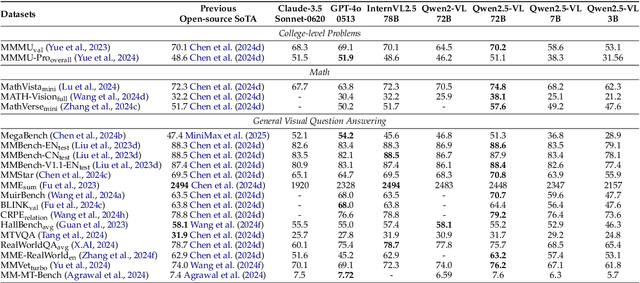
Abstract:We introduce Qwen2.5-VL, the latest flagship model of Qwen vision-language series, which demonstrates significant advancements in both foundational capabilities and innovative functionalities. Qwen2.5-VL achieves a major leap forward in understanding and interacting with the world through enhanced visual recognition, precise object localization, robust document parsing, and long-video comprehension. A standout feature of Qwen2.5-VL is its ability to localize objects using bounding boxes or points accurately. It provides robust structured data extraction from invoices, forms, and tables, as well as detailed analysis of charts, diagrams, and layouts. To handle complex inputs, Qwen2.5-VL introduces dynamic resolution processing and absolute time encoding, enabling it to process images of varying sizes and videos of extended durations (up to hours) with second-level event localization. This allows the model to natively perceive spatial scales and temporal dynamics without relying on traditional normalization techniques. By training a native dynamic-resolution Vision Transformer (ViT) from scratch and incorporating Window Attention, we reduce computational overhead while maintaining native resolution. As a result, Qwen2.5-VL excels not only in static image and document understanding but also as an interactive visual agent capable of reasoning, tool usage, and task execution in real-world scenarios such as operating computers and mobile devices. Qwen2.5-VL is available in three sizes, addressing diverse use cases from edge AI to high-performance computing. The flagship Qwen2.5-VL-72B model matches state-of-the-art models like GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet, particularly excelling in document and diagram understanding. Additionally, Qwen2.5-VL maintains robust linguistic performance, preserving the core language competencies of the Qwen2.5 LLM.
Cooperative ISAC-empowered Low-Altitude Economy
Dec 29, 2024Abstract:This paper proposes a cooperative integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) scheme for the low-altitude sensing scenario, aiming at estimating the parameters of the unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and enhancing the sensing performance via cooperation. The proposed scheme consists of two stages. In Stage I, we formulate the monostatic parameter estimation problem via using a tensor decomposition model. By leveraging the Vandermonde structure of the factor matrix, a spatial smoothing tensor decomposition scheme is introduced to estimate the UAVs' parameters. To further reduce the computational complexity, we design a reduced-dimensional (RD) angle of arrival (AoA) estimation algorithm based on generalized Rayleigh quotient (GRQ). In Stage II, the positions and true velocities of the UAVs are determined through the data fusion across multiple base stations (BSs). Specifically, we first develop a false removing minimum spanning tree (MST)-based data association method to accurately match the BSs' parameter estimations to the same UAV. Then, a Pareto optimality method and a residual weighting scheme are developed to facilitate the position and velocity estimation, respectively. We further extend our approach to the dual-polarized system. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed schemes in comparison to the conventional techniques.
CC-OCR: A Comprehensive and Challenging OCR Benchmark for Evaluating Large Multimodal Models in Literacy
Dec 03, 2024Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have demonstrated impressive performance on recognizing document images with natural language instructions. However, it remains unclear to what extent capabilities in literacy with rich structure and fine-grained visual challenges. The current landscape lacks a comprehensive benchmark to effectively measure the literate capabilities of LMMs. Existing benchmarks are often limited by narrow scenarios and specified tasks. To this end, we introduce CC-OCR, a comprehensive benchmark that possess a diverse range of scenarios, tasks, and challenges. CC-OCR comprises four OCR-centric tracks: multi-scene text reading, multilingual text reading, document parsing, and key information extraction. It includes 39 subsets with 7,058 full annotated images, of which 41% are sourced from real applications, being released for the first time. Furthermore, we evaluate nine prominent LMMs and reveal both the strengths and weaknesses of these models, particularly in text grounding, multi-orientation, and hallucination of repetition. CC-OCR aims to comprehensively evaluate the capabilities of LMMs on OCR-centered tasks, driving advancement in LMMs.
An Event-centric Framework for Predicting Crime Hotspots with Flexible Time Intervals
Nov 02, 2024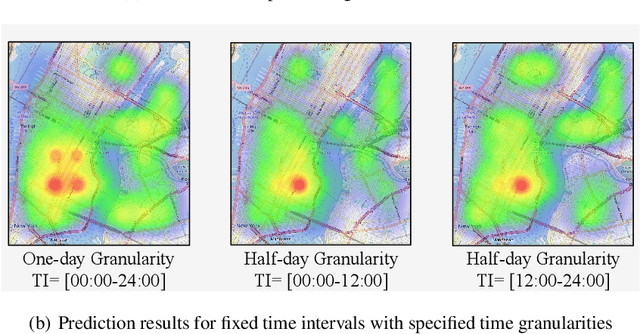
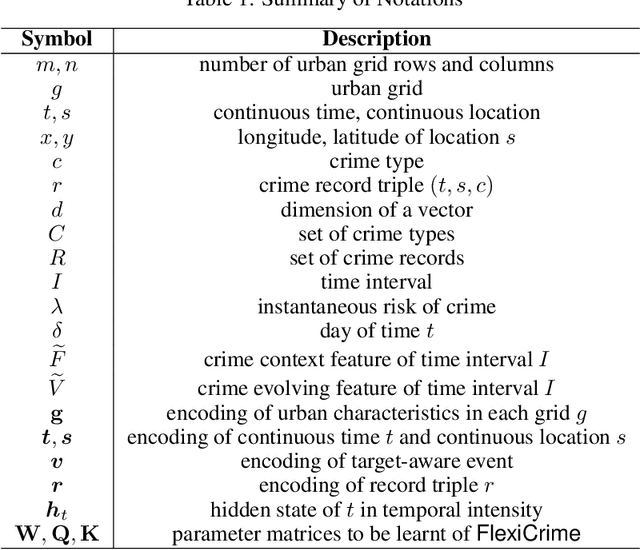
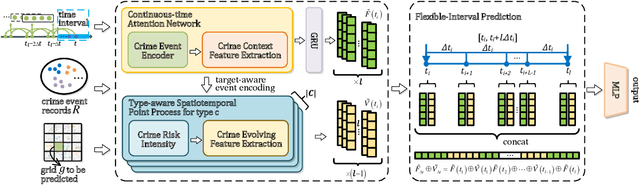

Abstract:Predicting crime hotspots in a city is a complex and critical task with significant societal implications. Numerous spatiotemporal correlations and irregularities pose substantial challenges to this endeavor. Existing methods commonly employ fixed-time granularities and sequence prediction models. However, determining appropriate time granularities is difficult, leading to inaccurate predictions for specific time windows. For example, users might ask: What are the crime hotspots during 12:00-20:00? To address this issue, we introduce FlexiCrime, a novel event-centric framework for predicting crime hotspots with flexible time intervals. FlexiCrime incorporates a continuous-time attention network to capture correlations between crime events, which learns crime context features, representing general crime patterns across time points and locations. Furthermore, we introduce a type-aware spatiotemporal point process that learns crime-evolving features, measuring the risk of specific crime types at a given time and location by considering the frequency of past crime events. The crime context and evolving features together allow us to predict whether an urban area is a crime hotspot given a future time interval. To evaluate FlexiCrime's effectiveness, we conducted experiments using real-world datasets from two cities, covering twelve crime types. The results show that our model outperforms baseline techniques in predicting crime hotspots over flexible time intervals.
VL-Reader: Vision and Language Reconstructor is an Effective Scene Text Recognizer
Sep 18, 2024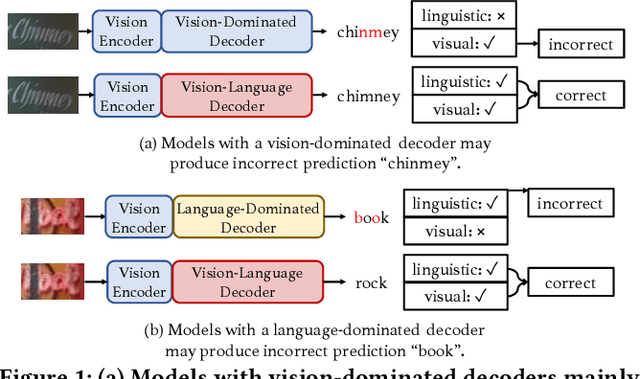
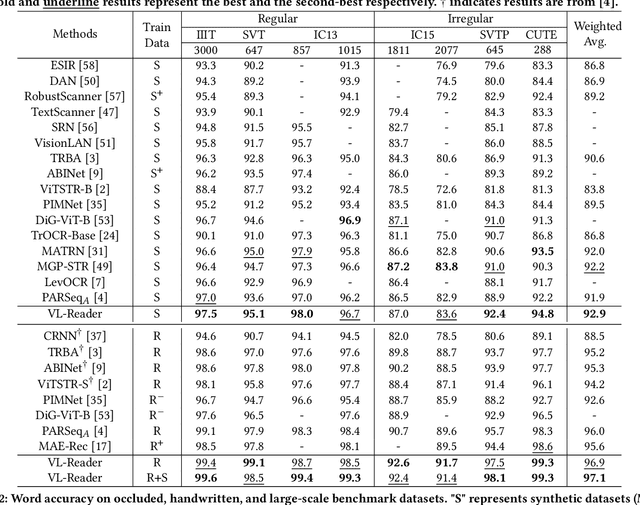
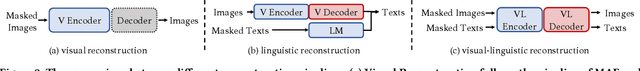
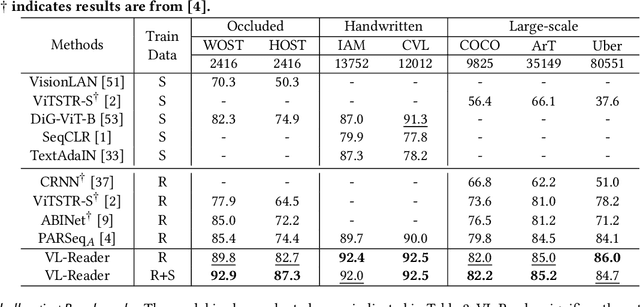
Abstract:Text recognition is an inherent integration of vision and language, encompassing the visual texture in stroke patterns and the semantic context among the character sequences. Towards advanced text recognition, there are three key challenges: (1) an encoder capable of representing the visual and semantic distributions; (2) a decoder that ensures the alignment between vision and semantics; and (3) consistency in the framework during pre-training, if it exists, and fine-tuning. Inspired by masked autoencoding, a successful pre-training strategy in both vision and language, we propose an innovative scene text recognition approach, named VL-Reader. The novelty of the VL-Reader lies in the pervasive interplay between vision and language throughout the entire process. Concretely, we first introduce a Masked Visual-Linguistic Reconstruction (MVLR) objective, which aims at simultaneously modeling visual and linguistic information. Then, we design a Masked Visual-Linguistic Decoder (MVLD) to further leverage masked vision-language context and achieve bi-modal feature interaction. The architecture of VL-Reader maintains consistency from pre-training to fine-tuning. In the pre-training stage, VL-Reader reconstructs both masked visual and text tokens, while in the fine-tuning stage, the network degrades to reconstruct all characters from an image without any masked regions. VL-reader achieves an average accuracy of 97.1% on six typical datasets, surpassing the SOTA by 1.1%. The improvement was even more significant on challenging datasets. The results demonstrate that vision and language reconstructor can serve as an effective scene text recognizer.
Platypus: A Generalized Specialist Model for Reading Text in Various Forms
Aug 27, 2024



Abstract:Reading text from images (either natural scenes or documents) has been a long-standing research topic for decades, due to the high technical challenge and wide application range. Previously, individual specialist models are developed to tackle the sub-tasks of text reading (e.g., scene text recognition, handwritten text recognition and mathematical expression recognition). However, such specialist models usually cannot effectively generalize across different sub-tasks. Recently, generalist models (such as GPT-4V), trained on tremendous data in a unified way, have shown enormous potential in reading text in various scenarios, but with the drawbacks of limited accuracy and low efficiency. In this work, we propose Platypus, a generalized specialist model for text reading. Specifically, Platypus combines the best of both worlds: being able to recognize text of various forms with a single unified architecture, while achieving excellent accuracy and high efficiency. To better exploit the advantage of Platypus, we also construct a text reading dataset (called Worms), the images of which are curated from previous datasets and partially re-labeled. Experiments on standard benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed Platypus model. Model and data will be made publicly available at https://github.com/AlibabaResearch/AdvancedLiterateMachinery/tree/main/OCR/Platypus.
A dataset of primary nasopharyngeal carcinoma MRI with multi-modalities segmentation
Apr 04, 2024Abstract:Multi-modality magnetic resonance imaging data with various sequences facilitate the early diagnosis, tumor segmentation, and disease staging in the management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). The lack of publicly available, comprehensive datasets limits advancements in diagnosis, treatment planning, and the development of machine learning algorithms for NPC. Addressing this critical need, we introduce the first comprehensive NPC MRI dataset, encompassing MR axial imaging of 277 primary NPC patients. This dataset includes T1-weighted, T2-weighted, and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted sequences, totaling 831 scans. In addition to the corresponding clinical data, manually annotated and labeled segmentations by experienced radiologists offer high-quality data resources from untreated primary NPC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge