Xi Wang
A Deployment-Friendly Foundational Framework for Efficient Computational Pathology
Feb 15, 2026Abstract:Pathology foundation models (PFMs) have enabled robust generalization in computational pathology through large-scale datasets and expansive architectures, but their substantial computational cost, particularly for gigapixel whole slide images, limits clinical accessibility and scalability. Here, we present LitePath, a deployment-friendly foundational framework designed to mitigate model over-parameterization and patch level redundancy. LitePath integrates LiteFM, a compact model distilled from three large PFMs (Virchow2, H-Optimus-1 and UNI2) using 190 million patches, and the Adaptive Patch Selector (APS), a lightweight component for task-specific patch selection. The framework reduces model parameters by 28x and lowers FLOPs by 403.5x relative to Virchow2, enabling deployment on low-power edge hardware such as the NVIDIA Jetson Orin Nano Super. On this device, LitePath processes 208 slides per hour, 104.5x faster than Virchow2, and consumes 0.36 kWh per 3,000 slides, 171x lower than Virchow2 on an RTX3090 GPU. We validated accuracy using 37 cohorts across four organs and 26 tasks (26 internal, 9 external, and 2 prospective), comprising 15,672 slides from 9,808 patients disjoint from the pretraining data. LitePath ranks second among 19 evaluated models and outperforms larger models including H-Optimus-1, mSTAR, UNI2 and GPFM, while retaining 99.71% of the AUC of Virchow2 on average. To quantify the balance between accuracy and efficiency, we propose the Deployability Score (D-Score), defined as the weighted geometric mean of normalized AUC and normalized FLOP, where LitePath achieves the highest value, surpassing Virchow2 by 10.64%. These results demonstrate that LitePath enables rapid, cost-effective and energy-efficient pathology image analysis on accessible hardware while maintaining accuracy comparable to state-of-the-art PFMs and reducing the carbon footprint of AI deployment.
Fundamental Reasoning Paradigms Induce Out-of-Domain Generalization in Language Models
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Deduction, induction, and abduction are fundamental reasoning paradigms, core for human logical thinking. Although improving Large Language Model (LLM) reasoning has attracted significant research efforts, the extent to which the fundamental paradigms induce generalization has yet to be systematically explored. In this study, we shed light on how the interplay between these core paradigms influences LLMs' reasoning behavior. To this end, we first collect a new dataset of reasoning trajectories from symbolic tasks, each targeting one of the three fundamental paradigms, to abstract from concrete world knowledge. Then, we investigate effective ways for inducing these skills into LLMs. We experiment with a battery of methods including simple fine-tuning, and more complex approaches to increase model depth, or transform a dense model to a mixture-of-experts. We comprehensively evaluate induced models on realistic out-of-domain tasks, that are entirely formulated in natural language and contain real-world knowledge. Our results reveal that our approach yields strong generalizability with substantial performance gains (up to $14.60$) across realistic tasks.
Conformal Thinking: Risk Control for Reasoning on a Compute Budget
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Reasoning Large Language Models (LLMs) enable test-time scaling, with dataset-level accuracy improving as the token budget increases, motivating adaptive reasoning -- spending tokens when they improve reliability and stopping early when additional computation is unlikely to help. However, setting the token budget, as well as the threshold for adaptive reasoning, is a practical challenge that entails a fundamental risk-accuracy trade-off. We re-frame the budget setting problem as risk control, limiting the error rate while minimizing compute. Our framework introduces an upper threshold that stops reasoning when the model is confident (risking incorrect output) and a novel parametric lower threshold that preemptively stops unsolvable instances (risking premature stoppage). Given a target risk and a validation set, we use distribution-free risk control to optimally specify these stopping mechanisms. For scenarios with multiple budget controlling criteria, we incorporate an efficiency loss to select the most computationally efficient exiting mechanism. Empirical results across diverse reasoning tasks and models demonstrate the effectiveness of our risk control approach, demonstrating computational efficiency gains from the lower threshold and ensemble stopping mechanisms while adhering to the user-specified risk target.
JPU: Bridging Jailbreak Defense and Unlearning via On-Policy Path Rectification
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Despite extensive safety alignment, Large Language Models (LLMs) often fail against jailbreak attacks. While machine unlearning has emerged as a promising defense by erasing specific harmful parameters, current methods remain vulnerable to diverse jailbreaks. We first conduct an empirical study and discover that this failure mechanism is caused by jailbreaks primarily activating non-erased parameters in the intermediate layers. Further, by probing the underlying mechanism through which these circumvented parameters reassemble into the prohibited output, we verify the persistent existence of dynamic $\textbf{jailbreak paths}$ and show that the inability to rectify them constitutes the fundamental gap in existing unlearning defenses. To bridge this gap, we propose $\textbf{J}$ailbreak $\textbf{P}$ath $\textbf{U}$nlearning (JPU), which is the first to rectify dynamic jailbreak paths towards safety anchors by dynamically mining on-policy adversarial samples to expose vulnerabilities and identify jailbreak paths. Extensive experiments demonstrate that JPU significantly enhances jailbreak resistance against dynamic attacks while preserving the model's utility.
RxnBench: A Multimodal Benchmark for Evaluating Large Language Models on Chemical Reaction Understanding from Scientific Literature
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:The integration of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) into chemistry promises to revolutionize scientific discovery, yet their ability to comprehend the dense, graphical language of reactions within authentic literature remains underexplored. Here, we introduce RxnBench, a multi-tiered benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate MLLMs on chemical reaction understanding from scientific PDFs. RxnBench comprises two tasks: Single-Figure QA (SF-QA), which tests fine-grained visual perception and mechanistic reasoning using 1,525 questions derived from 305 curated reaction schemes, and Full-Document QA (FD-QA), which challenges models to synthesize information from 108 articles, requiring cross-modal integration of text, schemes, and tables. Our evaluation of MLLMs reveals a critical capability gap: while models excel at extracting explicit text, they struggle with deep chemical logic and precise structural recognition. Notably, models with inference-time reasoning significantly outperform standard architectures, yet none achieve 50\% accuracy on FD-QA. These findings underscore the urgent need for domain-specific visual encoders and stronger reasoning engines to advance autonomous AI chemists.
Multi-Agent Intelligence for Multidisciplinary Decision-Making in Gastrointestinal Oncology
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Multimodal clinical reasoning in the field of gastrointestinal (GI) oncology necessitates the integrated interpretation of endoscopic imagery, radiological data, and biochemical markers. Despite the evident potential exhibited by Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), they frequently encounter challenges such as context dilution and hallucination when confronted with intricate, heterogeneous medical histories. In order to address these limitations, a hierarchical Multi-Agent Framework is proposed, which emulates the collaborative workflow of a human Multidisciplinary Team (MDT). The system attained a composite expert evaluation score of 4.60/5.00, thereby demonstrating a substantial improvement over the monolithic baseline. It is noteworthy that the agent-based architecture yielded the most substantial enhancements in reasoning logic and medical accuracy. The findings indicate that mimetic, agent-based collaboration provides a scalable, interpretable, and clinically robust paradigm for automated decision support in oncology.
Untethered thin dielectric elastomer actuated soft robot
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Thin dielectric elastomer actuator (DEA) features a unique in-plane configuration, enabling low-profile designs capable of accessing millimetre-scale narrow spaces. However, most existing DEA-powered soft robots require high voltages and wired power connections, limiting their ability to operate in confined environments. This study presents an untethered thin soft robot (UTS-Robot) powered by thin dielectric elastomer actuators (TS-DEA). The robot measures 38 mm in length, 6 mm in height, and weighs just 2.34 grams, integrating flexible onboard electronics to achieve fully untethered actuation. The TS-DEA, operating at resonant frequencies of 86 Hz under a low driving voltage of 220 V, adopts a dual-actuation sandwiched structure, comprising four dielectric elastomer layers bonded to a compressible tensioning mechanism at its core. This design enables high power density actuation and locomotion via three directional friction pads. The low-voltage actuation is achieved by fabricating each elastomer layer via spin coating to an initial thickness of 50 um, followed by biaxial stretching to 8 um. A comprehensive design and modelling framework has been developed to optimise TS-DEA performance. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that the bare TS-DEA achieves a locomotion speed of 12.36 mm/s at resonance, the untethered configuration achieves a locomotion speed of 0.5 mm/s, making it highly suitable for navigating confined and complex environments.
Autonomous Vehicle Path Planning by Searching With Differentiable Simulation
Nov 14, 2025



Abstract:Planning allows an agent to safely refine its actions before executing them in the real world. In autonomous driving, this is crucial to avoid collisions and navigate in complex, dense traffic scenarios. One way to plan is to search for the best action sequence. However, this is challenging when all necessary components - policy, next-state predictor, and critic - have to be learned. Here we propose Differentiable Simulation for Search (DSS), a framework that leverages the differentiable simulator Waymax as both a next state predictor and a critic. It relies on the simulator's hardcoded dynamics, making state predictions highly accurate, while utilizing the simulator's differentiability to effectively search across action sequences. Our DSS agent optimizes its actions using gradient descent over imagined future trajectories. We show experimentally that DSS - the combination of planning gradients and stochastic search - significantly improves tracking and path planning accuracy compared to sequence prediction, imitation learning, model-free RL, and other planning methods.
Self-Correcting Large Language Models: Generation vs. Multiple Choice
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Large language models have recently demonstrated remarkable abilities to self-correct their responses through iterative refinement, often referred to as self-consistency or self-reflection. However, the dynamics of this self-correction mechanism may differ substantially depending on whether the model is tasked with open-ended text generation or with selecting the most appropriate response from multiple predefined options. In this paper, we conduct a systematic investigation of these two paradigms by comparing performance trends and error-correction behaviors across various natural language understanding and reasoning tasks, covering language models of different scales and families. Our experimental results reveal distinct patterns of improvement and failure modes: \textit{While open-ended generation often benefits from the flexibility of re-interpretation and compositional refinement, multiple-choice selection can leverage clearer solution boundaries but may be limited by the provided options}. This contrast also reflects the dual demands faced by emerging agentic LLM applications: effective agents must not only generate and refine open-ended plans or explanations, but also make reliable discrete choices when operating within constrained action spaces. Our findings, therefore, highlight that the design of self-correction mechanisms should take into account the interaction between task structure and output space, with implications for both knowledge-intensive reasoning and decision-oriented applications of LLMs.
Queries Are Not Alone: Clustering Text Embeddings for Video Search
Oct 09, 2025
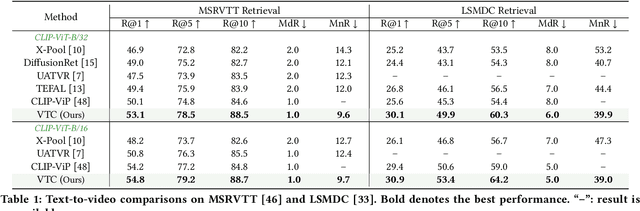
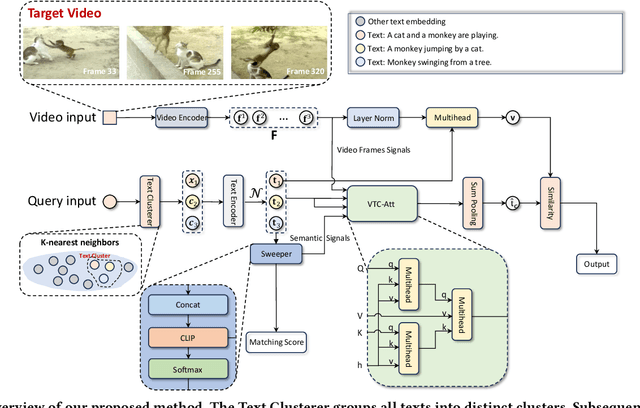
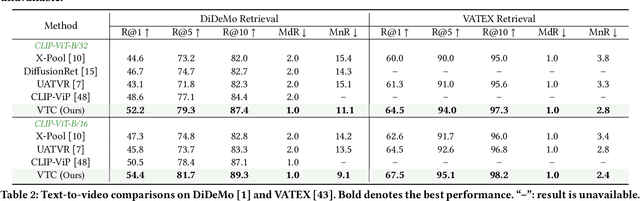
Abstract:The rapid proliferation of video content across various platforms has highlighted the urgent need for advanced video retrieval systems. Traditional methods, which primarily depend on directly matching textual queries with video metadata, often fail to bridge the semantic gap between text descriptions and the multifaceted nature of video content. This paper introduces a novel framework, the Video-Text Cluster (VTC), which enhances video retrieval by clustering text queries to capture a broader semantic scope. We propose a unique clustering mechanism that groups related queries, enabling our system to consider multiple interpretations and nuances of each query. This clustering is further refined by our innovative Sweeper module, which identifies and mitigates noise within these clusters. Additionally, we introduce the Video-Text Cluster-Attention (VTC-Att) mechanism, which dynamically adjusts focus within the clusters based on the video content, ensuring that the retrieval process emphasizes the most relevant textual features. Further experiments have demonstrated that our proposed model surpasses existing state-of-the-art models on five public datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge