Wenqing Cheng
Generative Compositor for Few-Shot Visual Information Extraction
Mar 21, 2025Abstract:Visual Information Extraction (VIE), aiming at extracting structured information from visually rich document images, plays a pivotal role in document processing. Considering various layouts, semantic scopes, and languages, VIE encompasses an extensive range of types, potentially numbering in the thousands. However, many of these types suffer from a lack of training data, which poses significant challenges. In this paper, we propose a novel generative model, named Generative Compositor, to address the challenge of few-shot VIE. The Generative Compositor is a hybrid pointer-generator network that emulates the operations of a compositor by retrieving words from the source text and assembling them based on the provided prompts. Furthermore, three pre-training strategies are employed to enhance the model's perception of spatial context information. Besides, a prompt-aware resampler is specially designed to enable efficient matching by leveraging the entity-semantic prior contained in prompts. The introduction of the prompt-based retrieval mechanism and the pre-training strategies enable the model to acquire more effective spatial and semantic clues with limited training samples. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed method achieves highly competitive results in the full-sample training, while notably outperforms the baseline in the 1-shot, 5-shot, and 10-shot settings.
OmniParser V2: Structured-Points-of-Thought for Unified Visual Text Parsing and Its Generality to Multimodal Large Language Models
Feb 22, 2025Abstract:Visually-situated text parsing (VsTP) has recently seen notable advancements, driven by the growing demand for automated document understanding and the emergence of large language models capable of processing document-based questions. While various methods have been proposed to tackle the complexities of VsTP, existing solutions often rely on task-specific architectures and objectives for individual tasks. This leads to modal isolation and complex workflows due to the diversified targets and heterogeneous schemas. In this paper, we introduce OmniParser V2, a universal model that unifies VsTP typical tasks, including text spotting, key information extraction, table recognition, and layout analysis, into a unified framework. Central to our approach is the proposed Structured-Points-of-Thought (SPOT) prompting schemas, which improves model performance across diverse scenarios by leveraging a unified encoder-decoder architecture, objective, and input\&output representation. SPOT eliminates the need for task-specific architectures and loss functions, significantly simplifying the processing pipeline. Our extensive evaluations across four tasks on eight different datasets show that OmniParser V2 achieves state-of-the-art or competitive results in VsTP. Additionally, we explore the integration of SPOT within a multimodal large language model structure, further enhancing text localization and recognition capabilities, thereby confirming the generality of SPOT prompting technique. The code is available at \href{https://github.com/AlibabaResearch/AdvancedLiterateMachinery}{AdvancedLiterateMachinery}.
VL-Reader: Vision and Language Reconstructor is an Effective Scene Text Recognizer
Sep 18, 2024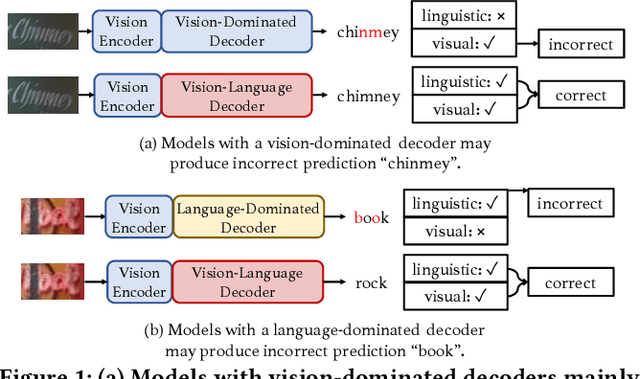
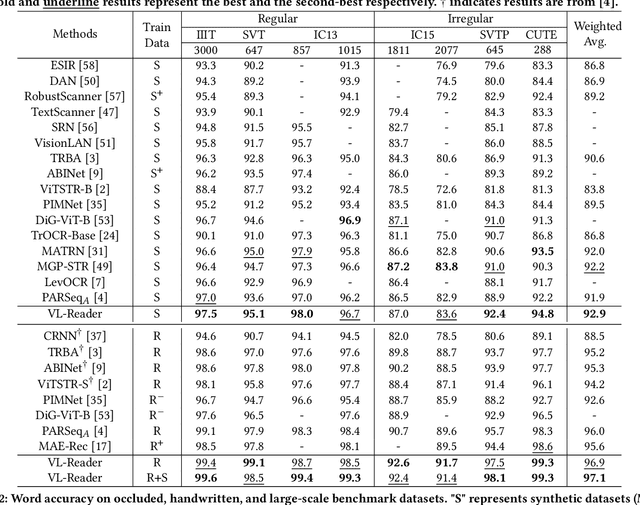
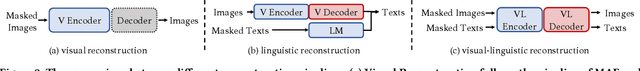
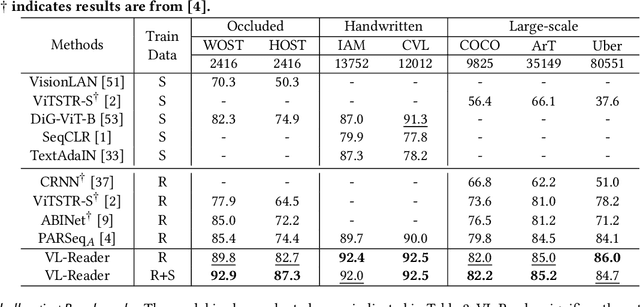
Abstract:Text recognition is an inherent integration of vision and language, encompassing the visual texture in stroke patterns and the semantic context among the character sequences. Towards advanced text recognition, there are three key challenges: (1) an encoder capable of representing the visual and semantic distributions; (2) a decoder that ensures the alignment between vision and semantics; and (3) consistency in the framework during pre-training, if it exists, and fine-tuning. Inspired by masked autoencoding, a successful pre-training strategy in both vision and language, we propose an innovative scene text recognition approach, named VL-Reader. The novelty of the VL-Reader lies in the pervasive interplay between vision and language throughout the entire process. Concretely, we first introduce a Masked Visual-Linguistic Reconstruction (MVLR) objective, which aims at simultaneously modeling visual and linguistic information. Then, we design a Masked Visual-Linguistic Decoder (MVLD) to further leverage masked vision-language context and achieve bi-modal feature interaction. The architecture of VL-Reader maintains consistency from pre-training to fine-tuning. In the pre-training stage, VL-Reader reconstructs both masked visual and text tokens, while in the fine-tuning stage, the network degrades to reconstruct all characters from an image without any masked regions. VL-reader achieves an average accuracy of 97.1% on six typical datasets, surpassing the SOTA by 1.1%. The improvement was even more significant on challenging datasets. The results demonstrate that vision and language reconstructor can serve as an effective scene text recognizer.
OmniParser: A Unified Framework for Text Spotting, Key Information Extraction and Table Recognition
Mar 28, 2024Abstract:Recently, visually-situated text parsing (VsTP) has experienced notable advancements, driven by the increasing demand for automated document understanding and the emergence of Generative Large Language Models (LLMs) capable of processing document-based questions. Various methods have been proposed to address the challenging problem of VsTP. However, due to the diversified targets and heterogeneous schemas, previous works usually design task-specific architectures and objectives for individual tasks, which inadvertently leads to modal isolation and complex workflow. In this paper, we propose a unified paradigm for parsing visually-situated text across diverse scenarios. Specifically, we devise a universal model, called OmniParser, which can simultaneously handle three typical visually-situated text parsing tasks: text spotting, key information extraction, and table recognition. In OmniParser, all tasks share the unified encoder-decoder architecture, the unified objective: point-conditioned text generation, and the unified input & output representation: prompt & structured sequences. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed OmniParser achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) or highly competitive performances on 7 datasets for the three visually-situated text parsing tasks, despite its unified, concise design. The code is available at https://github.com/AlibabaResearch/AdvancedLiterateMachinery.
DD-RobustBench: An Adversarial Robustness Benchmark for Dataset Distillation
Mar 20, 2024



Abstract:Dataset distillation is an advanced technique aimed at compressing datasets into significantly smaller counterparts, while preserving formidable training performance. Significant efforts have been devoted to promote evaluation accuracy under limited compression ratio while overlooked the robustness of distilled dataset. In this work, we introduce a comprehensive benchmark that, to the best of our knowledge, is the most extensive to date for evaluating the adversarial robustness of distilled datasets in a unified way. Our benchmark significantly expands upon prior efforts by incorporating a wider range of dataset distillation methods, including the latest advancements such as TESLA and SRe2L, a diverse array of adversarial attack methods, and evaluations across a broader and more extensive collection of datasets such as ImageNet-1K. Moreover, we assessed the robustness of these distilled datasets against representative adversarial attack algorithms like PGD and AutoAttack, while exploring their resilience from a frequency perspective. We also discovered that incorporating distilled data into the training batches of the original dataset can yield to improvement of robustness.
Modeling Entities as Semantic Points for Visual Information Extraction in the Wild
Mar 29, 2023



Abstract:Recently, Visual Information Extraction (VIE) has been becoming increasingly important in both the academia and industry, due to the wide range of real-world applications. Previously, numerous works have been proposed to tackle this problem. However, the benchmarks used to assess these methods are relatively plain, i.e., scenarios with real-world complexity are not fully represented in these benchmarks. As the first contribution of this work, we curate and release a new dataset for VIE, in which the document images are much more challenging in that they are taken from real applications, and difficulties such as blur, partial occlusion, and printing shift are quite common. All these factors may lead to failures in information extraction. Therefore, as the second contribution, we explore an alternative approach to precisely and robustly extract key information from document images under such tough conditions. Specifically, in contrast to previous methods, which usually either incorporate visual information into a multi-modal architecture or train text spotting and information extraction in an end-to-end fashion, we explicitly model entities as semantic points, i.e., center points of entities are enriched with semantic information describing the attributes and relationships of different entities, which could largely benefit entity labeling and linking. Extensive experiments on standard benchmarks in this field as well as the proposed dataset demonstrate that the proposed method can achieve significantly enhanced performance on entity labeling and linking, compared with previous state-of-the-art models. Dataset is available at https://www.modelscope.cn/datasets/damo/SIBR/summary.
Vision-Language Pre-Training for Boosting Scene Text Detectors
Apr 29, 2022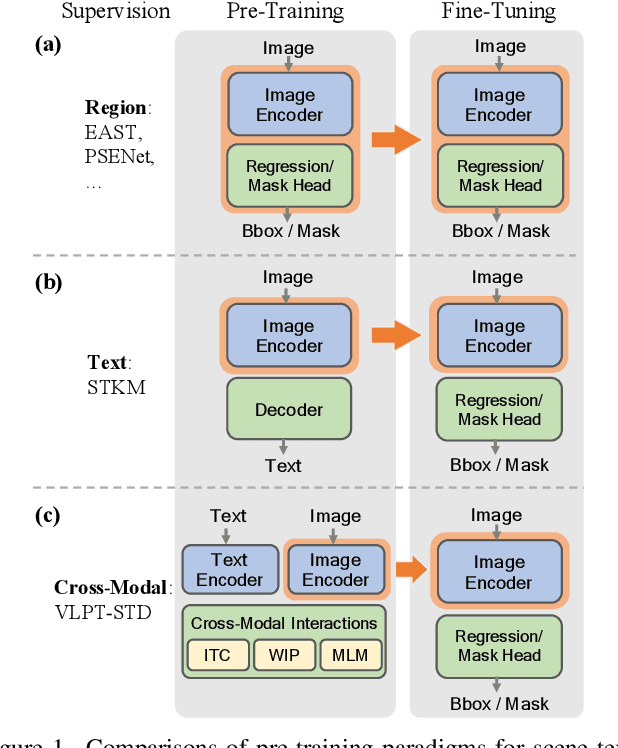
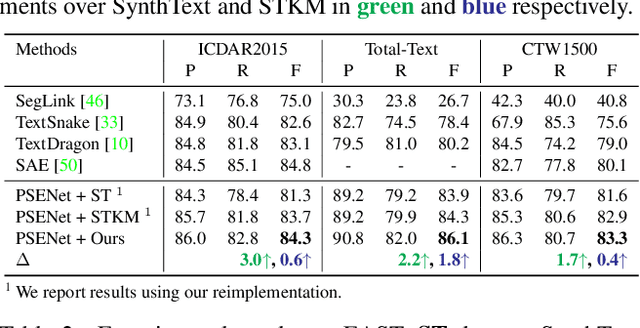
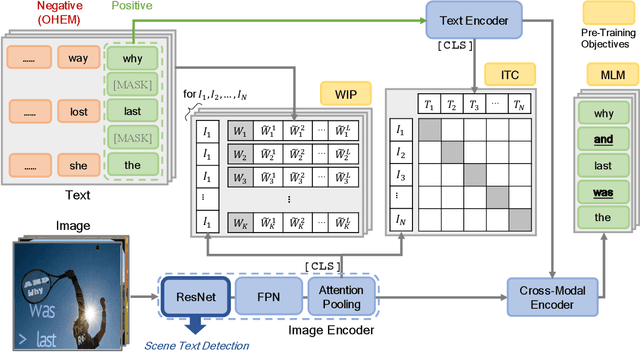
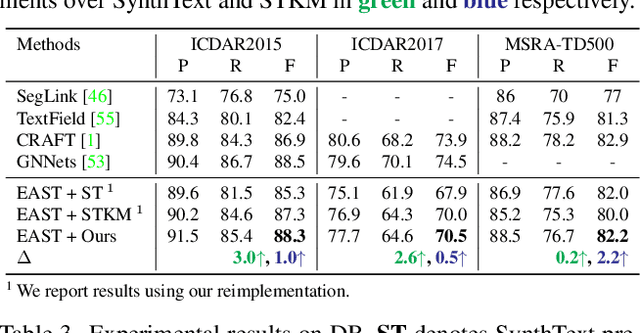
Abstract:Recently, vision-language joint representation learning has proven to be highly effective in various scenarios. In this paper, we specifically adapt vision-language joint learning for scene text detection, a task that intrinsically involves cross-modal interaction between the two modalities: vision and language, since text is the written form of language. Concretely, we propose to learn contextualized, joint representations through vision-language pre-training, for the sake of enhancing the performance of scene text detectors. Towards this end, we devise a pre-training architecture with an image encoder, a text encoder and a cross-modal encoder, as well as three pretext tasks: image-text contrastive learning (ITC), masked language modeling (MLM) and word-in-image prediction (WIP). The pre-trained model is able to produce more informative representations with richer semantics, which could readily benefit existing scene text detectors (such as EAST and PSENet) in the down-stream text detection task. Extensive experiments on standard benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed paradigm can significantly improve the performance of various representative text detectors, outperforming previous pre-training approaches. The code and pre-trained models will be publicly released.
MOST: A Multi-Oriented Scene Text Detector with Localization Refinement
Apr 05, 2021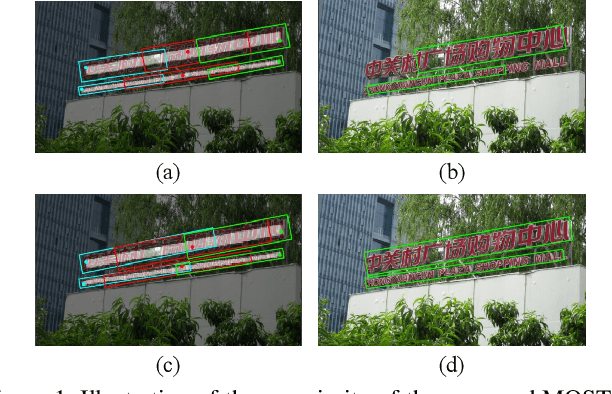
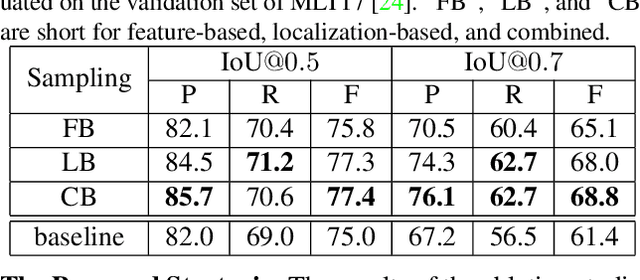
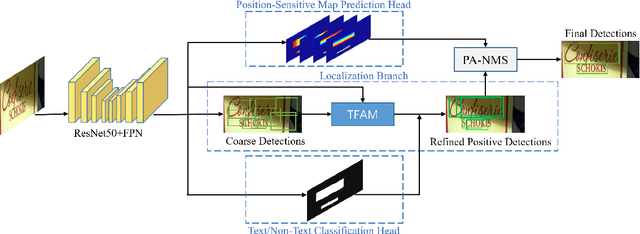
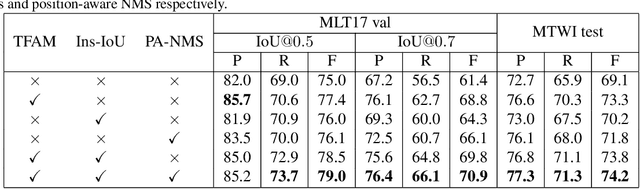
Abstract:Over the past few years, the field of scene text detection has progressed rapidly that modern text detectors are able to hunt text in various challenging scenarios. However, they might still fall short when handling text instances of extreme aspect ratios and varying scales. To tackle such difficulties, we propose in this paper a new algorithm for scene text detection, which puts forward a set of strategies to significantly improve the quality of text localization. Specifically, a Text Feature Alignment Module (TFAM) is proposed to dynamically adjust the receptive fields of features based on initial raw detections; a Position-Aware Non-Maximum Suppression (PA-NMS) module is devised to selectively concentrate on reliable raw detections and exclude unreliable ones; besides, we propose an Instance-wise IoU loss for balanced training to deal with text instances of different scales. An extensive ablation study demonstrates the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed strategies. The resulting text detection system, which integrates the proposed strategies with a leading scene text detector EAST, achieves state-of-the-art or competitive performance on various standard benchmarks for text detection while keeping a fast running speed.
Progressive and Aligned Pose Attention Transfer for Person Image Generation
Mar 22, 2021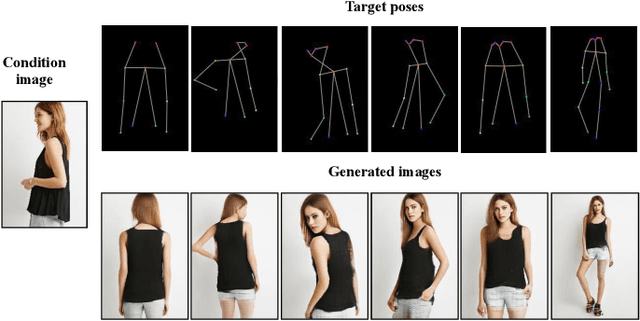
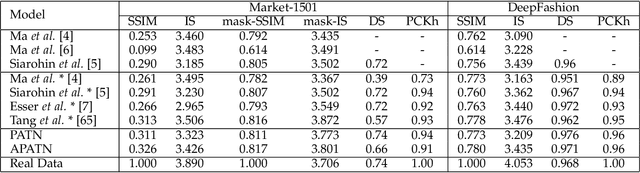
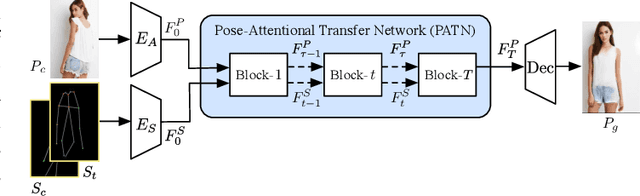
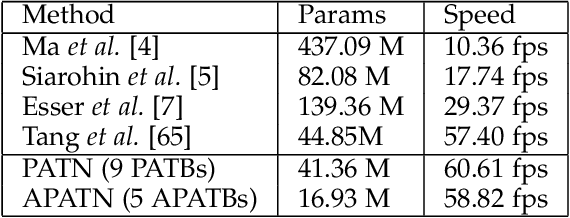
Abstract:This paper proposes a new generative adversarial network for pose transfer, i.e., transferring the pose of a given person to a target pose. We design a progressive generator which comprises a sequence of transfer blocks. Each block performs an intermediate transfer step by modeling the relationship between the condition and the target poses with attention mechanism. Two types of blocks are introduced, namely Pose-Attentional Transfer Block (PATB) and Aligned Pose-Attentional Transfer Bloc ~(APATB). Compared with previous works, our model generates more photorealistic person images that retain better appearance consistency and shape consistency compared with input images. We verify the efficacy of the model on the Market-1501 and DeepFashion datasets, using quantitative and qualitative measures. Furthermore, we show that our method can be used for data augmentation for the person re-identification task, alleviating the issue of data insufficiency. Code and pretrained models are available at https://github.com/tengteng95/Pose-Transfer.git.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge