Siwei Wang
Tsinghua University
Rising Multi-Armed Bandits with Known Horizons
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:The Rising Multi-Armed Bandit (RMAB) framework models environments where expected rewards of arms increase with plays, which models practical scenarios where performance of each option improves with the repeated usage, such as in robotics and hyperparameter tuning. For instance, in hyperparameter tuning, the validation accuracy of a model configuration (arm) typically increases with each training epoch. A defining characteristic of RMAB is em horizon-dependent optimality: unlike standard settings, the optimal strategy here shifts dramatically depending on the available budget $T$. This implies that knowledge of $T$ yields significantly greater utility in RMAB, empowering the learner to align its decision-making with this shifting optimality. However, the horizon-aware setting remains underexplored. To address this, we propose a novel CUmulative Reward Estimation UCB (CURE-UCB) that explicitly integrates the horizon. We provide a rigorous analysis establishing a new regret upper bound and prove that our method strictly outperforms horizon-agnostic strategies in structured environments like ``linear-then-flat'' instances. Extensive experiments demonstrate its significant superiority over baselines.
Trifuse: Enhancing Attention-Based GUI Grounding via Multimodal Fusion
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:GUI grounding maps natural language instructions to the correct interface elements, serving as the perception foundation for GUI agents. Existing approaches predominantly rely on fine-tuning multimodal large language models (MLLMs) using large-scale GUI datasets to predict target element coordinates, which is data-intensive and generalizes poorly to unseen interfaces. Recent attention-based alternatives exploit localization signals in MLLMs attention mechanisms without task-specific fine-tuning, but suffer from low reliability due to the lack of explicit and complementary spatial anchors in GUI images. To address this limitation, we propose Trifuse, an attention-based grounding framework that explicitly integrates complementary spatial anchors. Trifuse integrates attention, OCR-derived textual cues, and icon-level caption semantics via a Consensus-SinglePeak (CS) fusion strategy that enforces cross-modal agreement while retaining sharp localization peaks. Extensive evaluations on four grounding benchmarks demonstrate that Trifuse achieves strong performance without task-specific fine-tuning, substantially reducing the reliance on expensive annotated data. Moreover, ablation studies reveal that incorporating OCR and caption cues consistently improves attention-based grounding performance across different backbones, highlighting its effectiveness as a general framework for GUI grounding.
Beyond Parameter Finetuning: Test-Time Representation Refinement for Node Classification
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Graph Neural Networks frequently exhibit significant performance degradation in the out-of-distribution test scenario. While test-time training (TTT) offers a promising solution, existing Parameter Finetuning (PaFT) paradigm suffer from catastrophic forgetting, hindering their real-world applicability. We propose TTReFT, a novel Test-Time Representation FineTuning framework that transitions the adaptation target from model parameters to latent representations. Specifically, TTReFT achieves this through three key innovations: (1) uncertainty-guided node selection for specific interventions, (2) low-rank representation interventions that preserve pre-trained knowledge, and (3) an intervention-aware masked autoencoder that dynamically adjust masking strategy to accommodate the node selection scheme. Theoretically, we establish guarantees for TTReFT in OOD settings. Empirically, extensive experiments across five benchmark datasets demonstrate that TTReFT achieves consistent and superior performance. Our work establishes representation finetuning as a new paradigm for graph TTT, offering both theoretical grounding and immediate practical utility for real-world deployment.
Deep Temporal Graph Clustering: A Comprehensive Benchmark and Datasets
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Temporal Graph Clustering (TGC) is a new task with little attention, focusing on node clustering in temporal graphs. Compared with existing static graph clustering, it can find the balance between time requirement and space requirement (Time-Space Balance) through the interaction sequence-based batch-processing pattern. However, there are two major challenges that hinder the development of TGC, i.e., inapplicable clustering techniques and inapplicable datasets. To address these challenges, we propose a comprehensive benchmark, called BenchTGC. Specially, we design a BenchTGC Framework to illustrate the paradigm of temporal graph clustering and improve existing clustering techniques to fit temporal graphs. In addition, we also discuss problems with public temporal graph datasets and develop multiple datasets suitable for TGC task, called BenchTGC Datasets. According to extensive experiments, we not only verify the advantages of BenchTGC, but also demonstrate the necessity and importance of TGC task. We wish to point out that the dynamically changing and complex scenarios in real world are the foundation of temporal graph clustering. The code and data is available at: https://github.com/MGitHubL/BenchTGC.
Parameter-Free Clustering via Self-Supervised Consensus Maximization (Extended Version)
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Clustering is a fundamental task in unsupervised learning, but most existing methods heavily rely on hyperparameters such as the number of clusters or other sensitive settings, limiting their applicability in real-world scenarios. To address this long-standing challenge, we propose a novel and fully parameter-free clustering framework via Self-supervised Consensus Maximization, named SCMax. Our framework performs hierarchical agglomerative clustering and cluster evaluation in a single, integrated process. At each step of agglomeration, it creates a new, structure-aware data representation through a self-supervised learning task guided by the current clustering structure. We then introduce a nearest neighbor consensus score, which measures the agreement between the nearest neighbor-based merge decisions suggested by the original representation and the self-supervised one. The moment at which consensus maximization occurs can serve as a criterion for determining the optimal number of clusters. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate that the proposed framework outperforms existing clustering approaches designed for scenarios with an unknown number of clusters.
Benefits and Pitfalls of Reinforcement Learning for Language Model Planning: A Theoretical Perspective
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Recent reinforcement learning (RL) methods have substantially enhanced the planning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), yet the theoretical basis for their effectiveness remains elusive. In this work, we investigate RL's benefits and limitations through a tractable graph-based abstraction, focusing on policy gradient (PG) and Q-learning methods. Our theoretical analyses reveal that supervised fine-tuning (SFT) may introduce co-occurrence-based spurious solutions, whereas RL achieves correct planning primarily through exploration, underscoring exploration's role in enabling better generalization. However, we also show that PG suffers from diversity collapse, where output diversity decreases during training and persists even after perfect accuracy is attained. By contrast, Q-learning provides two key advantages: off-policy learning and diversity preservation at convergence. We further demonstrate that careful reward design is necessary to prevent reward hacking in Q-learning. Finally, applying our framework to the real-world planning benchmark Blocksworld, we confirm that these behaviors manifest in practice.
Generalized Deep Multi-view Clustering via Causal Learning with Partially Aligned Cross-view Correspondence
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Multi-view clustering (MVC) aims to explore the common clustering structure across multiple views. Many existing MVC methods heavily rely on the assumption of view consistency, where alignments for corresponding samples across different views are ordered in advance. However, real-world scenarios often present a challenge as only partial data is consistently aligned across different views, restricting the overall clustering performance. In this work, we consider the model performance decreasing phenomenon caused by data order shift (i.e., from fully to partially aligned) as a generalized multi-view clustering problem. To tackle this problem, we design a causal multi-view clustering network, termed CauMVC. We adopt a causal modeling approach to understand multi-view clustering procedure. To be specific, we formulate the partially aligned data as an intervention and multi-view clustering with partially aligned data as an post-intervention inference. However, obtaining invariant features directly can be challenging. Thus, we design a Variational Auto-Encoder for causal learning by incorporating an encoder from existing information to estimate the invariant features. Moreover, a decoder is designed to perform the post-intervention inference. Lastly, we design a contrastive regularizer to capture sample correlations. To the best of our knowledge, this paper is the first work to deal generalized multi-view clustering via causal learning. Empirical experiments on both fully and partially aligned data illustrate the strong generalization and effectiveness of CauMVC.
Semantic Caching for Low-Cost LLM Serving: From Offline Learning to Online Adaptation
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are revolutionizing how users interact with information systems, yet their high inference cost poses serious scalability and sustainability challenges. Caching inference responses, allowing them to be retrieved without another forward pass through the LLM, has emerged as one possible solution. Traditional exact-match caching, however, overlooks the semantic similarity between queries, leading to unnecessary recomputation. Semantic caching addresses this by retrieving responses based on semantic similarity, but introduces a fundamentally different cache eviction problem: one must account for mismatch costs between incoming queries and cached responses. Moreover, key system parameters, such as query arrival probabilities and serving costs, are often unknown and must be learned over time. Existing semantic caching methods are largely ad-hoc, lacking theoretical foundations and unable to adapt to real-world uncertainty. In this paper, we present a principled, learning-based framework for semantic cache eviction under unknown query and cost distributions. We formulate both offline optimization and online learning variants of the problem, and develop provably efficient algorithms with state-of-the-art guarantees. We also evaluate our framework on a synthetic dataset, showing that our proposed algorithms perform matching or superior performance compared with baselines.
Automatically Identify and Rectify: Robust Deep Contrastive Multi-view Clustering in Noisy Scenarios
May 27, 2025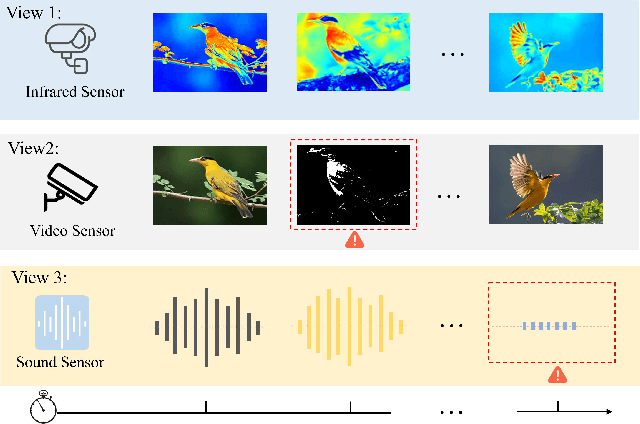
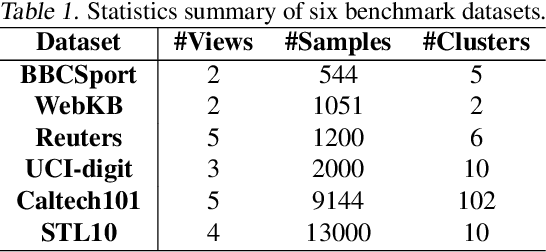
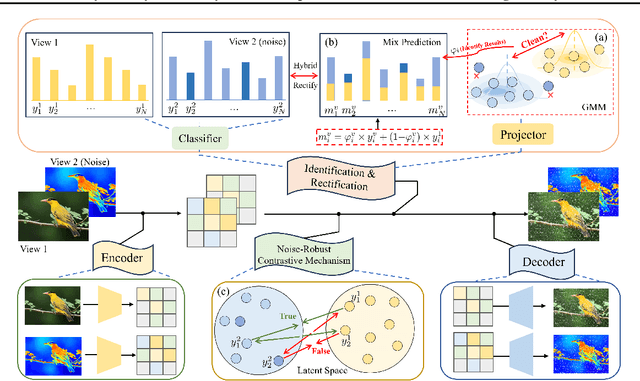

Abstract:Leveraging the powerful representation learning capabilities, deep multi-view clustering methods have demonstrated reliable performance by effectively integrating multi-source information from diverse views in recent years. Most existing methods rely on the assumption of clean views. However, noise is pervasive in real-world scenarios, leading to a significant degradation in performance. To tackle this problem, we propose a novel multi-view clustering framework for the automatic identification and rectification of noisy data, termed AIRMVC. Specifically, we reformulate noisy identification as an anomaly identification problem using GMM. We then design a hybrid rectification strategy to mitigate the adverse effects of noisy data based on the identification results. Furthermore, we introduce a noise-robust contrastive mechanism to generate reliable representations. Additionally, we provide a theoretical proof demonstrating that these representations can discard noisy information, thereby improving the performance of downstream tasks. Extensive experiments on six benchmark datasets demonstrate that AIRMVC outperforms state-of-the-art algorithms in terms of robustness in noisy scenarios. The code of AIRMVC are available at https://github.com/xihongyang1999/AIRMVC on Github.
Measure Domain's Gap: A Similar Domain Selection Principle for Multi-Domain Recommendation
May 26, 2025Abstract:Multi-Domain Recommendation (MDR) achieves the desirable recommendation performance by effectively utilizing the transfer information across different domains. Despite the great success, most existing MDR methods adopt a single structure to transfer complex domain-shared knowledge. However, the beneficial transferring information should vary across different domains. When there is knowledge conflict between domains or a domain is of poor quality, unselectively leveraging information from all domains will lead to a serious Negative Transfer Problem (NTP). Therefore, how to effectively model the complex transfer relationships between domains to avoid NTP is still a direction worth exploring. To address these issues, we propose a simple and dynamic Similar Domain Selection Principle (SDSP) for multi-domain recommendation in this paper. SDSP presents the initial exploration of selecting suitable domain knowledge for each domain to alleviate NTP. Specifically, we propose a novel prototype-based domain distance measure to effectively model the complexity relationship between domains. Thereafter, the proposed SDSP can dynamically find similar domains for each domain based on the supervised signals of the domain metrics and the unsupervised distance measure from the learned domain prototype. We emphasize that SDSP is a lightweight method that can be incorporated with existing MDR methods for better performance while not introducing excessive time overheads. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first solution that can explicitly measure domain-level gaps and dynamically select appropriate domains in the MDR field. Extensive experiments on three datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge