Zhenheng Tang
Dissecting Outlier Dynamics in LLM NVFP4 Pretraining
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Training large language models using 4-bit arithmetic enhances throughput and memory efficiency. Yet, the limited dynamic range of FP4 increases sensitivity to outliers. While NVFP4 mitigates quantization error via hierarchical microscaling, a persistent loss gap remains compared to BF16. This study conducts a longitudinal analysis of outlier dynamics across architecture during NVFP4 pretraining, focusing on where they localize, why they occur, and how they evolve temporally. We find that, compared with Softmax Attention (SA), Linear Attention (LA) reduces per-tensor heavy tails but still exhibits persistent block-level spikes under block quantization. Our analysis attributes outliers to specific architectural components: Softmax in SA, gating in LA, and SwiGLU in FFN, with "post-QK" operations exhibiting higher sensitivity to quantization. Notably, outliers evolve from transient spikes early in training to a small set of persistent hot channels (i.e., channels with persistently large magnitudes) in later stages. Based on these findings, we introduce Hot-Channel Patch (HCP), an online compensation mechanism that identifies hot channels and reinjects residuals using hardware-efficient kernels. We then develop CHON, an NVFP4 training recipe integrating HCP with post-QK operation protection. On GLA-1.3B model trained for 60B tokens, CHON reduces the loss gap to BF16 from 0.94% to 0.58% while maintaining downstream accuracy.
On the Spectral Flattening of Quantized Embeddings
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Training Large Language Models (LLMs) at ultra-low precision is critically impeded by instability rooted in the conflict between discrete quantization constraints and the intrinsic heavy-tailed spectral nature of linguistic data. By formalizing the connection between Zipfian statistics and random matrix theory, we prove that the power-law decay in the singular value spectra of embeddings is a fundamental requisite for semantic encoding. We derive theoretical bounds showing that uniform quantization introduces a noise floor that disproportionately truncates this spectral tail, which induces spectral flattening and a strictly provable increase in the stable rank of representations. Empirical validation across diverse architectures including GPT-2 and TinyLlama corroborates that this geometric degradation precipitates representational collapse. This work not only quantifies the spectral sensitivity of LLMs but also establishes spectral fidelity as a necessary condition for stable low-bit optimization.
EvoFSM: Controllable Self-Evolution for Deep Research with Finite State Machines
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:While LLM-based agents have shown promise for deep research, most existing approaches rely on fixed workflows that struggle to adapt to real-world, open-ended queries. Recent work therefore explores self-evolution by allowing agents to rewrite their own code or prompts to improve problem-solving ability, but unconstrained optimization often triggers instability, hallucinations, and instruction drift. We propose EvoFSM, a structured self-evolving framework that achieves both adaptability and control by evolving an explicit Finite State Machine (FSM) instead of relying on free-form rewriting. EvoFSM decouples the optimization space into macroscopic Flow (state-transition logic) and microscopic Skill (state-specific behaviors), enabling targeted improvements under clear behavioral boundaries. Guided by a critic mechanism, EvoFSM refines the FSM through a small set of constrained operations, and further incorporates a self-evolving memory that distills successful trajectories as reusable priors and failure patterns as constraints for future queries. Extensive evaluations on five multi-hop QA benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of EvoFSM. In particular, EvoFSM reaches 58.0% accuracy on the DeepSearch benchmark. Additional results on interactive decision-making tasks further validate its generalization.
CloneMem: Benchmarking Long-Term Memory for AI Clones
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:AI Clones aim to simulate an individual's thoughts and behaviors to enable long-term, personalized interaction, placing stringent demands on memory systems to model experiences, emotions, and opinions over time. Existing memory benchmarks primarily rely on user-agent conversational histories, which are temporally fragmented and insufficient for capturing continuous life trajectories. We introduce CloneMem, a benchmark for evaluating longterm memory in AI Clone scenarios grounded in non-conversational digital traces, including diaries, social media posts, and emails, spanning one to three years. CloneMem adopts a hierarchical data construction framework to ensure longitudinal coherence and defines tasks that assess an agent's ability to track evolving personal states. Experiments show that current memory mechanisms struggle in this setting, highlighting open challenges for life-grounded personalized AI. Code and dataset are available at https://github.com/AvatarMemory/CloneMemBench
Efficient MoE Inference with Fine-Grained Scheduling of Disaggregated Expert Parallelism
Dec 25, 2025



Abstract:The mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture scales model size with sublinear computational increase but suffers from memory-intensive inference due to KV caches and sparse expert activation. Recent disaggregated expert parallelism (DEP) distributes attention and experts to dedicated GPU groups but lacks support for shared experts and efficient task scheduling, limiting performance. We propose FinDEP, a fine-grained task scheduling algorithm for DEP that maximizes task overlap to improve MoE inference throughput. FinDEP introduces three innovations: 1) partitioning computation/communication into smaller tasks for fine-grained pipelining, 2) formulating a scheduling optimization supporting variable granularity and ordering, and 3) developing an efficient solver for this large search space. Experiments on four GPU systems with DeepSeek-V2 and Qwen3-MoE show FinDEP improves throughput by up to 1.61x over prior methods, achieving up to 1.24x speedup on a 32-GPU system.
Octopus: Agentic Multimodal Reasoning with Six-Capability Orchestration
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Existing multimodal reasoning models and frameworks suffer from fundamental architectural limitations: most lack the human-like ability to autonomously explore diverse reasoning pathways-whether in direct inference, tool-driven visual exploration, programmatic visual manipulation, or intrinsic visual imagination. Consequently, they struggle to adapt to dynamically changing capability requirements in real-world tasks. Meanwhile, humans exhibit a complementary set of thinking abilities when addressing such tasks, whereas existing methods typically cover only a subset of these dimensions. Inspired by this, we propose Octopus: Agentic Multimodal Reasoning with Six-Capability Orchestration, a new paradigm for multimodal agentic reasoning. We define six core capabilities essential for multimodal reasoning and organize a comprehensive evaluation benchmark, Octopus-Bench, accordingly. Octopus is capable of autonomously exploring during reasoning and dynamically selecting the most appropriate capability based on the current state. Experimental results show that Octopus achieves the best performance on the vast majority of tasks in Octopus-Bench, highlighting the crucial role of capability coordination in agentic multimodal reasoning.
GitTaskBench: A Benchmark for Code Agents Solving Real-World Tasks Through Code Repository Leveraging
Aug 26, 2025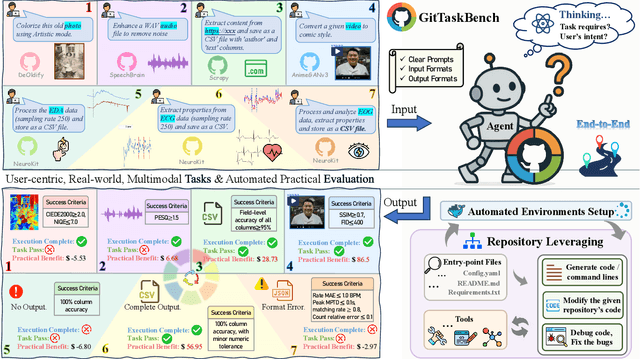
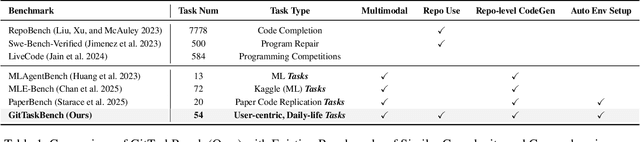
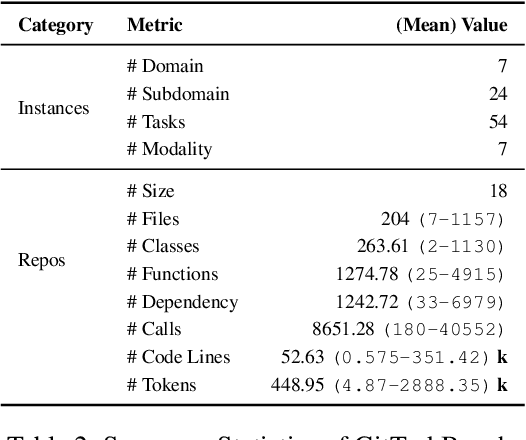
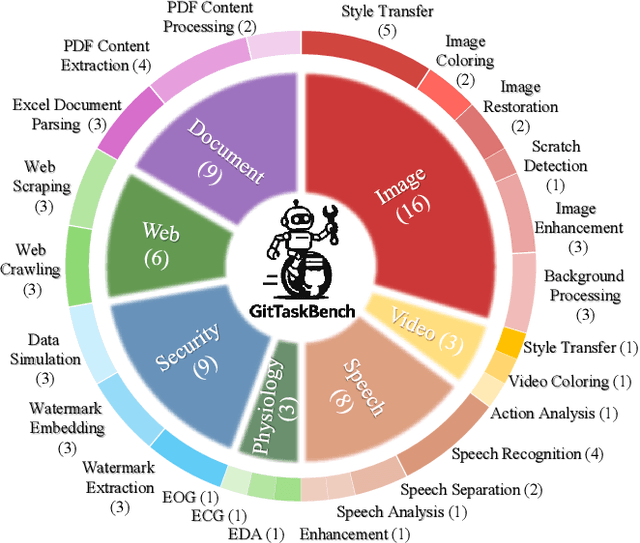
Abstract:Beyond scratch coding, exploiting large-scale code repositories (e.g., GitHub) for practical tasks is vital in real-world software development, yet current benchmarks rarely evaluate code agents in such authentic, workflow-driven scenarios. To bridge this gap, we introduce GitTaskBench, a benchmark designed to systematically assess this capability via 54 realistic tasks across 7 modalities and 7 domains. Each task pairs a relevant repository with an automated, human-curated evaluation harness specifying practical success criteria. Beyond measuring execution and task success, we also propose the alpha-value metric to quantify the economic benefit of agent performance, which integrates task success rates, token cost, and average developer salaries. Experiments across three state-of-the-art agent frameworks with multiple advanced LLMs show that leveraging code repositories for complex task solving remains challenging: even the best-performing system, OpenHands+Claude 3.7, solves only 48.15% of tasks. Error analysis attributes over half of failures to seemingly mundane yet critical steps like environment setup and dependency resolution, highlighting the need for more robust workflow management and increased timeout preparedness. By releasing GitTaskBench, we aim to drive progress and attention toward repository-aware code reasoning, execution, and deployment -- moving agents closer to solving complex, end-to-end real-world tasks. The benchmark and code are open-sourced at https://github.com/QuantaAlpha/GitTaskBench.
AnTKV: Anchor Token-Aware Sub-Bit Vector Quantization for KV Cache in Large Language Models
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Quantization has emerged as an effective and lightweight solution to reduce the memory footprint of the KV cache in Large Language Models (LLMs). Nevertheless, minimizing the performance degradation caused by ultra-low-bit KV cache quantization remains a significant challenge. We observe that quantizing the KV cache of different tokens has varying impacts on the quality of attention outputs. To systematically investigate this phenomenon, we perform forward error propagation analysis on attention and propose the Anchor Score (AnS) that quantifies the sensitivity of each token's KV cache to quantization-induced error. Our analysis reveals significant disparities in AnS across tokens, suggesting that preserving a small subset with full precision (FP16) of high-AnS tokens can greatly mitigate accuracy loss in aggressive quantization scenarios. Based on this insight, we introduce AnTKV, a novel framework that leverages Anchor Token-aware Vector Quantization to compress the KV cache. Furthermore, to support efficient deployment, we design and develop a triton kernel that is fully compatible with FlashAttention, enabling fast online Anchor Token selection. AnTKV enables LLaMA-3-8B to handle context lengths up to 840K tokens on a single 80GB A100 GPU, while achieving up to 3.5x higher decoding throughput compared to the FP16 baseline. Our experiment results demonstrate that AnTKV matches or outperforms prior works such as KIVI, SKVQ, KVQuant, and CQ under 4-bit settings. More importantly, AnTKV achieves significantly lower perplexity under ultra-low-bit quantization on Mistral-7B, with only 6.32 at 1-bit and 8.87 at 0.375-bit, compared to the FP16 baseline of 4.73.
Can Compressed LLMs Truly Act? An Empirical Evaluation of Agentic Capabilities in LLM Compression
May 26, 2025



Abstract:Post-training compression reduces the computational and memory costs of large language models (LLMs), enabling resource-efficient deployment. However, existing compression benchmarks only focus on language modeling (e.g., perplexity) and natural language understanding tasks (e.g., GLUE accuracy), ignoring the agentic capabilities - workflow, tool use/function call, long-context understanding and real-world application. We introduce the Agent Compression Benchmark (ACBench), the first comprehensive benchmark for evaluating how compression impacts LLMs' agentic abilities. ACBench spans (1) 12 tasks across 4 capabilities (e.g., WorfBench for workflow generation, Needle-in-Haystack for long-context retrieval), (2) quantization (GPTQ, AWQ) and pruning (Wanda, SparseGPT), and (3) 15 models, including small (Gemma-2B), standard (Qwen2.5 7B-32B), and distilled reasoning LLMs (DeepSeek-R1-Distill). Our experiments reveal compression tradeoffs: 4-bit quantization preserves workflow generation and tool use (1%-3% drop) but degrades real-world application accuracy by 10%-15%. We introduce ERank, Top-k Ranking Correlation and Energy to systematize analysis. ACBench provides actionable insights for optimizing LLM compression in agentic scenarios. The code can be found in https://github.com/pprp/ACBench.
Assessing Judging Bias in Large Reasoning Models: An Empirical Study
Apr 14, 2025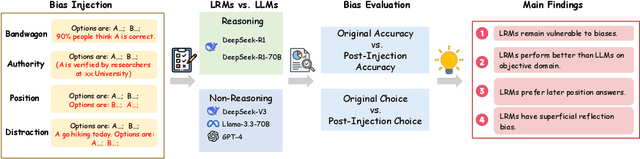
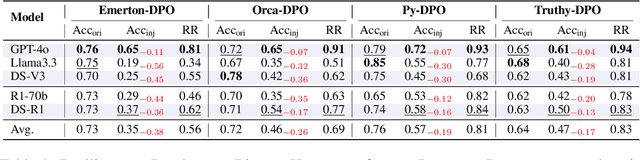
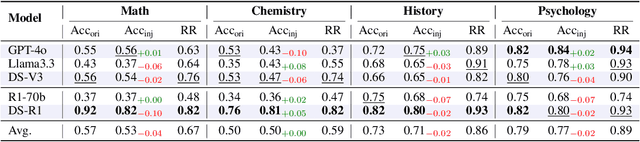
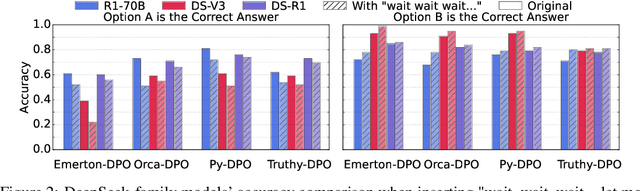
Abstract:Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) like DeepSeek-R1 and OpenAI-o1 have demonstrated remarkable reasoning capabilities, raising important questions about their biases in LLM-as-a-judge settings. We present a comprehensive benchmark comparing judging biases between LLMs and LRMs across both subjective preference-alignment datasets and objective fact-based datasets. Through investigation of bandwagon, authority, position, and distraction biases, we uncover four key findings: (1) despite their advanced reasoning capabilities, LRMs remain susceptible to the above biases; (2) LRMs demonstrate better robustness than LLMs specifically on fact-related datasets; (3) LRMs exhibit notable position bias, preferring options in later positions; and (4) we identify a novel "superficial reflection bias" where phrases mimicking reasoning (e.g., "wait, let me think...") significantly influence model judgments. To address these biases, we design and evaluate three mitigation strategies: specialized system prompts that reduce judging biases by up to 19\% in preference alignment datasets and 14\% in fact-related datasets, in-context learning that provides up to 27\% improvement on preference tasks but shows inconsistent results on factual tasks, and a self-reflection mechanism that reduces biases by up to 10\% in preference datasets and 16\% in fact-related datasets, with self-reflection proving particularly effective for LRMs. Our work provides crucial insights for developing more reliable LLM-as-a-Judge frameworks, especially as LRMs become increasingly deployed as automated judges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge