Christos Masouros
Overcoming BS Down-Tilt for Air-Ground ISAC Coverage: Antenna Design, Beamforming and User Scheduling
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication holds great promise for low-altitude economy applications. However, conventional downtilted base stations primarily provide sectorized forward lobes for ground services, failing to sense air targets due to backward blind zones. In this paper, a novel antenna structure is proposed to enable air-ground beam steering, facilitating simultaneous full-space sensing and communication (S&C). Specifically, instead of inserting a reflector behind the antenna array for backlobe mitigation, an omni-steering plate is introduced to collaborate with the active array for omnidirectional beamforming. Building on this hardware innovation, sum S&C mutual information (MI) is maximized, jointly optimizing user scheduling, passive coefficients of the omni-steering plate, and beamforming of the active array. The problem is decomposed into two subproblems: one for optimizing passive coefficients via Riemannian gradient on the manifold, and the other for optimizing user scheduling and active array beamforming. Exploiting relationships among S&C MI, data decoding MMSE, and parameter estimation MMSE, the original subproblem is equivalently transformed into a sum weighted MMSE problem, rigorously established via the Lagrangian and first-order optimality conditions. Simulations show that the proposed algorithm outperforms baselines in sum-MI and MSE, while providing 360 sensing coverage. Beampattern analysis further demonstrates effective user scheduling and accurate target alignment.
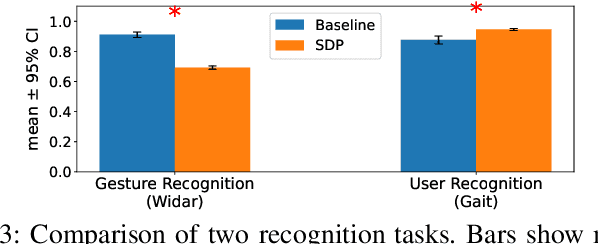
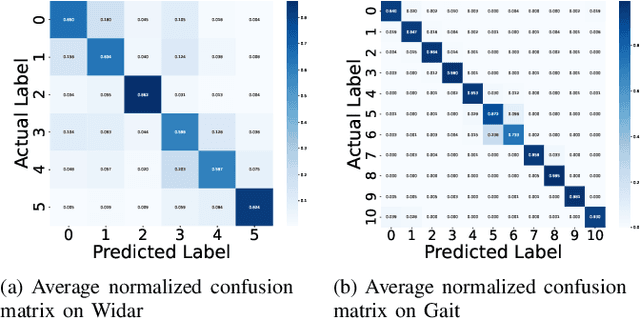
SDP: A Unified Protocol and Benchmarking Framework for Reproducible Wireless Sensing
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Learning-based wireless sensing has made rapid progress, yet the field still lacks a unified and reproducible experimental foundation. Unlike computer vision, wireless sensing relies on hardware-dependent channel measurements whose representations, preprocessing pipelines, and evaluation protocols vary significantly across devices and datasets, hindering fair comparison and reproducibility. This paper proposes the Sensing Data Protocol (SDP), a protocol-level abstraction and unified benchmark for scalable wireless sensing. SDP acts as a standardization layer that decouples learning tasks from hardware heterogeneity. To this end, SDP enforces deterministic physical-layer sanitization, canonical tensor construction, and standardized training and evaluation procedures, decoupling learning performance from hardware-specific artifacts. Rather than introducing task-specific models, SDP establishes a principled protocol foundation for fair evaluation across diverse sensing tasks and platforms. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SDP achieves competitive accuracy while substantially improving stability, reducing inter-seed performance variance by orders of magnitude on complex activity recognition tasks. A real-world experiment using commercial off-the-shelf Wi-Fi hardware further illustrating the protocol's interoperability across heterogeneous hardware. By providing a unified protocol and benchmark, SDP enables reproducible and comparable wireless sensing research and supports the transition from ad hoc experimentation toward reliable engineering practice.
A Uniform Pilot and Data Payload Optimization Framework for OTFS-Based ISAC
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:The orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) signal is considered a promising solution for high-mobility wireless environments. It manages Doppler effects by utilizing delay-Doppler (DD) domain processing. However, the relatively long OTFS frame duration could introduce considerable sensing or communication latency when radar and communication are performed separately. By operating in a dual-functional radar and communication (DFRC) mode, the OTFS system performs sensing and data transmission simultaneously, thereby reducing the resulting latency. Nevertheless, the optimal OTFS DFRC signal strategy remains insufficiently explored. This paper investigates the optimal signal design for OTFS DFRC systems, focusing on pilot symbol design and data symbol power allocation. Specifically, we derive a channel capacity lower bound metric for communication that considers channel estimation errors in OTFS. For sensing, we derive an integrated sidelobe level (ISL), accounting for the randomness of the data symbols alongside the deterministic pilot symbols. Leveraging the above metrics, we formulate an optimization problem that balances radar and communication performance, and then solve it using an alternating optimization framework. We validate the proposed signal through numerical analysis and Monte Carlo simulations. Our analysis shows that OTFS DFRC enforces a deterministic pilot signal that is characterized by a concentrated peak in the DD domain, which furnishes a common structure in the DD domain facilitating sensing and channel estimation, with data multiplexed in other DD grids, thereby unifying sensing and communication within a single OTFS signal. Compared with conventional OTFS signals, the proposed OTFS DFRC signal expands the achievable sensing-communication performance region, delivering at least a 9.45 dB ISL suppression for sensing and a 4.82 dB SINR ratio gain for communication.
Ultra-Massive MIMO with Orthogonal Chirp Division Multiplexing for Near-Field Sensing and Communication Integration
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:This paper integrates the emerging ultra-massive multiple-input multiple-output (UM-MIMO) technique with orthogonal chirp division multiplexing (OCDM) waveform to tackle the challenging near-field integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) problem. Specifically, we conceive a comprehensive ISAC architecture, where an UM-MIMO base station adopts OCDM waveform for communications and a co-located sensing receiver adopts the frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW) detection principle to simplify the associated hardware. For sensing tasks, several OCDM subcarriers, namely, dedicated sensing subcarriers (DSSs), are each transmitted through a dedicated sensing antenna (DSA) within the transmit antenna array. By judiciously designing the DSS selection scheme and optimizing receiver parameters, the FMCW-based sensing receiver can decouple the echo signals from different DSAs with significantly reduced hardware complexity. This setup enables the estimation of ranges and velocities of near-field targets in an antenna-pairwise manner. Moreover, by leveraging the spatial diversity of UM-MIMO, we introduce the concept of virtual bistatic sensing (VIBS), which incorporates the estimates from multiple antenna pairs to achieve high-accuracy target positioning and three-dimensional velocity measurement. The VIBS paradigm is immune to hostile channel environments characterized by spatial non-stationarity and uncorrelated multipath environment. Furthermore, the channel estimation of UM-MIMO OCDM systems enhanced by the sensing results is investigated. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed ISAC scheme enhances sensing accuracy, and also benefits communication performance.
A Sensing Dataset Protocol for Benchmarking and Multi-Task Wireless Sensing
Dec 13, 2025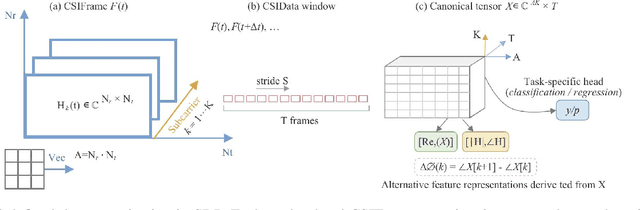
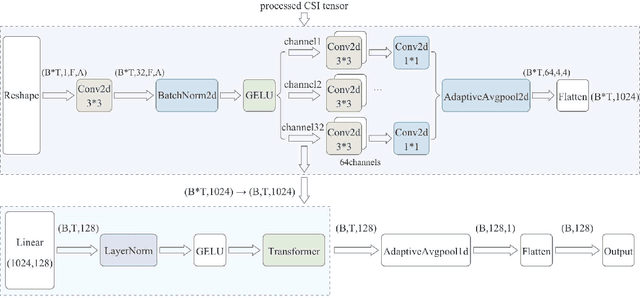
Abstract:Wireless sensing has become a fundamental enabler for intelligent environments, supporting applications such as human detection, activity recognition, localization, and vital sign monitoring. Despite rapid advances, existing datasets and pipelines remain fragmented across sensing modalities, hindering fair comparison, transfer, and reproducibility. We propose the Sensing Dataset Protocol (SDP), a protocol-level specification and benchmark framework for large-scale wireless sensing. SDP defines how heterogeneous wireless signals are mapped into a unified perception data-block schema through lightweight synchronization, frequency-time alignment, and resampling, while a Canonical Polyadic-Alternating Least Squares (CP-ALS) pooling stage provides a task-agnostic representation that preserves multipath, spectral, and temporal structures. Built upon this protocol, a unified benchmark is established for detection, recognition, and vital-sign estimation with consistent preprocessing, training, and evaluation. Experiments under the cross-user split demonstrate that SDP significantly reduces variance (approximately 88%) across seeds while maintaining competitive accuracy and latency, confirming its value as a reproducible foundation for multi-modal and multitask sensing research.
On Discrete Ambiguity Functions of Random Communication Waveforms
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:This paper provides a fundamental characterization of the discrete ambiguity functions (AFs) of random communication waveforms under arbitrary orthonormal modulation with random constellation symbols, which serve as a key metric for evaluating the delay-Doppler sensing performance in future ISAC applications. A unified analytical framework is developed for two types of AFs, namely the discrete periodic AF (DP-AF) and the fast-slow time AF (FST-AF), where the latter may be seen as a small-Doppler approximation of the DP-AF. By analyzing the expectation of squared AFs, we derive exact closed-form expressions for both the expected sidelobe level (ESL) and the expected integrated sidelobe level (EISL) under the DP-AF and FST-AF formulations. For the DP-AF, we prove that the normalized EISL is identical for all orthogonal waveforms. To gain structural insights, we introduce a matrix representation based on the finite Weyl-Heisenberg (WH) group, where each delay-Doppler shift corresponds to a WH operator acting on the ISAC signal. This WH-group viewpoint yields sharp geometric constraints on the lowest sidelobes: The minimum ESL can only occur along a one-dimensional cut or over a set of widely dispersed delay-Doppler bins. Consequently, no waveform can attain the minimum ESL over any compact two-dimensional region, leading to a no-optimality (no-go) result under the DP-AF framework. For the FST-AF, the closed-form ESL and EISL expressions reveal a constellation-dependent regime governed by its kurtosis: The OFDM modulation achieves the minimum ESL for sub-Gaussian constellations, whereas the OTFS waveform becomes optimal for super-Gaussian constellations. Finally, four representative waveforms, namely, SC, OFDM, OTFS, and AFDM, are examined under both frameworks, and all theoretical results are verified through numerical examples.
Look Before Switch: Sensing-Assisted Handover in 5G NR V2I Networks
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) has emerged as a promising solution in addressing the challenges of high-mobility scenarios in 5G NR Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) communications. This paper proposes a novel sensing-assisted handover framework that leverages ISAC capabilities to enable precise beamforming and proactive handover decisions. Two sensing-enabled handover triggering algorithms are developed: a distance-based scheme that utilizes estimated spatial positioning, and a probability-based approach that predicts vehicle maneuvers using interacting multiple model extended Kalman filter (IMM-EKF) tracking. The proposed methods eliminate the need for uplink feedback and beam sweeping, thus significantly reducing signaling overhead and handover interruption time. A sensing-assisted NR frame structure and corresponding protocol design are also introduced to support rapid synchronization and access under vehicular mobility. Extensive link-level simulations using real-world map data demonstrate that the proposed framework reduces the average handover interruption time by over 50%, achieves lower handover rates, and enhances overall communication performance.
From OFDM to AFDM: Enabling Adaptive Integrated Sensing and Communication in High-Mobility Scenarios
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) is a key feature of next-generation wireless networks, enabling a wide range of emerging applications such as vehicle-to-everything (V2X) and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), which operate in high-mobility scenarios. Notably, the wireless channels within these applications typically exhibit severe delay and Doppler spreads. The latter causes serious communication performance degradation in the Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) waveform that is widely adopted in current wireless networks. To address this challenge, the recently proposed Doppler-resilient affine frequency division multiplexing (AFDM) waveform, which uses flexible chirp signals as subcarriers, shows great potential for achieving adaptive ISAC in high-mobility scenarios. This article provides a comprehensive overview of AFDM-ISAC. We begin by presenting the fundamentals of AFDM-ISAC, highlighting its inherent frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW)-like characteristics. Then, we explore its ISAC performance limits by analyzing its diversity order, ambiguity function (AF), and Cramer-Rao Bound (CRB). Finally, we present several effective sensing algorithms and opportunities for AFDM-ISAC, with the aim of sparking new ideas in this emerging field.
Integrated Sensing and Communication with Tri-Hybrid Beamforming Across Electromagnetically Reconfigurable Antennas
Oct 16, 2025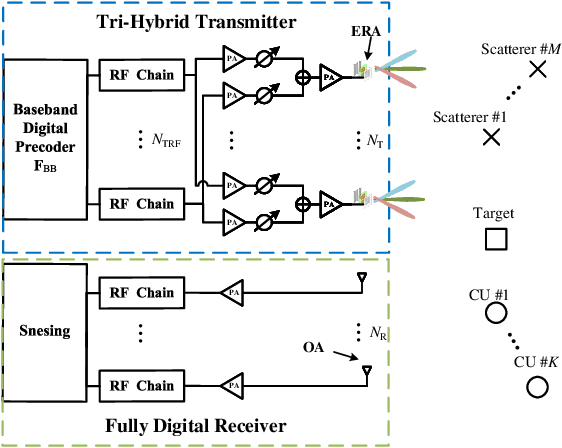
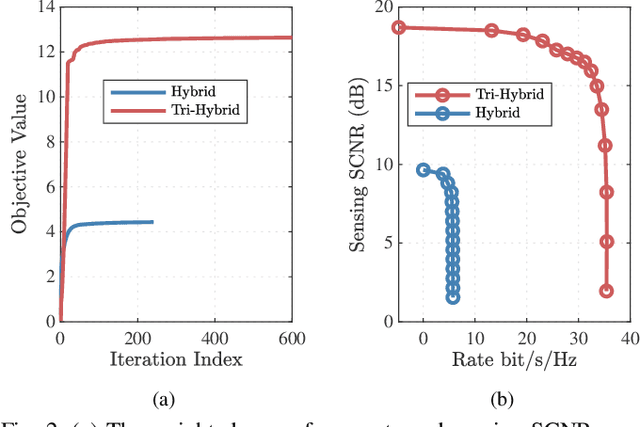
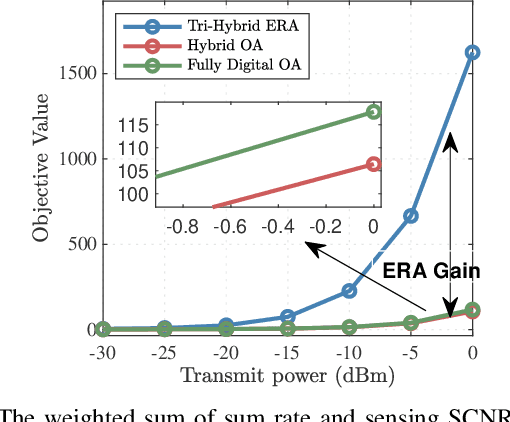
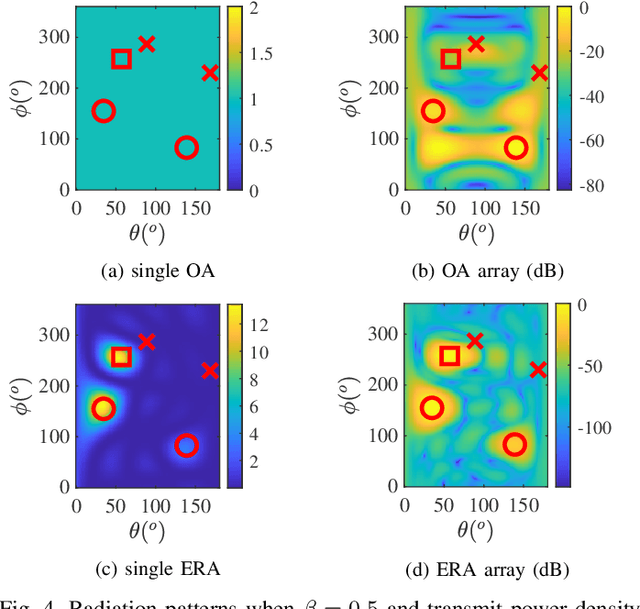
Abstract:Beamforming with a sufficient number of antennas is one of the most significant technologies for both Multi-user (MU) Multiple-input Multiple-output (MIMO) communication and MIMO radar sensing in Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) systems. However, its performance suffers from limited Degrees of Freedom (DoFs) in conventional hybrid beamforming systems. To overcome this, we propose an Electromagnetically Reconfigurable Antenna (ERA)-aided ISAC system, where transmit ERAs dynamically adjust their radiation patterns to enhance system DoFs and improve overall performance. Specifically, we design a tri-hybrid beamforming optimization framework combining digital, analog, and Electromagnetic (EM) beamforming to jointly maximize communication rate and sensing Signal-to-Clutter-plus-Noise Ratio (SCNR). Furthermore, an integrated Fractional Programming (FP) and Manifold Optimization (MO) approach is developed to transform the problem into tractable subproblems with closed-form updates. Simulation results verify that the proposed ERA-ISAC system achieves almost 10 dB Sensing and Communication (S&C) performance gain compared to its conventional hybrid beamforming counterparts with Omnidirectional Antenna (OA).
Integrated Sensing and Communication: Towards Multifunctional Perceptive Network
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:The capacity-maximization design philosophy has driven the growth of wireless networks for decades. However, with the slowdown in recent data traffic demand, the mobile industry can no longer rely solely on communication services to sustain development. In response, Integrated Sensing and Communications (ISAC) has emerged as a transformative solution, embedding sensing capabilities into communication networks to enable multifunctional wireless systems. This paradigm shift expands the role of networks from sole data transmission to versatile platforms supporting diverse applications. In this review, we provide a bird's-eye view of ISAC for new researchers, highlighting key challenges, opportunities, and application scenarios to guide future exploration in this field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge