Xiang Liu
SPWOOD: Sparse Partial Weakly-Supervised Oriented Object Detection
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:A consistent trend throughout the research of oriented object detection has been the pursuit of maintaining comparable performance with fewer and weaker annotations. This is particularly crucial in the remote sensing domain, where the dense object distribution and a wide variety of categories contribute to prohibitively high costs. Based on the supervision level, existing oriented object detection algorithms can be broadly grouped into fully supervised, semi-supervised, and weakly supervised methods. Within the scope of this work, we further categorize them to include sparsely supervised and partially weakly-supervised methods. To address the challenges of large-scale labeling, we introduce the first Sparse Partial Weakly-Supervised Oriented Object Detection framework, designed to efficiently leverage only a few sparse weakly-labeled data and plenty of unlabeled data. Our framework incorporates three key innovations: (1) We design a Sparse-annotation-Orientation-and-Scale-aware Student (SOS-Student) model to separate unlabeled objects from the background in a sparsely-labeled setting, and learn orientation and scale information from orientation-agnostic or scale-agnostic weak annotations. (2) We construct a novel Multi-level Pseudo-label Filtering strategy that leverages the distribution of model predictions, which is informed by the model's multi-layer predictions. (3) We propose a unique sparse partitioning approach, ensuring equal treatment for each category. Extensive experiments on the DOTA and DIOR datasets show that our framework achieves a significant performance gain over traditional oriented object detection methods mentioned above, offering a highly cost-effective solution. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/VisionXLab/SPWOOD.
SONIC: Segmented Optimized Nexus for Information Compression in Key-Value Caching
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:The linear growth of Key-Value (KV) cache remains a bottleneck for multi-turn LLM deployment. Existing KV cache compression methods often fail to account for the structural properties of multi-turn dialogues, relying on heuristic eviction that risks losing critical context. We propose \textbf{SONIC}, a learning-based framework that compresses historical segments into compact and semantically rich \textbf{Nexus} tokens. By integrating dynamic budget training, SONIC allows flexible adaptation to varying memory constraints without retraining. Experiments show that at compression ratios of 80\% and 50\%, SONIC consistently outperforms baselines such as H2O and StreamingLLM on four diverse multi-turn benchmarks. Specifically, on the widely used MTBench101 benchmark, SONIC achieves an average score improvement of 35.55\% over state-of-the-art baselines, validating its effectiveness in sustaining coherent multi-turn dialogues. Furthermore, SONIC enhances deployment efficiency, accelerating the overall inference process by 50.1\% compared to full-context generation.
Splatwizard: A Benchmark Toolkit for 3D Gaussian Splatting Compression
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:The recent advent of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has marked a significant breakthrough in real-time novel view synthesis. However, the rapid proliferation of 3DGS-based algorithms has created a pressing need for standardized and comprehensive evaluation tools, especially for compression task. Existing benchmarks often lack the specific metrics necessary to holistically assess the unique characteristics of different methods, such as rendering speed, rate distortion trade-offs memory efficiency, and geometric accuracy. To address this gap, we introduce Splatwizard, a unified benchmark toolkit designed specifically for benchmarking 3DGS compression models. Splatwizard provides an easy-to-use framework to implement new 3DGS compression model and utilize state-of-the-art techniques proposed by previous work. Besides, an integrated pipeline that automates the calculation of key performance indicators, including image-based quality metrics, chamfer distance of reconstruct mesh, rendering frame rates, and computational resource consumption is included in the framework as well. Code is available at https://github.com/splatwizard/splatwizard
Fuzzy Reasoning Chain (FRC): An Innovative Reasoning Framework from Fuzziness to Clarity
Sep 26, 2025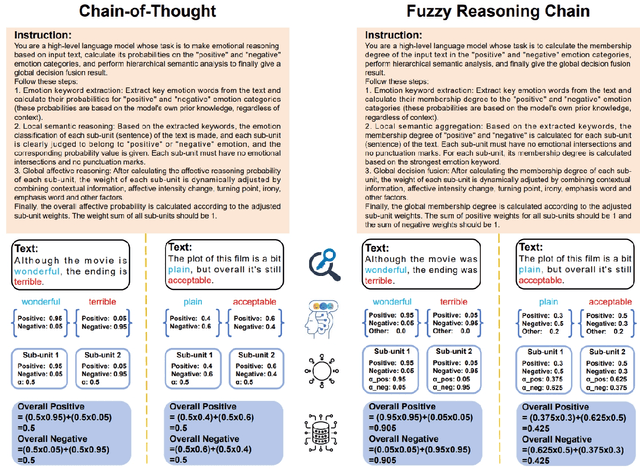
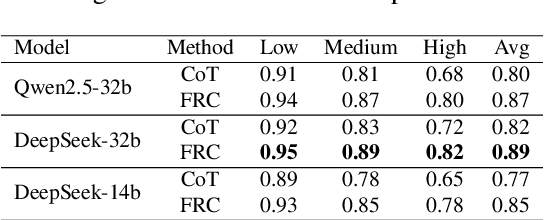
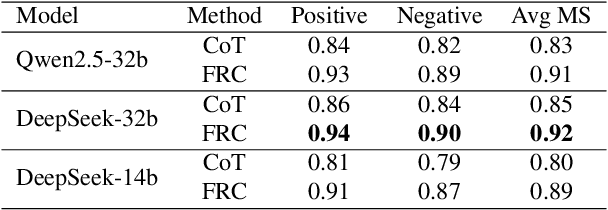
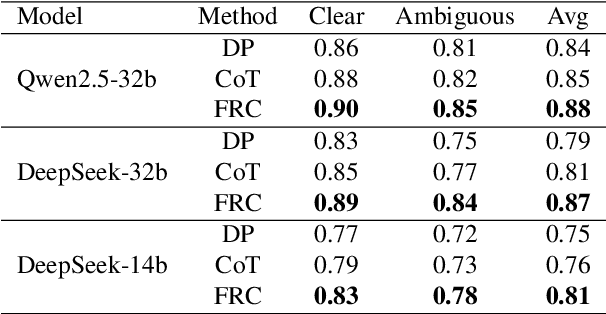
Abstract:With the rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs), natural language processing (NLP) has achieved remarkable progress. Nonetheless, significant challenges remain in handling texts with ambiguity, polysemy, or uncertainty. We introduce the Fuzzy Reasoning Chain (FRC) framework, which integrates LLM semantic priors with continuous fuzzy membership degrees, creating an explicit interaction between probability-based reasoning and fuzzy membership reasoning. This transition allows ambiguous inputs to be gradually transformed into clear and interpretable decisions while capturing conflicting or uncertain signals that traditional probability-based methods cannot. We validate FRC on sentiment analysis tasks, where both theoretical analysis and empirical results show that it ensures stable reasoning and facilitates knowledge transfer across different model scales. These findings indicate that FRC provides a general mechanism for managing subtle and ambiguous expressions with improved interpretability and robustness.
Hierarchical Deep Fusion Framework for Multi-dimensional Facial Forgery Detection -- The 2024 Global Deepfake Image Detection Challenge
Sep 16, 2025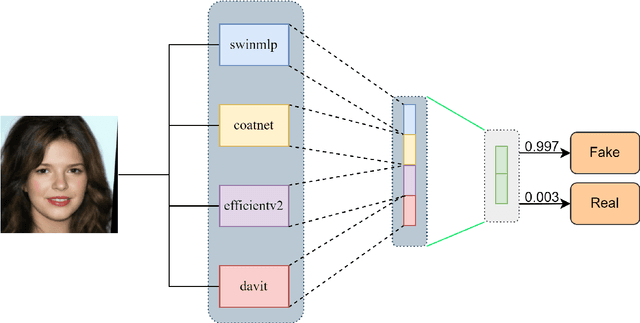
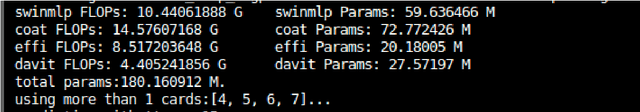
Abstract:The proliferation of sophisticated deepfake technology poses significant challenges to digital security and authenticity. Detecting these forgeries, especially across a wide spectrum of manipulation techniques, requires robust and generalized models. This paper introduces the Hierarchical Deep Fusion Framework (HDFF), an ensemble-based deep learning architecture designed for high-performance facial forgery detection. Our framework integrates four diverse pre-trained sub-models, Swin-MLP, CoAtNet, EfficientNetV2, and DaViT, which are meticulously fine-tuned through a multi-stage process on the MultiFFDI dataset. By concatenating the feature representations from these specialized models and training a final classifier layer, HDFF effectively leverages their collective strengths. This approach achieved a final score of 0.96852 on the competition's private leaderboard, securing the 20th position out of 184 teams, demonstrating the efficacy of hierarchical fusion for complex image classification tasks.
End to End Autoencoder MLP Framework for Sepsis Prediction
Aug 26, 2025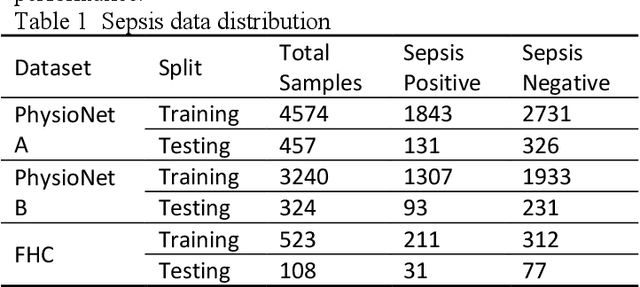
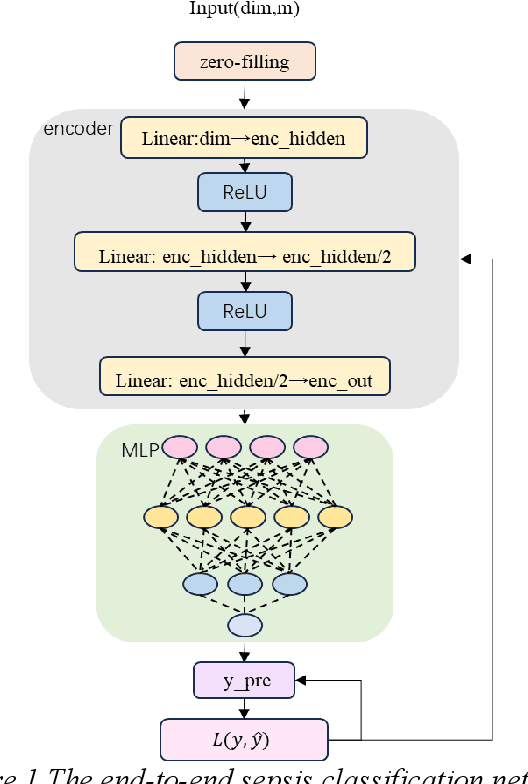
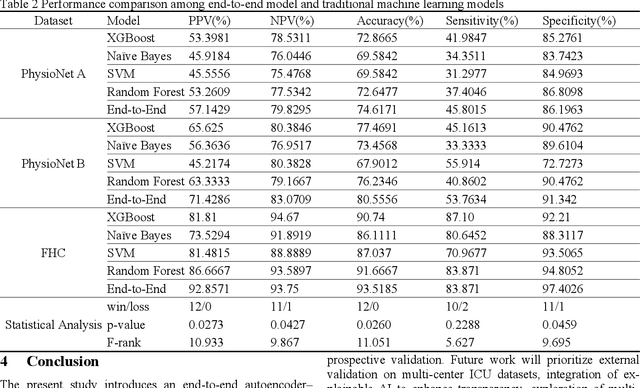
Abstract:Sepsis is a life threatening condition that requires timely detection in intensive care settings. Traditional machine learning approaches, including Naive Bayes, Support Vector Machine (SVM), Random Forest, and XGBoost, often rely on manual feature engineering and struggle with irregular, incomplete time-series data commonly present in electronic health records. We introduce an end-to-end deep learning framework integrating an unsupervised autoencoder for automatic feature extraction with a multilayer perceptron classifier for binary sepsis risk prediction. To enhance clinical applicability, we implement a customized down sampling strategy that extracts high information density segments during training and a non-overlapping dynamic sliding window mechanism for real-time inference. Preprocessed time series data are represented as fixed dimension vectors with explicit missingness indicators, mitigating bias and noise. We validate our approach on three ICU cohorts. Our end-to-end model achieves accuracies of 74.6 percent, 80.6 percent, and 93.5 percent, respectively, consistently outperforming traditional machine learning baselines. These results demonstrate the framework's superior robustness, generalizability, and clinical utility for early sepsis detection across heterogeneous ICU environments.
Hypernetworks for Model-Heterogeneous Personalized Federated Learning
Jul 30, 2025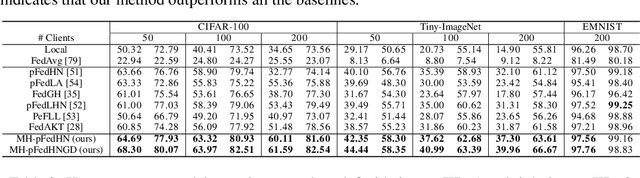
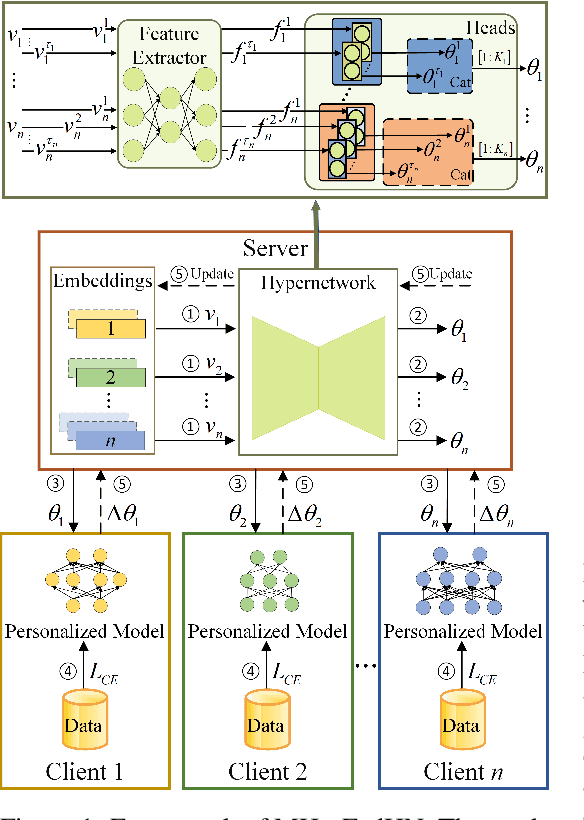
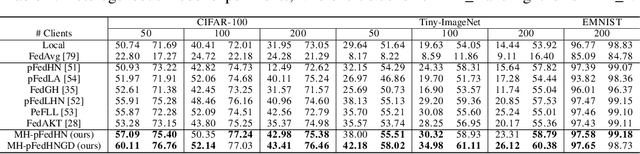
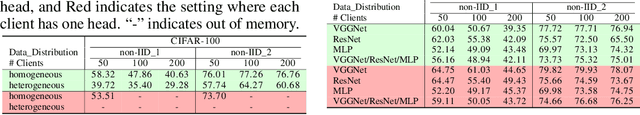
Abstract:Recent advances in personalized federated learning have focused on addressing client model heterogeneity. However, most existing methods still require external data, rely on model decoupling, or adopt partial learning strategies, which can limit their practicality and scalability. In this paper, we revisit hypernetwork-based methods and leverage their strong generalization capabilities to design a simple yet effective framework for heterogeneous personalized federated learning. Specifically, we propose MH-pFedHN, which leverages a server-side hypernetwork that takes client-specific embedding vectors as input and outputs personalized parameters tailored to each client's heterogeneous model. To promote knowledge sharing and reduce computation, we introduce a multi-head structure within the hypernetwork, allowing clients with similar model sizes to share heads. Furthermore, we further propose MH-pFedHNGD, which integrates an optional lightweight global model to improve generalization. Our framework does not rely on external datasets and does not require disclosure of client model architectures, thereby offering enhanced privacy and flexibility. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks and model settings demonstrate that our approach achieves competitive accuracy, strong generalization, and serves as a robust baseline for future research in model-heterogeneous personalized federated learning.
AnTKV: Anchor Token-Aware Sub-Bit Vector Quantization for KV Cache in Large Language Models
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Quantization has emerged as an effective and lightweight solution to reduce the memory footprint of the KV cache in Large Language Models (LLMs). Nevertheless, minimizing the performance degradation caused by ultra-low-bit KV cache quantization remains a significant challenge. We observe that quantizing the KV cache of different tokens has varying impacts on the quality of attention outputs. To systematically investigate this phenomenon, we perform forward error propagation analysis on attention and propose the Anchor Score (AnS) that quantifies the sensitivity of each token's KV cache to quantization-induced error. Our analysis reveals significant disparities in AnS across tokens, suggesting that preserving a small subset with full precision (FP16) of high-AnS tokens can greatly mitigate accuracy loss in aggressive quantization scenarios. Based on this insight, we introduce AnTKV, a novel framework that leverages Anchor Token-aware Vector Quantization to compress the KV cache. Furthermore, to support efficient deployment, we design and develop a triton kernel that is fully compatible with FlashAttention, enabling fast online Anchor Token selection. AnTKV enables LLaMA-3-8B to handle context lengths up to 840K tokens on a single 80GB A100 GPU, while achieving up to 3.5x higher decoding throughput compared to the FP16 baseline. Our experiment results demonstrate that AnTKV matches or outperforms prior works such as KIVI, SKVQ, KVQuant, and CQ under 4-bit settings. More importantly, AnTKV achieves significantly lower perplexity under ultra-low-bit quantization on Mistral-7B, with only 6.32 at 1-bit and 8.87 at 0.375-bit, compared to the FP16 baseline of 4.73.
Combining Self-attention and Dilation Convolutional for Semantic Segmentation of Coal Maceral Groups
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:The segmentation of coal maceral groups can be described as a semantic segmentation process of coal maceral group images, which is of great significance for studying the chemical properties of coal. Generally, existing semantic segmentation models of coal maceral groups use the method of stacking parameters to achieve higher accuracy. It leads to increased computational requirements and impacts model training efficiency. At the same time, due to the professionalism and diversity of coal maceral group images sampling, obtaining the number of samples for model training requires a long time and professional personnel operation. To address these issues, We have innovatively developed an IoT-based DA-VIT parallel network model. By utilizing this model, we can continuously broaden the dataset through IoT and achieving sustained improvement in the accuracy of coal maceral groups segmentation. Besides, we decouple the parallel network from the backbone network to ensure the normal using of the backbone network during model data updates. Secondly, DCSA mechanism of DA-VIT is introduced to enhance the local feature information of coal microscopic images. This DCSA can decompose the large kernels of convolutional attention into multiple scales and reduce 81.18% of parameters.Finally, we performed the contrast experiment and ablation experiment between DA-VIT and state-of-the-art methods at lots of evaluation metrics. Experimental results show that DA-VIT-Base achieves 92.14% pixel accuracy and 63.18% mIoU. Params and FLOPs of DA-VIT-Tiny are 4.95M and 8.99G, respectively. All of the evaluation metrics of the proposed DA-VIT are better than other state-of-the-art methods.
Styl3R: Instant 3D Stylized Reconstruction for Arbitrary Scenes and Styles
May 27, 2025Abstract:Stylizing 3D scenes instantly while maintaining multi-view consistency and faithfully resembling a style image remains a significant challenge. Current state-of-the-art 3D stylization methods typically involve computationally intensive test-time optimization to transfer artistic features into a pretrained 3D representation, often requiring dense posed input images. In contrast, leveraging recent advances in feed-forward reconstruction models, we demonstrate a novel approach to achieve direct 3D stylization in less than a second using unposed sparse-view scene images and an arbitrary style image. To address the inherent decoupling between reconstruction and stylization, we introduce a branched architecture that separates structure modeling and appearance shading, effectively preventing stylistic transfer from distorting the underlying 3D scene structure. Furthermore, we adapt an identity loss to facilitate pre-training our stylization model through the novel view synthesis task. This strategy also allows our model to retain its original reconstruction capabilities while being fine-tuned for stylization. Comprehensive evaluations, using both in-domain and out-of-domain datasets, demonstrate that our approach produces high-quality stylized 3D content that achieve a superior blend of style and scene appearance, while also outperforming existing methods in terms of multi-view consistency and efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge