Fan Liu
Overcoming BS Down-Tilt for Air-Ground ISAC Coverage: Antenna Design, Beamforming and User Scheduling
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication holds great promise for low-altitude economy applications. However, conventional downtilted base stations primarily provide sectorized forward lobes for ground services, failing to sense air targets due to backward blind zones. In this paper, a novel antenna structure is proposed to enable air-ground beam steering, facilitating simultaneous full-space sensing and communication (S&C). Specifically, instead of inserting a reflector behind the antenna array for backlobe mitigation, an omni-steering plate is introduced to collaborate with the active array for omnidirectional beamforming. Building on this hardware innovation, sum S&C mutual information (MI) is maximized, jointly optimizing user scheduling, passive coefficients of the omni-steering plate, and beamforming of the active array. The problem is decomposed into two subproblems: one for optimizing passive coefficients via Riemannian gradient on the manifold, and the other for optimizing user scheduling and active array beamforming. Exploiting relationships among S&C MI, data decoding MMSE, and parameter estimation MMSE, the original subproblem is equivalently transformed into a sum weighted MMSE problem, rigorously established via the Lagrangian and first-order optimality conditions. Simulations show that the proposed algorithm outperforms baselines in sum-MI and MSE, while providing 360 sensing coverage. Beampattern analysis further demonstrates effective user scheduling and accurate target alignment.
Disentangle Object and Non-object Infrared Features via Language Guidance
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Infrared object detection focuses on identifying and locating objects in complex environments (\eg, dark, snow, and rain) where visible imaging cameras are disabled by poor illumination. However, due to low contrast and weak edge information in infrared images, it is challenging to extract discriminative object features for robust detection. To deal with this issue, we propose a novel vision-language representation learning paradigm for infrared object detection. An additional textual supervision with rich semantic information is explored to guide the disentanglement of object and non-object features. Specifically, we propose a Semantic Feature Alignment (SFA) module to align the object features with the corresponding text features. Furthermore, we develop an Object Feature Disentanglement (OFD) module that disentangles text-aligned object features and non-object features by minimizing their correlation. Finally, the disentangled object features are entered into the detection head. In this manner, the detection performance can be remarkably enhanced via more discriminative and less noisy features. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves superior performance on two benchmarks: M\textsuperscript{3}FD (83.7\% mAP), FLIR (86.1\% mAP). Our code will be publicly available once the paper is accepted.
MemGovern: Enhancing Code Agents through Learning from Governed Human Experiences
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:While autonomous software engineering (SWE) agents are reshaping programming paradigms, they currently suffer from a "closed-world" limitation: they attempt to fix bugs from scratch or solely using local context, ignoring the immense historical human experience available on platforms like GitHub. Accessing this open-world experience is hindered by the unstructured and fragmented nature of real-world issue-tracking data. In this paper, we introduce MemGovern, a framework designed to govern and transform raw GitHub data into actionable experiential memory for agents. MemGovern employs experience governance to convert human experience into agent-friendly experience cards and introduces an agentic experience search strategy that enables logic-driven retrieval of human expertise. By producing 135K governed experience cards, MemGovern achieves a significant performance boost, improving resolution rates on the SWE-bench Verified by 4.65%. As a plug-in approach, MemGovern provides a solution for agent-friendly memory infrastructure.
Integrating Low-Altitude SAR Imaging into UAV Data Backhaul
Dec 26, 2025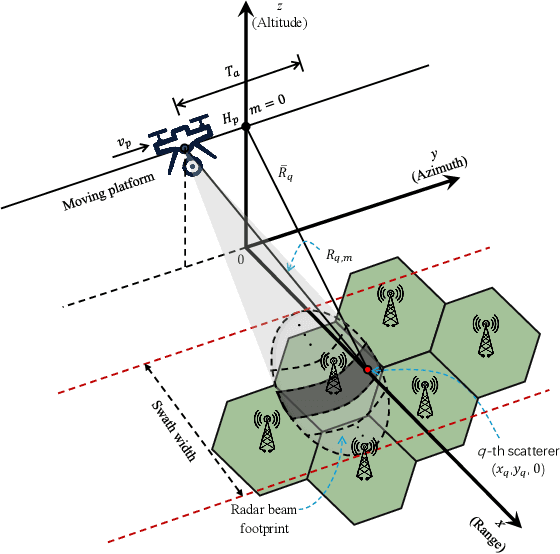
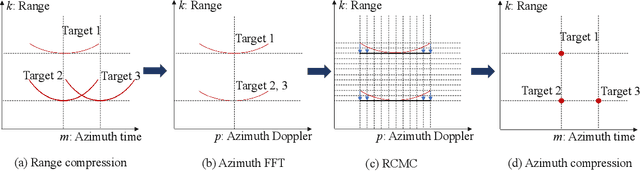
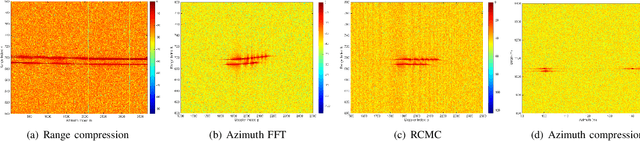
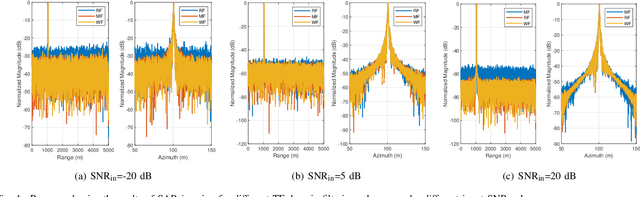
Abstract:Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) deployed on unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) is expected to provide burgeoning imaging services for low-altitude wireless networks (LAWNs), thereby enabling large-scale environmental sensing and timely situational awareness. Conventional SAR systems typically leverages a deterministic radar waveform, while it conflicts with the integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) paradigm by discarding signaling randomness, in whole or in part. In fact, this approach reduces to the uplink pilot sensing in 5G New Radio (NR) with sounding reference signals (SRS), underutilizing data symbols. To explore the potential of data-aided imaging, we develop a low-altitude SAR imaging framework that sufficiently leverages data symbols carried by the native orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) communication waveform. The randomness of modulated data in the temporal-frequency (TF) domain, introduced by non-constant modulus constellations such as quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM), may however severely degrade the imaging quality. To mitigate this effect, we incorporate several TF-domain filtering schemes within a rangeDoppler (RD) imaging framework and evaluate their impact. We further propose using the normalized mean square error (NMSE) of a reference point target's profile as an imaging performance metric. Simulation results with 5G NR parameters demonstrate that data-aided imaging substantially outperforms pilot-only counterpart, accordingly validating the effectiveness of the proposed OFDM-SAR imaging approach in LAWNs.
QoS-Aware Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning for Joint Link Selection and Trajectory Optimization in SAGIN-Supported UAV Mobility Management
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Due to the significant variations in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) altitude and horizontal mobility, it becomes difficult for any single network to ensure continuous and reliable threedimensional coverage. Towards that end, the space-air-ground integrated network (SAGIN) has emerged as an essential architecture for enabling ubiquitous UAV connectivity. To address the pronounced disparities in coverage and signal characteristics across heterogeneous networks, this paper formulates UAV mobility management in SAGIN as a constrained multi-objective joint optimization problem. The formulation couples discrete link selection with continuous trajectory optimization. Building on this, we propose a two-level multi-agent hierarchical deep reinforcement learning (HDRL) framework that decomposes the problem into two alternately solvable subproblems. To map complex link selection decisions into a compact discrete action space, we conceive a double deep Q-network (DDQN) algorithm in the top-level, which achieves stable and high-quality policy learning through double Q-value estimation. To handle the continuous trajectory action space while satisfying quality of service (QoS) constraints, we integrate the maximum-entropy mechanism of the soft actor-critic (SAC) and employ a Lagrangian-based constrained SAC (CSAC) algorithm in the lower-level that dynamically adjusts the Lagrange multipliers to balance constraint satisfaction and policy optimization. Moreover, the proposed algorithm can be extended to multi-UAV scenarios under the centralized training and decentralized execution (CTDE) paradigm, which enables more generalizable policies. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed scheme substantially outperforms existing benchmarks in throughput, link switching frequency and QoS satisfaction.
On Discrete Ambiguity Functions of Random Communication Waveforms
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:This paper provides a fundamental characterization of the discrete ambiguity functions (AFs) of random communication waveforms under arbitrary orthonormal modulation with random constellation symbols, which serve as a key metric for evaluating the delay-Doppler sensing performance in future ISAC applications. A unified analytical framework is developed for two types of AFs, namely the discrete periodic AF (DP-AF) and the fast-slow time AF (FST-AF), where the latter may be seen as a small-Doppler approximation of the DP-AF. By analyzing the expectation of squared AFs, we derive exact closed-form expressions for both the expected sidelobe level (ESL) and the expected integrated sidelobe level (EISL) under the DP-AF and FST-AF formulations. For the DP-AF, we prove that the normalized EISL is identical for all orthogonal waveforms. To gain structural insights, we introduce a matrix representation based on the finite Weyl-Heisenberg (WH) group, where each delay-Doppler shift corresponds to a WH operator acting on the ISAC signal. This WH-group viewpoint yields sharp geometric constraints on the lowest sidelobes: The minimum ESL can only occur along a one-dimensional cut or over a set of widely dispersed delay-Doppler bins. Consequently, no waveform can attain the minimum ESL over any compact two-dimensional region, leading to a no-optimality (no-go) result under the DP-AF framework. For the FST-AF, the closed-form ESL and EISL expressions reveal a constellation-dependent regime governed by its kurtosis: The OFDM modulation achieves the minimum ESL for sub-Gaussian constellations, whereas the OTFS waveform becomes optimal for super-Gaussian constellations. Finally, four representative waveforms, namely, SC, OFDM, OTFS, and AFDM, are examined under both frameworks, and all theoretical results are verified through numerical examples.
Adaptive Matched Filtering for Sensing With Communication Signals in Cluttered Environments
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates the performance of the adaptive matched filtering (AMF) in cluttered environments, particularly when operating with superimposed signals. Since the instantaneous signal-to-clutter-plus-noise ratio (SCNR) is a random variable dependent on the data payload, using it directly as a design objective poses severe practical challenges, such as prohibitive computational burdens and signaling overhead. To address this, we propose shifting the optimization objective from an instantaneous to a statistical metric, which focuses on maximizing the average SCNR over all possible payloads. Due to its analytical intractability, we leverage tools from random matrix theory (RMT) to derive an asymptotic approximation for the average SCNR, which remains accurate even in moderate-dimensional regimes. A key finding from our theoretical analysis is that, for a fixed modulation basis, the PSK achieves a superior average SCNR compared to QAM and the pure Gaussian constellation. Furthermore, for any given constellation, the OFDM achieves a higher average SCNR than SC and AFDM. Then, we propose two pilot design schemes to enhance system performance: a Data-Payload-Dependent (DPD) scheme and a Data-Payload-Independent (DPI) scheme. The DPD approach maximizes the instantaneous SCNR for each transmission. Conversely, the DPI scheme optimizes the average SCNR, offering a flexible trade-off between sensing performance and implementation complexity. Then, we develop two dedicated optimization algorithms for DPD and DPI schemes. In particular, for the DPD problem, we employ fractional optimization and the KKT conditions to derive a closed-form solution. For the DPI problem, we adopt a manifold optimization approach to handle the inherent rank-one constraint efficiently. Simulation results validate the accuracy of our theoretical analysis and demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed methods.
ISAC with Affine Frequency Division Multiplexing: An FMCW-Based Signal Processing Perspective
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates the sensing potential of affine frequency division multiplexing (AFDM) in high-mobility integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) from the perspective of radar waveforms. We introduce an innovative parameter selection criterion that establishes a precise mathematical equivalence between AFDM subcarriers and Nyquist-sampled frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW). This connection not only provides a clear physical insight into AFDM's sensing mechanism but also enables a direct mapping from the DAFT index to delay-Doppler (DD) parameters of wireless channels. Building on this, we develop a novel input-output model in a DD-parameterized DAFT (DD-DAFT) domain for AFDM, which explicitly reveals the inherent DD coupling effect arising from the chirp-channel interaction. Subsequently, we design two matched-filtering sensing algorithms. The first is performed in the time-frequency domain with low complexity, while the second is operated in the DD-DAFT domain to precisely resolve the DD coupling. Simulations show that our algorithms achieve effective pilot-free sensing and demonstrate a fundamental trade-off between sensing performance, communication overhead, and computational complexity. The proposed AFDM outperforms classical AFDM and other variants in most scenarios.
Look Before Switch: Sensing-Assisted Handover in 5G NR V2I Networks
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) has emerged as a promising solution in addressing the challenges of high-mobility scenarios in 5G NR Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) communications. This paper proposes a novel sensing-assisted handover framework that leverages ISAC capabilities to enable precise beamforming and proactive handover decisions. Two sensing-enabled handover triggering algorithms are developed: a distance-based scheme that utilizes estimated spatial positioning, and a probability-based approach that predicts vehicle maneuvers using interacting multiple model extended Kalman filter (IMM-EKF) tracking. The proposed methods eliminate the need for uplink feedback and beam sweeping, thus significantly reducing signaling overhead and handover interruption time. A sensing-assisted NR frame structure and corresponding protocol design are also introduced to support rapid synchronization and access under vehicular mobility. Extensive link-level simulations using real-world map data demonstrate that the proposed framework reduces the average handover interruption time by over 50%, achieves lower handover rates, and enhances overall communication performance.
Ambiguity Function Analysis of AFDM Under Pulse-Shaped Random ISAC Signaling
Nov 06, 2025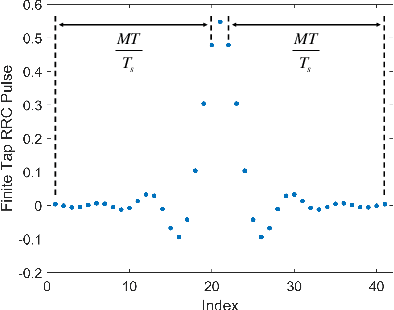
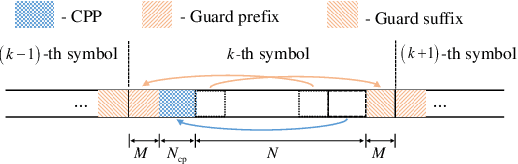
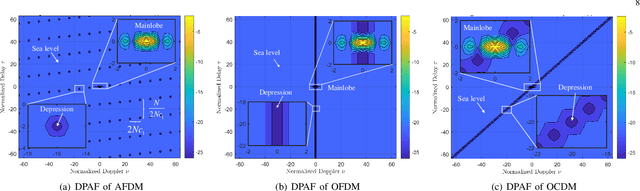
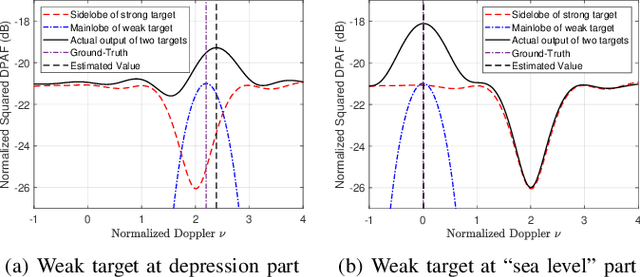
Abstract:This paper investigates the ambiguity function (AF) of the emerging affine frequency division multiplexing (AFDM) waveform for Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) signaling under a pulse shaping regime. Specifically, we first derive the closed-form expression of the average squared discrete period AF (DPAF) for AFDM waveform without pulse shaping, revealing that the AF depends on the parameter $c_1$ and the kurtosis of random communication data, while being independent of the parameter $c_2$. As a step further, we conduct a comprehensive analysis on the AFs of various waveforms, including AFDM, orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) and orthogonal chirp-division multiplexing (OCDM). Our results indicate that all three waveforms exhibit the same number of regular depressions in the sidelobes of their AFs, which incurs performance loss for detecting and estimating weak targets. However, the AFDM waveform can flexibly control the positions of depressions by adjusting the parameter $c_1$, which motivates a novel design approach of the AFDM parameters to mitigate the adverse impact of depressions of the strong target on the weak target. Furthermore, a closed-form expression of the average squared DPAF for pulse-shaped random AFDM waveform is derived, which demonstrates that the pulse shaping filter generates the shaped mainlobe along the delay axis and the rapid roll-off sidelobes along the Doppler axis. Numerical results verify the effectiveness of our theoretical analysis and proposed design methodology for the AFDM modulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge