Haonan Lin
DISCOVERSE: Efficient Robot Simulation in Complex High-Fidelity Environments
Jul 29, 2025Abstract:We present the first unified, modular, open-source 3DGS-based simulation framework for Real2Sim2Real robot learning. It features a holistic Real2Sim pipeline that synthesizes hyper-realistic geometry and appearance of complex real-world scenarios, paving the way for analyzing and bridging the Sim2Real gap. Powered by Gaussian Splatting and MuJoCo, Discoverse enables massively parallel simulation of multiple sensor modalities and accurate physics, with inclusive supports for existing 3D assets, robot models, and ROS plugins, empowering large-scale robot learning and complex robotic benchmarks. Through extensive experiments on imitation learning, Discoverse demonstrates state-of-the-art zero-shot Sim2Real transfer performance compared to existing simulators. For code and demos: https://air-discoverse.github.io/.
FlexIP: Dynamic Control of Preservation and Personality for Customized Image Generation
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:With the rapid advancement of 2D generative models, preserving subject identity while enabling diverse editing has emerged as a critical research focus. Existing methods typically face inherent trade-offs between identity preservation and personalized manipulation. We introduce FlexIP, a novel framework that decouples these objectives through two dedicated components: a Personalization Adapter for stylistic manipulation and a Preservation Adapter for identity maintenance. By explicitly injecting both control mechanisms into the generative model, our framework enables flexible parameterized control during inference through dynamic tuning of the weight adapter. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach breaks through the performance limitations of conventional methods, achieving superior identity preservation while supporting more diverse personalized generation capabilities (Project Page: https://flexip-tech.github.io/flexip/).
Unleashing the Potential of Model Bias for Generalized Category Discovery
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Generalized Category Discovery is a significant and complex task that aims to identify both known and undefined novel categories from a set of unlabeled data, leveraging another labeled dataset containing only known categories. The primary challenges stem from model bias induced by pre-training on only known categories and the lack of precise supervision for novel ones, leading to category bias towards known categories and category confusion among different novel categories, which hinders models' ability to identify novel categories effectively. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework named Self-Debiasing Calibration (SDC). Unlike prior methods that regard model bias towards known categories as an obstacle to novel category identification, SDC provides a novel insight into unleashing the potential of the bias to facilitate novel category learning. Specifically, the output of the biased model serves two key purposes. First, it provides an accurate modeling of category bias, which can be utilized to measure the degree of bias and debias the output of the current training model. Second, it offers valuable insights for distinguishing different novel categories by transferring knowledge between similar categories. Based on these insights, SDC dynamically adjusts the output logits of the current training model using the output of the biased model. This approach produces less biased logits to effectively address the issue of category bias towards known categories, and generates more accurate pseudo labels for unlabeled data, thereby mitigating category confusion for novel categories. Experiments on three benchmark datasets show that SDC outperforms SOTA methods, especially in the identification of novel categories. Our code and data are available at \url{https://github.com/Lackel/SDC}.
Schedule Your Edit: A Simple yet Effective Diffusion Noise Schedule for Image Editing
Oct 24, 2024



Abstract:Text-guided diffusion models have significantly advanced image editing, enabling high-quality and diverse modifications driven by text prompts. However, effective editing requires inverting the source image into a latent space, a process often hindered by prediction errors inherent in DDIM inversion. These errors accumulate during the diffusion process, resulting in inferior content preservation and edit fidelity, especially with conditional inputs. We address these challenges by investigating the primary contributors to error accumulation in DDIM inversion and identify the singularity problem in traditional noise schedules as a key issue. To resolve this, we introduce the Logistic Schedule, a novel noise schedule designed to eliminate singularities, improve inversion stability, and provide a better noise space for image editing. This schedule reduces noise prediction errors, enabling more faithful editing that preserves the original content of the source image. Our approach requires no additional retraining and is compatible with various existing editing methods. Experiments across eight editing tasks demonstrate the Logistic Schedule's superior performance in content preservation and edit fidelity compared to traditional noise schedules, highlighting its adaptability and effectiveness.
Flipped Classroom: Aligning Teacher Attention with Student in Generalized Category Discovery
Sep 29, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements have shown promise in applying traditional Semi-Supervised Learning strategies to the task of Generalized Category Discovery (GCD). Typically, this involves a teacher-student framework in which the teacher imparts knowledge to the student to classify categories, even in the absence of explicit labels. Nevertheless, GCD presents unique challenges, particularly the absence of priors for new classes, which can lead to the teacher's misguidance and unsynchronized learning with the student, culminating in suboptimal outcomes. In our work, we delve into why traditional teacher-student designs falter in open-world generalized category discovery as compared to their success in closed-world semi-supervised learning. We identify inconsistent pattern learning across attention layers as the crux of this issue and introduce FlipClass, a method that dynamically updates the teacher to align with the student's attention, instead of maintaining a static teacher reference. Our teacher-student attention alignment strategy refines the teacher's focus based on student feedback from an energy perspective, promoting consistent pattern recognition and synchronized learning across old and new classes. Extensive experiments on a spectrum of benchmarks affirm that FlipClass significantly surpasses contemporary GCD methods, establishing new standards for the field.
Self-Supervised Elimination of Non-Independent Noise in Hyperspectral Imaging
Sep 16, 2024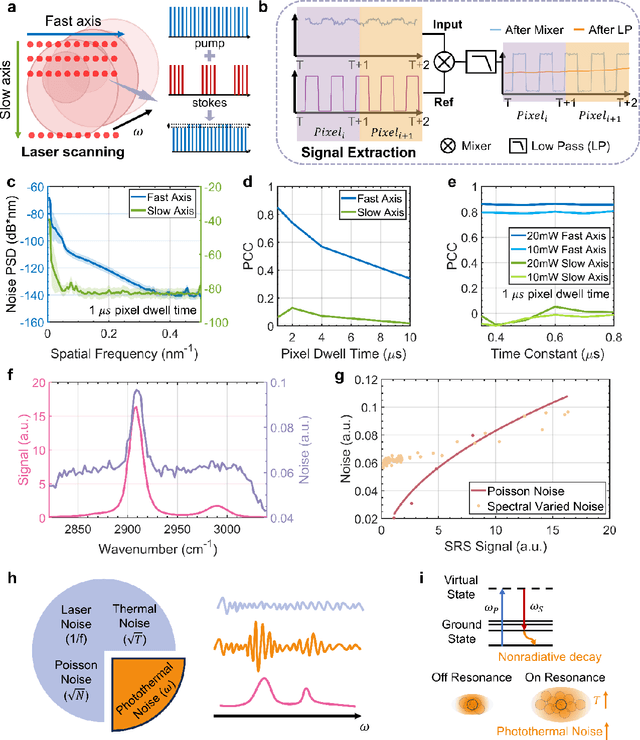
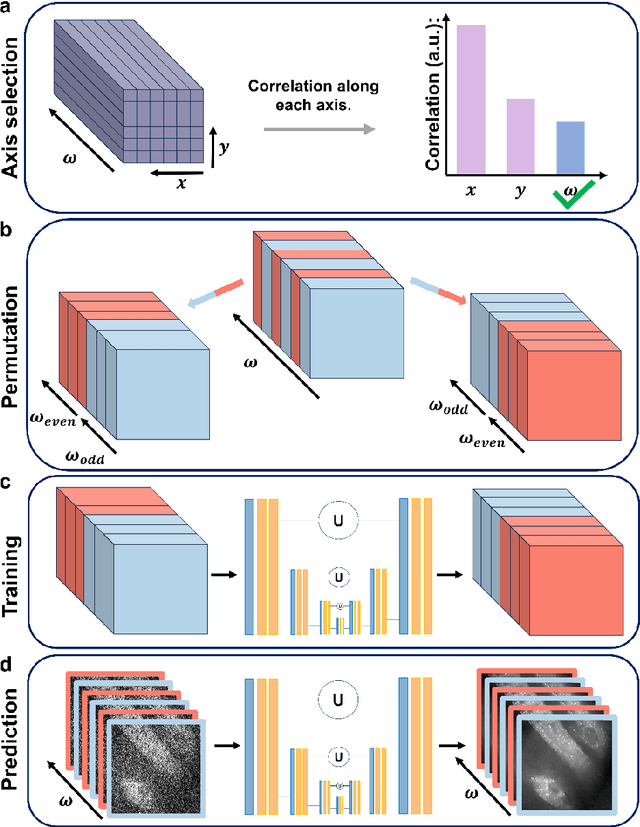
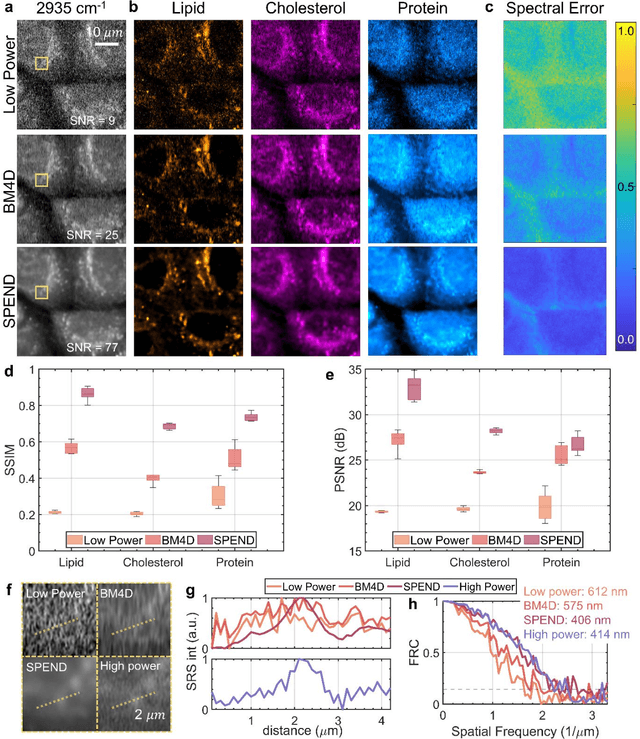
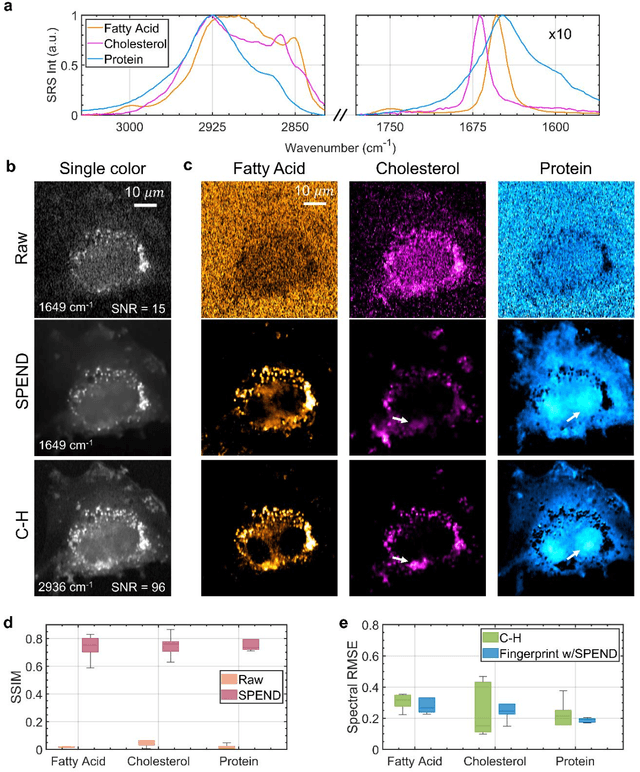
Abstract:Hyperspectral imaging has been widely used for spectral and spatial identification of target molecules, yet often contaminated by sophisticated noise. Current denoising methods generally rely on independent and identically distributed noise statistics, showing corrupted performance for non-independent noise removal. Here, we demonstrate Self-supervised PErmutation Noise2noise Denoising (SPEND), a deep learning denoising architecture tailor-made for removing non-independent noise from a single hyperspectral image stack. We utilize hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering and mid-infrared photothermal microscopy as the testbeds, where the noise is spatially correlated and spectrally varied. Based on single hyperspectral images, SPEND permutates odd and even spectral frames to generate two stacks with identical noise properties, and uses the pairs for efficient self-supervised noise-to-noise training. SPEND achieved an 8-fold signal-to-noise improvement without having access to the ground truth data. SPEND enabled accurate mapping of low concentration biomolecules in both fingerprint and silent regions, demonstrating its robustness in sophisticated cellular environments.
SpotActor: Training-Free Layout-Controlled Consistent Image Generation
Sep 07, 2024



Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models significantly enhance the efficiency of artistic creation with high-fidelity image generation. However, in typical application scenarios like comic book production, they can neither place each subject into its expected spot nor maintain the consistent appearance of each subject across images. For these issues, we pioneer a novel task, Layout-to-Consistent-Image (L2CI) generation, which produces consistent and compositional images in accordance with the given layout conditions and text prompts. To accomplish this challenging task, we present a new formalization of dual energy guidance with optimization in a dual semantic-latent space and thus propose a training-free pipeline, SpotActor, which features a layout-conditioned backward update stage and a consistent forward sampling stage. In the backward stage, we innovate a nuanced layout energy function to mimic the attention activations with a sigmoid-like objective. While in the forward stage, we design Regional Interconnection Self-Attention (RISA) and Semantic Fusion Cross-Attention (SFCA) mechanisms that allow mutual interactions across images. To evaluate the performance, we present ActorBench, a specified benchmark with hundreds of reasonable prompt-box pairs stemming from object detection datasets. Comprehensive experiments are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. The results prove that SpotActor fulfills the expectations of this task and showcases the potential for practical applications with superior layout alignment, subject consistency, prompt conformity and background diversity.
Knowledge Acquisition Disentanglement for Knowledge-based Visual Question Answering with Large Language Models
Jul 22, 2024



Abstract:Knowledge-based Visual Question Answering (KVQA) requires both image and world knowledge to answer questions. Current methods first retrieve knowledge from the image and external knowledge base with the original complex question, then generate answers with Large Language Models (LLMs). However, since the original question contains complex elements that require knowledge from different sources, acquiring different kinds of knowledge in a coupled manner may confuse models and hinder them from retrieving precise knowledge. Furthermore, the ``forward-only'' answering process fails to explicitly capture the knowledge needs of LLMs, which can further hurt answering quality. To cope with the above limitations, we propose DKA: Disentangled Knowledge Acquisition from LLM feedback, a training-free framework that disentangles knowledge acquisition to avoid confusion and uses LLM's feedback to specify the required knowledge. Specifically, DKA requires LLMs to specify what knowledge they need to answer the question and decompose the original complex question into two simple sub-questions: Image-based sub-question and Knowledge-based sub-question. Then we use the two sub-questions to retrieve knowledge from the image and knowledge base, respectively. In this way, two knowledge acquisition models can focus on the content that corresponds to them and avoid disturbance of irrelevant elements in the original complex question, which can help to provide more precise knowledge and better align the knowledge needs of LLMs to yield correct answers. Experiments on benchmark datasets show that DKA significantly outperforms SOTA models. To facilitate future research, our data and code are available at \url{https://github.com/Lackel/DKA}.
Timestep-Aware Correction for Quantized Diffusion Models
Jul 04, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models have marked a significant breakthrough in the synthesis of semantically coherent images. However, their extensive noise estimation networks and the iterative generation process limit their wider application, particularly on resource-constrained platforms like mobile devices. Existing post-training quantization (PTQ) methods have managed to compress diffusion models to low precision. Nevertheless, due to the iterative nature of diffusion models, quantization errors tend to accumulate throughout the generation process. This accumulation of error becomes particularly problematic in low-precision scenarios, leading to significant distortions in the generated images. We attribute this accumulation issue to two main causes: error propagation and exposure bias. To address these problems, we propose a timestep-aware correction method for quantized diffusion model, which dynamically corrects the quantization error. By leveraging the proposed method in low-precision diffusion models, substantial enhancement of output quality could be achieved with only negligible computation overhead. Extensive experiments underscore our method's effectiveness and generalizability. By employing the proposed correction strategy, we achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on low-precision models.
AGLA: Mitigating Object Hallucinations in Large Vision-Language Models with Assembly of Global and Local Attention
Jun 18, 2024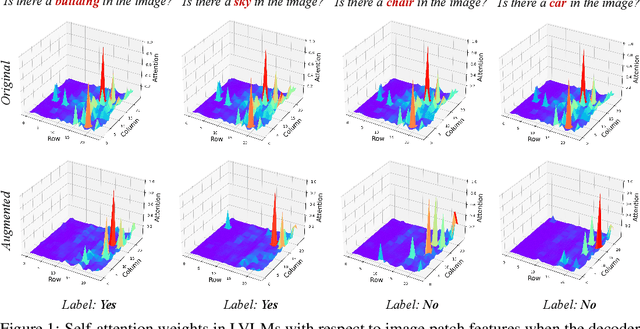
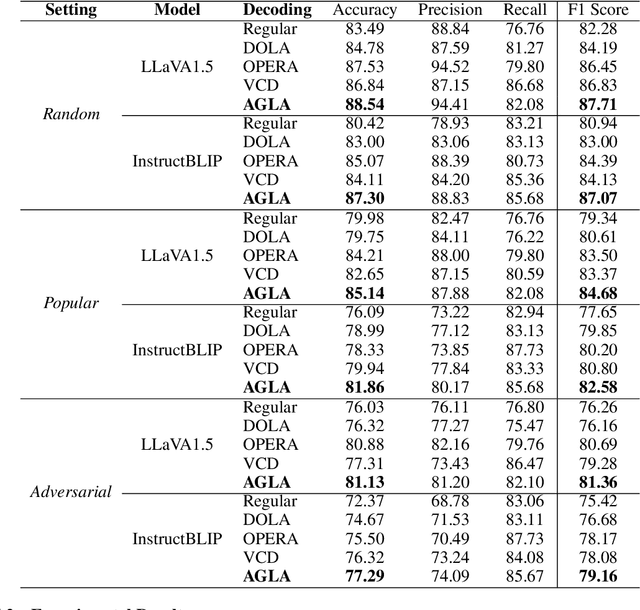
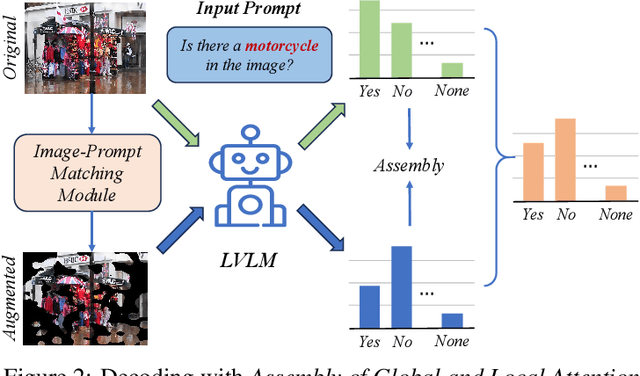
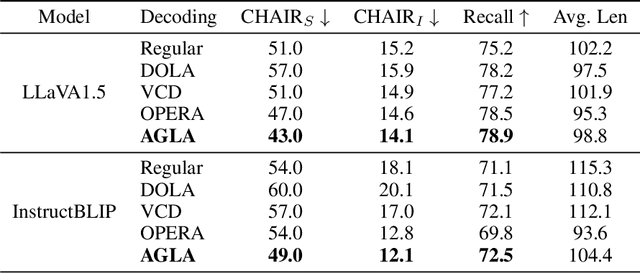
Abstract:Despite their great success across various multimodal tasks, Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) are facing a prevalent problem with object hallucinations, where the generated textual responses are inconsistent with ground-truth objects in the given image. This paper investigates various LVLMs and pinpoints attention deficiency toward discriminative local image features as one root cause of object hallucinations. Specifically, LVLMs predominantly attend to prompt-independent global image features, while failing to capture prompt-relevant local features, consequently undermining the visual grounding capacity of LVLMs and leading to hallucinations. To this end, we propose Assembly of Global and Local Attention (AGLA), a training-free and plug-and-play approach that mitigates object hallucinations by exploring an ensemble of global features for response generation and local features for visual discrimination simultaneously. Our approach exhibits an image-prompt matching scheme that captures prompt-relevant local features from images, leading to an augmented view of the input image where prompt-relevant content is reserved while irrelevant distractions are masked. With the augmented view, a calibrated decoding distribution can be derived by integrating generative global features from the original image and discriminative local features from the augmented image. Extensive experiments show that AGLA consistently mitigates object hallucinations and enhances general perception capability for LVLMs across various discriminative and generative benchmarks. Our code will be released at https://github.com/Lackel/AGLA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge