Jiaqi Chen
Visionary: The World Model Carrier Built on WebGPU-Powered Gaussian Splatting Platform
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Neural rendering, particularly 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), has evolved rapidly and become a key component for building world models. However, existing viewer solutions remain fragmented, heavy, or constrained by legacy pipelines, resulting in high deployment friction and limited support for dynamic content and generative models. In this work, we present Visionary, an open, web-native platform for real-time various Gaussian Splatting and meshes rendering. Built on an efficient WebGPU renderer with per-frame ONNX inference, Visionary enables dynamic neural processing while maintaining a lightweight, "click-to-run" browser experience. It introduces a standardized Gaussian Generator contract, which not only supports standard 3DGS rendering but also allows plug-and-play algorithms to generate or update Gaussians each frame. Such inference also enables us to apply feedforward generative post-processing. The platform further offers a plug in three.js library with a concise TypeScript API for seamless integration into existing web applications. Experiments show that, under identical 3DGS assets, Visionary achieves superior rendering efficiency compared to current Web viewers due to GPU-based primitive sorting. It already supports multiple variants, including MLP-based 3DGS, 4DGS, neural avatars, and style transformation or enhancement networks. By unifying inference and rendering directly in the browser, Visionary significantly lowers the barrier to reproduction, comparison, and deployment of 3DGS-family methods, serving as a unified World Model Carrier for both reconstructive and generative paradigms.
Unlocking the Black Box: A Five-Dimensional Framework for Evaluating Explainable AI in Credit Risk
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:The financial industry faces a significant challenge modeling and risk portfolios: balancing the predictability of advanced machine learning models, neural network models, and explainability required by regulatory entities (such as Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, Consumer Financial Protection Bureau). This paper intends to fill the gap in the application between these "black box" models and explainability frameworks, such as LIME and SHAP. Authors elaborate on the application of these frameworks on different models and demonstrates the more complex models with better prediction powers could be applied and reach the same level of the explainability, using SHAP and LIME. Beyond the comparison and discussion of performances, this paper proposes a novel five dimensional framework evaluating Inherent Interpretability, Global Explanations, Local Explanations, Consistency, and Complexity to offer a nuanced method for assessing and comparing model explainability beyond simple accuracy metrics. This research demonstrates the feasibility of employing sophisticated, high performing ML models in regulated financial environments by utilizing modern explainability techniques and provides a structured approach to evaluate the crucial trade offs between model performance and interpretability.
Switchable Token-Specific Codebook Quantization For Face Image Compression
Oct 27, 2025Abstract:With the ever-increasing volume of visual data, the efficient and lossless transmission, along with its subsequent interpretation and understanding, has become a critical bottleneck in modern information systems. The emerged codebook-based solution utilize a globally shared codebook to quantize and dequantize each token, controlling the bpp by adjusting the number of tokens or the codebook size. However, for facial images, which are rich in attributes, such global codebook strategies overlook both the category-specific correlations within images and the semantic differences among tokens, resulting in suboptimal performance, especially at low bpp. Motivated by these observations, we propose a Switchable Token-Specific Codebook Quantization for face image compression, which learns distinct codebook groups for different image categories and assigns an independent codebook to each token. By recording the codebook group to which each token belongs with a small number of bits, our method can reduce the loss incurred when decreasing the size of each codebook group. This enables a larger total number of codebooks under a lower overall bpp, thereby enhancing the expressive capability and improving reconstruction performance. Owing to its generalizable design, our method can be integrated into any existing codebook-based representation learning approach and has demonstrated its effectiveness on face recognition datasets, achieving an average accuracy of 93.51% for reconstructed images at 0.05 bpp.
Direct Estimation of Eigenvalues of Large Dimensional Precision Matrix
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we consider directly estimating the eigenvalues of precision matrix, without inverting the corresponding estimator for the eigenvalues of covariance matrix. We focus on a general asymptotic regime, i.e., the large dimensional regime, where both the dimension $N$ and the sample size $K$ tend to infinity whereas their quotient $N/K$ converges to a positive constant. By utilizing tools from random matrix theory, we construct an improved estimator for eigenvalues of precision matrix. We prove the consistency of the new estimator under large dimensional regime. In order to obtain the asymptotic bias term of the proposed estimator, we provide a theoretical result that characterizes the convergence rate of the expected Stieltjes transform (with its derivative) of the spectra of the sample covariance matrix. Using this result, we prove that the asymptotic bias term of the proposed estimator is of order $O(1/K^2)$. Additionally, we establish a central limiting theorem (CLT) to describe the fluctuations of the new estimator. Finally, some numerical examples are presented to validate the excellent performance of the new estimator and to verify the accuracy of the CLT.
Generative Interfaces for Language Models
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly seen as assistants, copilots, and consultants, capable of supporting a wide range of tasks through natural conversation. However, most systems remain constrained by a linear request-response format that often makes interactions inefficient in multi-turn, information-dense, and exploratory tasks. To address these limitations, we propose Generative Interfaces for Language Models, a paradigm in which LLMs respond to user queries by proactively generating user interfaces (UIs) that enable more adaptive and interactive engagement. Our framework leverages structured interface-specific representations and iterative refinements to translate user queries into task-specific UIs. For systematic evaluation, we introduce a multidimensional assessment framework that compares generative interfaces with traditional chat-based ones across diverse tasks, interaction patterns, and query types, capturing functional, interactive, and emotional aspects of user experience. Results show that generative interfaces consistently outperform conversational ones, with humans preferring them in over 70% of cases. These findings clarify when and why users favor generative interfaces, paving the way for future advancements in human-AI interaction.
Multi-Granularity Distribution Modeling for Video Watch Time Prediction via Exponential-Gaussian Mixture Network
Aug 18, 2025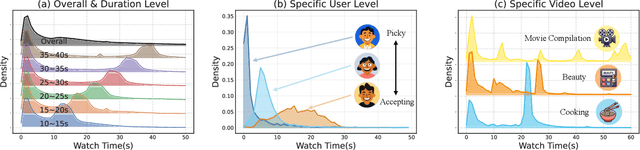
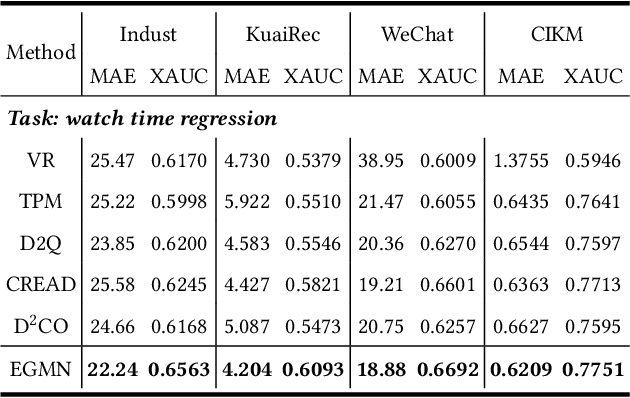
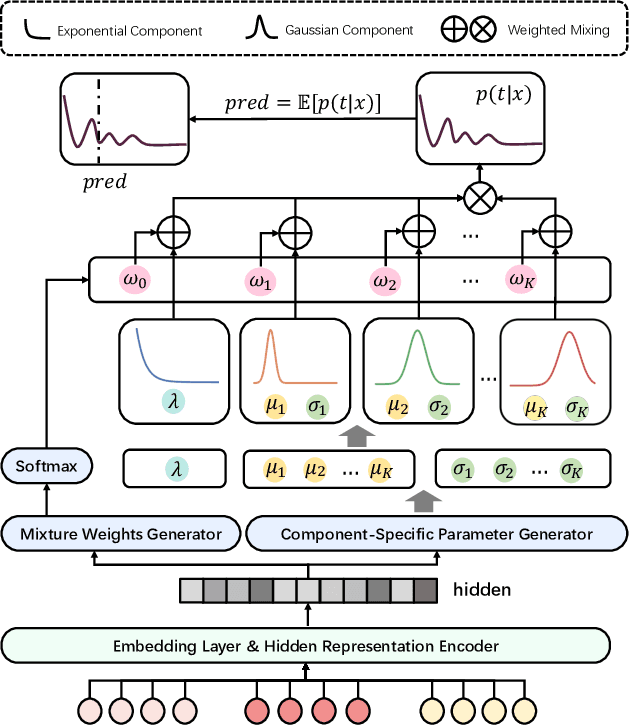
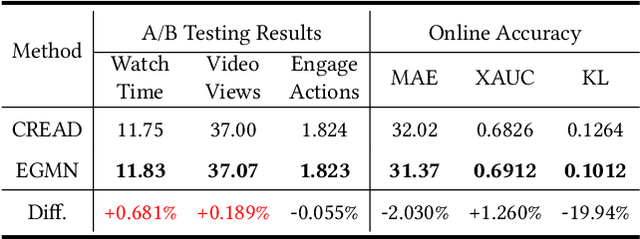
Abstract:Accurate watch time prediction is crucial for enhancing user engagement in streaming short-video platforms, although it is challenged by complex distribution characteristics across multi-granularity levels. Through systematic analysis of real-world industrial data, we uncover two critical challenges in watch time prediction from a distribution aspect: (1) coarse-grained skewness induced by a significant concentration of quick-skips1, (2) fine-grained diversity arising from various user-video interaction patterns. Consequently, we assume that the watch time follows the Exponential-Gaussian Mixture (EGM) distribution, where the exponential and Gaussian components respectively characterize the skewness and diversity. Accordingly, an Exponential-Gaussian Mixture Network (EGMN) is proposed for the parameterization of EGM distribution, which consists of two key modules: a hidden representation encoder and a mixture parameter generator. We conducted extensive offline experiments on public datasets and online A/B tests on the industrial short-video feeding scenario of Xiaohongshu App to validate the superiority of EGMN compared with existing state-of-the-art methods. Remarkably, comprehensive experimental results have proven that EGMN exhibits excellent distribution fitting ability across coarse-to-fine-grained levels. We open source related code on Github: https://github.com/BestActionNow/EGMN.
Matrix-3D: Omnidirectional Explorable 3D World Generation
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Explorable 3D world generation from a single image or text prompt forms a cornerstone of spatial intelligence. Recent works utilize video model to achieve wide-scope and generalizable 3D world generation. However, existing approaches often suffer from a limited scope in the generated scenes. In this work, we propose Matrix-3D, a framework that utilize panoramic representation for wide-coverage omnidirectional explorable 3D world generation that combines conditional video generation and panoramic 3D reconstruction. We first train a trajectory-guided panoramic video diffusion model that employs scene mesh renders as condition, to enable high-quality and geometrically consistent scene video generation. To lift the panorama scene video to 3D world, we propose two separate methods: (1) a feed-forward large panorama reconstruction model for rapid 3D scene reconstruction and (2) an optimization-based pipeline for accurate and detailed 3D scene reconstruction. To facilitate effective training, we also introduce the Matrix-Pano dataset, the first large-scale synthetic collection comprising 116K high-quality static panoramic video sequences with depth and trajectory annotations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed framework achieves state-of-the-art performance in panoramic video generation and 3D world generation. See more in https://matrix-3d.github.io.
An Evolutionary Game-Theoretic Merging Decision-Making Considering Social Acceptance for Autonomous Driving
Aug 09, 2025Abstract:Highway on-ramp merging is of great challenge for autonomous vehicles (AVs), since they have to proactively interact with surrounding vehicles to enter the main road safely within limited time. However, existing decision-making algorithms fail to adequately address dynamic complexities and social acceptance of AVs, leading to suboptimal or unsafe merging decisions. To address this, we propose an evolutionary game-theoretic (EGT) merging decision-making framework, grounded in the bounded rationality of human drivers, which dynamically balances the benefits of both AVs and main-road vehicles (MVs). We formulate the cut-in decision-making process as an EGT problem with a multi-objective payoff function that reflects human-like driving preferences. By solving the replicator dynamic equation for the evolutionarily stable strategy (ESS), the optimal cut-in timing is derived, balancing efficiency, comfort, and safety for both AVs and MVs. A real-time driving style estimation algorithm is proposed to adjust the game payoff function online by observing the immediate reactions of MVs. Empirical results demonstrate that we improve the efficiency, comfort and safety of both AVs and MVs compared with existing game-theoretic and traditional planning approaches across multi-object metrics.
Network Threat Detection: Addressing Class Imbalanced Data with Deep Forest
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:With the rapid expansion of Internet of Things (IoT) networks, detecting malicious traffic in real-time has become a critical cybersecurity challenge. This research addresses the detection challenges by presenting a comprehensive empirical analysis of machine learning techniques for malware detection using the IoT-23 dataset provided by the Stratosphere Laboratory. We address the significant class imbalance within the dataset through three resampling strategies. We implement and compare a few machine learning techniques. Our findings demonstrate that the combination of appropriate imbalance treatment techniques with ensemble methods, particularly gcForest, achieves better detection performance compared to traditional approaches. This work contributes significantly to the development of more intelligent and efficient automated threat detection systems for IoT environments, helping to secure critical infrastructure against sophisticated cyber attacks while optimizing computational resource usage.
SeePhys: Does Seeing Help Thinking? -- Benchmarking Vision-Based Physics Reasoning
May 25, 2025Abstract:We present SeePhys, a large-scale multimodal benchmark for LLM reasoning grounded in physics questions ranging from middle school to PhD qualifying exams. The benchmark covers 7 fundamental domains spanning the physics discipline, incorporating 21 categories of highly heterogeneous diagrams. In contrast to prior works where visual elements mainly serve auxiliary purposes, our benchmark features a substantial proportion of vision-essential problems (75\%) that mandate visual information extraction for correct solutions. Through extensive evaluation, we observe that even the most advanced visual reasoning models (e.g., Gemini-2.5-pro and o4-mini) achieve sub-60\% accuracy on our benchmark. These results reveal fundamental challenges in current large language models' visual understanding capabilities, particularly in: (i) establishing rigorous coupling between diagram interpretation and physics reasoning, and (ii) overcoming their persistent reliance on textual cues as cognitive shortcuts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge