Yangfan He
ShieldedCode: Learning Robust Representations for Virtual Machine Protected Code
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable progress in code generation, yet their potential for software protection remains largely untapped. Reverse engineering continues to threaten software security, while traditional virtual machine protection (VMP) relies on rigid, rule-based transformations that are costly to design and vulnerable to automated analysis. In this work, we present the first protection-aware framework that learns robust representations of VMP-protected code. Our approach builds large-scale paired datasets of source code and normalized VM implementations, and introduces hierarchical dependency modeling at intra-, preceding-, and inter-instruction levels. We jointly optimize language modeling with functionality-aware and protection-aware contrastive objectives to capture both semantic equivalence and protection strength. To further assess resilience, we propose a protection effectiveness optimization task that quantifies and ranks different VM variants derived from the same source. Coupled with a two-stage continual pre-training and fine-tuning pipeline, our method enables models to generate, compare, and reason over protected code. Extensive experiments show that our framework significantly improves robustness across diverse protection levels, opening a new research direction for learning-based software defense. In this work, we present ShieldedCode, the first protection-aware framework that learns robust representations of VMP-protected code. Our method achieves 26.95% Pass@1 on L0 VM code generation compared to 22.58% for GPT-4o., and improves binary similarity detection Recall@1 by 10% over state of art methods like jTrans.
PhysicsMind: Sim and Real Mechanics Benchmarking for Physical Reasoning and Prediction in Foundational VLMs and World Models
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Modern foundational Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) and video world models have advanced significantly in mathematical, common-sense, and visual reasoning, but their grasp of the underlying physics remains underexplored. Existing benchmarks attempting to measure this matter rely on synthetic, Visual Question Answer templates or focus on perceptual video quality that is tangential to measuring how well the video abides by physical laws. To address this fragmentation, we introduce PhysicsMind, a unified benchmark with both real and simulation environments that evaluates law-consistent reasoning and generation over three canonical principles: Center of Mass, Lever Equilibrium, and Newton's First Law. PhysicsMind comprises two main tasks: i) VQA tasks, testing whether models can reason and determine physical quantities and values from images or short videos, and ii) Video Generation(VG) tasks, evaluating if predicted motion trajectories obey the same center-of-mass, torque, and inertial constraints as the ground truth. A broad range of recent models and video generation models is evaluated on PhysicsMind and found to rely on appearance heuristics while often violating basic mechanics. These gaps indicate that current scaling and training are still insufficient for robust physical understanding, underscoring PhysicsMind as a focused testbed for physics-aware multimodal models. Our data will be released upon acceptance.
DTP: A Simple yet Effective Distracting Token Pruning Framework for Vision-Language Action Models
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Action (VLA) models have shown remarkable progress in robotic manipulation by leveraging the powerful perception abilities of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to understand environments and directly output actions. However, by default, VLA models may overly attend to image tokens in the task-irrelevant region, which we describe as 'distracting tokens'. This behavior can disturb the model from the generation of the desired action tokens in each step, affecting the success rate of tasks. In this paper, we introduce a simple yet effective plug-and-play Distracting Token Pruning (DTP) framework, which dynamically detects and prunes these distracting image tokens. By correcting the model's visual attention patterns, we aim to improve the task success rate, as well as exploring the performance upper boundaries of the model without altering its original architecture or adding additional inputs. Experiments on the SIMPLER Benchmark (Li et al., 2024) show that our method consistently achieving relative improvements in task success rates across different types of novel VLA models, demonstrating generalizability to transformer-based VLAs. Further analysis reveals a negative correlation between the task success rate and the amount of attentions in the task-irrelevant region for all models tested, highlighting a common phenomenon of VLA models that could guide future research. We also publish our code at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/CBD3.
PurifyGen: A Risk-Discrimination and Semantic-Purification Model for Safe Text-to-Image Generation
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion models have notably enhanced text-to-image (T2I) generation quality, but they also raise the risk of generating unsafe content. Traditional safety methods like text blacklisting or harmful content classification have significant drawbacks: they can be easily circumvented or require extensive datasets and extra training. To overcome these challenges, we introduce PurifyGen, a novel, training-free approach for safe T2I generation that retains the model's original weights. PurifyGen introduces a dual-stage strategy for prompt purification. First, we evaluate the safety of each token in a prompt by computing its complementary semantic distance, which measures the semantic proximity between the prompt tokens and concept embeddings from predefined toxic and clean lists. This enables fine-grained prompt classification without explicit keyword matching or retraining. Tokens closer to toxic concepts are flagged as risky. Second, for risky prompts, we apply a dual-space transformation: we project toxic-aligned embeddings into the null space of the toxic concept matrix, effectively removing harmful semantic components, and simultaneously align them into the range space of clean concepts. This dual alignment purifies risky prompts by both subtracting unsafe semantics and reinforcing safe ones, while retaining the original intent and coherence. We further define a token-wise strategy to selectively replace only risky token embeddings, ensuring minimal disruption to safe content. PurifyGen offers a plug-and-play solution with theoretical grounding and strong generalization to unseen prompts and models. Extensive testing shows that PurifyGen surpasses current methods in reducing unsafe content across five datasets and competes well with training-dependent approaches. The code can refer to https://github.com/AI-Researcher-Team/PurifyGen.
CoFi-Dec: Hallucination-Resistant Decoding via Coarse-to-Fine Generative Feedback in Large Vision-Language Models
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have achieved impressive progress in multi-modal understanding and generation. However, they still tend to produce hallucinated content that is inconsistent with the visual input, which limits their reliability in real-world applications. We propose \textbf{CoFi-Dec}, a training-free decoding framework that mitigates hallucinations by integrating generative self-feedback with coarse-to-fine visual conditioning. Inspired by the human visual process from global scene perception to detailed inspection, CoFi-Dec first generates two intermediate textual responses conditioned on coarse- and fine-grained views of the original image. These responses are then transformed into synthetic images using a text-to-image model, forming multi-level visual hypotheses that enrich grounding cues. To unify the predictions from these multiple visual conditions, we introduce a Wasserstein-based fusion mechanism that aligns their predictive distributions into a geometrically consistent decoding trajectory. This principled fusion reconciles high-level semantic consistency with fine-grained visual grounding, leading to more robust and faithful outputs. Extensive experiments on six hallucination-focused benchmarks show that CoFi-Dec substantially reduces both entity-level and semantic-level hallucinations, outperforming existing decoding strategies. The framework is model-agnostic, requires no additional training, and can be seamlessly applied to a wide range of LVLMs. The implementation is available at https://github.com/AI-Researcher-Team/CoFi-Dec.
TV-RAG: A Temporal-aware and Semantic Entropy-Weighted Framework for Long Video Retrieval and Understanding
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Large Video Language Models (LVLMs) have rapidly emerged as the focus of multimedia AI research. Nonetheless, when confronted with lengthy videos, these models struggle: their temporal windows are narrow, and they fail to notice fine-grained semantic shifts that unfold over extended durations. Moreover, mainstream text-based retrieval pipelines, which rely chiefly on surface-level lexical overlap, ignore the rich temporal interdependence among visual, audio, and subtitle channels. To mitigate these limitations, we propose TV-RAG, a training-free architecture that couples temporal alignment with entropy-guided semantics to improve long-video reasoning. The framework contributes two main mechanisms: \emph{(i)} a time-decay retrieval module that injects explicit temporal offsets into the similarity computation, thereby ranking text queries according to their true multimedia context; and \emph{(ii)} an entropy-weighted key-frame sampler that selects evenly spaced, information-dense frames, reducing redundancy while preserving representativeness. By weaving these temporal and semantic signals together, TV-RAG realises a dual-level reasoning routine that can be grafted onto any LVLM without re-training or fine-tuning. The resulting system offers a lightweight, budget-friendly upgrade path and consistently surpasses most leading baselines across established long-video benchmarks such as Video-MME, MLVU, and LongVideoBench, confirming the effectiveness of our model. The code can be found at https://github.com/AI-Researcher-Team/TV-RAG.
dMLLM-TTS: Self-Verified and Efficient Test-Time Scaling for Diffusion Multi-Modal Large Language Models
Dec 22, 2025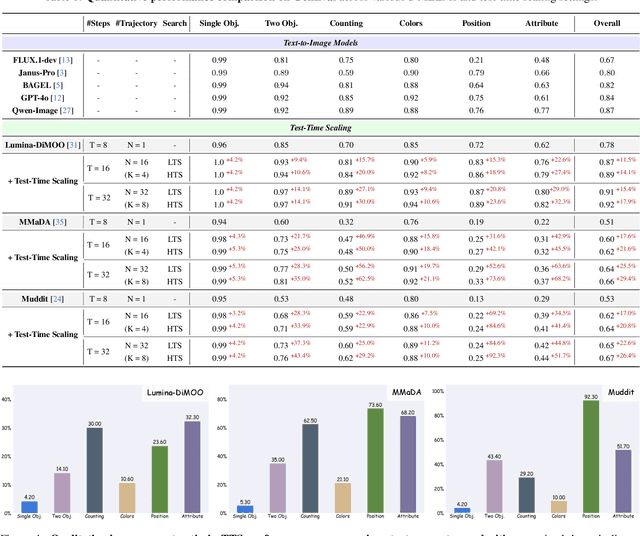
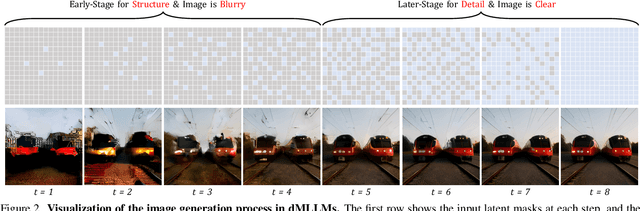
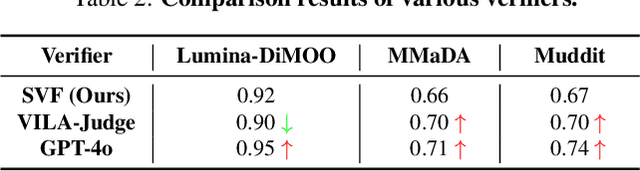
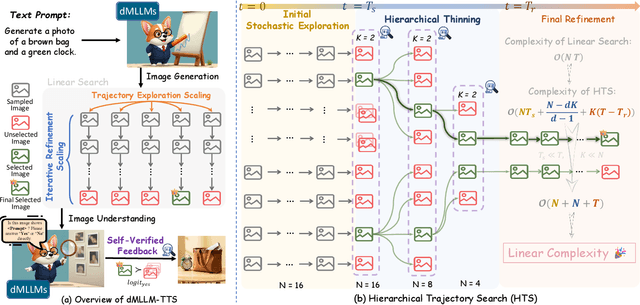
Abstract:Diffusion Multi-modal Large Language Models (dMLLMs) have recently emerged as a novel architecture unifying image generation and understanding. However, developing effective and efficient Test-Time Scaling (TTS) methods to unlock their full generative potential remains an underexplored challenge. To address this, we propose dMLLM-TTS, a novel framework operating on two complementary scaling axes: (1) trajectory exploration scaling to enhance the diversity of generated hypotheses, and (2) iterative refinement scaling for stable generation. Conventional TTS approaches typically perform linear search across these two dimensions, incurring substantial computational costs of O(NT) and requiring an external verifier for best-of-N selection. To overcome these limitations, we propose two innovations. First, we design an efficient hierarchical search algorithm with O(N+T) complexity that adaptively expands and prunes sampling trajectories. Second, we introduce a self-verified feedback mechanism that leverages the dMLLMs' intrinsic image understanding capabilities to assess text-image alignment, eliminating the need for external verifier. Extensive experiments on the GenEval benchmark across three representative dMLLMs (e.g., Lumina-DiMOO, MMaDA, Muddit) show that our framework substantially improves generation quality while achieving up to 6x greater efficiency than linear search. Project page: https://github.com/Alpha-VLLM/Lumina-DiMOO.
Attention and Risk-Aware Decision Framework for Safe Autonomous Driving
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:Autonomous driving has attracted great interest due to its potential capability in full-unsupervised driving. Model-based and learning-based methods are widely used in autonomous driving. Model-based methods rely on pre-defined models of the environment and may struggle with unforeseen events. Proximal policy optimization (PPO), an advanced learning-based method, can adapt to the above limits by learning from interactions with the environment. However, existing PPO faces challenges with poor training results, and low training efficiency in long sequences. Moreover, the poor training results are equivalent to collisions in driving tasks. To solve these issues, this paper develops an improved PPO by introducing the risk-aware mechanism, a risk-attention decision network, a balanced reward function, and a safety-assisted mechanism. The risk-aware mechanism focuses on highlighting areas with potential collisions, facilitating safe-driving learning of the PPO. The balanced reward function adjusts rewards based on the number of surrounding vehicles, promoting efficient exploration of the control strategy during training. Additionally, the risk-attention network enhances the PPO to hold channel and spatial attention for the high-risk areas of input images. Moreover, the safety-assisted mechanism supervises and prevents the actions with risks of collisions during the lane keeping and lane changing. Simulation results on a physical engine demonstrate that the proposed algorithm outperforms benchmark algorithms in collision avoidance, achieving higher peak reward with less training time, and shorter driving time remaining on the risky areas among multiple testing traffic flow scenarios.
EMPOWER: Evolutionary Medical Prompt Optimization With Reinforcement Learning
Aug 25, 2025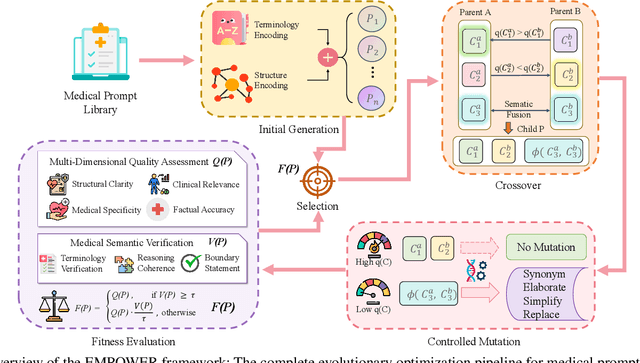
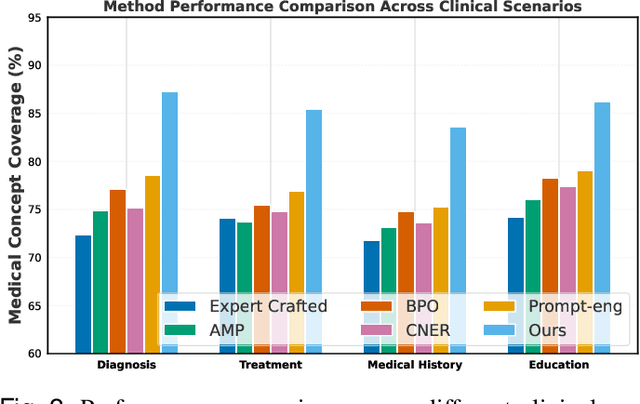
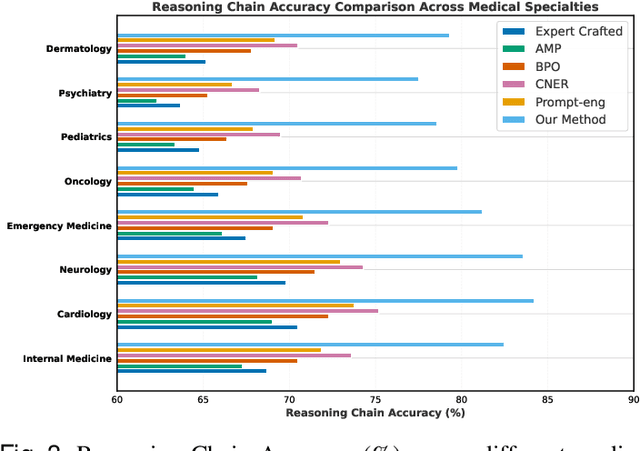
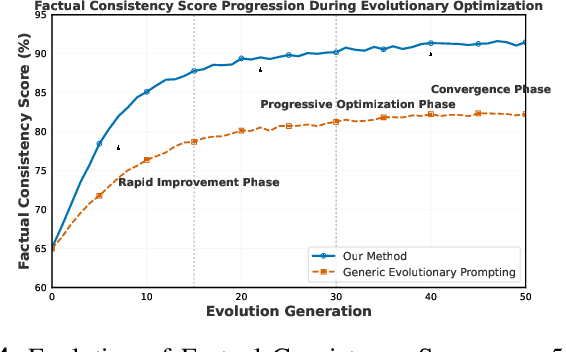
Abstract:Prompt engineering significantly influences the reliability and clinical utility of Large Language Models (LLMs) in medical applications. Current optimization approaches inadequately address domain-specific medical knowledge and safety requirements. This paper introduces EMPOWER, a novel evolutionary framework that enhances medical prompt quality through specialized representation learning, multi-dimensional evaluation, and structure-preserving algorithms. Our methodology incorporates: (1) a medical terminology attention mechanism, (2) a comprehensive assessment architecture evaluating clarity, specificity, clinical relevance, and factual accuracy, (3) a component-level evolutionary algorithm preserving clinical reasoning integrity, and (4) a semantic verification module ensuring adherence to medical knowledge. Evaluation across diagnostic, therapeutic, and educational tasks demonstrates significant improvements: 24.7% reduction in factually incorrect content, 19.6% enhancement in domain specificity, and 15.3% higher clinician preference in blinded evaluations. The framework addresses critical challenges in developing clinically appropriate prompts, facilitating more responsible integration of LLMs into healthcare settings.
Low-Cost Test-Time Adaptation for Robust Video Editing
Jul 29, 2025



Abstract:Video editing is a critical component of content creation that transforms raw footage into coherent works aligned with specific visual and narrative objectives. Existing approaches face two major challenges: temporal inconsistencies due to failure in capturing complex motion patterns, and overfitting to simple prompts arising from limitations in UNet backbone architectures. While learning-based methods can enhance editing quality, they typically demand substantial computational resources and are constrained by the scarcity of high-quality annotated data. In this paper, we present Vid-TTA, a lightweight test-time adaptation framework that personalizes optimization for each test video during inference through self-supervised auxiliary tasks. Our approach incorporates a motion-aware frame reconstruction mechanism that identifies and preserves crucial movement regions, alongside a prompt perturbation and reconstruction strategy that strengthens model robustness to diverse textual descriptions. These innovations are orchestrated by a meta-learning driven dynamic loss balancing mechanism that adaptively adjusts the optimization process based on video characteristics. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Vid-TTA significantly improves video temporal consistency and mitigates prompt overfitting while maintaining low computational overhead, offering a plug-and-play performance boost for existing video editing models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge