Ping Chen
APEX: A Decoupled Memory-based Explorer for Asynchronous Aerial Object Goal Navigation
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Aerial Object Goal Navigation, a challenging frontier in Embodied AI, requires an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) agent to autonomously explore, reason, and identify a specific target using only visual perception and language description. However, existing methods struggle with the memorization of complex spatial representations in aerial environments, reliable and interpretable action decision-making, and inefficient exploration and information gathering. To address these challenges, we introduce \textbf{APEX} (Aerial Parallel Explorer), a novel hierarchical agent designed for efficient exploration and target acquisition in complex aerial settings. APEX is built upon a modular, three-part architecture: 1) Dynamic Spatio-Semantic Mapping Memory, which leverages the zero-shot capability of a Vision-Language Model (VLM) to dynamically construct high-resolution 3D Attraction, Exploration, and Obstacle maps, serving as an interpretable memory mechanism. 2) Action Decision Module, trained with reinforcement learning, which translates this rich spatial understanding into a fine-grained and robust control policy. 3) Target Grounding Module, which employs an open-vocabulary detector to achieve definitive and generalizable target identification. All these components are integrated into a hierarchical, asynchronous, and parallel framework, effectively bypassing the VLM's inference latency and boosting the agent's proactivity in exploration. Extensive experiments show that APEX outperforms the previous state of the art by +4.2\% SR and +2.8\% SPL on challenging UAV-ON benchmarks, demonstrating its superior efficiency and the effectiveness of its hierarchical asynchronous design. Our source code is provided in \href{https://github.com/4amGodvzx/apex}{GitHub}
Vision-Language Controlled Deep Unfolding for Joint Medical Image Restoration and Segmentation
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:We propose VL-DUN, a principled framework for joint All-in-One Medical Image Restoration and Segmentation (AiOMIRS) that bridges the gap between low-level signal recovery and high-level semantic understanding. While standard pipelines treat these tasks in isolation, our core insight is that they are fundamentally synergistic: restoration provides clean anatomical structures to improve segmentation, while semantic priors regularize the restoration process. VL-DUN resolves the sub-optimality of sequential processing through two primary innovations. (1) We formulate AiOMIRS as a unified optimization problem, deriving an interpretable joint unfolding mechanism where restoration and segmentation are mathematically coupled for mutual refinement. (2) We introduce a frequency-aware Mamba mechanism to capture long-range dependencies for global segmentation while preserving the high-frequency textures necessary for restoration. This allows for efficient global context modeling with linear complexity, effectively mitigating the spectral bias of standard architectures. As a pioneering work in the AiOMIRS task, VL-DUN establishes a new state-of-the-art across multi-modal benchmarks, improving PSNR by 0.92 dB and the Dice coefficient by 9.76\%. Our results demonstrate that joint collaborative learning offers a superior, more robust solution for complex clinical workflows compared to isolated task processing. The codes are provided in https://github.com/cipi666/VLDUN.
MeanCache: From Instantaneous to Average Velocity for Accelerating Flow Matching Inference
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:We present MeanCache, a training-free caching framework for efficient Flow Matching inference. Existing caching methods reduce redundant computation but typically rely on instantaneous velocity information (e.g., feature caching), which often leads to severe trajectory deviations and error accumulation under high acceleration ratios. MeanCache introduces an average-velocity perspective: by leveraging cached Jacobian--vector products (JVP) to construct interval average velocities from instantaneous velocities, it effectively mitigates local error accumulation. To further improve cache timing and JVP reuse stability, we develop a trajectory-stability scheduling strategy as a practical tool, employing a Peak-Suppressed Shortest Path under budget constraints to determine the schedule. Experiments on FLUX.1, Qwen-Image, and HunyuanVideo demonstrate that MeanCache achieves 4.12X and 4.56X and 3.59X acceleration, respectively, while consistently outperforming state-of-the-art caching baselines in generation quality. We believe this simple yet effective approach provides a new perspective for Flow Matching inference and will inspire further exploration of stability-driven acceleration in commercial-scale generative models.
MARO: Learning Stronger Reasoning from Social Interaction
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Humans face countless scenarios that require reasoning and judgment in daily life. However, existing large language model training methods primarily allow models to learn from existing textual content or solve predetermined problems, lacking experience in real scenarios involving interaction, negotiation, and competition with others. To address this, this paper proposes Multi-Agent Reward Optimization (MARO), a method that enables large language models (LLMs) to acquire stronger reasoning abilities by learning and practicing in multi-agent social environments. Specifically, MARO first addresses the sparse learning signal problem by decomposing final success or failure outcomes into each specific behavior during the interaction process; second, it handles the uneven role distribution problem by balancing the training sample weights of different roles; finally, it addresses environmental instability issues by directly evaluating the utility of each behavior. Experimental results demonstrate that MARO not only achieves significant improvements in social reasoning capabilities, but also that the abilities acquired through social simulation learning can effectively transfer to other tasks such as mathematical reasoning and instruction following. This reveals the tremendous potential of multi-agent social learning in enhancing the general reasoning capabilities of LLMs.
TCDE: Topic-Centric Dual Expansion of Queries and Documents with Large Language Models for Information Retrieval
Dec 19, 2025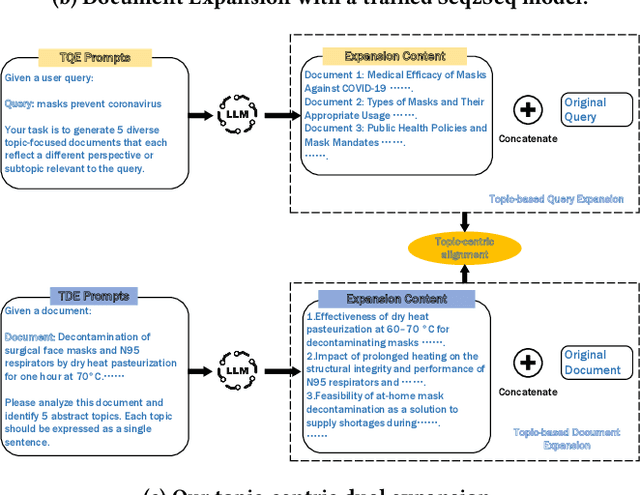

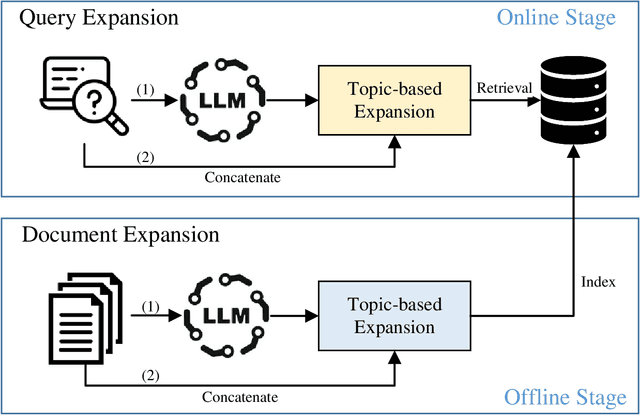

Abstract:Query Expansion (QE) enriches queries and Document Expansion (DE) enriches documents, and these two techniques are often applied separately. However, such separate application may lead to semantic misalignment between the expanded queries (or documents) and their relevant documents (or queries). To address this serious issue, we propose TCDE, a dual expansion strategy that leverages large language models (LLMs) for topic-centric enrichment on both queries and documents. In TCDE, we design two distinct prompt templates for processing each query and document. On the query side, an LLM is guided to identify distinct sub-topics within each query and generate a focused pseudo-document for each sub-topic. On the document side, an LLM is guided to distill each document into a set of core topic sentences. The resulting outputs are used to expand the original query and document. This topic-centric dual expansion process establishes semantic bridges between queries and their relevant documents, enabling better alignment for downstream retrieval models. Experiments on two challenging benchmarks, TREC Deep Learning and BEIR, demonstrate that TCDE achieves substantial improvements over strong state-of-the-art expansion baselines. In particular, on dense retrieval tasks, it outperforms several state-of-the-art methods, with a relative improvement of 2.8\% in NDCG@10 on the SciFact dataset. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of our topic-centric and dual expansion strategy.
HiMo-CLIP: Modeling Semantic Hierarchy and Monotonicity in Vision-Language Alignment
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Contrastive vision-language models like CLIP have achieved impressive results in image-text retrieval by aligning image and text representations in a shared embedding space. However, these models often treat text as flat sequences, limiting their ability to handle complex, compositional, and long-form descriptions. In particular, they fail to capture two essential properties of language: semantic hierarchy, which reflects the multi-level compositional structure of text, and semantic monotonicity, where richer descriptions should result in stronger alignment with visual content.To address these limitations, we propose HiMo-CLIP, a representation-level framework that enhances CLIP-style models without modifying the encoder architecture. HiMo-CLIP introduces two key components: a hierarchical decomposition (HiDe) module that extracts latent semantic components from long-form text via in-batch PCA, enabling flexible, batch-aware alignment across different semantic granularities, and a monotonicity-aware contrastive loss (MoLo) that jointly aligns global and component-level representations, encouraging the model to internalize semantic ordering and alignment strength as a function of textual completeness.These components work in concert to produce structured, cognitively-aligned cross-modal representations. Experiments on multiple image-text retrieval benchmarks show that HiMo-CLIP consistently outperforms strong baselines, particularly under long or compositional descriptions. The code is available at https://github.com/UnicomAI/HiMo-CLIP.
* Accepted by AAAI 2026 as an Oral Presentation (13 pages, 7 figures, 7 tables)
Fuzzy Reasoning Chain (FRC): An Innovative Reasoning Framework from Fuzziness to Clarity
Sep 26, 2025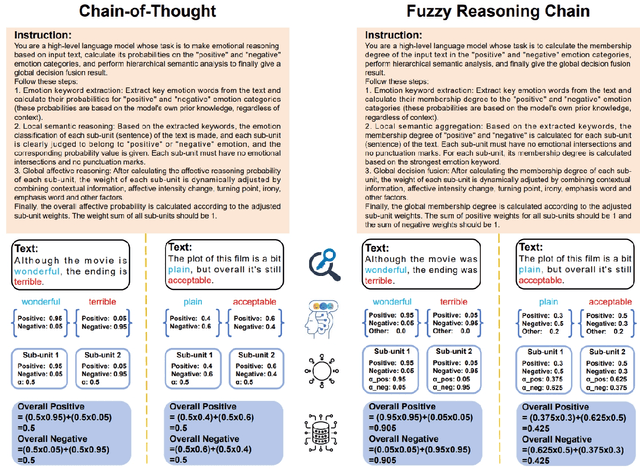
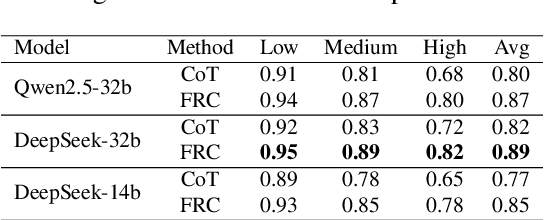
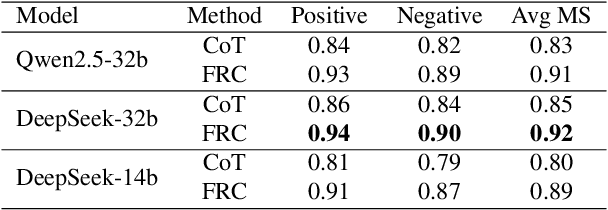
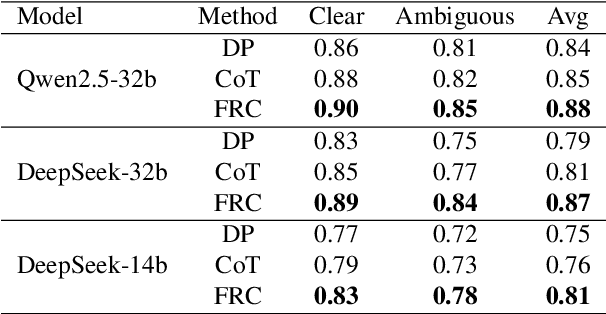
Abstract:With the rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs), natural language processing (NLP) has achieved remarkable progress. Nonetheless, significant challenges remain in handling texts with ambiguity, polysemy, or uncertainty. We introduce the Fuzzy Reasoning Chain (FRC) framework, which integrates LLM semantic priors with continuous fuzzy membership degrees, creating an explicit interaction between probability-based reasoning and fuzzy membership reasoning. This transition allows ambiguous inputs to be gradually transformed into clear and interpretable decisions while capturing conflicting or uncertain signals that traditional probability-based methods cannot. We validate FRC on sentiment analysis tasks, where both theoretical analysis and empirical results show that it ensures stable reasoning and facilitates knowledge transfer across different model scales. These findings indicate that FRC provides a general mechanism for managing subtle and ambiguous expressions with improved interpretability and robustness.
Hierarchical Deep Fusion Framework for Multi-dimensional Facial Forgery Detection -- The 2024 Global Deepfake Image Detection Challenge
Sep 16, 2025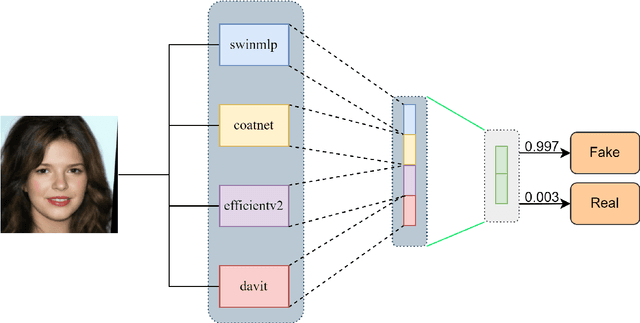
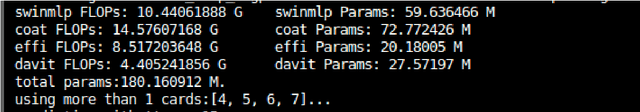
Abstract:The proliferation of sophisticated deepfake technology poses significant challenges to digital security and authenticity. Detecting these forgeries, especially across a wide spectrum of manipulation techniques, requires robust and generalized models. This paper introduces the Hierarchical Deep Fusion Framework (HDFF), an ensemble-based deep learning architecture designed for high-performance facial forgery detection. Our framework integrates four diverse pre-trained sub-models, Swin-MLP, CoAtNet, EfficientNetV2, and DaViT, which are meticulously fine-tuned through a multi-stage process on the MultiFFDI dataset. By concatenating the feature representations from these specialized models and training a final classifier layer, HDFF effectively leverages their collective strengths. This approach achieved a final score of 0.96852 on the competition's private leaderboard, securing the 20th position out of 184 teams, demonstrating the efficacy of hierarchical fusion for complex image classification tasks.
Adacc: Adaptive Compression and Activation Checkpointing for LLM Memory Management
Aug 01, 2025Abstract:Training large language models often employs recomputation to alleviate memory pressure, which can introduce up to 30% overhead in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we propose Adacc, a novel memory management framework that combines adaptive compression and activation checkpointing to reduce the GPU memory footprint. It comprises three modules: (1) We design layer-specific compression algorithms that account for outliers in LLM tensors, instead of directly quantizing floats from FP16 to INT4, to ensure model accuracy. (2) We propose an optimal scheduling policy that employs MILP to determine the best memory optimization for each tensor. (3) To accommodate changes in training tensors, we introduce an adaptive policy evolution mechanism that adjusts the policy during training to enhance throughput. Experimental results show that Adacc can accelerate the LLM training by 1.01x to 1.37x compared to state-of-the-art frameworks, while maintaining comparable model accuracy to the Baseline.
A Dataset and Toolkit for Multiparameter Cardiovascular Physiology Sensing on Rings
May 08, 2025



Abstract:Smart rings offer a convenient way to continuously and unobtrusively monitor cardiovascular physiological signals. However, a gap remains between the ring hardware and reliable methods for estimating cardiovascular parameters, partly due to the lack of publicly available datasets and standardized analysis tools. In this work, we present $\tau$-Ring, the first open-source ring-based dataset designed for cardiovascular physiological sensing. The dataset comprises photoplethysmography signals (infrared and red channels) and 3-axis accelerometer data collected from two rings (reflective and transmissive optical paths), with 28.21 hours of raw data from 34 subjects across seven activities. $\tau$-Ring encompasses both stationary and motion scenarios, as well as stimulus-evoked abnormal physiological states, annotated with four ground-truth labels: heart rate, respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, and blood pressure. Using our proposed RingTool toolkit, we evaluated three widely-used physics-based methods and four cutting-edge deep learning approaches. Our results show superior performance compared to commercial rings, achieving best MAE values of 5.18 BPM for heart rate, 2.98 BPM for respiratory rate, 3.22\% for oxygen saturation, and 13.33/7.56 mmHg for systolic/diastolic blood pressure estimation. The open-sourced dataset and toolkit aim to foster further research and community-driven advances in ring-based cardiovascular health sensing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge