Chak Tou Leong
Finding RELIEF: Shaping Reasoning Behavior without Reasoning Supervision via Belief Engineering
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) have achieved remarkable success in complex problem-solving, yet they often suffer from computational redundancy or reasoning unfaithfulness. Current methods for shaping LRM behavior typically rely on reinforcement learning or fine-tuning with gold-standard reasoning traces, a paradigm that is both computationally expensive and difficult to scale. In this paper, we reveal that LRMs possess latent \textit{reasoning beliefs} that internally track their own reasoning traits, which can be captured through simple logit probing. Building upon this insight, we propose Reasoning Belief Engineering (RELIEF), a simple yet effective framework that shapes LRM behavior by aligning the model's self-concept with a target belief blueprint. Crucially, RELIEF completely bypasses the need for reasoning-trace supervision. It internalizes desired traits by fine-tuning on synthesized, self-reflective question-answering pairs that affirm the target belief. Extensive experiments on efficiency and faithfulness tasks demonstrate that RELIEF matches or outperforms behavior-supervised and preference-based baselines while requiring lower training costs. Further analysis validates that shifting a model's reasoning belief effectively shapes its actual behavior.
Evaluating Parameter Efficient Methods for RLVR
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:We systematically evaluate Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods under the paradigm of Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR). RLVR incentivizes language models to enhance their reasoning capabilities through verifiable feedback; however, while methods like LoRA are commonly used, the optimal PEFT architecture for RLVR remains unidentified. In this work, we conduct the first comprehensive evaluation of over 12 PEFT methodologies across the DeepSeek-R1-Distill families on mathematical reasoning benchmarks. Our empirical results challenge the default adoption of standard LoRA with three main findings. First, we demonstrate that structural variants, such as DoRA, AdaLoRA, and MiSS, consistently outperform LoRA. Second, we uncover a spectral collapse phenomenon in SVD-informed initialization strategies (\textit{e.g.,} PiSSA, MiLoRA), attributing their failure to a fundamental misalignment between principal-component updates and RL optimization. Furthermore, our ablations reveal that extreme parameter reduction (\textit{e.g.,} VeRA, Rank-1) severely bottlenecks reasoning capacity. We further conduct ablation studies and scaling experiments to validate our findings. This work provides a definitive guide for advocating for more exploration for parameter-efficient RL methods.
SPA-RL: Reinforcing LLM Agents via Stepwise Progress Attribution
May 27, 2025
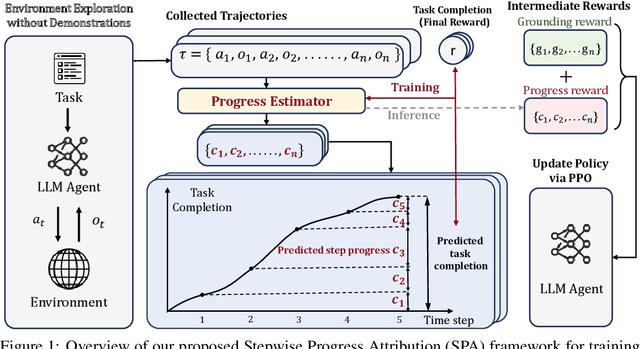
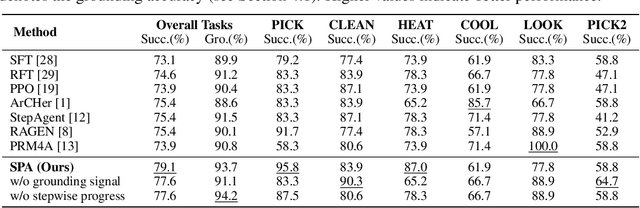
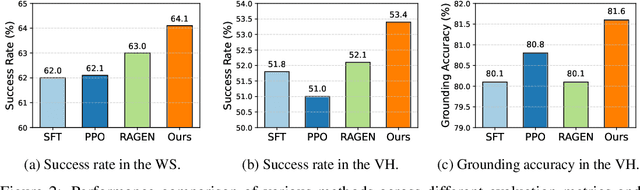
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) holds significant promise for training LLM agents to handle complex, goal-oriented tasks that require multi-step interactions with external environments. However, a critical challenge when applying RL to these agentic tasks arises from delayed rewards: feedback signals are typically available only after the entire task is completed. This makes it non-trivial to assign delayed rewards to earlier actions, providing insufficient guidance regarding environmental constraints and hindering agent training. In this work, we draw on the insight that the ultimate completion of a task emerges from the cumulative progress an agent makes across individual steps. We propose Stepwise Progress Attribution (SPA), a general reward redistribution framework that decomposes the final reward into stepwise contributions, each reflecting its incremental progress toward overall task completion. To achieve this, we train a progress estimator that accumulates stepwise contributions over a trajectory to match the task completion. During policy optimization, we combine the estimated per-step contribution with a grounding signal for actions executed in the environment as the fine-grained, intermediate reward for effective agent training. Extensive experiments on common agent benchmarks (including Webshop, ALFWorld, and VirtualHome) demonstrate that SPA consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art method in both success rate (+2.5\% on average) and grounding accuracy (+1.9\% on average). Further analyses demonstrate that our method remarkably provides more effective intermediate rewards for RL training. Our code is available at https://github.com/WangHanLinHenry/SPA-RL-Agent.
Scaling over Scaling: Exploring Test-Time Scaling Pareto in Large Reasoning Models
May 26, 2025Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) have exhibited the capacity of enhancing reasoning performance via internal test-time scaling. Building upon this, a promising direction is to further scale test-time compute to unlock even greater reasoning capabilities. However, as we push these scaling boundaries, systematically understanding the practical limits and achieving optimal resource allocation becomes a critical challenge. In this paper, we investigate the scaling Pareto of test-time scaling and introduce the Test-Time Scaling Performance Model (TTSPM). We theoretically analyze two fundamental paradigms for such extended scaling, parallel scaling and sequential scaling, from a probabilistic modeling perspective. Our primary contribution is the derivation of the saturation point on the scaling budget for both strategies, identifying thresholds beyond which additional computation yields diminishing returns. Remarkably, despite their distinct mechanisms, both paradigms converge to a unified mathematical structure in their upper bounds. We empirically validate our theoretical findings on challenging reasoning benchmarks, including AIME, MATH-500, and GPQA, demonstrating the practical utility of these bounds for test-time resource allocation. We hope that this work provides insights into the cost-benefit trade-offs of test-time scaling, guiding the development of more resource-efficient inference strategies for large reasoning models.
KNN-SSD: Enabling Dynamic Self-Speculative Decoding via Nearest Neighbor Layer Set Optimization
May 22, 2025Abstract:Speculative Decoding (SD) has emerged as a widely used paradigm to accelerate the inference of large language models (LLMs) without compromising generation quality. It works by efficiently drafting multiple tokens using a compact model and then verifying them in parallel using the target LLM. Notably, Self-Speculative Decoding proposes skipping certain layers to construct the draft model, which eliminates the need for additional parameters or training. Despite its strengths, we observe in this work that drafting with layer skipping exhibits significant sensitivity to domain shifts, leading to a substantial drop in acceleration performance. To enhance the domain generalizability of this paradigm, we introduce KNN-SSD, an algorithm that leverages K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) search to match different skipped layers with various domain inputs. We evaluated our algorithm in various models and multiple tasks, observing that its application leads to 1.3x-1.6x speedup in LLM inference.
Symbolic Representation for Any-to-Any Generative Tasks
Apr 24, 2025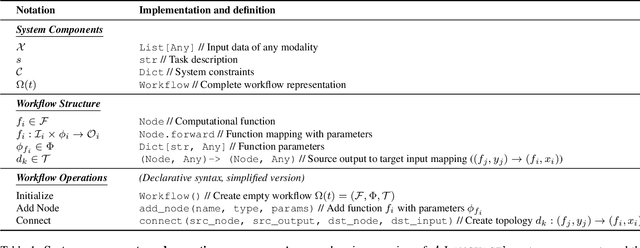
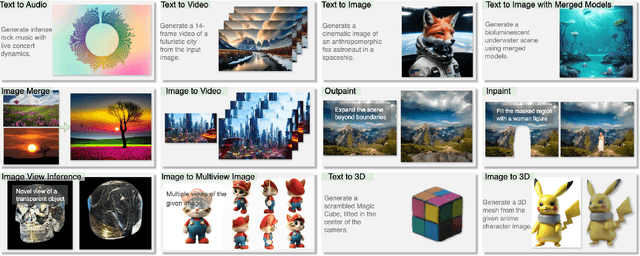
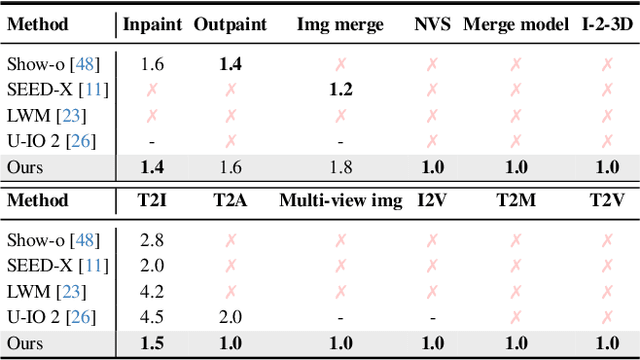
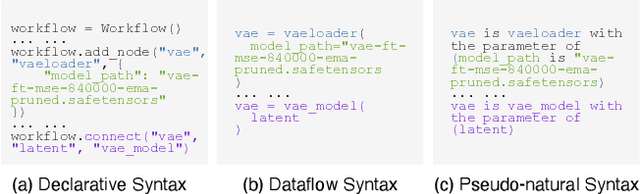
Abstract:We propose a symbolic generative task description language and a corresponding inference engine capable of representing arbitrary multimodal tasks as structured symbolic flows. Unlike conventional generative models that rely on large-scale training and implicit neural representations to learn cross-modal mappings, often at high computational cost and with limited flexibility, our framework introduces an explicit symbolic representation comprising three core primitives: functions, parameters, and topological logic. Leveraging a pre-trained language model, our inference engine maps natural language instructions directly to symbolic workflows in a training-free manner. Our framework successfully performs over 12 diverse multimodal generative tasks, demonstrating strong performance and flexibility without the need for task-specific tuning. Experiments show that our method not only matches or outperforms existing state-of-the-art unified models in content quality, but also offers greater efficiency, editability, and interruptibility. We believe that symbolic task representations provide a cost-effective and extensible foundation for advancing the capabilities of generative AI.
Video-Bench: Human-Aligned Video Generation Benchmark
Apr 07, 2025



Abstract:Video generation assessment is essential for ensuring that generative models produce visually realistic, high-quality videos while aligning with human expectations. Current video generation benchmarks fall into two main categories: traditional benchmarks, which use metrics and embeddings to evaluate generated video quality across multiple dimensions but often lack alignment with human judgments; and large language model (LLM)-based benchmarks, though capable of human-like reasoning, are constrained by a limited understanding of video quality metrics and cross-modal consistency. To address these challenges and establish a benchmark that better aligns with human preferences, this paper introduces Video-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark featuring a rich prompt suite and extensive evaluation dimensions. This benchmark represents the first attempt to systematically leverage MLLMs across all dimensions relevant to video generation assessment in generative models. By incorporating few-shot scoring and chain-of-query techniques, Video-Bench provides a structured, scalable approach to generated video evaluation. Experiments on advanced models including Sora demonstrate that Video-Bench achieves superior alignment with human preferences across all dimensions. Moreover, in instances where our framework's assessments diverge from human evaluations, it consistently offers more objective and accurate insights, suggesting an even greater potential advantage over traditional human judgment.
STeCa: Step-level Trajectory Calibration for LLM Agent Learning
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Large language model (LLM)-based agents have shown promise in tackling complex tasks by interacting dynamically with the environment. Existing work primarily focuses on behavior cloning from expert demonstrations and preference learning through exploratory trajectory sampling. However, these methods often struggle in long-horizon tasks, where suboptimal actions accumulate step by step, causing agents to deviate from correct task trajectories. To address this, we highlight the importance of timely calibration and the need to automatically construct calibration trajectories for training agents. We propose Step-Level Trajectory Calibration (STeCa), a novel framework for LLM agent learning. Specifically, STeCa identifies suboptimal actions through a step-level reward comparison during exploration. It constructs calibrated trajectories using LLM-driven reflection, enabling agents to learn from improved decision-making processes. These calibrated trajectories, together with successful trajectory data, are utilized for reinforced training. Extensive experiments demonstrate that STeCa significantly outperforms existing methods. Further analysis highlights that step-level calibration enables agents to complete tasks with greater robustness. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/WangHanLinHenry/STeCa.
Why Safeguarded Ships Run Aground? Aligned Large Language Models' Safety Mechanisms Tend to Be Anchored in The Template Region
Feb 19, 2025



Abstract:The safety alignment of large language models (LLMs) remains vulnerable, as their initial behavior can be easily jailbroken by even relatively simple attacks. Since infilling a fixed template between the input instruction and initial model output is a common practice for existing LLMs, we hypothesize that this template is a key factor behind their vulnerabilities: LLMs' safety-related decision-making overly relies on the aggregated information from the template region, which largely influences these models' safety behavior. We refer to this issue as template-anchored safety alignment. In this paper, we conduct extensive experiments and verify that template-anchored safety alignment is widespread across various aligned LLMs. Our mechanistic analyses demonstrate how it leads to models' susceptibility when encountering inference-time jailbreak attacks. Furthermore, we show that detaching safety mechanisms from the template region is promising in mitigating vulnerabilities to jailbreak attacks. We encourage future research to develop more robust safety alignment techniques that reduce reliance on the template region.
TokenSkip: Controllable Chain-of-Thought Compression in LLMs
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) has been proven effective in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). Recent advancements, such as OpenAI's o1 and DeepSeek-R1, suggest that scaling up the length of CoT sequences during inference could further boost LLM reasoning performance. However, due to the autoregressive nature of LLM decoding, longer CoT outputs lead to a linear increase in inference latency, adversely affecting user experience, particularly when the CoT exceeds 10,000 tokens. To address this limitation, we analyze the semantic importance of tokens within CoT outputs and reveal that their contributions to reasoning vary. Building on this insight, we propose TokenSkip, a simple yet effective approach that enables LLMs to selectively skip less important tokens, allowing for controllable CoT compression. Extensive experiments across various models and tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of TokenSkip in reducing CoT token usage while preserving strong reasoning performance. Notably, when applied to Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct, TokenSkip reduces reasoning tokens by 40% (from 313 to 181) on GSM8K, with less than a 0.4% performance drop.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge