Zhanzhi Lou
Making Bias Non-Predictive: Training Robust LLM Judges via Reinforcement Learning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) increasingly serve as automated judges, yet they remain susceptible to cognitive biases -- often altering their reasoning when faced with spurious prompt-level cues such as consensus claims or authority appeals. Existing mitigations via prompting or supervised fine-tuning fail to generalize, as they modify surface behavior without changing the optimization objective that makes bias cues predictive. To address this gap, we propose Epistemic Independence Training (EIT), a reinforcement learning framework grounded in a key principle: to learn independence, bias cues must be made non-predictive of reward. EIT operationalizes this through a balanced conflict strategy where bias signals are equally likely to support correct and incorrect answers, combined with a reward design that penalizes bias-following without rewarding bias agreement. Experiments on Qwen3-4B demonstrate that EIT improves both accuracy and robustness under adversarial biases, while preserving performance when bias aligns with truth. Notably, models trained only on bandwagon bias generalize to unseen bias types such as authority and distraction, indicating that EIT induces transferable epistemic independence rather than bias-specific heuristics. Code and data are available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/bias-mitigation-with-rl-BC47.
Assessing Judging Bias in Large Reasoning Models: An Empirical Study
Apr 14, 2025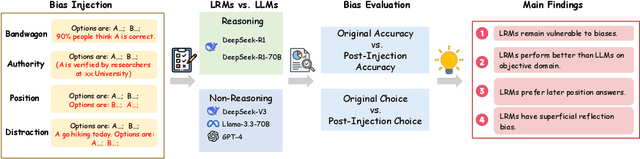
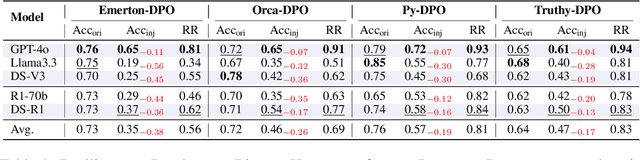
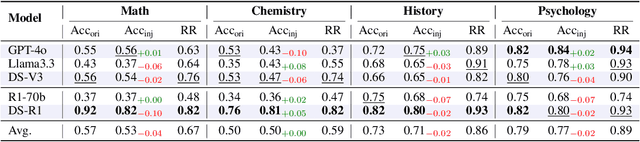
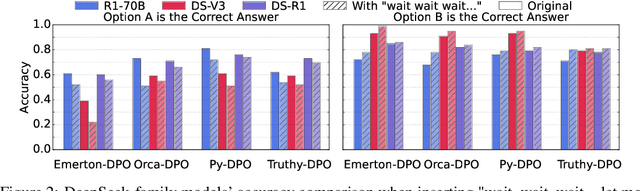
Abstract:Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) like DeepSeek-R1 and OpenAI-o1 have demonstrated remarkable reasoning capabilities, raising important questions about their biases in LLM-as-a-judge settings. We present a comprehensive benchmark comparing judging biases between LLMs and LRMs across both subjective preference-alignment datasets and objective fact-based datasets. Through investigation of bandwagon, authority, position, and distraction biases, we uncover four key findings: (1) despite their advanced reasoning capabilities, LRMs remain susceptible to the above biases; (2) LRMs demonstrate better robustness than LLMs specifically on fact-related datasets; (3) LRMs exhibit notable position bias, preferring options in later positions; and (4) we identify a novel "superficial reflection bias" where phrases mimicking reasoning (e.g., "wait, let me think...") significantly influence model judgments. To address these biases, we design and evaluate three mitigation strategies: specialized system prompts that reduce judging biases by up to 19\% in preference alignment datasets and 14\% in fact-related datasets, in-context learning that provides up to 27\% improvement on preference tasks but shows inconsistent results on factual tasks, and a self-reflection mechanism that reduces biases by up to 10\% in preference datasets and 16\% in fact-related datasets, with self-reflection proving particularly effective for LRMs. Our work provides crucial insights for developing more reliable LLM-as-a-Judge frameworks, especially as LRMs become increasingly deployed as automated judges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge