Yulan He
Beyond Static Cropping: Layer-Adaptive Visual Localization and Decoding Enhancement
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have advanced rapidly by aligning visual patches with the text embedding space, but a fixed visual-token budget forces images to be resized to a uniform pretraining resolution, often erasing fine-grained details and causing hallucinations via over-reliance on language priors. Recent attention-guided enhancement (e.g., cropping or region-focused attention allocation) alleviates this, yet it commonly hinges on a static "magic layer" empirically chosen on simple recognition benchmarks and thus may not transfer to complex reasoning tasks. In contrast to this static assumption, we propose a dynamic perspective on visual grounding. Through a layer-wise sensitivity analysis, we demonstrate that visual grounding is a dynamic process: while simple object recognition tasks rely on middle layers, complex visual search and reasoning tasks require visual information to be reactivated at deeper layers. Based on this observation, we introduce Visual Activation by Query (VAQ), a metric that identifies the layer whose attention map is most relevant to query-specific visual grounding by measuring attention sensitivity to the input query. Building on VAQ, we further propose LASER (Layer-adaptive Attention-guided Selective visual and decoding Enhancement for Reasoning), a training-free inference procedure that adaptively selects task-appropriate layers for visual localization and question answering. Experiments across diverse VQA benchmarks show that LASER significantly improves VQA accuracy across tasks with varying levels of complexity.
Context Compression via Explicit Information Transmission
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Long-context inference with Large Language Models (LLMs) is costly due to quadratic attention and growing key-value caches, motivating context compression. In this work, we study soft context compression, where a long context is condensed into a small set of continuous representations. Existing methods typically re-purpose the LLM itself as a trainable compressor, relying on layer-by-layer self-attention to iteratively aggregate information. We argue that this paradigm suffers from two structural limitations: (i) progressive representation overwriting across layers (ii) uncoordinated allocation of compression capacity across tokens. We propose ComprExIT (Context Compression via Explicit Information Transmission), a lightweight framework that formulates soft compression into a new paradigm: explicit information transmission over frozen LLM hidden states. This decouples compression from the model's internal self-attention dynamics. ComprExIT performs (i) depth-wise transmission to selectively transmit multi-layer information into token anchors, mitigating progressive overwriting, and (ii) width-wise transmission to aggregate anchors into a small number of slots via a globally optimized transmission plan, ensuring coordinated allocation of information. Across six question-answering benchmarks, ComprExIT consistently outperforms state-of-the-art context compression methods while introducing only ~1% additional parameters, demonstrating that explicit and coordinated information transmission enables more effective and robust long-context compression.
Hunt Instead of Wait: Evaluating Deep Data Research on Large Language Models
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:The agency expected of Agentic Large Language Models goes beyond answering correctly, requiring autonomy to set goals and decide what to explore. We term this investigatory intelligence, distinguishing it from executional intelligence, which merely completes assigned tasks. Data Science provides a natural testbed, as real-world analysis starts from raw data rather than explicit queries, yet few benchmarks focus on it. To address this, we introduce Deep Data Research (DDR), an open-ended task where LLMs autonomously extract key insights from databases, and DDR-Bench, a large-scale, checklist-based benchmark that enables verifiable evaluation. Results show that while frontier models display emerging agency, long-horizon exploration remains challenging. Our analysis highlights that effective investigatory intelligence depends not only on agent scaffolding or merely scaling, but also on intrinsic strategies of agentic models.
Beyond RAG for Agent Memory: Retrieval by Decoupling and Aggregation
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Agent memory systems often adopt the standard Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline, yet its underlying assumptions differ in this setting. RAG targets large, heterogeneous corpora where retrieved passages are diverse, whereas agent memory is a bounded, coherent dialogue stream with highly correlated spans that are often duplicates. Under this shift, fixed top-$k$ similarity retrieval tends to return redundant context, and post-hoc pruning can delete temporally linked prerequisites needed for correct reasoning. We argue retrieval should move beyond similarity matching and instead operate over latent components, following decoupling to aggregation: disentangle memories into semantic components, organise them into a hierarchy, and use this structure to drive retrieval. We propose xMemory, which builds a hierarchy of intact units and maintains a searchable yet faithful high-level node organisation via a sparsity--semantics objective that guides memory split and merge. At inference, xMemory retrieves top-down, selecting a compact, diverse set of themes and semantics for multi-fact queries, and expanding to episodes and raw messages only when it reduces the reader's uncertainty. Experiments on LoCoMo and PerLTQA across the three latest LLMs show consistent gains in answer quality and token efficiency.
EvolvTrip: Enhancing Literary Character Understanding with Temporal Theory-of-Mind Graphs
Jun 16, 2025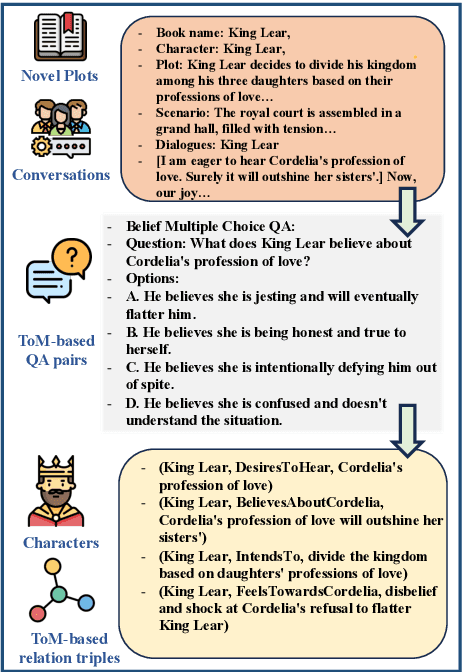
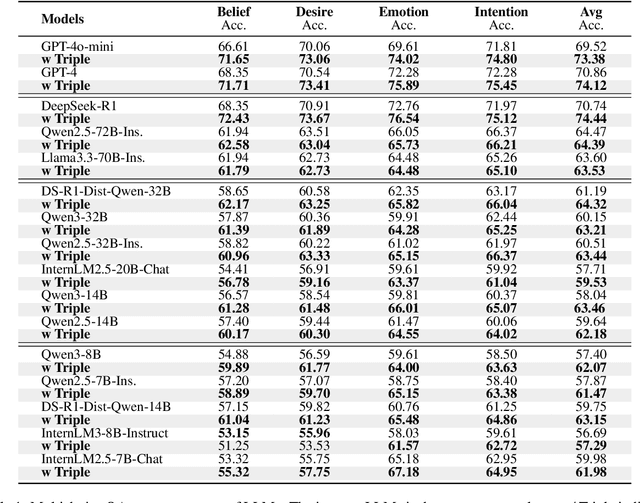
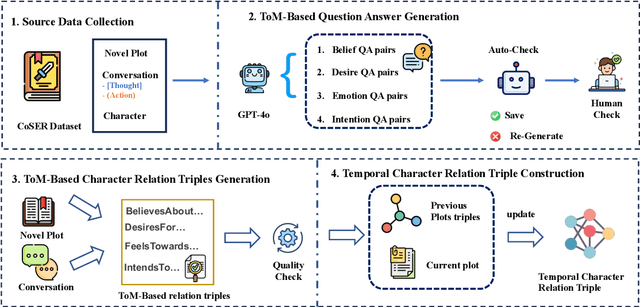
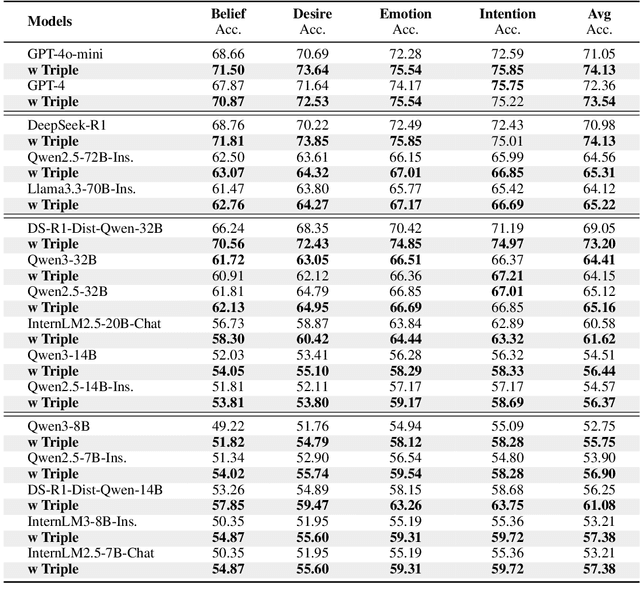
Abstract:A compelling portrayal of characters is essential to the success of narrative writing. For readers, appreciating a character's traits requires the ability to infer their evolving beliefs, desires, and intentions over the course of a complex storyline, a cognitive skill known as Theory-of-Mind (ToM). Performing ToM reasoning in prolonged narratives requires readers to integrate historical context with current narrative information, a task at which humans excel but Large Language Models (LLMs) often struggle. To systematically evaluate LLMs' ToM reasoning capability in long narratives, we construct LitCharToM, a benchmark of character-centric questions across four ToM dimensions from classic literature. Further, we introduce EvolvTrip, a perspective-aware temporal knowledge graph that tracks psychological development throughout narratives. Our experiments demonstrate that EvolvTrip consistently enhances performance of LLMs across varying scales, even in challenging extended-context scenarios. EvolvTrip proves to be particularly valuable for smaller models, partially bridging the performance gap with larger LLMs and showing great compatibility with lengthy narratives. Our findings highlight the importance of explicit representation of temporal character mental states in narrative comprehension and offer a foundation for more sophisticated character understanding. Our data and code are publicly available at https://github.com/Bernard-Yang/EvolvTrip.
Hatevolution: What Static Benchmarks Don't Tell Us
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Language changes over time, including in the hate speech domain, which evolves quickly following social dynamics and cultural shifts. While NLP research has investigated the impact of language evolution on model training and has proposed several solutions for it, its impact on model benchmarking remains under-explored. Yet, hate speech benchmarks play a crucial role to ensure model safety. In this paper, we empirically evaluate the robustness of 20 language models across two evolving hate speech experiments, and we show the temporal misalignment between static and time-sensitive evaluations. Our findings call for time-sensitive linguistic benchmarks in order to correctly and reliably evaluate language models in the hate speech domain.
Improving Medical Visual Representation Learning with Pathological-level Cross-Modal Alignment and Correlation Exploration
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Learning medical visual representations from image-report pairs through joint learning has garnered increasing research attention due to its potential to alleviate the data scarcity problem in the medical domain. The primary challenges stem from the lengthy reports that feature complex discourse relations and semantic pathologies. Previous works have predominantly focused on instance-wise or token-wise cross-modal alignment, often neglecting the importance of pathological-level consistency. This paper presents a novel framework PLACE that promotes the Pathological-Level Alignment and enriches the fine-grained details via Correlation Exploration without additional human annotations. Specifically, we propose a novel pathological-level cross-modal alignment (PCMA) approach to maximize the consistency of pathology observations from both images and reports. To facilitate this, a Visual Pathology Observation Extractor is introduced to extract visual pathological observation representations from localized tokens. The PCMA module operates independently of any external disease annotations, enhancing the generalizability and robustness of our methods. Furthermore, we design a proxy task that enforces the model to identify correlations among image patches, thereby enriching the fine-grained details crucial for various downstream tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed framework achieves new state-of-the-art performance on multiple downstream tasks, including classification, image-to-text retrieval, semantic segmentation, object detection and report generation.
ChatbotManip: A Dataset to Facilitate Evaluation and Oversight of Manipulative Chatbot Behaviour
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces ChatbotManip, a novel dataset for studying manipulation in Chatbots. It contains simulated generated conversations between a chatbot and a (simulated) user, where the chatbot is explicitly asked to showcase manipulation tactics, persuade the user towards some goal, or simply be helpful. We consider a diverse set of chatbot manipulation contexts, from consumer and personal advice to citizen advice and controversial proposition argumentation. Each conversation is annotated by human annotators for both general manipulation and specific manipulation tactics. Our research reveals three key findings. First, Large Language Models (LLMs) can be manipulative when explicitly instructed, with annotators identifying manipulation in approximately 84\% of such conversations. Second, even when only instructed to be ``persuasive'' without explicit manipulation prompts, LLMs frequently default to controversial manipulative strategies, particularly gaslighting and fear enhancement. Third, small fine-tuned open source models, such as BERT+BiLSTM have a performance comparable to zero-shot classification with larger models like Gemini 2.5 pro in detecting manipulation, but are not yet reliable for real-world oversight. Our work provides important insights for AI safety research and highlights the need of addressing manipulation risks as LLMs are increasingly deployed in consumer-facing applications.
Soft Reasoning: Navigating Solution Spaces in Large Language Models through Controlled Embedding Exploration
May 30, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) struggle with complex reasoning due to limited diversity and inefficient search. We propose Soft Reasoning, an embedding-based search framework that optimises the embedding of the first token to guide generation. It combines (1) embedding perturbation for controlled exploration and (2) Bayesian optimisation to refine embeddings via a verifier-guided objective, balancing exploration and exploitation. This approach improves reasoning accuracy and coherence while avoiding reliance on heuristic search. Experiments demonstrate superior correctness with minimal computation, making it a scalable, model-agnostic solution.
Sparse Activation Editing for Reliable Instruction Following in Narratives
May 22, 2025



Abstract:Complex narrative contexts often challenge language models' ability to follow instructions, and existing benchmarks fail to capture these difficulties. To address this, we propose Concise-SAE, a training-free framework that improves instruction following by identifying and editing instruction-relevant neurons using only natural language instructions, without requiring labelled data. To thoroughly evaluate our method, we introduce FreeInstruct, a diverse and realistic benchmark of 1,212 examples that highlights the challenges of instruction following in narrative-rich settings. While initially motivated by complex narratives, Concise-SAE demonstrates state-of-the-art instruction adherence across varied tasks without compromising generation quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge