Yaqi Liu
AgentSense: Virtual Sensor Data Generation Using LLM Agents in Simulated Home Environments
Jun 16, 2025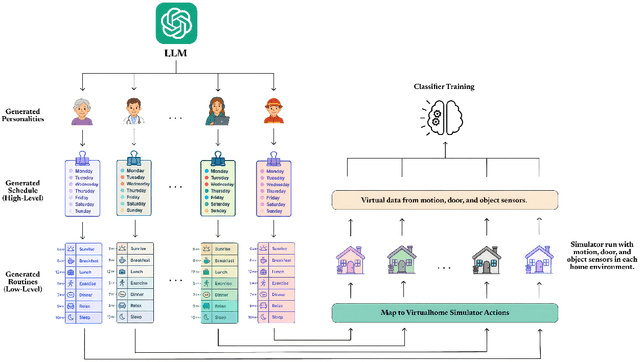
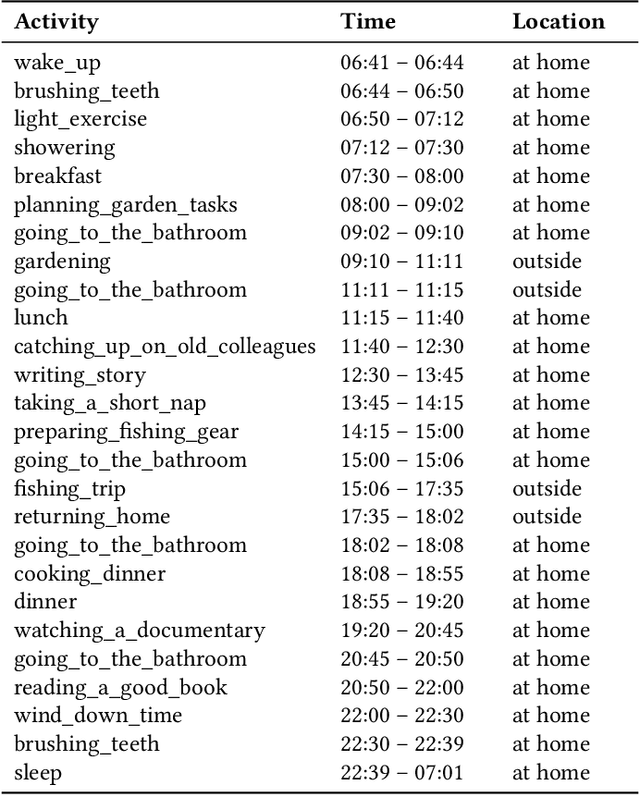
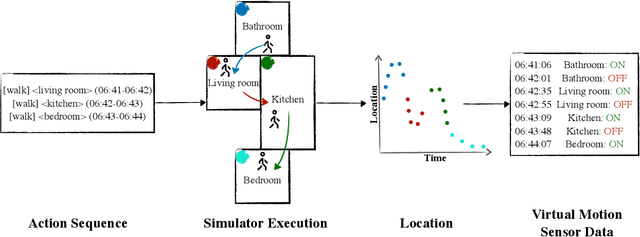
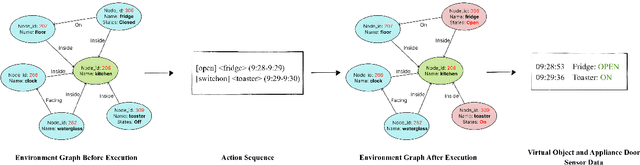
Abstract:A major obstacle in developing robust and generalizable smart home-based Human Activity Recognition (HAR) systems is the lack of large-scale, diverse labeled datasets. Variability in home layouts, sensor configurations, and user behavior adds further complexity, as individuals follow varied routines and perform activities in distinct ways. Building HAR systems that generalize well requires training data that captures the diversity across users and environments. To address these challenges, we introduce AgentSense, a virtual data generation pipeline where diverse personas are generated by leveraging Large Language Models. These personas are used to create daily routines, which are then decomposed into low-level action sequences. Subsequently, the actions are executed in a simulated home environment called VirtualHome that we extended with virtual ambient sensors capable of recording the agents activities as they unfold. Overall, AgentSense enables the generation of rich, virtual sensor datasets that represent a wide range of users and home settings. Across five benchmark HAR datasets, we show that leveraging our virtual sensor data substantially improves performance, particularly when real data are limited. Notably, models trained on a combination of virtual data and just a few days of real data achieve performance comparable to those trained on the entire real datasets. These results demonstrate and prove the potential of virtual data to address one of the most pressing challenges in ambient sensing, which is the distinct lack of large-scale, annotated datasets without requiring any manual data collection efforts.
Combining Self-attention and Dilation Convolutional for Semantic Segmentation of Coal Maceral Groups
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:The segmentation of coal maceral groups can be described as a semantic segmentation process of coal maceral group images, which is of great significance for studying the chemical properties of coal. Generally, existing semantic segmentation models of coal maceral groups use the method of stacking parameters to achieve higher accuracy. It leads to increased computational requirements and impacts model training efficiency. At the same time, due to the professionalism and diversity of coal maceral group images sampling, obtaining the number of samples for model training requires a long time and professional personnel operation. To address these issues, We have innovatively developed an IoT-based DA-VIT parallel network model. By utilizing this model, we can continuously broaden the dataset through IoT and achieving sustained improvement in the accuracy of coal maceral groups segmentation. Besides, we decouple the parallel network from the backbone network to ensure the normal using of the backbone network during model data updates. Secondly, DCSA mechanism of DA-VIT is introduced to enhance the local feature information of coal microscopic images. This DCSA can decompose the large kernels of convolutional attention into multiple scales and reduce 81.18% of parameters.Finally, we performed the contrast experiment and ablation experiment between DA-VIT and state-of-the-art methods at lots of evaluation metrics. Experimental results show that DA-VIT-Base achieves 92.14% pixel accuracy and 63.18% mIoU. Params and FLOPs of DA-VIT-Tiny are 4.95M and 8.99G, respectively. All of the evaluation metrics of the proposed DA-VIT are better than other state-of-the-art methods.
Road Traffic Sign Recognition method using Siamese network Combining Efficient-CNN based Encoder
Feb 21, 2025



Abstract:Traffic signs recognition (TSR) plays an essential role in assistant driving and intelligent transportation system. However, the noise of complex environment may lead to motion-blur or occlusion problems, which raise the tough challenge to real-time recognition with high accuracy and robust. In this article, we propose IECES-network which with improved encoders and Siamese net. The three-stage approach of our method includes Efficient-CNN based encoders, Siamese backbone and the fully-connected layers. We firstly use convolutional encoders to extract and encode the traffic sign features of augmented training samples and standard images. Then, we design the Siamese neural network with Efficient-CNN based encoder and contrastive loss function, which can be trained to improve the robustness of TSR problem when facing the samples of motion-blur and occlusion by computing the distance between inputs and templates. Additionally, the template branch of the proposed network can be stopped when executing the recognition tasks after training to raise the process speed of our real-time model, and alleviate the computational resource and parameter scale. Finally, we recombined the feature code and a fully-connected layer with SoftMax function to classify the codes of samples and recognize the category of traffic signs. The results of experiments on the Tsinghua-Tencent 100K dataset and the German Traffic Sign Recognition Benchmark dataset demonstrate the performance of the proposed IECESnetwork. Compared with other state-of-the-art methods, in the case of motion-blur and occluded environment, the proposed method achieves competitive performance precision-recall and accuracy metric average is 88.1%, 86.43% and 86.1% with a 2.9M lightweight scale, respectively. Moreover, processing time of our model is 0.1s per frame, of which the speed is increased by 1.5 times compared with existing methods.
Understanding Before Recommendation: Semantic Aspect-Aware Review Exploitation via Large Language Models
Dec 26, 2023Abstract:Recommendation systems harness user-item interactions like clicks and reviews to learn their representations. Previous studies improve recommendation accuracy and interpretability by modeling user preferences across various aspects and intents. However, the aspects and intents are inferred directly from user reviews or behavior patterns, suffering from the data noise and the data sparsity problem. Furthermore, it is difficult to understand the reasons behind recommendations due to the challenges of interpreting implicit aspects and intents. Inspired by the deep semantic understanding offered by large language models (LLMs), we introduce a chain-based prompting approach to uncover semantic aspect-aware interactions, which provide clearer insights into user behaviors at a fine-grained semantic level. To incorporate the abundant interactions of various aspects, we propose the simple yet effective Semantic Aspect-based Graph Convolution Network (short for SAGCN). By performing graph convolutions on multiple semantic aspect graphs, SAGCN efficiently combines embeddings across multiple semantic aspects for final user and item representations. The effectiveness of the SAGCN was evaluated on three publicly available datasets through extensive experiments, which revealed that it outperforms all other competitors. Furthermore, interpretability analysis experiments were conducted to demonstrate the interpretability of incorporating semantic aspects into the model.
kNN-CTC: Enhancing ASR via Retrieval of CTC Pseudo Labels
Dec 21, 2023Abstract:The success of retrieval-augmented language models in various natural language processing (NLP) tasks has been constrained in automatic speech recognition (ASR) applications due to challenges in constructing fine-grained audio-text datastores. This paper presents kNN-CTC, a novel approach that overcomes these challenges by leveraging Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) pseudo labels to establish frame-level audio-text key-value pairs, circumventing the need for precise ground truth alignments. We further introduce a skip-blank strategy, which strategically ignores CTC blank frames, to reduce datastore size. kNN-CTC incorporates a k-nearest neighbors retrieval mechanism into pre-trained CTC ASR systems, achieving significant improvements in performance. By incorporating a k-nearest neighbors retrieval mechanism into pre-trained CTC ASR systems and leveraging a fine-grained, pruned datastore, kNN-CTC consistently achieves substantial improvements in performance under various experimental settings. Our code is available at https://github.com/NKU-HLT/KNN-CTC.
Predicting Scores of Various Aesthetic Attribute Sets by Learning from Overall Score Labels
Dec 06, 2023Abstract:Now many mobile phones embed deep-learning models for evaluation or guidance on photography. These models cannot provide detailed results like human pose scores or scene color scores because of the rare of corresponding aesthetic attribute data. However, the annotation of image aesthetic attribute scores requires experienced artists and professional photographers, which hinders the collection of large-scale fully-annotated datasets. In this paper, we propose to replace image attribute labels with feature extractors. First, a novel aesthetic attribute evaluation framework based on attribute features is proposed to predict attribute scores and overall scores. We call it the F2S (attribute features to attribute scores) model. We use networks from different tasks to provide attribute features to our F2S models. Then, we define an aesthetic attribute contribution to describe the role of aesthetic attributes throughout an image and use it with the attribute scores and the overall scores to train our F2S model. Sufficient experiments on publicly available datasets demonstrate that our F2S model achieves comparable performance with those trained on the datasets with fully-annotated aesthetic attribute score labels. Our method makes it feasible to learn meaningful attribute scores for various aesthetic attribute sets in different types of images with only overall aesthetic scores.
CMFDFormer: Transformer-based Copy-Move Forgery Detection with Continual Learning
Nov 22, 2023Abstract:Copy-move forgery detection aims at detecting duplicated regions in a suspected forged image, and deep learning based copy-move forgery detection methods are in the ascendant. These deep learning based methods heavily rely on synthetic training data, and the performance will degrade when facing new tasks. In this paper, we propose a Transformer-style copy-move forgery detection network named as CMFDFormer, and provide a novel PCSD (Pooled Cube and Strip Distillation) continual learning framework to help CMFDFormer handle new tasks. CMFDFormer consists of a MiT (Mix Transformer) backbone network and a PHD (Pluggable Hybrid Decoder) mask prediction network. The MiT backbone network is a Transformer-style network which is adopted on the basis of comprehensive analyses with CNN-style and MLP-style backbones. The PHD network is constructed based on self-correlation computation, hierarchical feature integration, a multi-scale cycle fully-connected block and a mask reconstruction block. The PHD network is applicable to feature extractors of different styles for hierarchical multi-scale information extraction, achieving comparable performance. Last but not least, we propose a PCSD continual learning framework to improve the forgery detectability and avoid catastrophic forgetting when handling new tasks. Our continual learning framework restricts intermediate features from the PHD network, and takes advantage of both cube pooling and strip pooling. Extensive experiments on publicly available datasets demonstrate the good performance of CMFDFormer and the effectiveness of the PCSD continual learning framework.
TBFormer: Two-Branch Transformer for Image Forgery Localization
Feb 25, 2023Abstract:Image forgery localization aims to identify forged regions by capturing subtle traces from high-quality discriminative features. In this paper, we propose a Transformer-style network with two feature extraction branches for image forgery localization, and it is named as Two-Branch Transformer (TBFormer). Firstly, two feature extraction branches are elaborately designed, taking advantage of the discriminative stacked Transformer layers, for both RGB and noise domain features. Secondly, an Attention-aware Hierarchical-feature Fusion Module (AHFM) is proposed to effectively fuse hierarchical features from two different domains. Although the two feature extraction branches have the same architecture, their features have significant differences since they are extracted from different domains. We adopt position attention to embed them into a unified feature domain for hierarchical feature investigation. Finally, a Transformer decoder is constructed for feature reconstruction to generate the predicted mask. Extensive experiments on publicly available datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed model.
GAN-based Medical Image Small Region Forgery Detection via a Two-Stage Cascade Framework
May 30, 2022



Abstract:Using generative adversarial network (GAN)\cite{RN90} for data enhancement of medical images is significantly helpful for many computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) tasks. A new attack called CT-GAN has emerged. It can inject or remove lung cancer lesions to CT scans. Because the tampering region may even account for less than 1\% of the original image, even state-of-the-art methods are challenging to detect the traces of such tampering. This paper proposes a cascade framework to detect GAN-based medical image small region forgery like CT-GAN. In the local detection stage, we train the detector network with small sub-images so that interference information in authentic regions will not affect the detector. We use depthwise separable convolution and residual to prevent the detector from over-fitting and enhance the ability to find forged regions through the attention mechanism. The detection results of all sub-images in the same image will be combined into a heatmap. In the global classification stage, using gray level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM) can better extract features of the heatmap. Because the shape and size of the tampered area are uncertain, we train PCA and SVM methods for classification. Our method can classify whether a CT image has been tampered and locate the tampered position. Sufficient experiments show that our method can achieve excellent performance.
Fine-Grained Element Identification in Complaint Text of Internet Fraud
Aug 19, 2021



Abstract:Existing system dealing with online complaint provides a final decision without explanations. We propose to analyse the complaint text of internet fraud in a fine-grained manner. Considering the complaint text includes multiple clauses with various functions, we propose to identify the role of each clause and classify them into different types of fraud element. We construct a large labeled dataset originated from a real finance service platform. We build an element identification model on top of BERT and propose additional two modules to utilize the context of complaint text for better element label classification, namely, global context encoder and label refiner. Experimental results show the effectiveness of our model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge