Yuanzhi Zhu
Bridging Continuous and Discrete Tokens for Autoregressive Visual Generation
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:Autoregressive visual generation models typically rely on tokenizers to compress images into tokens that can be predicted sequentially. A fundamental dilemma exists in token representation: discrete tokens enable straightforward modeling with standard cross-entropy loss, but suffer from information loss and tokenizer training instability; continuous tokens better preserve visual details, but require complex distribution modeling, complicating the generation pipeline. In this paper, we propose TokenBridge, which bridges this gap by maintaining the strong representation capacity of continuous tokens while preserving the modeling simplicity of discrete tokens. To achieve this, we decouple discretization from the tokenizer training process through post-training quantization that directly obtains discrete tokens from continuous representations. Specifically, we introduce a dimension-wise quantization strategy that independently discretizes each feature dimension, paired with a lightweight autoregressive prediction mechanism that efficiently model the resulting large token space. Extensive experiments show that our approach achieves reconstruction and generation quality on par with continuous methods while using standard categorical prediction. This work demonstrates that bridging discrete and continuous paradigms can effectively harness the strengths of both approaches, providing a promising direction for high-quality visual generation with simple autoregressive modeling. Project page: https://yuqingwang1029.github.io/TokenBridge.
Di$\mathtt{[M]}$O: Distilling Masked Diffusion Models into One-step Generator
Mar 19, 2025![Figure 1 for Di$\mathtt{[M]}$O: Distilling Masked Diffusion Models into One-step Generator](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Ffigures.semanticscholar.org%2F6c219ad77dbeec39e8440063d2e7b0d4c97cbd9a%2F6-Table1-1.png&w=640&q=75)
![Figure 2 for Di$\mathtt{[M]}$O: Distilling Masked Diffusion Models into One-step Generator](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Ffigures.semanticscholar.org%2F6c219ad77dbeec39e8440063d2e7b0d4c97cbd9a%2F3-Figure2-1.png&w=640&q=75)
![Figure 3 for Di$\mathtt{[M]}$O: Distilling Masked Diffusion Models into One-step Generator](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Ffigures.semanticscholar.org%2F6c219ad77dbeec39e8440063d2e7b0d4c97cbd9a%2F8-Table2-1.png&w=640&q=75)
![Figure 4 for Di$\mathtt{[M]}$O: Distilling Masked Diffusion Models into One-step Generator](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Ffigures.semanticscholar.org%2F6c219ad77dbeec39e8440063d2e7b0d4c97cbd9a%2F5-Figure3-1.png&w=640&q=75)
Abstract:Masked Diffusion Models (MDMs) have emerged as a powerful generative modeling technique. Despite their remarkable results, they typically suffer from slow inference with several steps. In this paper, we propose Di$\mathtt{[M]}$O, a novel approach that distills masked diffusion models into a one-step generator. Di$\mathtt{[M]}$O addresses two key challenges: (1) the intractability of using intermediate-step information for one-step generation, which we solve through token-level distribution matching that optimizes model output logits by an 'on-policy framework' with the help of an auxiliary model; and (2) the lack of entropy in the initial distribution, which we address through a token initialization strategy that injects randomness while maintaining similarity to teacher training distribution. We show Di$\mathtt{[M]}$O's effectiveness on both class-conditional and text-conditional image generation, impressively achieving performance competitive to multi-step teacher outputs while drastically reducing inference time. To our knowledge, we are the first to successfully achieve one-step distillation of masked diffusion models and the first to apply discrete distillation to text-to-image generation, opening new paths for efficient generative modeling.
Qwen2.5-VL Technical Report
Feb 19, 2025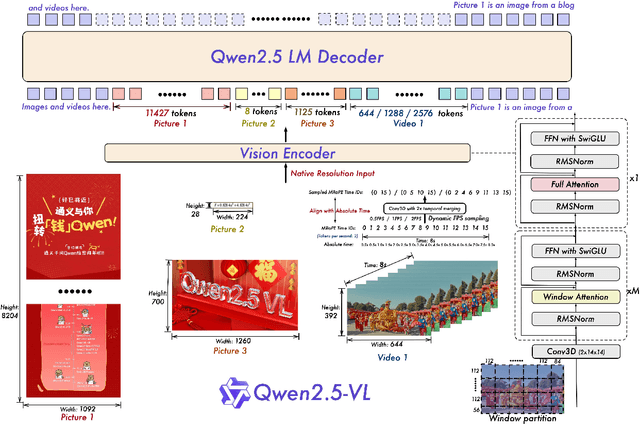
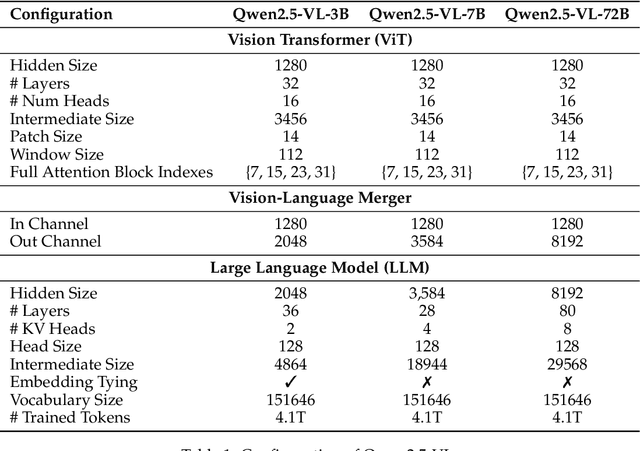
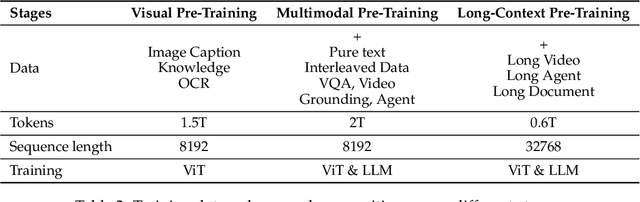
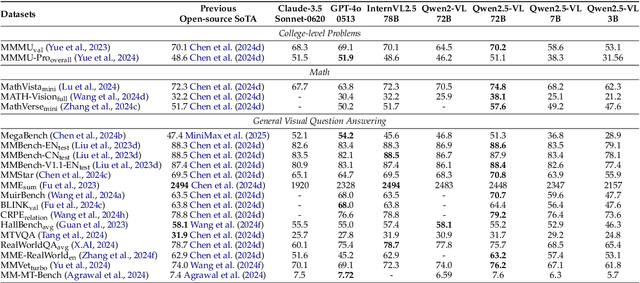
Abstract:We introduce Qwen2.5-VL, the latest flagship model of Qwen vision-language series, which demonstrates significant advancements in both foundational capabilities and innovative functionalities. Qwen2.5-VL achieves a major leap forward in understanding and interacting with the world through enhanced visual recognition, precise object localization, robust document parsing, and long-video comprehension. A standout feature of Qwen2.5-VL is its ability to localize objects using bounding boxes or points accurately. It provides robust structured data extraction from invoices, forms, and tables, as well as detailed analysis of charts, diagrams, and layouts. To handle complex inputs, Qwen2.5-VL introduces dynamic resolution processing and absolute time encoding, enabling it to process images of varying sizes and videos of extended durations (up to hours) with second-level event localization. This allows the model to natively perceive spatial scales and temporal dynamics without relying on traditional normalization techniques. By training a native dynamic-resolution Vision Transformer (ViT) from scratch and incorporating Window Attention, we reduce computational overhead while maintaining native resolution. As a result, Qwen2.5-VL excels not only in static image and document understanding but also as an interactive visual agent capable of reasoning, tool usage, and task execution in real-world scenarios such as operating computers and mobile devices. Qwen2.5-VL is available in three sizes, addressing diverse use cases from edge AI to high-performance computing. The flagship Qwen2.5-VL-72B model matches state-of-the-art models like GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet, particularly excelling in document and diagram understanding. Additionally, Qwen2.5-VL maintains robust linguistic performance, preserving the core language competencies of the Qwen2.5 LLM.
SceneVTG++: Controllable Multilingual Visual Text Generation in the Wild
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Generating visual text in natural scene images is a challenging task with many unsolved problems. Different from generating text on artificially designed images (such as posters, covers, cartoons, etc.), the text in natural scene images needs to meet the following four key criteria: (1) Fidelity: the generated text should appear as realistic as a photograph and be completely accurate, with no errors in any of the strokes. (2) Reasonability: the text should be generated on reasonable carrier areas (such as boards, signs, walls, etc.), and the generated text content should also be relevant to the scene. (3) Utility: the generated text can facilitate to the training of natural scene OCR (Optical Character Recognition) tasks. (4) Controllability: The attribute of the text (such as font and color) should be controllable as needed. In this paper, we propose a two stage method, SceneVTG++, which simultaneously satisfies the four aspects mentioned above. SceneVTG++ consists of a Text Layout and Content Generator (TLCG) and a Controllable Local Text Diffusion (CLTD). The former utilizes the world knowledge of multi modal large language models to find reasonable text areas and recommend text content according to the nature scene background images, while the latter generates controllable multilingual text based on the diffusion model. Through extensive experiments, we respectively verified the effectiveness of TLCG and CLTD, and demonstrated the state-of-the-art text generation performance of SceneVTG++. In addition, the generated images have superior utility in OCR tasks like text detection and text recognition. Codes and datasets will be available.
OFTSR: One-Step Flow for Image Super-Resolution with Tunable Fidelity-Realism Trade-offs
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion and flow-based generative models have demonstrated remarkable success in image restoration tasks, achieving superior perceptual quality compared to traditional deep learning approaches. However, these methods either require numerous sampling steps to generate high-quality images, resulting in significant computational overhead, or rely on model distillation, which usually imposes a fixed fidelity-realism trade-off and thus lacks flexibility. In this paper, we introduce OFTSR, a novel flow-based framework for one-step image super-resolution that can produce outputs with tunable levels of fidelity and realism. Our approach first trains a conditional flow-based super-resolution model to serve as a teacher model. We then distill this teacher model by applying a specialized constraint. Specifically, we force the predictions from our one-step student model for same input to lie on the same sampling ODE trajectory of the teacher model. This alignment ensures that the student model's single-step predictions from initial states match the teacher's predictions from a closer intermediate state. Through extensive experiments on challenging datasets including FFHQ (256$\times$256), DIV2K, and ImageNet (256$\times$256), we demonstrate that OFTSR achieves state-of-the-art performance for one-step image super-resolution, while having the ability to flexibly tune the fidelity-realism trade-off. Code and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/yuanzhi-zhu/OFTSR and https://huggingface.co/Yuanzhi/OFTSR, respectively.
Accelerating Video Diffusion Models via Distribution Matching
Dec 08, 2024



Abstract:Generative models, particularly diffusion models, have made significant success in data synthesis across various modalities, including images, videos, and 3D assets. However, current diffusion models are computationally intensive, often requiring numerous sampling steps that limit their practical application, especially in video generation. This work introduces a novel framework for diffusion distillation and distribution matching that dramatically reduces the number of inference steps while maintaining-and potentially improving-generation quality. Our approach focuses on distilling pre-trained diffusion models into a more efficient few-step generator, specifically targeting video generation. By leveraging a combination of video GAN loss and a novel 2D score distribution matching loss, we demonstrate the potential to generate high-quality video frames with substantially fewer sampling steps. To be specific, the proposed method incorporates a denoising GAN discriminator to distil from the real data and a pre-trained image diffusion model to enhance the frame quality and the prompt-following capabilities. Experimental results using AnimateDiff as the teacher model showcase the method's effectiveness, achieving superior performance in just four sampling steps compared to existing techniques.
Generalizable Single-Source Cross-modality Medical Image Segmentation via Invariant Causal Mechanisms
Nov 07, 2024Abstract:Single-source domain generalization (SDG) aims to learn a model from a single source domain that can generalize well on unseen target domains. This is an important task in computer vision, particularly relevant to medical imaging where domain shifts are common. In this work, we consider a challenging yet practical setting: SDG for cross-modality medical image segmentation. We combine causality-inspired theoretical insights on learning domain-invariant representations with recent advancements in diffusion-based augmentation to improve generalization across diverse imaging modalities. Guided by the ``intervention-augmentation equivariant'' principle, we use controlled diffusion models (DMs) to simulate diverse imaging styles while preserving the content, leveraging rich generative priors in large-scale pretrained DMs to comprehensively perturb the multidimensional style variable. Extensive experiments on challenging cross-modality segmentation tasks demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms state-of-the-art SDG methods across three distinct anatomies and imaging modalities. The source code is available at \href{https://github.com/ratschlab/ICMSeg}{https://github.com/ratschlab/ICMSeg}.
Robust Watermarking Using Generative Priors Against Image Editing: From Benchmarking to Advances
Oct 24, 2024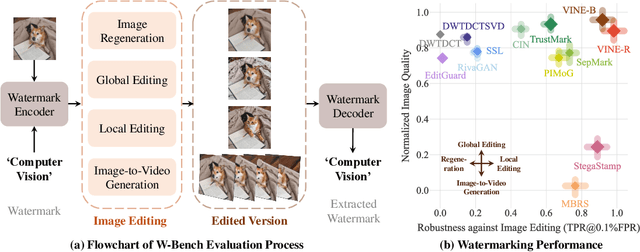
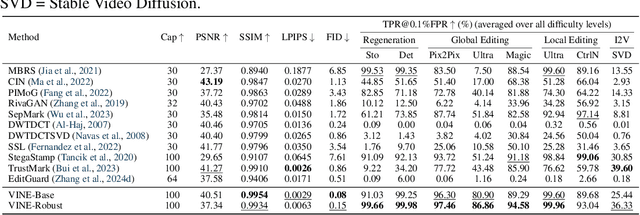
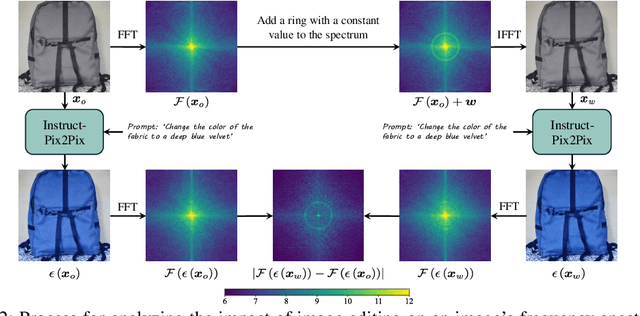
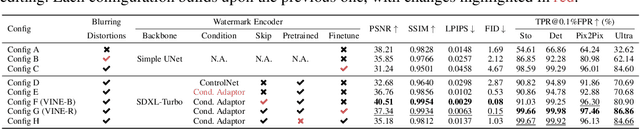
Abstract:Current image watermarking methods are vulnerable to advanced image editing techniques enabled by large-scale text-to-image models. These models can distort embedded watermarks during editing, posing significant challenges to copyright protection. In this work, we introduce W-Bench, the first comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate the robustness of watermarking methods against a wide range of image editing techniques, including image regeneration, global editing, local editing, and image-to-video generation. Through extensive evaluations of eleven representative watermarking methods against prevalent editing techniques, we demonstrate that most methods fail to detect watermarks after such edits. To address this limitation, we propose VINE, a watermarking method that significantly enhances robustness against various image editing techniques while maintaining high image quality. Our approach involves two key innovations: (1) we analyze the frequency characteristics of image editing and identify that blurring distortions exhibit similar frequency properties, which allows us to use them as surrogate attacks during training to bolster watermark robustness; (2) we leverage a large-scale pretrained diffusion model SDXL-Turbo, adapting it for the watermarking task to achieve more imperceptible and robust watermark embedding. Experimental results show that our method achieves outstanding watermarking performance under various image editing techniques, outperforming existing methods in both image quality and robustness. Code is available at https://github.com/Shilin-LU/VINE.
Visual Text Generation in the Wild
Jul 19, 2024



Abstract:Recently, with the rapid advancements of generative models, the field of visual text generation has witnessed significant progress. However, it is still challenging to render high-quality text images in real-world scenarios, as three critical criteria should be satisfied: (1) Fidelity: the generated text images should be photo-realistic and the contents are expected to be the same as specified in the given conditions; (2) Reasonability: the regions and contents of the generated text should cohere with the scene; (3) Utility: the generated text images can facilitate related tasks (e.g., text detection and recognition). Upon investigation, we find that existing methods, either rendering-based or diffusion-based, can hardly meet all these aspects simultaneously, limiting their application range. Therefore, we propose in this paper a visual text generator (termed SceneVTG), which can produce high-quality text images in the wild. Following a two-stage paradigm, SceneVTG leverages a Multimodal Large Language Model to recommend reasonable text regions and contents across multiple scales and levels, which are used by a conditional diffusion model as conditions to generate text images. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed SceneVTG significantly outperforms traditional rendering-based methods and recent diffusion-based methods in terms of fidelity and reasonability. Besides, the generated images provide superior utility for tasks involving text detection and text recognition. Code and datasets are available at AdvancedLiterateMachinery.
SlimFlow: Training Smaller One-Step Diffusion Models with Rectified Flow
Jul 18, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models excel in high-quality generation but suffer from slow inference due to iterative sampling. While recent methods have successfully transformed diffusion models into one-step generators, they neglect model size reduction, limiting their applicability in compute-constrained scenarios. This paper aims to develop small, efficient one-step diffusion models based on the powerful rectified flow framework, by exploring joint compression of inference steps and model size. The rectified flow framework trains one-step generative models using two operations, reflow and distillation. Compared with the original framework, squeezing the model size brings two new challenges: (1) the initialization mismatch between large teachers and small students during reflow; (2) the underperformance of naive distillation on small student models. To overcome these issues, we propose Annealing Reflow and Flow-Guided Distillation, which together comprise our SlimFlow framework. With our novel framework, we train a one-step diffusion model with an FID of 5.02 and 15.7M parameters, outperforming the previous state-of-the-art one-step diffusion model (FID=6.47, 19.4M parameters) on CIFAR10. On ImageNet 64$\times$64 and FFHQ 64$\times$64, our method yields small one-step diffusion models that are comparable to larger models, showcasing the effectiveness of our method in creating compact, efficient one-step diffusion models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge