Yanning Zhou
StdGEN++: A Comprehensive System for Semantic-Decomposed 3D Character Generation
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:We present StdGEN++, a novel and comprehensive system for generating high-fidelity, semantically decomposed 3D characters from diverse inputs. Existing 3D generative methods often produce monolithic meshes that lack the structural flexibility required by industrial pipelines in gaming and animation. Addressing this gap, StdGEN++ is built upon a Dual-branch Semantic-aware Large Reconstruction Model (Dual-Branch S-LRM), which jointly reconstructs geometry, color, and per-component semantics in a feed-forward manner. To achieve production-level fidelity, we introduce a novel semantic surface extraction formalism compatible with hybrid implicit fields. This mechanism is accelerated by a coarse-to-fine proposal scheme, which significantly reduces memory footprint and enables high-resolution mesh generation. Furthermore, we propose a video-diffusion-based texture decomposition module that disentangles appearance into editable layers (e.g., separated iris and skin), resolving semantic confusion in facial regions. Experiments demonstrate that StdGEN++ achieves state-of-the-art performance, significantly outperforming existing methods in geometric accuracy and semantic disentanglement. Crucially, the resulting structural independence unlocks advanced downstream capabilities, including non-destructive editing, physics-compliant animation, and gaze tracking, making it a robust solution for automated character asset production.
OmniX: From Unified Panoramic Generation and Perception to Graphics-Ready 3D Scenes
Oct 30, 2025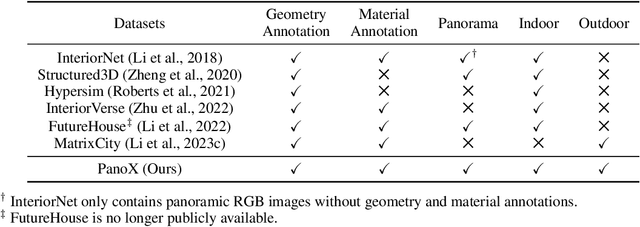
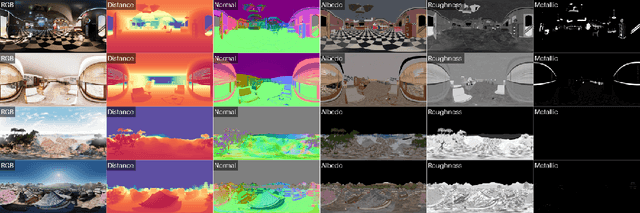
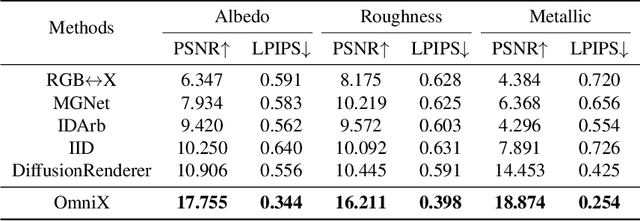
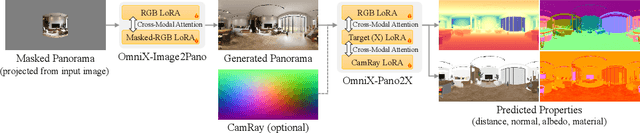
Abstract:There are two prevalent ways to constructing 3D scenes: procedural generation and 2D lifting. Among them, panorama-based 2D lifting has emerged as a promising technique, leveraging powerful 2D generative priors to produce immersive, realistic, and diverse 3D environments. In this work, we advance this technique to generate graphics-ready 3D scenes suitable for physically based rendering (PBR), relighting, and simulation. Our key insight is to repurpose 2D generative models for panoramic perception of geometry, textures, and PBR materials. Unlike existing 2D lifting approaches that emphasize appearance generation and ignore the perception of intrinsic properties, we present OmniX, a versatile and unified framework. Based on a lightweight and efficient cross-modal adapter structure, OmniX reuses 2D generative priors for a broad range of panoramic vision tasks, including panoramic perception, generation, and completion. Furthermore, we construct a large-scale synthetic panorama dataset containing high-quality multimodal panoramas from diverse indoor and outdoor scenes. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our model in panoramic visual perception and graphics-ready 3D scene generation, opening new possibilities for immersive and physically realistic virtual world generation.
Segment Anything in Pathology Images with Natural Language
Jun 26, 2025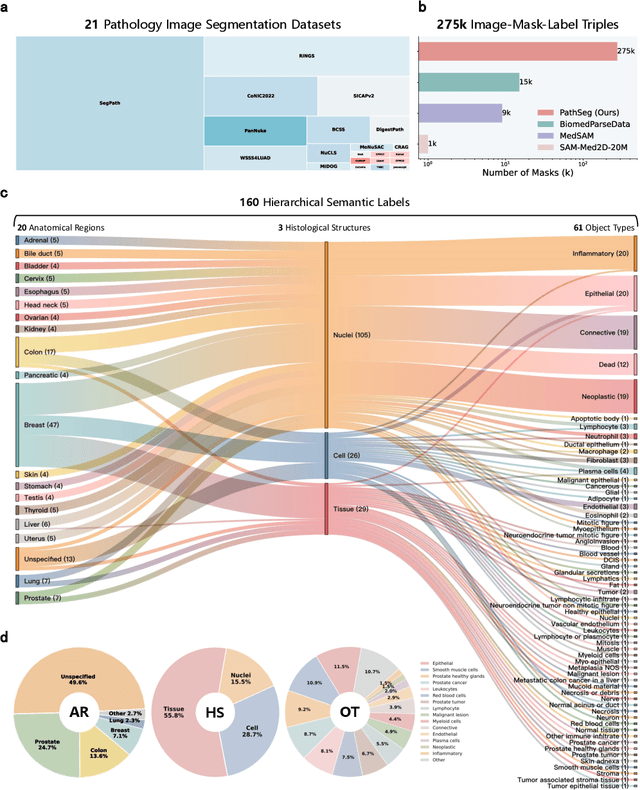
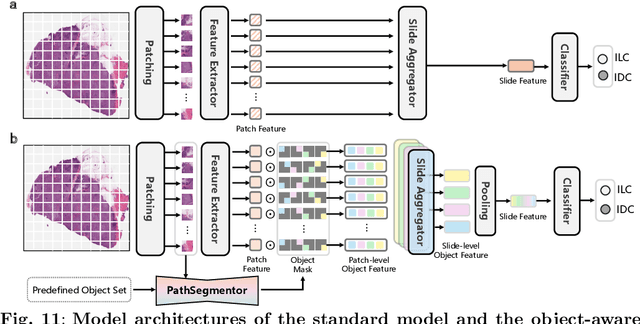
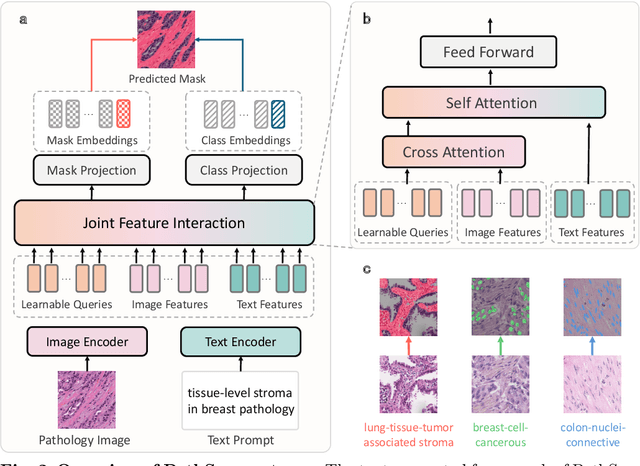
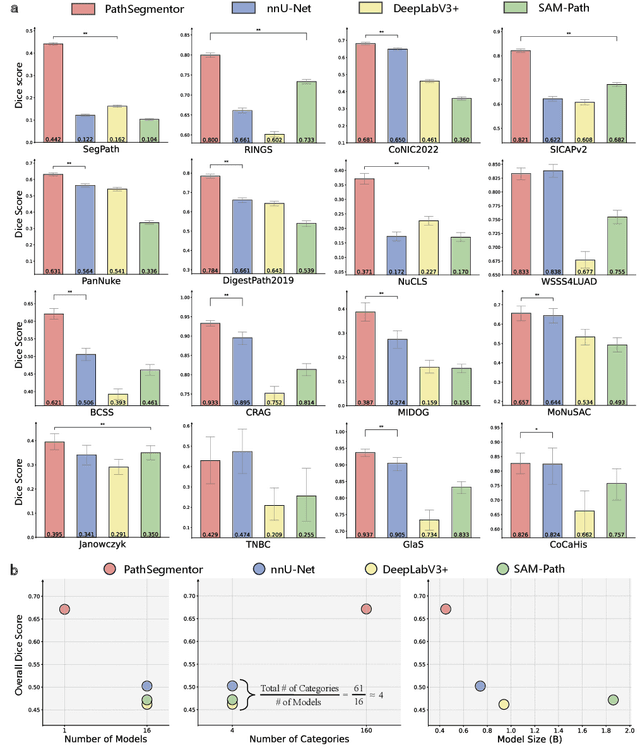
Abstract:Pathology image segmentation is crucial in computational pathology for analyzing histological features relevant to cancer diagnosis and prognosis. However, current methods face major challenges in clinical applications due to limited annotated data and restricted category definitions. To address these limitations, we propose PathSegmentor, the first text-prompted segmentation foundation model designed specifically for pathology images. We also introduce PathSeg , the largest and most comprehensive dataset for pathology segmentation, built from 17 public sources and containing 275k image-mask-label triples across 160 diverse categories. With PathSegmentor, users can perform semantic segmentation using natural language prompts, eliminating the need for laborious spatial inputs such as points or boxes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PathSegmentor outperforms specialized models with higher accuracy and broader applicability, while maintaining a compact architecture. It significantly surpasses existing spatial- and text-prompted models by 0.145 and 0.429 in overall Dice scores, respectively, showing strong robustness in segmenting complex structures and generalizing to external datasets. Moreover, PathSegmentor's outputs enhance the interpretability of diagnostic models through feature importance estimation and imaging biomarker discovery, offering pathologists evidence-based support for clinical decision-making. This work advances the development of explainable AI in precision oncology.
PrimitiveAnything: Human-Crafted 3D Primitive Assembly Generation with Auto-Regressive Transformer
May 07, 2025
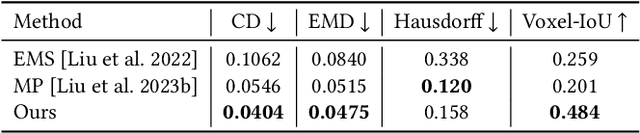
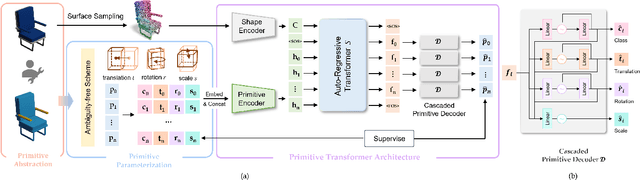
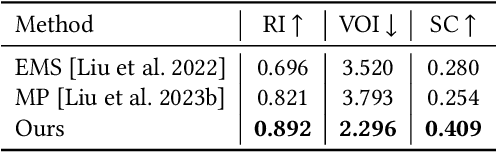
Abstract:Shape primitive abstraction, which decomposes complex 3D shapes into simple geometric elements, plays a crucial role in human visual cognition and has broad applications in computer vision and graphics. While recent advances in 3D content generation have shown remarkable progress, existing primitive abstraction methods either rely on geometric optimization with limited semantic understanding or learn from small-scale, category-specific datasets, struggling to generalize across diverse shape categories. We present PrimitiveAnything, a novel framework that reformulates shape primitive abstraction as a primitive assembly generation task. PrimitiveAnything includes a shape-conditioned primitive transformer for auto-regressive generation and an ambiguity-free parameterization scheme to represent multiple types of primitives in a unified manner. The proposed framework directly learns the process of primitive assembly from large-scale human-crafted abstractions, enabling it to capture how humans decompose complex shapes into primitive elements. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that PrimitiveAnything can generate high-quality primitive assemblies that better align with human perception while maintaining geometric fidelity across diverse shape categories. It benefits various 3D applications and shows potential for enabling primitive-based user-generated content (UGC) in games. Project page: https://primitiveanything.github.io
FlexIP: Dynamic Control of Preservation and Personality for Customized Image Generation
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:With the rapid advancement of 2D generative models, preserving subject identity while enabling diverse editing has emerged as a critical research focus. Existing methods typically face inherent trade-offs between identity preservation and personalized manipulation. We introduce FlexIP, a novel framework that decouples these objectives through two dedicated components: a Personalization Adapter for stylistic manipulation and a Preservation Adapter for identity maintenance. By explicitly injecting both control mechanisms into the generative model, our framework enables flexible parameterized control during inference through dynamic tuning of the weight adapter. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach breaks through the performance limitations of conventional methods, achieving superior identity preservation while supporting more diverse personalized generation capabilities (Project Page: https://flexip-tech.github.io/flexip/).
FreeTumor: Large-Scale Generative Tumor Synthesis in Computed Tomography Images for Improving Tumor Recognition
Feb 23, 2025Abstract:Tumor is a leading cause of death worldwide, with an estimated 10 million deaths attributed to tumor-related diseases every year. AI-driven tumor recognition unlocks new possibilities for more precise and intelligent tumor screening and diagnosis. However, the progress is heavily hampered by the scarcity of annotated datasets, which demands extensive annotation efforts by radiologists. To tackle this challenge, we introduce FreeTumor, an innovative Generative AI (GAI) framework to enable large-scale tumor synthesis for mitigating data scarcity. Specifically, FreeTumor effectively leverages a combination of limited labeled data and large-scale unlabeled data for tumor synthesis training. Unleashing the power of large-scale data, FreeTumor is capable of synthesizing a large number of realistic tumors on images for augmenting training datasets. To this end, we create the largest training dataset for tumor synthesis and recognition by curating 161,310 publicly available Computed Tomography (CT) volumes from 33 sources, with only 2.3% containing annotated tumors. To validate the fidelity of synthetic tumors, we engaged 13 board-certified radiologists in a Visual Turing Test to discern between synthetic and real tumors. Rigorous clinician evaluation validates the high quality of our synthetic tumors, as they achieved only 51.1% sensitivity and 60.8% accuracy in distinguishing our synthetic tumors from real ones. Through high-quality tumor synthesis, FreeTumor scales up the recognition training datasets by over 40 times, showcasing a notable superiority over state-of-the-art AI methods including various synthesis methods and foundation models. These findings indicate promising prospects of FreeTumor in clinical applications, potentially advancing tumor treatments and improving the survival rates of patients.
StdGEN: Semantic-Decomposed 3D Character Generation from Single Images
Nov 08, 2024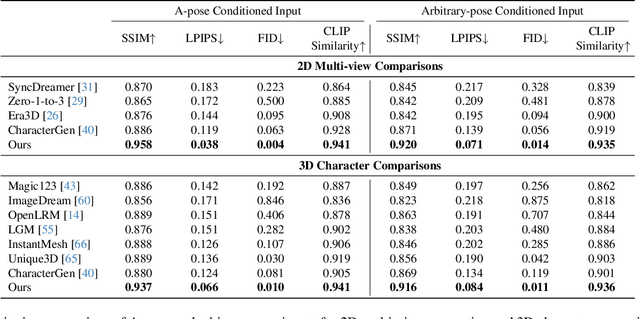
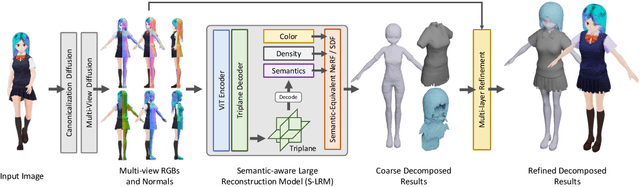
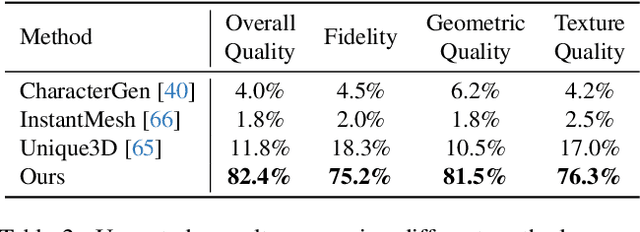
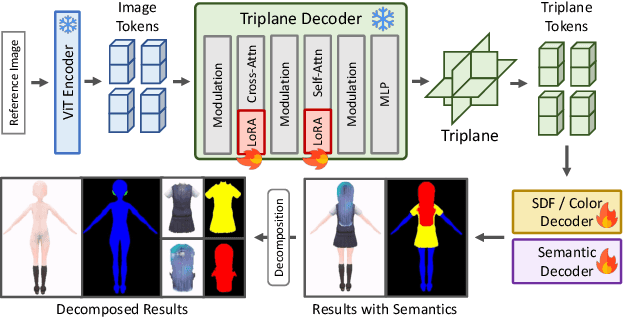
Abstract:We present StdGEN, an innovative pipeline for generating semantically decomposed high-quality 3D characters from single images, enabling broad applications in virtual reality, gaming, and filmmaking, etc. Unlike previous methods which struggle with limited decomposability, unsatisfactory quality, and long optimization times, StdGEN features decomposability, effectiveness and efficiency; i.e., it generates intricately detailed 3D characters with separated semantic components such as the body, clothes, and hair, in three minutes. At the core of StdGEN is our proposed Semantic-aware Large Reconstruction Model (S-LRM), a transformer-based generalizable model that jointly reconstructs geometry, color and semantics from multi-view images in a feed-forward manner. A differentiable multi-layer semantic surface extraction scheme is introduced to acquire meshes from hybrid implicit fields reconstructed by our S-LRM. Additionally, a specialized efficient multi-view diffusion model and an iterative multi-layer surface refinement module are integrated into the pipeline to facilitate high-quality, decomposable 3D character generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate our state-of-the-art performance in 3D anime character generation, surpassing existing baselines by a significant margin in geometry, texture and decomposability. StdGEN offers ready-to-use semantic-decomposed 3D characters and enables flexible customization for a wide range of applications. Project page: https://stdgen.github.io
Holistic and Historical Instance Comparison for Cervical Cell Detection
Sep 21, 2024



Abstract:Cytology screening from Papanicolaou (Pap) smears is a common and effective tool for the preventive clinical management of cervical cancer, where abnormal cell detection from whole slide images serves as the foundation for reporting cervical cytology. However, cervical cell detection remains challenging due to 1) hazily-defined cell types (e.g., ASC-US) with subtle morphological discrepancies caused by the dynamic cancerization process, i.e., cell class ambiguity, and 2) imbalanced class distributions of clinical data may cause missed detection, especially for minor categories, i.e., cell class imbalance. To this end, we propose a holistic and historical instance comparison approach for cervical cell detection. Specifically, we first develop a holistic instance comparison scheme enforcing both RoI-level and class-level cell discrimination. This coarse-to-fine cell comparison encourages the model to learn foreground-distinguishable and class-wise representations. To emphatically improve the distinguishability of minor classes, we then introduce a historical instance comparison scheme with a confident sample selection-based memory bank, which involves comparing current embeddings with historical embeddings for better cell instance discrimination. Extensive experiments and analysis on two large-scale cytology datasets including 42,592 and 114,513 cervical cells demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. The code is available at https://github.com/hjiangaz/HERO.
GAInS: Gradient Anomaly-aware Biomedical Instance Segmentation
Sep 21, 2024



Abstract:Instance segmentation plays a vital role in the morphological quantification of biomedical entities such as tissues and cells, enabling precise identification and delineation of different structures. Current methods often address the challenges of touching, overlapping or crossing instances through individual modeling, while neglecting the intrinsic interrelation between these conditions. In this work, we propose a Gradient Anomaly-aware Biomedical Instance Segmentation approach (GAInS), which leverages instance gradient information to perceive local gradient anomaly regions, thus modeling the spatial relationship between instances and refining local region segmentation. Specifically, GAInS is firstly built on a Gradient Anomaly Mapping Module (GAMM), which encodes the radial fields of instances through window sliding to obtain instance gradient anomaly maps. To efficiently refine boundaries and regions with gradient anomaly attention, we propose an Adaptive Local Refinement Module (ALRM) with a gradient anomaly-aware loss function. Extensive comparisons and ablation experiments in three biomedical scenarios demonstrate that our proposed GAInS outperforms other state-of-the-art (SOTA) instance segmentation methods. The code is available at https://github.com/DeepGAInS/GAInS.
DoNet: Deep De-overlapping Network for Cytology Instance Segmentation
Mar 25, 2023



Abstract:Cell instance segmentation in cytology images has significant importance for biology analysis and cancer screening, while remains challenging due to 1) the extensive overlapping translucent cell clusters that cause the ambiguous boundaries, and 2) the confusion of mimics and debris as nuclei. In this work, we proposed a De-overlapping Network (DoNet) in a decompose-and-recombined strategy. A Dual-path Region Segmentation Module (DRM) explicitly decomposes the cell clusters into intersection and complement regions, followed by a Semantic Consistency-guided Recombination Module (CRM) for integration. To further introduce the containment relationship of the nucleus in the cytoplasm, we design a Mask-guided Region Proposal Strategy (MRP) that integrates the cell attention maps for inner-cell instance prediction. We validate the proposed approach on ISBI2014 and CPS datasets. Experiments show that our proposed DoNet significantly outperforms other state-of-the-art (SOTA) cell instance segmentation methods. The code is available at https://github.com/DeepDoNet/DoNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge