Yu Zhou
National Laboratory of Pattern Recognition, Institute of Automation, CAS, Beijing, China, Fanyu AI Laboratory, Zhongke Fanyu Technology Co., Ltd, Beijing, China
Point2Insert: Video Object Insertion via Sparse Point Guidance
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:This paper introduces Point2Insert, a sparse-point-based framework for flexible and user-friendly object insertion in videos, motivated by the growing popularity of accurate, low-effort object placement. Existing approaches face two major challenges: mask-based insertion methods require labor-intensive mask annotations, while instruction-based methods struggle to place objects at precise locations. Point2Insert addresses these issues by requiring only a small number of sparse points instead of dense masks, eliminating the need for tedious mask drawing. Specifically, it supports both positive and negative points to indicate regions that are suitable or unsuitable for insertion, enabling fine-grained spatial control over object locations. The training of Point2Insert consists of two stages. In Stage 1, we train an insertion model that generates objects in given regions conditioned on either sparse-point prompts or a binary mask. In Stage 2, we further train the model on paired videos synthesized by an object removal model, adapting it to video insertion. Moreover, motivated by the higher insertion success rate of mask-guided editing, we leverage a mask-guided insertion model as a teacher to distill reliable insertion behavior into the point-guided model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Point2Insert consistently outperforms strong baselines and even surpasses models with $\times$10 more parameters.
STEP3-VL-10B Technical Report
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:We present STEP3-VL-10B, a lightweight open-source foundation model designed to redefine the trade-off between compact efficiency and frontier-level multimodal intelligence. STEP3-VL-10B is realized through two strategic shifts: first, a unified, fully unfrozen pre-training strategy on 1.2T multimodal tokens that integrates a language-aligned Perception Encoder with a Qwen3-8B decoder to establish intrinsic vision-language synergy; and second, a scaled post-training pipeline featuring over 1k iterations of reinforcement learning. Crucially, we implement Parallel Coordinated Reasoning (PaCoRe) to scale test-time compute, allocating resources to scalable perceptual reasoning that explores and synthesizes diverse visual hypotheses. Consequently, despite its compact 10B footprint, STEP3-VL-10B rivals or surpasses models 10$\times$-20$\times$ larger (e.g., GLM-4.6V-106B, Qwen3-VL-235B) and top-tier proprietary flagships like Gemini 2.5 Pro and Seed-1.5-VL. Delivering best-in-class performance, it records 92.2% on MMBench and 80.11% on MMMU, while excelling in complex reasoning with 94.43% on AIME2025 and 75.95% on MathVision. We release the full model suite to provide the community with a powerful, efficient, and reproducible baseline.
PROMISE: Process Reward Models Unlock Test-Time Scaling Laws in Generative Recommendations
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Generative Recommendation has emerged as a promising paradigm, reformulating recommendation as a sequence-to-sequence generation task over hierarchical Semantic IDs. However, existing methods suffer from a critical issue we term Semantic Drift, where errors in early, high-level tokens irreversibly divert the generation trajectory into irrelevant semantic subspaces. Inspired by Process Reward Models (PRMs) that enhance reasoning in Large Language Models, we propose Promise, a novel framework that integrates dense, step-by-step verification into generative models. Promise features a lightweight PRM to assess the quality of intermediate inference steps, coupled with a PRM-guided Beam Search strategy that leverages dense feedback to dynamically prune erroneous branches. Crucially, our approach unlocks Test-Time Scaling Laws for recommender systems: by increasing inference compute, smaller models can match or surpass larger models. Extensive offline experiments and online A/B tests on a large-scale platform demonstrate that Promise effectively mitigates Semantic Drift, significantly improving recommendation accuracy while enabling efficient deployment.
HiSciBench: A Hierarchical Multi-disciplinary Benchmark for Scientific Intelligence from Reading to Discovery
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) and multimodal foundation models has sparked growing interest in their potential for scientific research. However, scientific intelligence encompasses a broad spectrum of abilities ranging from understanding fundamental knowledge to conducting creative discovery, and existing benchmarks remain fragmented. Most focus on narrow tasks and fail to reflect the hierarchical and multi-disciplinary nature of real scientific inquiry. We introduce \textbf{HiSciBench}, a hierarchical benchmark designed to evaluate foundation models across five levels that mirror the complete scientific workflow: \textit{Scientific Literacy} (L1), \textit{Literature Parsing} (L2), \textit{Literature-based Question Answering} (L3), \textit{Literature Review Generation} (L4), and \textit{Scientific Discovery} (L5). HiSciBench contains 8,735 carefully curated instances spanning six major scientific disciplines, including mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology, geography, and astronomy, and supports multimodal inputs including text, equations, figures, and tables, as well as cross-lingual evaluation. Unlike prior benchmarks that assess isolated abilities, HiSciBench provides an integrated, dependency-aware framework that enables detailed diagnosis of model capabilities across different stages of scientific reasoning. Comprehensive evaluations of leading models, including GPT-5, DeepSeek-R1, and several multimodal systems, reveal substantial performance gaps: while models achieve up to 69\% accuracy on basic literacy tasks, performance declines sharply to 25\% on discovery-level challenges. HiSciBench establishes a new standard for evaluating scientific Intelligence and offers actionable insights for developing models that are not only more capable but also more reliable. The benchmark will be publicly released to facilitate future research.
UniPercept: Towards Unified Perceptual-Level Image Understanding across Aesthetics, Quality, Structure, and Texture
Dec 25, 2025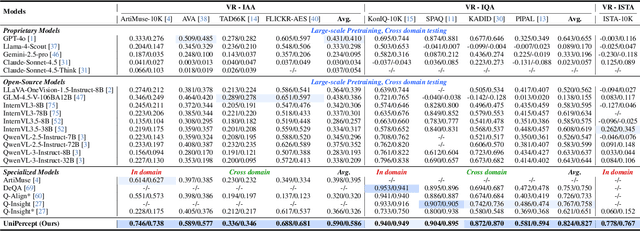
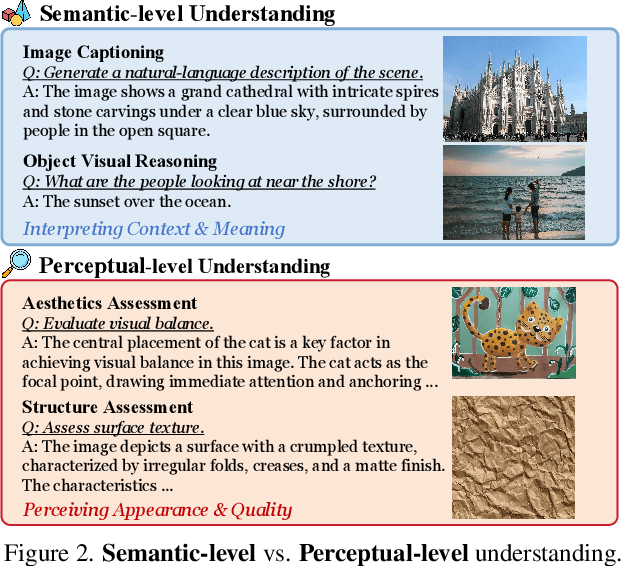
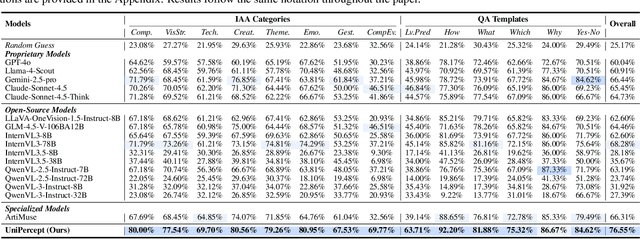
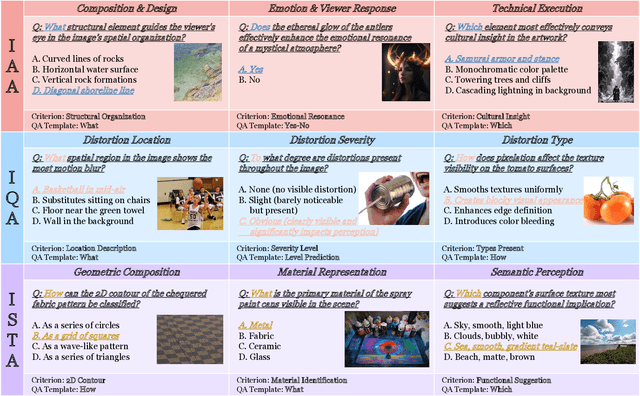
Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable progress in visual understanding tasks such as visual grounding, segmentation, and captioning. However, their ability to perceive perceptual-level image features remains limited. In this work, we present UniPercept-Bench, a unified framework for perceptual-level image understanding across three key domains: Aesthetics, Quality, Structure and Texture. We establish a hierarchical definition system and construct large-scale datasets to evaluate perceptual-level image understanding. Based on this foundation, we develop a strong baseline UniPercept trained via Domain-Adaptive Pre-Training and Task-Aligned RL, enabling robust generalization across both Visual Rating (VR) and Visual Question Answering (VQA) tasks. UniPercept outperforms existing MLLMs on perceptual-level image understanding and can serve as a plug-and-play reward model for text-to-image generation. This work defines Perceptual-Level Image Understanding in the era of MLLMs and, through the introduction of a comprehensive benchmark together with a strong baseline, provides a solid foundation for advancing perceptual-level multimodal image understanding.
Mirage Persistent Kernel: A Compiler and Runtime for Mega-Kernelizing Tensor Programs
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:We introduce Mirage Persistent Kernel (MPK), the first compiler and runtime system that automatically transforms multi-GPU model inference into a single high-performance megakernel. MPK introduces an SM-level graph representation that captures data dependencies at the granularity of individual streaming multiprocessors (SMs), enabling cross-operator software pipelining, fine-grained kernel overlap, and other previously infeasible GPU optimizations. The MPK compiler lowers tensor programs into highly optimized SM-level task graphs and generates optimized CUDA implementations for all tasks, while the MPK in-kernel parallel runtime executes these tasks within a single mega-kernel using decentralized scheduling across SMs. Together, these components provide end-to-end kernel fusion with minimal developer effort, while preserving the flexibility of existing programming models. Our evaluation shows that MPK significantly outperforms existing kernel-per-operator LLM serving systems by reducing end-to-end inference latency by up to 1.7x, pushing LLM inference performance close to hardware limits. MPK is publicly available at https://github.com/mirage-project/mirage.
EmoCaliber: Advancing Reliable Visual Emotion Comprehension via Confidence Verbalization and Calibration
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Visual Emotion Comprehension (VEC) aims to infer sentiment polarities or emotion categories from affective cues embedded in images. In recent years, Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have established a popular paradigm in VEC, leveraging their generalizability to unify VEC tasks defined under diverse emotion taxonomies. While this paradigm achieves notable success, it typically formulates VEC as a deterministic task, requiring the model to output a single, definitive emotion label for each image. Such a formulation insufficiently accounts for the inherent subjectivity of emotion perception, overlooking alternative interpretations that may be equally plausible to different viewers. To address this limitation, we propose equipping MLLMs with capabilities to verbalize their confidence in emotion predictions. This additional signal provides users with an estimate of both the plausibility of alternative interpretations and the MLLMs' self-assessed competence, thereby enhancing reliability in practice. Building on this insight, we introduce a three-stage training framework that progressively endows with structured reasoning, teaches to verbalize confidence, and calibrates confidence expression, culminating in EmoCaliber, a confidence-aware MLLM for VEC. Through fair and comprehensive evaluations on the unified benchmark VECBench, EmoCaliber demonstrates overall superiority against existing methods in both emotion prediction and confidence estimation. These results validate the effectiveness of our approach and mark a feasible step toward more reliable VEC systems. Project page: https://github.com/wdqqdw/EmoCaliber.
MuSc-V2: Zero-Shot Multimodal Industrial Anomaly Classification and Segmentation with Mutual Scoring of Unlabeled Samples
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Zero-shot anomaly classification (AC) and segmentation (AS) methods aim to identify and outline defects without using any labeled samples. In this paper, we reveal a key property that is overlooked by existing methods: normal image patches across industrial products typically find many other similar patches, not only in 2D appearance but also in 3D shapes, while anomalies remain diverse and isolated. To explicitly leverage this discriminative property, we propose a Mutual Scoring framework (MuSc-V2) for zero-shot AC/AS, which flexibly supports single 2D/3D or multimodality. Specifically, our method begins by improving 3D representation through Iterative Point Grouping (IPG), which reduces false positives from discontinuous surfaces. Then we use Similarity Neighborhood Aggregation with Multi-Degrees (SNAMD) to fuse 2D/3D neighborhood cues into more discriminative multi-scale patch features for mutual scoring. The core comprises a Mutual Scoring Mechanism (MSM) that lets samples within each modality to assign score to each other, and Cross-modal Anomaly Enhancement (CAE) that fuses 2D and 3D scores to recover modality-specific missing anomalies. Finally, Re-scoring with Constrained Neighborhood (RsCon) suppresses false classification based on similarity to more representative samples. Our framework flexibly works on both the full dataset and smaller subsets with consistently robust performance, ensuring seamless adaptability across diverse product lines. In aid of the novel framework, MuSc-V2 achieves significant performance improvements: a $\textbf{+23.7\%}$ AP gain on the MVTec 3D-AD dataset and a $\textbf{+19.3\%}$ boost on the Eyecandies dataset, surpassing previous zero-shot benchmarks and even outperforming most few-shot methods. The code will be available at The code will be available at \href{https://github.com/HUST-SLOW/MuSc-V2}{https://github.com/HUST-SLOW/MuSc-V2}.
When Eyes and Ears Disagree: Can MLLMs Discern Audio-Visual Confusion?
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Can Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) discern confused objects that are visually present but audio-absent? To study this, we introduce a new benchmark, AV-ConfuseBench, which simulates an ``Audio-Visual Confusion'' scene by modifying the corresponding sound of an object in the video, e.g., mute the sounding object and ask MLLMs Is there a/an muted-object sound''. Experimental results reveal that MLLMs, such as Qwen2.5-Omni and Gemini 2.5, struggle to discriminate non-existent audio due to visually dominated reasoning. Motivated by this observation, we introduce RL-CoMM, a Reinforcement Learning-based Collaborative Multi-MLLM that is built upon the Qwen2.5-Omni foundation. RL-CoMM includes two stages: 1) To alleviate visually dominated ambiguities, we introduce an external model, a Large Audio Language Model (LALM), as the reference model to generate audio-only reasoning. Then, we design a Step-wise Reasoning Reward function that enables MLLMs to self-improve audio-visual reasoning with the audio-only reference. 2) To ensure an accurate answer prediction, we introduce Answer-centered Confidence Optimization to reduce the uncertainty of potential heterogeneous reasoning differences. Extensive experiments on audio-visual question answering and audio-visual hallucination show that RL-CoMM improves the accuracy by 10~30\% over the baseline model with limited training data. Follow: https://github.com/rikeilong/AVConfusion.
SUGAR: Learning Skeleton Representation with Visual-Motion Knowledge for Action Recognition
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) hold rich implicit knowledge and powerful transferability. In this paper, we explore the combination of LLMs with the human skeleton to perform action classification and description. However, when treating LLM as a recognizer, two questions arise: 1) How can LLMs understand skeleton? 2) How can LLMs distinguish among actions? To address these problems, we introduce a novel paradigm named learning Skeleton representation with visUal-motion knowledGe for Action Recognition (SUGAR). In our pipeline, we first utilize off-the-shelf large-scale video models as a knowledge base to generate visual, motion information related to actions. Then, we propose to supervise skeleton learning through this prior knowledge to yield discrete representations. Finally, we use the LLM with untouched pre-training weights to understand these representations and generate the desired action targets and descriptions. Notably, we present a Temporal Query Projection (TQP) module to continuously model the skeleton signals with long sequences. Experiments on several skeleton-based action classification benchmarks demonstrate the efficacy of our SUGAR. Moreover, experiments on zero-shot scenarios show that SUGAR is more versatile than linear-based methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge