Dongbao Yang
EmoCaliber: Advancing Reliable Visual Emotion Comprehension via Confidence Verbalization and Calibration
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Visual Emotion Comprehension (VEC) aims to infer sentiment polarities or emotion categories from affective cues embedded in images. In recent years, Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have established a popular paradigm in VEC, leveraging their generalizability to unify VEC tasks defined under diverse emotion taxonomies. While this paradigm achieves notable success, it typically formulates VEC as a deterministic task, requiring the model to output a single, definitive emotion label for each image. Such a formulation insufficiently accounts for the inherent subjectivity of emotion perception, overlooking alternative interpretations that may be equally plausible to different viewers. To address this limitation, we propose equipping MLLMs with capabilities to verbalize their confidence in emotion predictions. This additional signal provides users with an estimate of both the plausibility of alternative interpretations and the MLLMs' self-assessed competence, thereby enhancing reliability in practice. Building on this insight, we introduce a three-stage training framework that progressively endows with structured reasoning, teaches to verbalize confidence, and calibrates confidence expression, culminating in EmoCaliber, a confidence-aware MLLM for VEC. Through fair and comprehensive evaluations on the unified benchmark VECBench, EmoCaliber demonstrates overall superiority against existing methods in both emotion prediction and confidence estimation. These results validate the effectiveness of our approach and mark a feasible step toward more reliable VEC systems. Project page: https://github.com/wdqqdw/EmoCaliber.
Customizing Visual Emotion Evaluation for MLLMs: An Open-vocabulary, Multifaceted, and Scalable Approach
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Recently, Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved exceptional performance across diverse tasks, continually surpassing previous expectations regarding their capabilities. Nevertheless, their proficiency in perceiving emotions from images remains debated, with studies yielding divergent results in zero-shot scenarios. We argue that this inconsistency stems partly from constraints in existing evaluation methods, including the oversight of plausible responses, limited emotional taxonomies, neglect of contextual factors, and labor-intensive annotations. To facilitate customized visual emotion evaluation for MLLMs, we propose an Emotion Statement Judgment task that overcomes these constraints. Complementing this task, we devise an automated pipeline that efficiently constructs emotion-centric statements with minimal human effort. Through systematically evaluating prevailing MLLMs, our study showcases their stronger performance in emotion interpretation and context-based emotion judgment, while revealing relative limitations in comprehending perception subjectivity. When compared to humans, even top-performing MLLMs like GPT4o demonstrate remarkable performance gaps, underscoring key areas for future improvement. By developing a fundamental evaluation framework and conducting a comprehensive MLLM assessment, we hope this work contributes to advancing emotional intelligence in MLLMs. Project page: https://github.com/wdqqdw/MVEI.
TADoc: Robust Time-Aware Document Image Dewarping
Aug 09, 2025



Abstract:Flattening curved, wrinkled, and rotated document images captured by portable photographing devices, termed document image dewarping, has become an increasingly important task with the rise of digital economy and online working. Although many methods have been proposed recently, they often struggle to achieve satisfactory results when confronted with intricate document structures and higher degrees of deformation in real-world scenarios. Our main insight is that, unlike other document restoration tasks (e.g., deblurring), dewarping in real physical scenes is a progressive motion rather than a one-step transformation. Based on this, we have undertaken two key initiatives. Firstly, we reformulate this task, modeling it for the first time as a dynamic process that encompasses a series of intermediate states. Secondly, we design a lightweight framework called TADoc (Time-Aware Document Dewarping Network) to address the geometric distortion of document images. In addition, due to the inadequacy of OCR metrics for document images containing sparse text, the comprehensiveness of evaluation is insufficient. To address this shortcoming, we propose a new metric -- DLS (Document Layout Similarity) -- to evaluate the effectiveness of document dewarping in downstream tasks. Extensive experiments and in-depth evaluations have been conducted and the results indicate that our model possesses strong robustness, achieving superiority on several benchmarks with different document types and degrees of distortion.
Uni-DocDiff: A Unified Document Restoration Model Based on Diffusion
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Removing various degradations from damaged documents greatly benefits digitization, downstream document analysis, and readability. Previous methods often treat each restoration task independently with dedicated models, leading to a cumbersome and highly complex document processing system. Although recent studies attempt to unify multiple tasks, they often suffer from limited scalability due to handcrafted prompts and heavy preprocessing, and fail to fully exploit inter-task synergy within a shared architecture. To address the aforementioned challenges, we propose Uni-DocDiff, a Unified and highly scalable Document restoration model based on Diffusion. Uni-DocDiff develops a learnable task prompt design, ensuring exceptional scalability across diverse tasks. To further enhance its multi-task capabilities and address potential task interference, we devise a novel \textbf{Prior \textbf{P}ool}, a simple yet comprehensive mechanism that combines both local high-frequency features and global low-frequency features. Additionally, we design the \textbf{Prior \textbf{F}usion \textbf{M}odule (PFM)}, which enables the model to adaptively select the most relevant prior information for each specific task. Extensive experiments show that the versatile Uni-DocDiff achieves performance comparable or even superior performance compared with task-specific expert models, and simultaneously holds the task scalability for seamless adaptation to new tasks.
The Role of Video Generation in Enhancing Data-Limited Action Understanding
May 26, 2025



Abstract:Video action understanding tasks in real-world scenarios always suffer data limitations. In this paper, we address the data-limited action understanding problem by bridging data scarcity. We propose a novel method that employs a text-to-video diffusion transformer to generate annotated data for model training. This paradigm enables the generation of realistic annotated data on an infinite scale without human intervention. We proposed the information enhancement strategy and the uncertainty-based label smoothing tailored to generate sample training. Through quantitative and qualitative analysis, we observed that real samples generally contain a richer level of information than generated samples. Based on this observation, the information enhancement strategy is proposed to enhance the informative content of the generated samples from two aspects: the environments and the characters. Furthermore, we observed that some low-quality generated samples might negatively affect model training. To address this, we devised the uncertainty-based label smoothing strategy to increase the smoothing of these samples, thus reducing their impact. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method on four datasets across five tasks and achieve state-of-the-art performance for zero-shot action recognition.
An Empirical Study on Configuring In-Context Learning Demonstrations for Unleashing MLLMs' Sentimental Perception Capability
May 22, 2025Abstract:The advancements in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have enabled various multimodal tasks to be addressed under a zero-shot paradigm. This paradigm sidesteps the cost of model fine-tuning, emerging as a dominant trend in practical application. Nevertheless, Multimodal Sentiment Analysis (MSA), a pivotal challenge in the quest for general artificial intelligence, fails to accommodate this convenience. The zero-shot paradigm exhibits undesirable performance on MSA, casting doubt on whether MLLMs can perceive sentiments as competent as supervised models. By extending the zero-shot paradigm to In-Context Learning (ICL) and conducting an in-depth study on configuring demonstrations, we validate that MLLMs indeed possess such capability. Specifically, three key factors that cover demonstrations' retrieval, presentation, and distribution are comprehensively investigated and optimized. A sentimental predictive bias inherent in MLLMs is also discovered and later effectively counteracted. By complementing each other, the devised strategies for three factors result in average accuracy improvements of 15.9% on six MSA datasets against the zero-shot paradigm and 11.2% against the random ICL baseline.
DCA: Dividing and Conquering Amnesia in Incremental Object Detection
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Incremental object detection (IOD) aims to cultivate an object detector that can continuously localize and recognize novel classes while preserving its performance on previous classes. Existing methods achieve certain success by improving knowledge distillation and exemplar replay for transformer-based detection frameworks, but the intrinsic forgetting mechanisms remain underexplored. In this paper, we dive into the cause of forgetting and discover forgetting imbalance between localization and recognition in transformer-based IOD, which means that localization is less-forgetting and can generalize to future classes, whereas catastrophic forgetting occurs primarily on recognition. Based on these insights, we propose a Divide-and-Conquer Amnesia (DCA) strategy, which redesigns the transformer-based IOD into a localization-then-recognition process. DCA can well maintain and transfer the localization ability, leaving decoupled fragile recognition to be specially conquered. To reduce feature drift in recognition, we leverage semantic knowledge encoded in pre-trained language models to anchor class representations within a unified feature space across incremental tasks. This involves designing a duplex classifier fusion and embedding class semantic features into the recognition decoding process in the form of queries. Extensive experiments validate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance, especially for long-term incremental scenarios. For example, under the four-step setting on MS-COCO, our DCA strategy significantly improves the final AP by 6.9%.
Arbitrary Reading Order Scene Text Spotter with Local Semantics Guidance
Dec 13, 2024Abstract:Scene text spotting has attracted the enthusiasm of relative researchers in recent years. Most existing scene text spotters follow the detection-then-recognition paradigm, where the vanilla detection module hardly determines the reading order and leads to failure recognition. After rethinking the auto-regressive scene text recognition method, we find that a well-trained recognizer can implicitly perceive the local semantics of all characters in a complete word or a sentence without a character-level detection module. Local semantic knowledge not only includes text content but also spatial information in the right reading order. Motivated by the above analysis, we propose the Local Semantics Guided scene text Spotter (LSGSpotter), which auto-regressively decodes the position and content of characters guided by the local semantics. Specifically, two effective modules are proposed in LSGSpotter. On the one hand, we design a Start Point Localization Module (SPLM) for locating text start points to determine the right reading order. On the other hand, a Multi-scale Adaptive Attention Module (MAAM) is proposed to adaptively aggregate text features in a local area. In conclusion, LSGSpotter achieves the arbitrary reading order spotting task without the limitation of sophisticated detection, while alleviating the cost of computational resources with the grid sampling strategy. Extensive experiment results show LSGSpotter achieves state-of-the-art performance on the InverseText benchmark. Moreover, our spotter demonstrates superior performance on English benchmarks for arbitrary-shaped text, achieving improvements of 0.7\% and 2.5\% on Total-Text and SCUT-CTW1500, respectively. These results validate our text spotter is effective for scene texts in arbitrary reading order and shape.
TextCtrl: Diffusion-based Scene Text Editing with Prior Guidance Control
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:Centred on content modification and style preservation, Scene Text Editing (STE) remains a challenging task despite considerable progress in text-to-image synthesis and text-driven image manipulation recently. GAN-based STE methods generally encounter a common issue of model generalization, while Diffusion-based STE methods suffer from undesired style deviations. To address these problems, we propose TextCtrl, a diffusion-based method that edits text with prior guidance control. Our method consists of two key components: (i) By constructing fine-grained text style disentanglement and robust text glyph structure representation, TextCtrl explicitly incorporates Style-Structure guidance into model design and network training, significantly improving text style consistency and rendering accuracy. (ii) To further leverage the style prior, a Glyph-adaptive Mutual Self-attention mechanism is proposed which deconstructs the implicit fine-grained features of the source image to enhance style consistency and vision quality during inference. Furthermore, to fill the vacancy of the real-world STE evaluation benchmark, we create the first real-world image-pair dataset termed ScenePair for fair comparisons. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of TextCtrl compared with previous methods concerning both style fidelity and text accuracy.
First Creating Backgrounds Then Rendering Texts: A New Paradigm for Visual Text Blending
Oct 14, 2024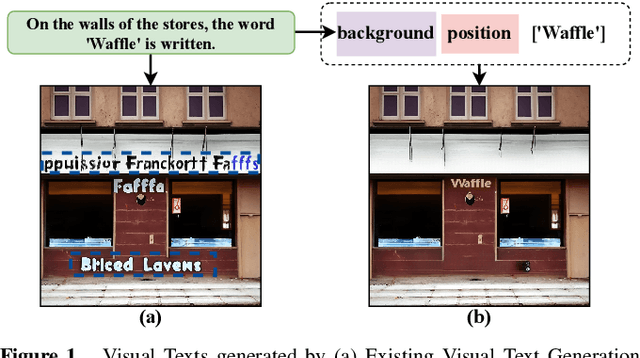
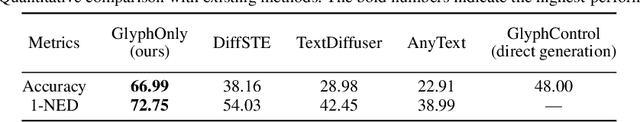
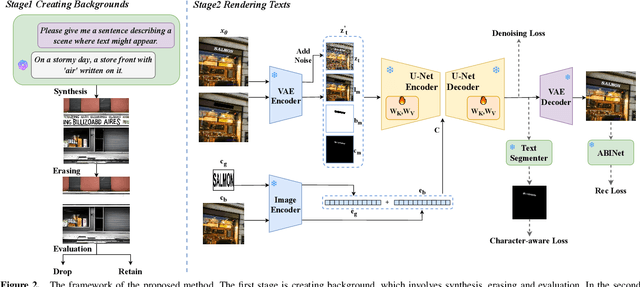
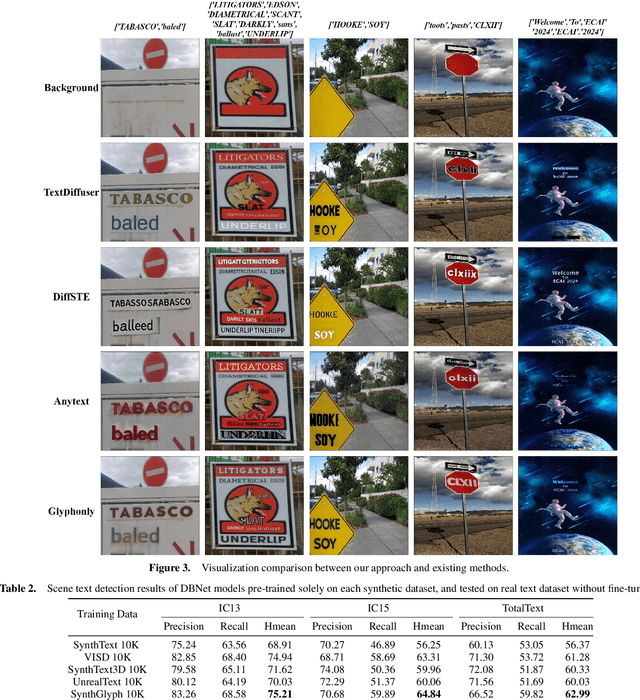
Abstract:Diffusion models, known for their impressive image generation abilities, have played a pivotal role in the rise of visual text generation. Nevertheless, existing visual text generation methods often focus on generating entire images with text prompts, leading to imprecise control and limited practicality. A more promising direction is visual text blending, which focuses on seamlessly merging texts onto text-free backgrounds. However, existing visual text blending methods often struggle to generate high-fidelity and diverse images due to a shortage of backgrounds for synthesis and limited generalization capabilities. To overcome these challenges, we propose a new visual text blending paradigm including both creating backgrounds and rendering texts. Specifically, a background generator is developed to produce high-fidelity and text-free natural images. Moreover, a text renderer named GlyphOnly is designed for achieving visually plausible text-background integration. GlyphOnly, built on a Stable Diffusion framework, utilizes glyphs and backgrounds as conditions for accurate rendering and consistency control, as well as equipped with an adaptive text block exploration strategy for small-scale text rendering. We also explore several downstream applications based on our method, including scene text dataset synthesis for boosting scene text detectors, as well as text image customization and editing. Code and model will be available at \url{https://github.com/Zhenhang-Li/GlyphOnly}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge