Yongpan Wang
Context-Aware Selective Label Smoothing for Calibrating Sequence Recognition Model
Mar 13, 2023Abstract:Despite the success of deep neural network (DNN) on sequential data (i.e., scene text and speech) recognition, it suffers from the over-confidence problem mainly due to overfitting in training with the cross-entropy loss, which may make the decision-making less reliable. Confidence calibration has been recently proposed as one effective solution to this problem. Nevertheless, the majority of existing confidence calibration methods aims at non-sequential data, which is limited if directly applied to sequential data since the intrinsic contextual dependency in sequences or the class-specific statistical prior is seldom exploited. To the end, we propose a Context-Aware Selective Label Smoothing (CASLS) method for calibrating sequential data. The proposed CASLS fully leverages the contextual dependency in sequences to construct confusion matrices of contextual prediction statistics over different classes. Class-specific error rates are then used to adjust the weights of smoothing strength in order to achieve adaptive calibration. Experimental results on sequence recognition tasks, including scene text recognition and speech recognition, demonstrate that our method can achieve the state-of-the-art performance.
Decoupling Visual-Semantic Feature Learning for Robust Scene Text Recognition
Nov 24, 2021
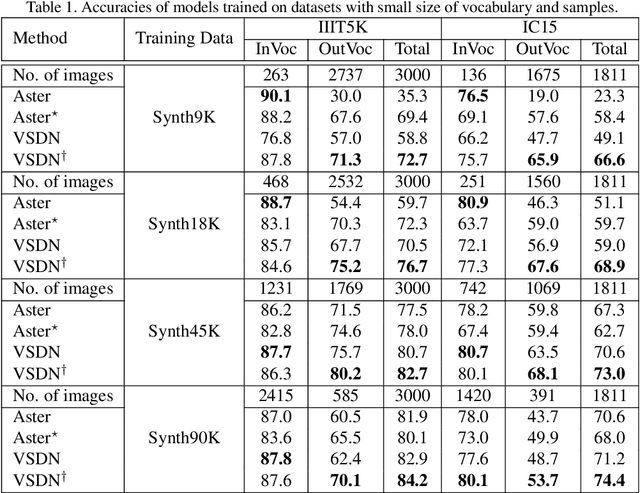
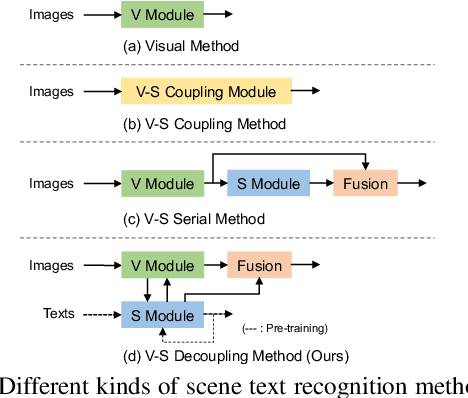

Abstract:Semantic information has been proved effective in scene text recognition. Most existing methods tend to couple both visual and semantic information in an attention-based decoder. As a result, the learning of semantic features is prone to have a bias on the limited vocabulary of the training set, which is called vocabulary reliance. In this paper, we propose a novel Visual-Semantic Decoupling Network (VSDN) to address the problem. Our VSDN contains a Visual Decoder (VD) and a Semantic Decoder (SD) to learn purer visual and semantic feature representation respectively. Besides, a Semantic Encoder (SE) is designed to match SD, which can be pre-trained together by additional inexpensive large vocabulary via a simple word correction task. Thus the semantic feature is more unbiased and precise to guide the visual feature alignment and enrich the final character representation. Experiments show that our method achieves state-of-the-art or competitive results on the standard benchmarks, and outperforms the popular baseline by a large margin under circumstances where the training set has a small size of vocabulary.
SentiPrompt: Sentiment Knowledge Enhanced Prompt-Tuning for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis
Sep 17, 2021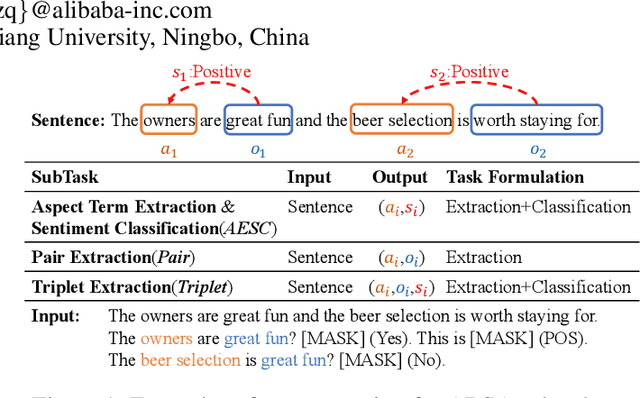
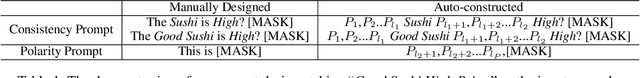
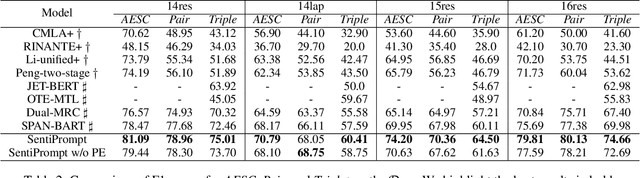
Abstract:Aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA) is an emerging fine-grained sentiment analysis task that aims to extract aspects, classify corresponding sentiment polarities and find opinions as the causes of sentiment. The latest research tends to solve the ABSA task in a unified way with end-to-end frameworks. Yet, these frameworks get fine-tuned from downstream tasks without any task-adaptive modification. Specifically, they do not use task-related knowledge well or explicitly model relations between aspect and opinion terms, hindering them from better performance. In this paper, we propose SentiPrompt to use sentiment knowledge enhanced prompts to tune the language model in the unified framework. We inject sentiment knowledge regarding aspects, opinions, and polarities into prompt and explicitly model term relations via constructing consistency and polarity judgment templates from the ground truth triplets. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach can outperform strong baselines on Triplet Extraction, Pair Extraction, and Aspect Term Extraction with Sentiment Classification by a notable margin.
Parsing Table Structures in the Wild
Sep 06, 2021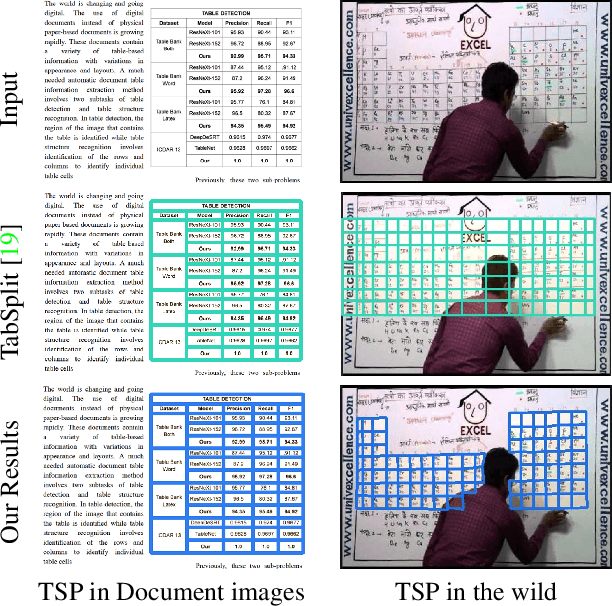
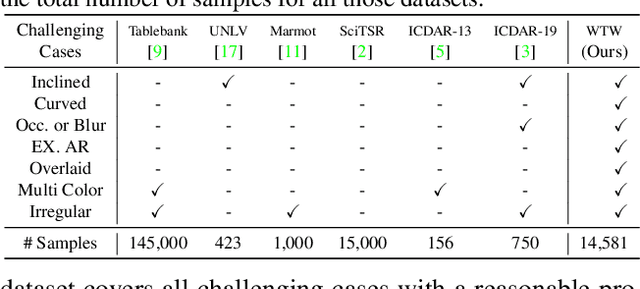
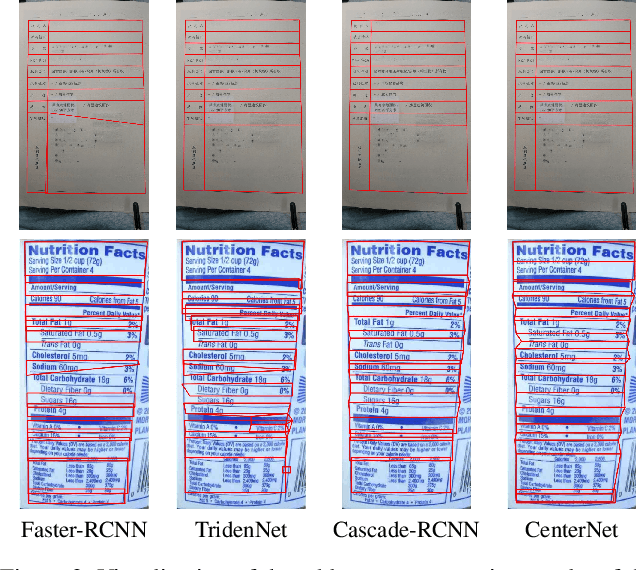
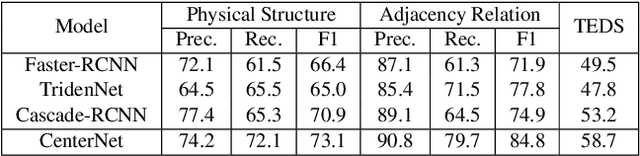
Abstract:This paper tackles the problem of table structure parsing (TSP) from images in the wild. In contrast to existing studies that mainly focus on parsing well-aligned tabular images with simple layouts from scanned PDF documents, we aim to establish a practical table structure parsing system for real-world scenarios where tabular input images are taken or scanned with severe deformation, bending or occlusions. For designing such a system, we propose an approach named Cycle-CenterNet on the top of CenterNet with a novel cycle-pairing module to simultaneously detect and group tabular cells into structured tables. In the cycle-pairing module, a new pairing loss function is proposed for the network training. Alongside with our Cycle-CenterNet, we also present a large-scale dataset, named Wired Table in the Wild (WTW), which includes well-annotated structure parsing of multiple style tables in several scenes like the photo, scanning files, web pages, \emph{etc.}. In experiments, we demonstrate that our Cycle-CenterNet consistently achieves the best accuracy of table structure parsing on the new WTW dataset by 24.6\% absolute improvement evaluated by the TEDS metric. A more comprehensive experimental analysis also validates the advantages of our proposed methods for the TSP task.
Implicit Feature Alignment: Learn to Convert Text Recognizer to Text Spotter
Jun 10, 2021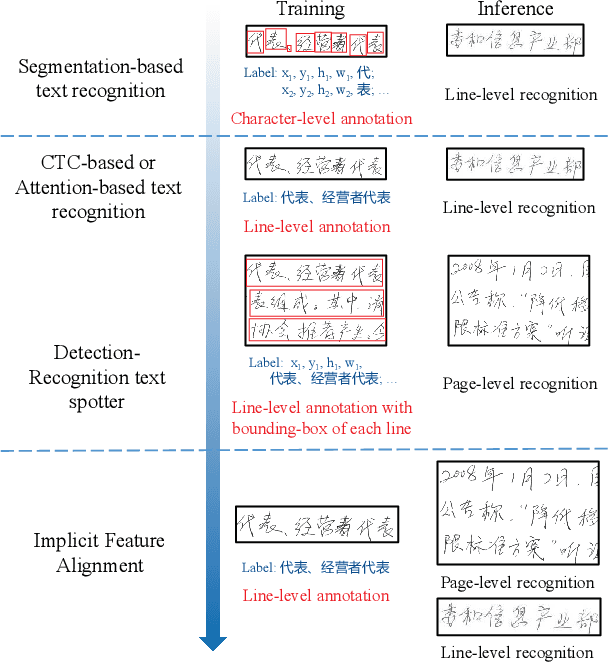
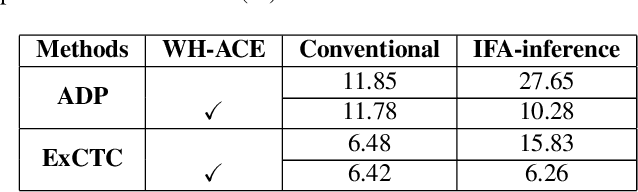
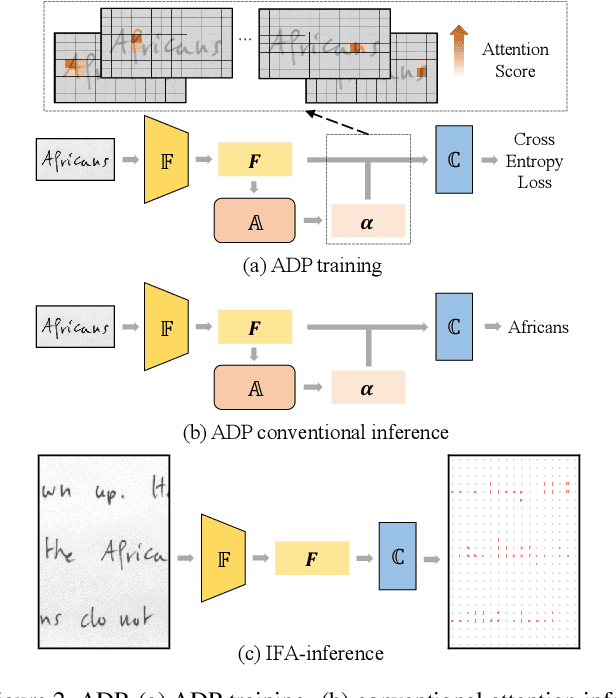
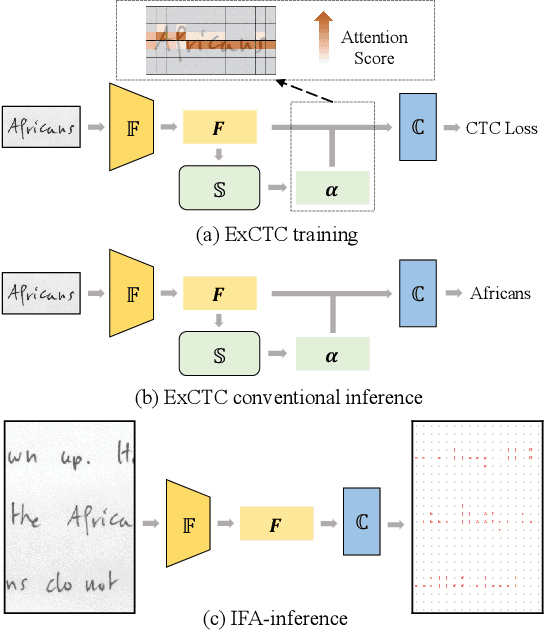
Abstract:Text recognition is a popular research subject with many associated challenges. Despite the considerable progress made in recent years, the text recognition task itself is still constrained to solve the problem of reading cropped line text images and serves as a subtask of optical character recognition (OCR) systems. As a result, the final text recognition result is limited by the performance of the text detector. In this paper, we propose a simple, elegant and effective paradigm called Implicit Feature Alignment (IFA), which can be easily integrated into current text recognizers, resulting in a novel inference mechanism called IFAinference. This enables an ordinary text recognizer to process multi-line text such that text detection can be completely freed. Specifically, we integrate IFA into the two most prevailing text recognition streams (attention-based and CTC-based) and propose attention-guided dense prediction (ADP) and Extended CTC (ExCTC). Furthermore, the Wasserstein-based Hollow Aggregation Cross-Entropy (WH-ACE) is proposed to suppress negative predictions to assist in training ADP and ExCTC. We experimentally demonstrate that IFA achieves state-of-the-art performance on end-to-end document recognition tasks while maintaining the fastest speed, and ADP and ExCTC complement each other on the perspective of different application scenarios. Code will be available at https://github.com/WangTianwei/Implicit-feature-alignment.
MOST: A Multi-Oriented Scene Text Detector with Localization Refinement
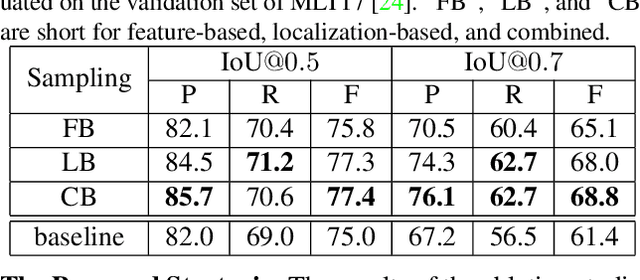
Apr 05, 2021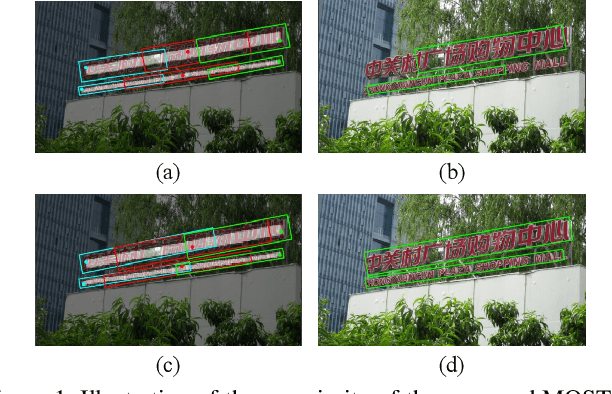
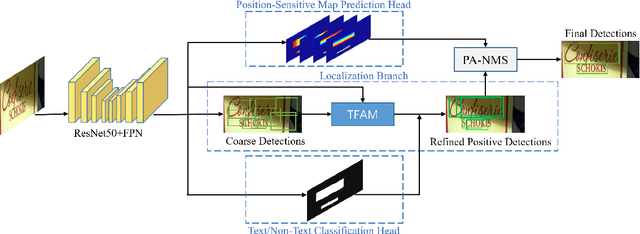
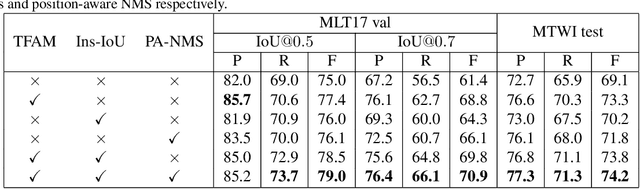
Abstract:Over the past few years, the field of scene text detection has progressed rapidly that modern text detectors are able to hunt text in various challenging scenarios. However, they might still fall short when handling text instances of extreme aspect ratios and varying scales. To tackle such difficulties, we propose in this paper a new algorithm for scene text detection, which puts forward a set of strategies to significantly improve the quality of text localization. Specifically, a Text Feature Alignment Module (TFAM) is proposed to dynamically adjust the receptive fields of features based on initial raw detections; a Position-Aware Non-Maximum Suppression (PA-NMS) module is devised to selectively concentrate on reliable raw detections and exclude unreliable ones; besides, we propose an Instance-wise IoU loss for balanced training to deal with text instances of different scales. An extensive ablation study demonstrates the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed strategies. The resulting text detection system, which integrates the proposed strategies with a leading scene text detector EAST, achieves state-of-the-art or competitive performance on various standard benchmarks for text detection while keeping a fast running speed.
Joint Layout Analysis, Character Detection and Recognition for Historical Document Digitization
Jul 14, 2020
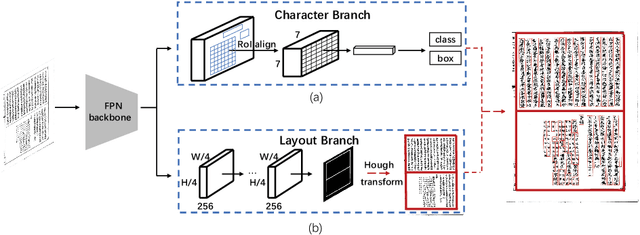


Abstract:In this paper, we propose an end-to-end trainable framework for restoring historical documents content that follows the correct reading order. In this framework, two branches named character branch and layout branch are added behind the feature extraction network. The character branch localizes individual characters in a document image and recognizes them simultaneously. Then we adopt a post-processing method to group them into text lines. The layout branch based on fully convolutional network outputs a binary mask. We then use Hough transform for line detection on the binary mask and combine character results with the layout information to restore document content. These two branches can be trained in parallel and are easy to train. Furthermore, we propose a re-score mechanism to minimize recognition error. Experiment results on the extended Chinese historical document MTHv2 dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework.
Learn to Augment: Joint Data Augmentation and Network Optimization for Text Recognition
Mar 14, 2020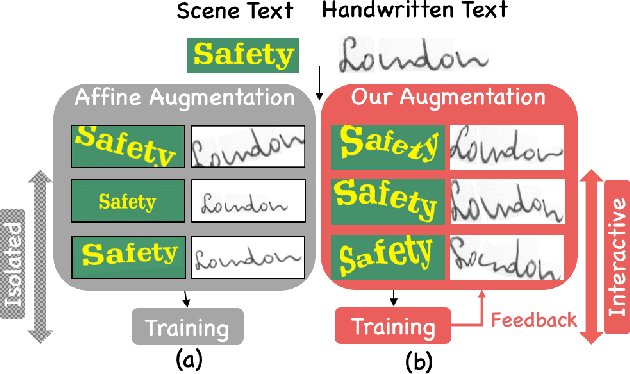
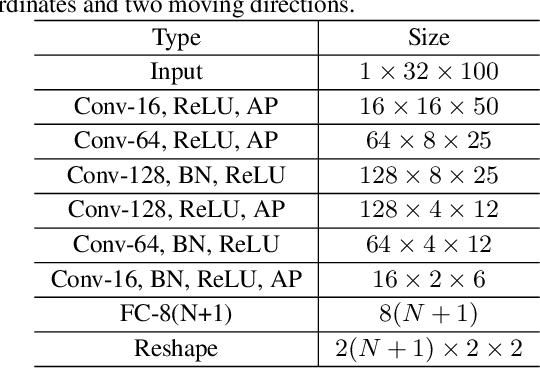
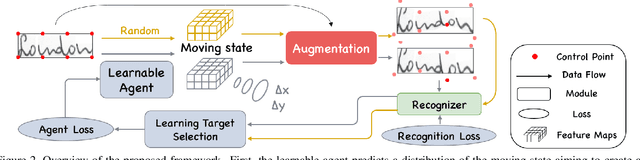
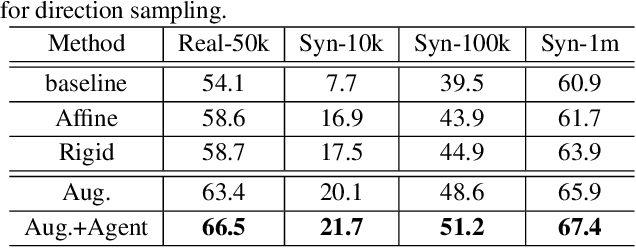
Abstract:Handwritten text and scene text suffer from various shapes and distorted patterns. Thus training a robust recognition model requires a large amount of data to cover diversity as much as possible. In contrast to data collection and annotation, data augmentation is a low cost way. In this paper, we propose a new method for text image augmentation. Different from traditional augmentation methods such as rotation, scaling and perspective transformation, our proposed augmentation method is designed to learn proper and efficient data augmentation which is more effective and specific for training a robust recognizer. By using a set of custom fiducial points, the proposed augmentation method is flexible and controllable. Furthermore, we bridge the gap between the isolated processes of data augmentation and network optimization by joint learning. An agent network learns from the output of the recognition network and controls the fiducial points to generate more proper training samples for the recognition network. Extensive experiments on various benchmarks, including regular scene text, irregular scene text and handwritten text, show that the proposed augmentation and the joint learning methods significantly boost the performance of the recognition networks. A general toolkit for geometric augmentation is available.
All You Need Is Boundary: Toward Arbitrary-Shaped Text Spotting
Nov 21, 2019
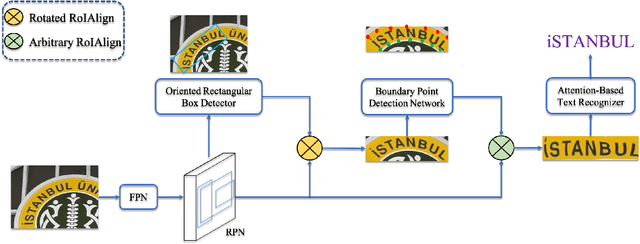

Abstract:Recently, end-to-end text spotting that aims to detect and recognize text from cluttered images simultaneously has received particularly growing interest in computer vision. Different from the existing approaches that formulate text detection as bounding box extraction or instance segmentation, we localize a set of points on the boundary of each text instance. With the representation of such boundary points, we establish a simple yet effective scheme for end-to-end text spotting, which can read the text of arbitrary shapes. Experiments on three challenging datasets, including ICDAR2015, TotalText and COCO-Text demonstrate that the proposed method consistently surpasses the state-of-the-art in both scene text detection and end-to-end text recognition tasks.
TextField: Learning A Deep Direction Field for Irregular Scene Text Detection
Dec 04, 2018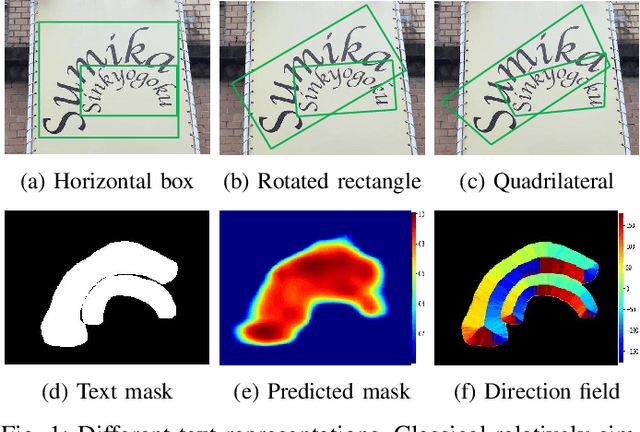

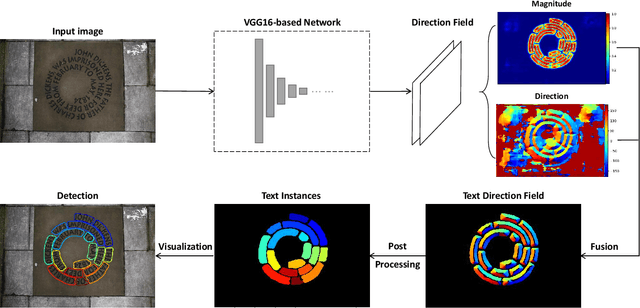
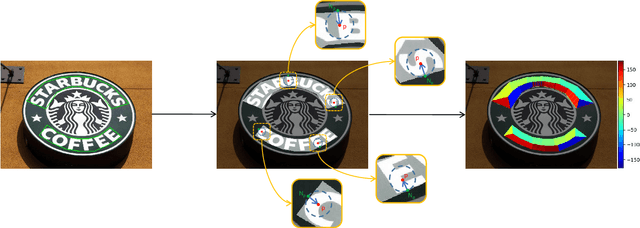
Abstract:Scene text detection is an important step of scene text reading system. The main challenges lie on significantly varied sizes and aspect ratios, arbitrary orientations and shapes. Driven by recent progress in deep learning, impressive performances have been achieved for multi-oriented text detection. Yet, the performance drops dramatically in detecting curved texts due to the limited text representation (e.g., horizontal bounding boxes, rotated rectangles, or quadrilaterals). It is of great interest to detect curved texts, which are actually very common in natural scenes. In this paper, we present a novel text detector named TextField for detecting irregular scene texts. Specifically, we learn a direction field pointing away from the nearest text boundary to each text point. This direction field is represented by an image of two-dimensional vectors and learned via a fully convolutional neural network. It encodes both binary text mask and direction information used to separate adjacent text instances, which is challenging for classical segmentation-based approaches. Based on the learned direction field, we apply a simple yet effective morphological-based post-processing to achieve the final detection. Experimental results show that the proposed TextField outperforms the state-of-the-art methods by a large margin (28% and 8%) on two curved text datasets: Total-Text and CTW1500, respectively, and also achieves very competitive performance on multi-oriented datasets: ICDAR 2015 and MSRA-TD500. Furthermore, TextField is robust in generalizing to unseen datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge