Yongbing Zhang
PathReasoner-R1: Instilling Structured Reasoning into Pathology Vision-Language Model via Knowledge-Guided Policy Optimization
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are advancing computational pathology with superior visual understanding capabilities. However, current systems often reduce diagnosis to directly output conclusions without verifiable evidence-linked reasoning, which severely limits clinical trust and hinders expert error rectification. To address these barriers, we construct PathReasoner, the first large-scale dataset of whole-slide image (WSI) reasoning. Unlike previous work reliant on unverified distillation, we develop a rigorous knowledge-guided generation pipeline. By leveraging medical knowledge graphs, we explicitly align structured pathological findings and clinical reasoning with diagnoses, generating over 20K high-quality instructional samples. Based on the database, we propose PathReasoner-R1, which synergizes trajectory-masked supervised fine-tuning with reasoning-oriented reinforcement learning to instill structured chain-of-thought capabilities. To ensure medical rigor, we engineer a knowledge-aware multi-granular reward function incorporating an Entity Reward mechanism strictly aligned with knowledge graphs. This effectively guides the model to optimize for logical consistency rather than mere outcome matching, thereby enhancing robustness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PathReasoner-R1 achieves state-of-the-art performance on both PathReasoner and public benchmarks across various image scales, equipping pathology models with transparent, clinically grounded reasoning capabilities. Dataset and code are available at https://github.com/cyclexfy/PathReasoner-R1.
Toward Auditable Neuro-Symbolic Reasoning in Pathology: SQL as an Explicit Trace of Evidence
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Automated pathology image analysis is central to clinical diagnosis, but clinicians still ask which slide features drive a model's decision and why. Vision-language models can produce natural language explanations, but these are often correlational and lack verifiable evidence. In this paper, we introduce an SQL-centered agentic framework that enables both feature measurement and reasoning to be auditable. Specifically, after extracting human-interpretable cellular features, Feature Reasoning Agents compose and execute SQL queries over feature tables to aggregate visual evidence into quantitative findings. A Knowledge Comparison Agent then evaluates these findings against established pathological knowledge, mirroring how pathologists justify diagnoses from measurable observations. Extensive experiments evaluated on two pathology visual question answering datasets demonstrate our method improves interpretability and decision traceability while producing executable SQL traces that link cellular measurements to diagnostic conclusions.
PathFLIP: Fine-grained Language-Image Pretraining for Versatile Computational Pathology
Dec 19, 2025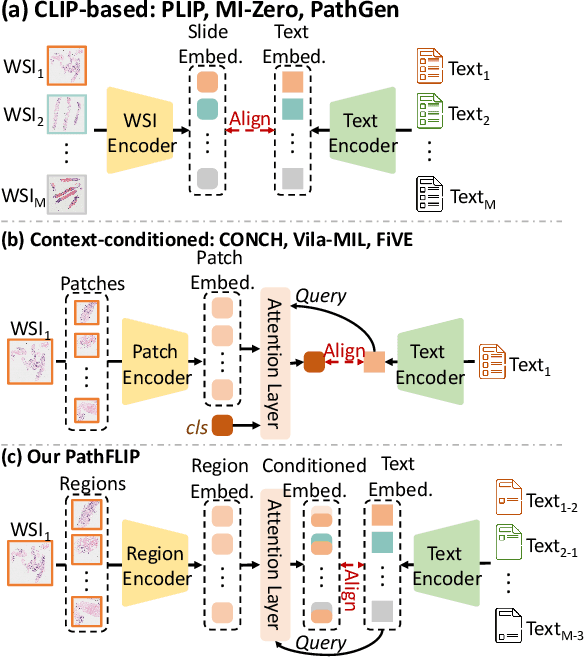
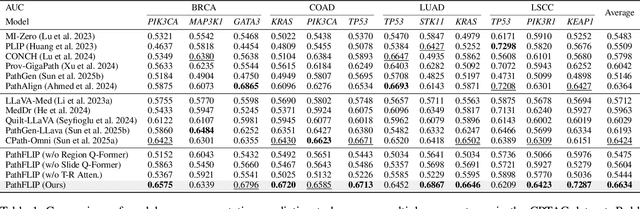
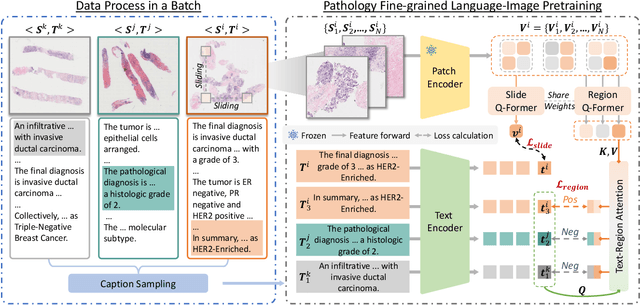
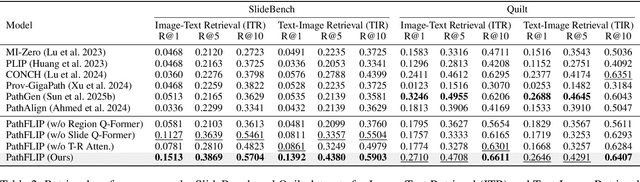
Abstract:While Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have achieved notable progress in computational pathology (CPath), the gigapixel scale and spatial heterogeneity of Whole Slide Images (WSIs) continue to pose challenges for multimodal understanding. Existing alignment methods struggle to capture fine-grained correspondences between textual descriptions and visual cues across thousands of patches from a slide, compromising their performance on downstream tasks. In this paper, we propose PathFLIP (Pathology Fine-grained Language-Image Pretraining), a novel framework for holistic WSI interpretation. PathFLIP decomposes slide-level captions into region-level subcaptions and generates text-conditioned region embeddings to facilitate precise visual-language grounding. By harnessing Large Language Models (LLMs), PathFLIP can seamlessly follow diverse clinical instructions and adapt to varied diagnostic contexts. Furthermore, it exhibits versatile capabilities across multiple paradigms, efficiently handling slide-level classification and retrieval, fine-grained lesion localization, and instruction following. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PathFLIP outperforms existing large-scale pathological VLMs on four representative benchmarks while requiring significantly less training data, paving the way for fine-grained, instruction-aware WSI interpretation in clinical practice.
A Semantically Enhanced Generative Foundation Model Improves Pathological Image Synthesis
Dec 16, 2025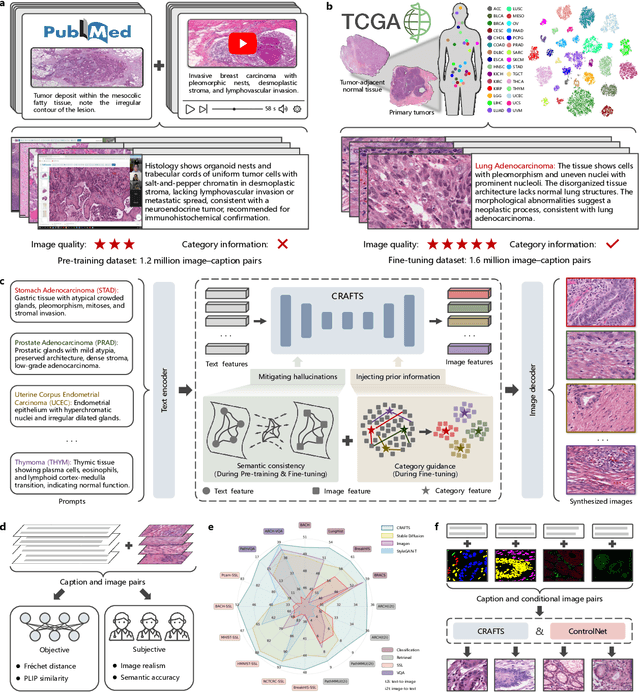
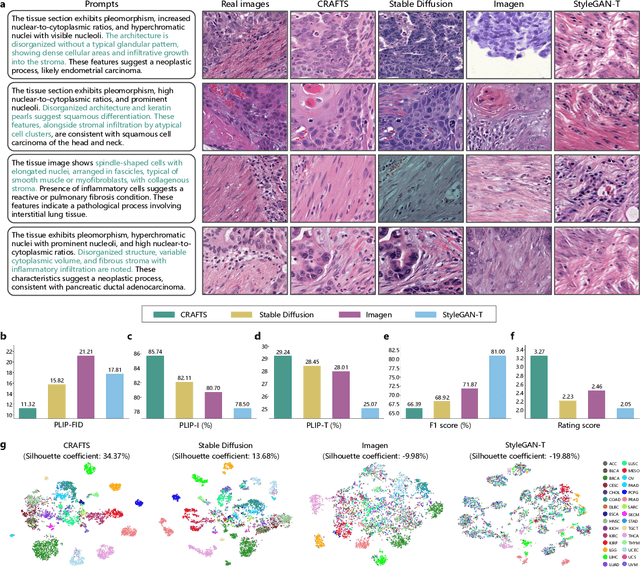
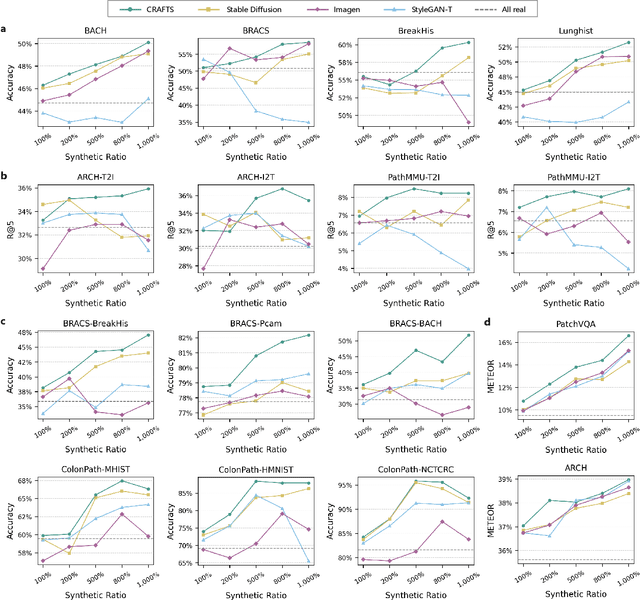
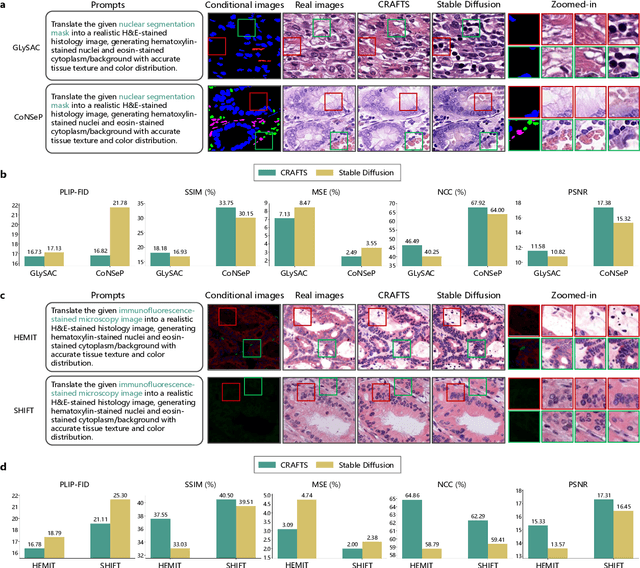
Abstract:The development of clinical-grade artificial intelligence in pathology is limited by the scarcity of diverse, high-quality annotated datasets. Generative models offer a potential solution but suffer from semantic instability and morphological hallucinations that compromise diagnostic reliability. To address this challenge, we introduce a Correlation-Regulated Alignment Framework for Tissue Synthesis (CRAFTS), the first generative foundation model for pathology-specific text-to-image synthesis. By leveraging a dual-stage training strategy on approximately 2.8 million image-caption pairs, CRAFTS incorporates a novel alignment mechanism that suppresses semantic drift to ensure biological accuracy. This model generates diverse pathological images spanning 30 cancer types, with quality rigorously validated by objective metrics and pathologist evaluations. Furthermore, CRAFTS-augmented datasets enhance the performance across various clinical tasks, including classification, cross-modal retrieval, self-supervised learning, and visual question answering. In addition, coupling CRAFTS with ControlNet enables precise control over tissue architecture from inputs such as nuclear segmentation masks and fluorescence images. By overcoming the critical barriers of data scarcity and privacy concerns, CRAFTS provides a limitless source of diverse, annotated histology data, effectively unlocking the creation of robust diagnostic tools for rare and complex cancer phenotypes.
PathMR: Multimodal Visual Reasoning for Interpretable Pathology Diagnosis
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:Deep learning based automated pathological diagnosis has markedly improved diagnostic efficiency and reduced variability between observers, yet its clinical adoption remains limited by opaque model decisions and a lack of traceable rationale. To address this, recent multimodal visual reasoning architectures provide a unified framework that generates segmentation masks at the pixel level alongside semantically aligned textual explanations. By localizing lesion regions and producing expert style diagnostic narratives, these models deliver the transparent and interpretable insights necessary for dependable AI assisted pathology. Building on these advancements, we propose PathMR, a cell-level Multimodal visual Reasoning framework for Pathological image analysis. Given a pathological image and a textual query, PathMR generates expert-level diagnostic explanations while simultaneously predicting cell distribution patterns. To benchmark its performance, we evaluated our approach on the publicly available PathGen dataset as well as on our newly developed GADVR dataset. Extensive experiments on these two datasets demonstrate that PathMR consistently outperforms state-of-the-art visual reasoning methods in text generation quality, segmentation accuracy, and cross-modal alignment. These results highlight the potential of PathMR for improving interpretability in AI-driven pathological diagnosis. The code will be publicly available in https://github.com/zhangye-zoe/PathMR.
IPGPhormer: Interpretable Pathology Graph-Transformer for Survival Analysis
Aug 17, 2025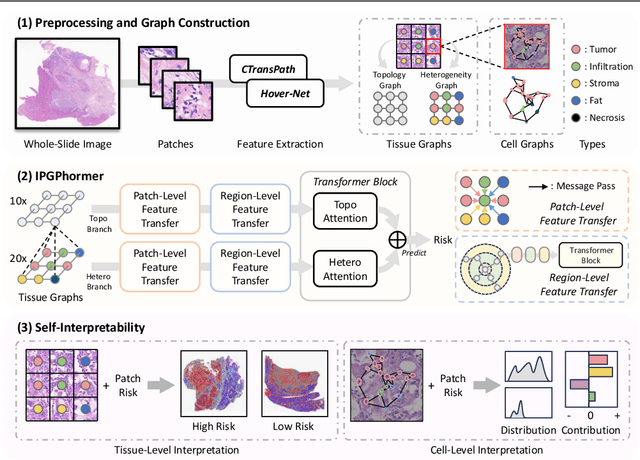
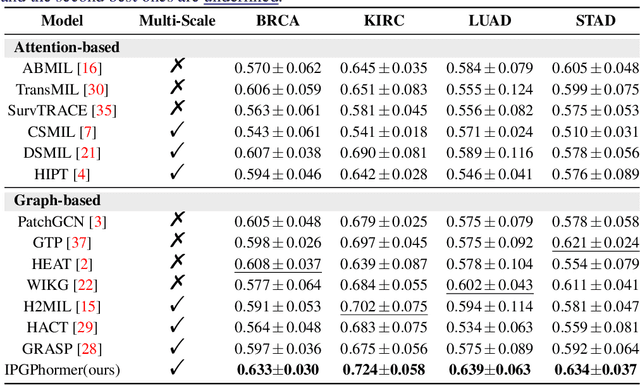
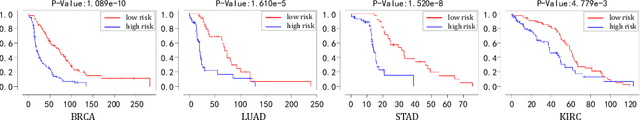
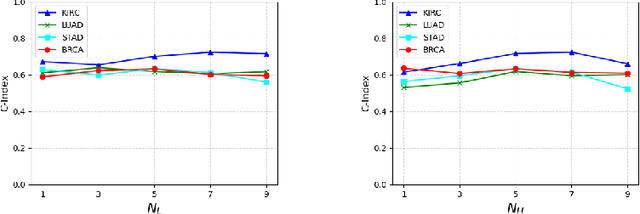
Abstract:Pathological images play an essential role in cancer prognosis, while survival analysis, which integrates computational techniques, can predict critical clinical events such as patient mortality or disease recurrence from whole-slide images (WSIs). Recent advancements in multiple instance learning have significantly improved the efficiency of survival analysis. However, existing methods often struggle to balance the modeling of long-range spatial relationships with local contextual dependencies and typically lack inherent interpretability, limiting their clinical utility. To address these challenges, we propose the Interpretable Pathology Graph-Transformer (IPGPhormer), a novel framework that captures the characteristics of the tumor microenvironment and models their spatial dependencies across the tissue. IPGPhormer uniquely provides interpretability at both tissue and cellular levels without requiring post-hoc manual annotations, enabling detailed analyses of individual WSIs and cross-cohort assessments. Comprehensive evaluations on four public benchmark datasets demonstrate that IPGPhormer outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both predictive accuracy and interpretability. In summary, our method, IPGPhormer, offers a promising tool for cancer prognosis assessment, paving the way for more reliable and interpretable decision-support systems in pathology. The code is publicly available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/IPGPhormer-6EEB.
AHDMIL: Asymmetric Hierarchical Distillation Multi-Instance Learning for Fast and Accurate Whole-Slide Image Classification
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Although multi-instance learning (MIL) has succeeded in pathological image classification, it faces the challenge of high inference costs due to the need to process thousands of patches from each gigapixel whole slide image (WSI). To address this, we propose AHDMIL, an Asymmetric Hierarchical Distillation Multi-Instance Learning framework that enables fast and accurate classification by eliminating irrelevant patches through a two-step training process. AHDMIL comprises two key components: the Dynamic Multi-Instance Network (DMIN), which operates on high-resolution WSIs, and the Dual-Branch Lightweight Instance Pre-screening Network (DB-LIPN), which analyzes corresponding low-resolution counterparts. In the first step, self-distillation (SD), DMIN is trained for WSI classification while generating per-instance attention scores to identify irrelevant patches. These scores guide the second step, asymmetric distillation (AD), where DB-LIPN learns to predict the relevance of each low-resolution patch. The relevant patches predicted by DB-LIPN have spatial correspondence with patches in high-resolution WSIs, which are used for fine-tuning and efficient inference of DMIN. In addition, we design the first Chebyshev-polynomial-based Kolmogorov-Arnold (CKA) classifier in computational pathology, which improves classification performance through learnable activation layers. Extensive experiments on four public datasets demonstrate that AHDMIL consistently outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods in both classification performance and inference speed. For example, on the Camelyon16 dataset, it achieves a relative improvement of 5.3% in accuracy and accelerates inference by 1.2.times. Across all datasets, area under the curve (AUC), accuracy, f1 score, and brier score show consistent gains, with average inference speedups ranging from 1.2 to 2.1 times. The code is available.
The Four Color Theorem for Cell Instance Segmentation
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Cell instance segmentation is critical to analyzing biomedical images, yet accurately distinguishing tightly touching cells remains a persistent challenge. Existing instance segmentation frameworks, including detection-based, contour-based, and distance mapping-based approaches, have made significant progress, but balancing model performance with computational efficiency remains an open problem. In this paper, we propose a novel cell instance segmentation method inspired by the four-color theorem. By conceptualizing cells as countries and tissues as oceans, we introduce a four-color encoding scheme that ensures adjacent instances receive distinct labels. This reformulation transforms instance segmentation into a constrained semantic segmentation problem with only four predicted classes, substantially simplifying the instance differentiation process. To solve the training instability caused by the non-uniqueness of four-color encoding, we design an asymptotic training strategy and encoding transformation method. Extensive experiments on various modes demonstrate our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance. The code is available at https://github.com/zhangye-zoe/FCIS.
RadioDUN: A Physics-Inspired Deep Unfolding Network for Radio Map Estimation
Jun 10, 2025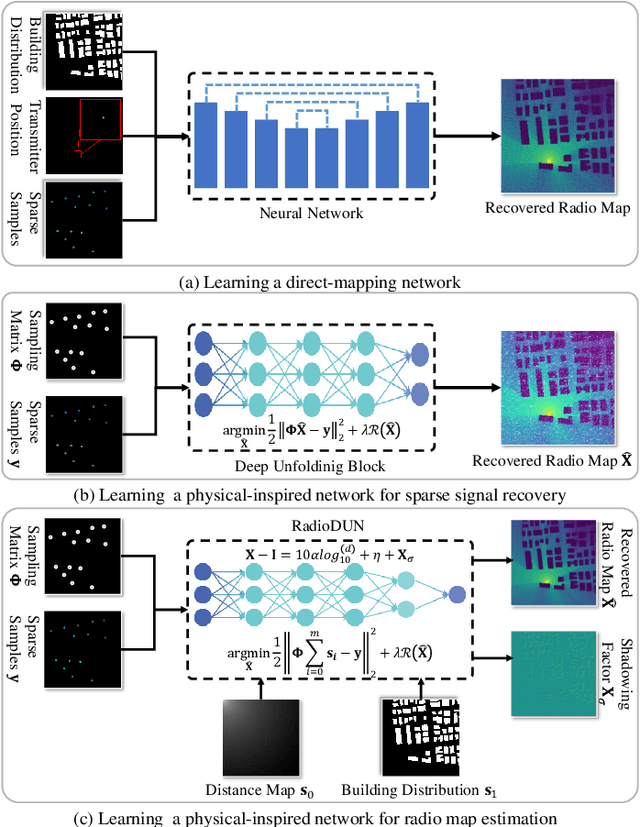
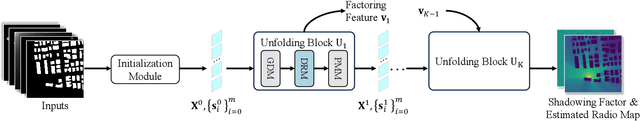
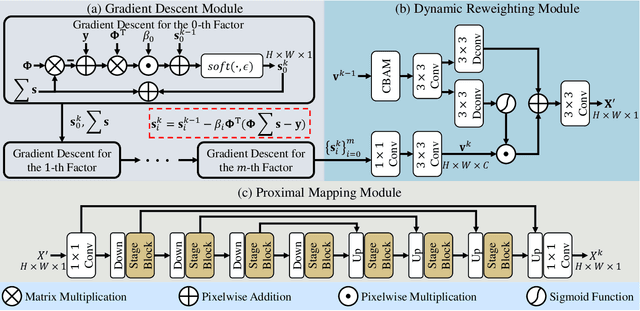
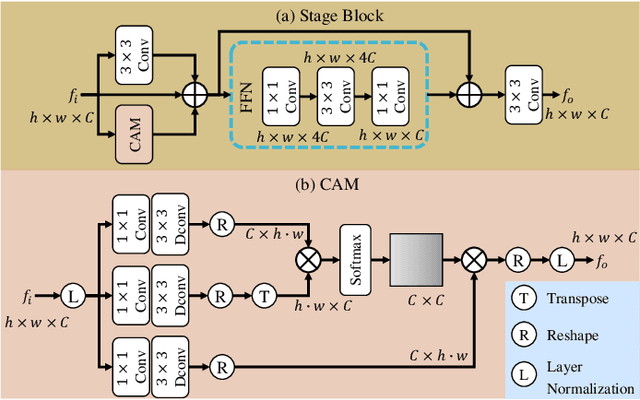
Abstract:The radio map represents the spatial distribution of spectrum resources within a region, supporting efficient resource allocation and interference mitigation. However, it is difficult to construct a dense radio map as a limited number of samples can be measured in practical scenarios. While existing works have used deep learning to estimate dense radio maps from sparse samples, they are hard to integrate with the physical characteristics of the radio map. To address this challenge, we cast radio map estimation as the sparse signal recovery problem. A physical propagation model is further incorporated to decompose the problem into multiple factor optimization sub-problems, thereby reducing recovery complexity. Inspired by the existing compressive sensing methods, we propose the Radio Deep Unfolding Network (RadioDUN) to unfold the optimization process, achieving adaptive parameter adjusting and prior fitting in a learnable manner. To account for the radio propagation characteristics, we develop a dynamic reweighting module (DRM) to adaptively model the importance of each factor for the radio map. Inspired by the shadowing factor in the physical propagation model, we integrate obstacle-related factors to express the obstacle-induced signal stochastic decay. The shadowing loss is further designed to constrain the factor prediction and act as a supplementary supervised objective, which enhances the performance of RadioDUN. Extensive experiments have been conducted to demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods. Our code will be made publicly available upon publication.
Category Prompt Mamba Network for Nuclei Segmentation and Classification
Mar 13, 2025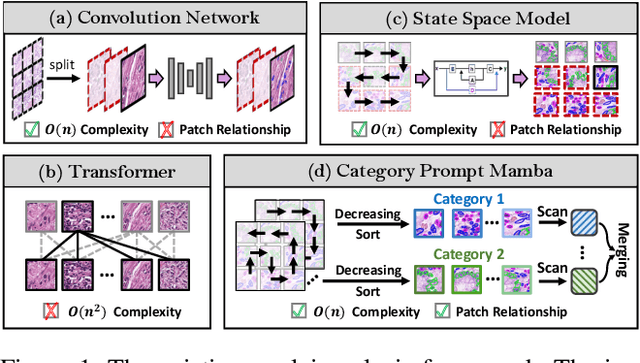
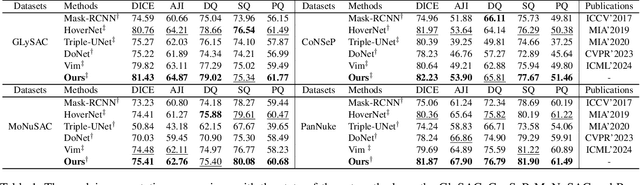
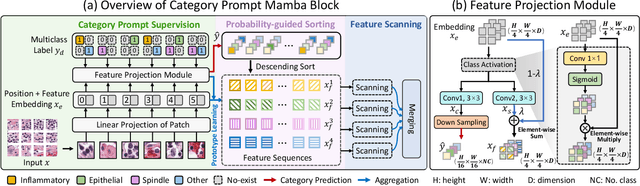
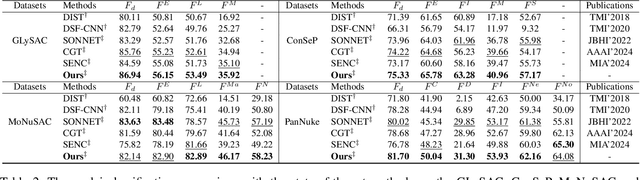
Abstract:Nuclei segmentation and classification provide an essential basis for tumor immune microenvironment analysis. The previous nuclei segmentation and classification models require splitting large images into smaller patches for training, leading to two significant issues. First, nuclei at the borders of adjacent patches often misalign during inference. Second, this patch-based approach significantly increases the model's training and inference time. Recently, Mamba has garnered attention for its ability to model large-scale images with linear time complexity and low memory consumption. It offers a promising solution for training nuclei segmentation and classification models on full-sized images. However, the Mamba orientation-based scanning method lacks account for category-specific features, resulting in sub-optimal performance in scenarios with imbalanced class distributions. To address these challenges, this paper introduces a novel scanning strategy based on category probability sorting, which independently ranks and scans features for each category according to confidence from high to low. This approach enhances the feature representation of uncertain samples and mitigates the issues caused by imbalanced distributions. Extensive experiments conducted on four public datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, delivering superior performance in nuclei segmentation and classification tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge