Zhifei Yang
ComLQ: Benchmarking Complex Logical Queries in Information Retrieval
Nov 15, 2025

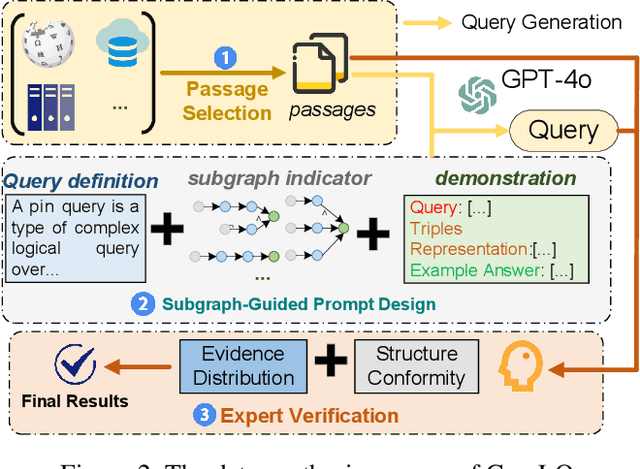
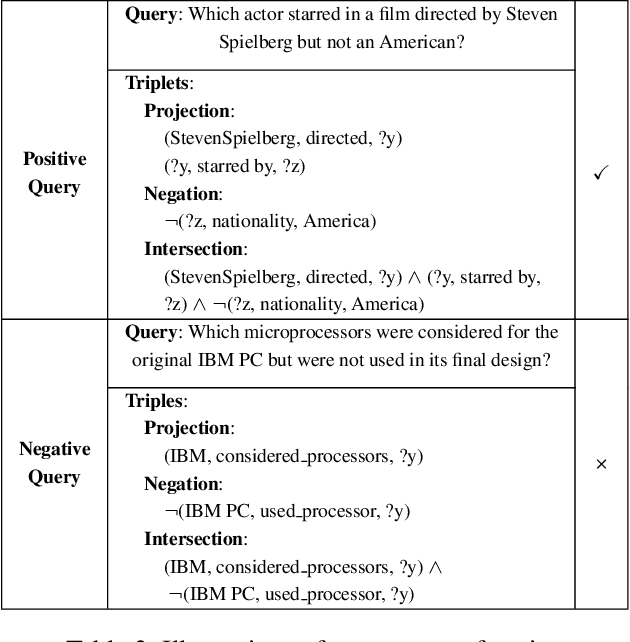
Abstract:Information retrieval (IR) systems play a critical role in navigating information overload across various applications. Existing IR benchmarks primarily focus on simple queries that are semantically analogous to single- and multi-hop relations, overlooking \emph{complex logical queries} involving first-order logic operations such as conjunction ($\land$), disjunction ($\lor$), and negation ($\lnot$). Thus, these benchmarks can not be used to sufficiently evaluate the performance of IR models on complex queries in real-world scenarios. To address this problem, we propose a novel method leveraging large language models (LLMs) to construct a new IR dataset \textbf{ComLQ} for \textbf{Com}plex \textbf{L}ogical \textbf{Q}ueries, which comprises 2,909 queries and 11,251 candidate passages. A key challenge in constructing the dataset lies in capturing the underlying logical structures within unstructured text. Therefore, by designing the subgraph-guided prompt with the subgraph indicator, an LLM (such as GPT-4o) is guided to generate queries with specific logical structures based on selected passages. All query-passage pairs in ComLQ are ensured \emph{structure conformity} and \emph{evidence distribution} through expert annotation. To better evaluate whether retrievers can handle queries with negation, we further propose a new evaluation metric, \textbf{Log-Scaled Negation Consistency} (\textbf{LSNC@$K$}). As a supplement to standard relevance-based metrics (such as nDCG and mAP), LSNC@$K$ measures whether top-$K$ retrieved passages violate negation conditions in queries. Our experimental results under zero-shot settings demonstrate existing retrieval models' limited performance on complex logical queries, especially on queries with negation, exposing their inferior capabilities of modeling exclusion.
Spatial 3D-LLM: Exploring Spatial Awareness in 3D Vision-Language Models
Jul 22, 2025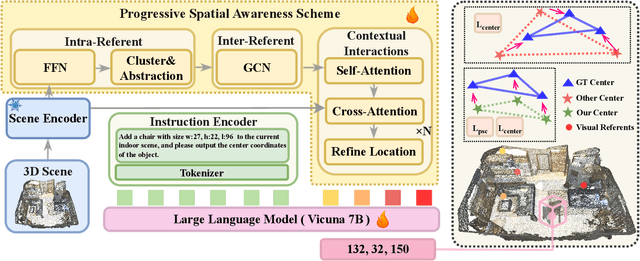
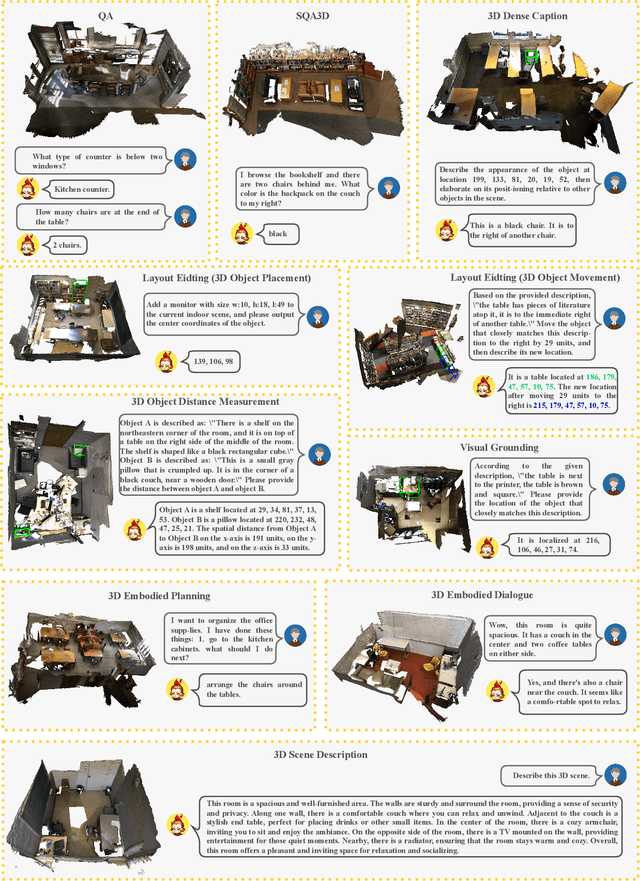
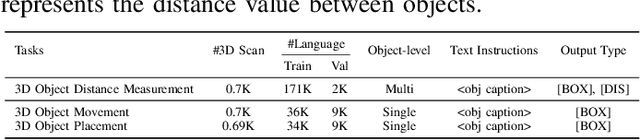
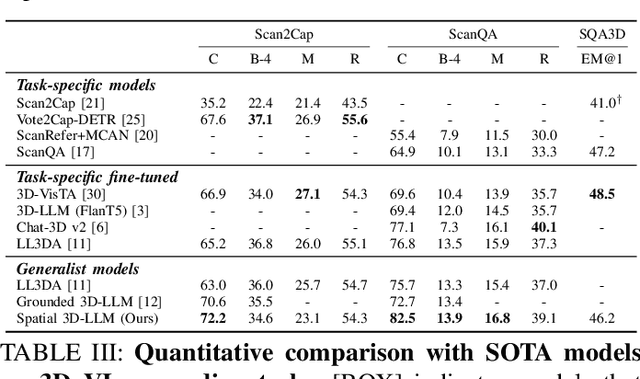
Abstract:New era has unlocked exciting possibilities for extending Large Language Models (LLMs) to tackle 3D vision-language tasks. However, most existing 3D multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) rely on compressing holistic 3D scene information or segmenting independent objects to perform these tasks, which limits their spatial awareness due to insufficient representation of the richness inherent in 3D scenes. To overcome these limitations, we propose Spatial 3D-LLM, a 3D MLLM specifically designed to enhance spatial awareness for 3D vision-language tasks by enriching the spatial embeddings of 3D scenes. Spatial 3D-LLM integrates an LLM backbone with a progressive spatial awareness scheme that progressively captures spatial information as the perception field expands, generating location-enriched 3D scene embeddings to serve as visual prompts. Furthermore, we introduce two novel tasks: 3D object distance measurement and 3D layout editing, and construct a 3D instruction dataset, MODEL, to evaluate the model's spatial awareness capabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that Spatial 3D-LLM achieves state-of-the-art performance across a wide range of 3D vision-language tasks, revealing the improvements stemmed from our progressive spatial awareness scheme of mining more profound spatial information. Our code is available at https://github.com/bjshuyuan/Spatial-3D-LLM.
Logical Consistency is Vital: Neural-Symbolic Information Retrieval for Negative-Constraint Queries
May 29, 2025

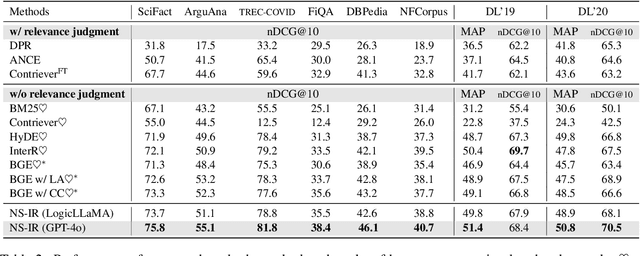
Abstract:Information retrieval plays a crucial role in resource localization. Current dense retrievers retrieve the relevant documents within a corpus via embedding similarities, which compute similarities between dense vectors mainly depending on word co-occurrence between queries and documents, but overlook the real query intents. Thus, they often retrieve numerous irrelevant documents. Particularly in the scenarios of complex queries such as \emph{negative-constraint queries}, their retrieval performance could be catastrophic. To address the issue, we propose a neuro-symbolic information retrieval method, namely \textbf{NS-IR}, that leverages first-order logic (FOL) to optimize the embeddings of naive natural language by considering the \emph{logical consistency} between queries and documents. Specifically, we introduce two novel techniques, \emph{logic alignment} and \emph{connective constraint}, to rerank candidate documents, thereby enhancing retrieval relevance. Furthermore, we construct a new dataset \textbf{NegConstraint} including negative-constraint queries to evaluate our NS-IR's performance on such complex IR scenarios. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that NS-IR not only achieves superior zero-shot retrieval performance on web search and low-resource retrieval tasks, but also performs better on negative-constraint queries. Our scource code and dataset are available at https://github.com/xgl-git/NS-IR-main.
VidText: Towards Comprehensive Evaluation for Video Text Understanding
May 28, 2025Abstract:Visual texts embedded in videos carry rich semantic information, which is crucial for both holistic video understanding and fine-grained reasoning about local human actions. However, existing video understanding benchmarks largely overlook textual information, while OCR-specific benchmarks are constrained to static images, limiting their ability to capture the interaction between text and dynamic visual contexts. To address this gap, we propose VidText, a new benchmark designed for comprehensive and in-depth evaluation of video text understanding. VidText offers the following key features: 1) It covers a wide range of real-world scenarios and supports multilingual content, encompassing diverse settings where video text naturally appears. 2) It introduces a hierarchical evaluation framework with video-level, clip-level, and instance-level tasks, enabling assessment of both global summarization and local retrieval capabilities. 3) The benchmark also introduces a set of paired perception reasoning tasks, ranging from visual text perception to cross-modal reasoning between textual and visual information. Extensive experiments on 18 state-of-the-art Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) reveal that current models struggle across most tasks, with significant room for improvement. Further analysis highlights the impact of both model-intrinsic factors, such as input resolution and OCR capability, and external factors, including the use of auxiliary information and Chain-of-Thought reasoning strategies. We hope VidText will fill the current gap in video understanding benchmarks and serve as a foundation for future research on multimodal reasoning with video text in dynamic environments.
UORA: Uniform Orthogonal Reinitialization Adaptation in Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Large Models
May 26, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces Uniform Orthogonal Reinitialization Adaptation (UORA), a novel parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) approach for Large Language Models (LLMs). UORA achieves state-of-the-art performance and parameter efficiency by leveraging a low-rank approximation method to reduce the number of trainable parameters. Unlike existing methods such as LoRA and VeRA, UORA employs an interpolation-based reparametrization mechanism that selectively reinitializes rows and columns in frozen projection matrices, guided by the vector magnitude heuristic. This results in substantially fewer trainable parameters compared to LoRA and outperforms VeRA in computation and storage efficiency. Comprehensive experiments across various benchmarks demonstrate UORA's superiority in achieving competitive fine-tuning performance with negligible computational overhead. We demonstrate its performance on GLUE and E2E benchmarks and its effectiveness in instruction-tuning large language models and image classification models. Our contributions establish a new paradigm for scalable and resource-efficient fine-tuning of LLMs.
* 20 pages, 2 figures, 15 tables
SepPrune: Structured Pruning for Efficient Deep Speech Separation
May 17, 2025Abstract:Although deep learning has substantially advanced speech separation in recent years, most existing studies continue to prioritize separation quality while overlooking computational efficiency, an essential factor for low-latency speech processing in real-time applications. In this paper, we propose SepPrune, the first structured pruning framework specifically designed to compress deep speech separation models and reduce their computational cost. SepPrune begins by analyzing the computational structure of a given model to identify layers with the highest computational burden. It then introduces a differentiable masking strategy to enable gradient-driven channel selection. Based on the learned masks, SepPrune prunes redundant channels and fine-tunes the remaining parameters to recover performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that this learnable pruning paradigm yields substantial advantages for channel pruning in speech separation models, outperforming existing methods. Notably, a model pruned with SepPrune can recover 85% of the performance of a pre-trained model (trained over hundreds of epochs) with only one epoch of fine-tuning, and achieves convergence 36$\times$ faster than training from scratch. Code is available at https://github.com/itsnotacie/SepPrune.
Beyond Degradation Conditions: All-in-One Image Restoration via HOG Transformers
Apr 12, 2025



Abstract:All-in-one image restoration, which aims to address diverse degradations within a unified framework, is critical for practical applications. However, existing methods rely on predicting and integrating degradation conditions, which can misactivate degradation-specific features in complex scenarios, limiting their restoration performance. To address this issue, we propose a novel all-in-one image restoration framework guided by Histograms of Oriented Gradients (HOG), named HOGformer. By leveraging the degradation-discriminative capability of HOG descriptors, HOGformer employs a dynamic self-attention mechanism that adaptively attends to long-range spatial dependencies based on degradation-aware HOG cues. To enhance the degradation sensitivity of attention inputs, we design a HOG-guided local dynamic-range convolution module that captures long-range degradation similarities while maintaining awareness of global structural information. Furthermore, we propose a dynamic interaction feed-forward module, efficiently increasing the model capacity to adapt to different degradations through channel-spatial interactions. Extensive experiments across diverse benchmarks, including adverse weather and natural degradations, demonstrate that HOGformer achieves state-of-the-art performance and generalizes effectively to complex real-world degradations. Code is available at https://github.com/Fire-friend/HOGformer.
MaRI: Material Retrieval Integration across Domains
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Accurate material retrieval is critical for creating realistic 3D assets. Existing methods rely on datasets that capture shape-invariant and lighting-varied representations of materials, which are scarce and face challenges due to limited diversity and inadequate real-world generalization. Most current approaches adopt traditional image search techniques. They fall short in capturing the unique properties of material spaces, leading to suboptimal performance in retrieval tasks. Addressing these challenges, we introduce MaRI, a framework designed to bridge the feature space gap between synthetic and real-world materials. MaRI constructs a shared embedding space that harmonizes visual and material attributes through a contrastive learning strategy by jointly training an image and a material encoder, bringing similar materials and images closer while separating dissimilar pairs within the feature space. To support this, we construct a comprehensive dataset comprising high-quality synthetic materials rendered with controlled shape variations and diverse lighting conditions, along with real-world materials processed and standardized using material transfer techniques. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance, accuracy, and generalization capabilities of MaRI across diverse and complex material retrieval tasks, outperforming existing methods.
DiffPO: Diffusion-styled Preference Optimization for Efficient Inference-Time Alignment of Large Language Models
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Inference-time alignment provides an efficient alternative for aligning LLMs with humans. However, these approaches still face challenges, such as limited scalability due to policy-specific value functions and latency during the inference phase. In this paper, we propose a novel approach, Diffusion-styled Preference Optimization (\model), which provides an efficient and policy-agnostic solution for aligning LLMs with humans. By directly performing alignment at sentence level, \model~avoids the time latency associated with token-level generation. Designed as a plug-and-play module, \model~can be seamlessly integrated with various base models to enhance their alignment. Extensive experiments on AlpacaEval 2, MT-bench, and HH-RLHF demonstrate that \model~achieves superior alignment performance across various settings, achieving a favorable trade-off between alignment quality and inference-time latency. Furthermore, \model~demonstrates model-agnostic scalability, significantly improving the performance of large models such as Llama-3-70B.
MMGDreamer: Mixed-Modality Graph for Geometry-Controllable 3D Indoor Scene Generation
Feb 09, 2025Abstract:Controllable 3D scene generation has extensive applications in virtual reality and interior design, where the generated scenes should exhibit high levels of realism and controllability in terms of geometry. Scene graphs provide a suitable data representation that facilitates these applications. However, current graph-based methods for scene generation are constrained to text-based inputs and exhibit insufficient adaptability to flexible user inputs, hindering the ability to precisely control object geometry. To address this issue, we propose MMGDreamer, a dual-branch diffusion model for scene generation that incorporates a novel Mixed-Modality Graph, visual enhancement module, and relation predictor. The mixed-modality graph allows object nodes to integrate textual and visual modalities, with optional relationships between nodes. It enhances adaptability to flexible user inputs and enables meticulous control over the geometry of objects in the generated scenes. The visual enhancement module enriches the visual fidelity of text-only nodes by constructing visual representations using text embeddings. Furthermore, our relation predictor leverages node representations to infer absent relationships between nodes, resulting in more coherent scene layouts. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that MMGDreamer exhibits superior control of object geometry, achieving state-of-the-art scene generation performance. Project page: https://yangzhifeio.github.io/project/MMGDreamer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge