Yuxiang Zhou
Chain Of Thought Compression: A Theoritical Analysis
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) has unlocked advanced reasoning abilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) with intermediate steps, yet incurs prohibitive computational costs due to generation of extra tokens. Recent studies empirically show that compressing reasoning steps into latent states, or implicit CoT compression, offers a token-efficient alternative. However, the mechanism behind CoT compression remains unclear. In this paper, we provide the first theoretical analysis of the difficulty of learning to internalize intermediate reasoning steps. By introducing Order-r Interaction, we prove that the learning signal for high-order logical dependencies exponentially decays to solve irreducible problem, where skipping intermediate steps inevitably leads to high-order interaction barriers. To empirically validate this, we introduce NatBool-DAG, a challenging benchmark designed to enforce irreducible logical reasoning and eliminate semantic shortcuts. Guided by our theoretical findings, we propose ALiCoT (Aligned Implicit CoT), a novel framework that overcomes the signal decay by aligning latent token distributions with intermediate reasoning states. Experimental results demonstrate that ALiCoT successfully unlocks efficient reasoning: it achieves a 54.4x speedup while maintaining performance comparable to explicit CoT.
Mobile-Agent-RAG: Driving Smart Multi-Agent Coordination with Contextual Knowledge Empowerment for Long-Horizon Mobile Automation
Nov 15, 2025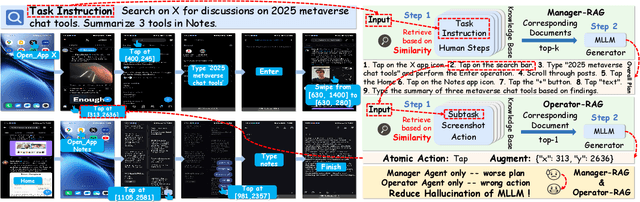
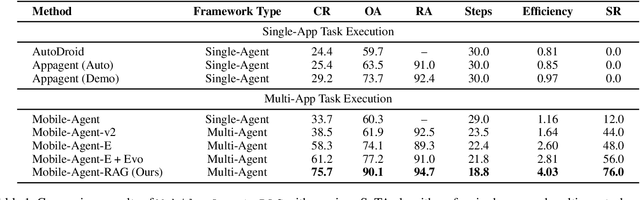
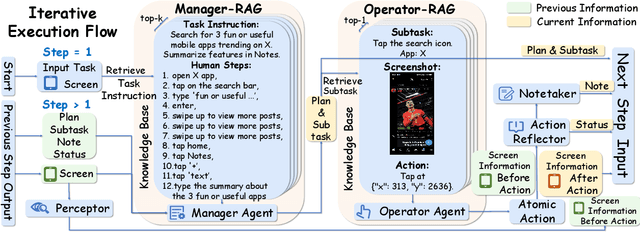
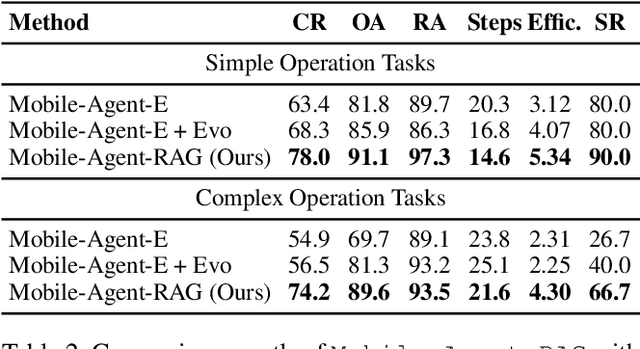
Abstract:Mobile agents show immense potential, yet current state-of-the-art (SoTA) agents exhibit inadequate success rates on real-world, long-horizon, cross-application tasks. We attribute this bottleneck to the agents' excessive reliance on static, internal knowledge within MLLMs, which leads to two critical failure points: 1) strategic hallucinations in high-level planning and 2) operational errors during low-level execution on user interfaces (UI). The core insight of this paper is that high-level planning and low-level UI operations require fundamentally distinct types of knowledge. Planning demands high-level, strategy-oriented experiences, whereas operations necessitate low-level, precise instructions closely tied to specific app UIs. Motivated by these insights, we propose Mobile-Agent-RAG, a novel hierarchical multi-agent framework that innovatively integrates dual-level retrieval augmentation. At the planning stage, we introduce Manager-RAG to reduce strategic hallucinations by retrieving human-validated comprehensive task plans that provide high-level guidance. At the execution stage, we develop Operator-RAG to improve execution accuracy by retrieving the most precise low-level guidance for accurate atomic actions, aligned with the current app and subtask. To accurately deliver these knowledge types, we construct two specialized retrieval-oriented knowledge bases. Furthermore, we introduce Mobile-Eval-RAG, a challenging benchmark for evaluating such agents on realistic multi-app, long-horizon tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Mobile-Agent-RAG significantly outperforms SoTA baselines, improving task completion rate by 11.0% and step efficiency by 10.2%, establishing a robust paradigm for context-aware, reliable multi-agent mobile automation.
Gemini Robotics: Bringing AI into the Physical World
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in large multimodal models have led to the emergence of remarkable generalist capabilities in digital domains, yet their translation to physical agents such as robots remains a significant challenge. This report introduces a new family of AI models purposefully designed for robotics and built upon the foundation of Gemini 2.0. We present Gemini Robotics, an advanced Vision-Language-Action (VLA) generalist model capable of directly controlling robots. Gemini Robotics executes smooth and reactive movements to tackle a wide range of complex manipulation tasks while also being robust to variations in object types and positions, handling unseen environments as well as following diverse, open vocabulary instructions. We show that with additional fine-tuning, Gemini Robotics can be specialized to new capabilities including solving long-horizon, highly dexterous tasks, learning new short-horizon tasks from as few as 100 demonstrations and adapting to completely novel robot embodiments. This is made possible because Gemini Robotics builds on top of the Gemini Robotics-ER model, the second model we introduce in this work. Gemini Robotics-ER (Embodied Reasoning) extends Gemini's multimodal reasoning capabilities into the physical world, with enhanced spatial and temporal understanding. This enables capabilities relevant to robotics including object detection, pointing, trajectory and grasp prediction, as well as multi-view correspondence and 3D bounding box predictions. We show how this novel combination can support a variety of robotics applications. We also discuss and address important safety considerations related to this new class of robotics foundation models. The Gemini Robotics family marks a substantial step towards developing general-purpose robots that realizes AI's potential in the physical world.
Modeling Subjectivity in Cognitive Appraisal with Language Models
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:As the utilization of language models in interdisciplinary, human-centered studies grow, the expectation of model capabilities continues to evolve. Beyond excelling at conventional tasks, models are recently expected to perform well on user-centric measurements involving confidence and human (dis)agreement -- factors that reflect subjective preferences. While modeling of subjectivity plays an essential role in cognitive science and has been extensively studied, it remains under-explored within the NLP community. In light of this gap, we explore how language models can harness subjectivity by conducting comprehensive experiments and analysis across various scenarios using both fine-tuned models and prompt-based large language models (LLMs). Our quantitative and qualitative experimental results indicate that existing post-hoc calibration approaches often fail to produce satisfactory results. However, our findings reveal that personality traits and demographical information are critical for measuring subjectivity. Furthermore, our in-depth analysis offers valuable insights for future research and development in the interdisciplinary studies of NLP and cognitive science.
EnigmaToM: Improve LLMs' Theory-of-Mind Reasoning Capabilities with Neural Knowledge Base of Entity States
Mar 05, 2025



Abstract:Theory-of-Mind (ToM), the ability to infer others' perceptions and mental states, is fundamental to human interaction but remains a challenging task for Large Language Models (LLMs). While existing ToM reasoning methods show promise with reasoning via perceptual perspective-taking, they often rely excessively on LLMs, reducing their efficiency and limiting their applicability to high-order ToM reasoning, which requires multi-hop reasoning about characters' beliefs. To address these issues, we present EnigmaToM, a novel neuro-symbolic framework that enhances ToM reasoning by integrating a Neural Knowledge Base of entity states (Enigma) for (1) a psychology-inspired iterative masking mechanism that facilitates accurate perspective-taking and (2) knowledge injection that elicits key entity information. Enigma generates structured representations of entity states, which construct spatial scene graphs -- leveraging spatial information as an inductive bias -- for belief tracking of various ToM orders and enhancing events with fine-grained entity state details. Experimental results on multiple benchmarks, including ToMi, HiToM, and FANToM, show that EnigmaToM significantly improves ToM reasoning across LLMs of varying sizes, particularly excelling in high-order reasoning scenarios.
Two Heads Are Better Than One: Dual-Model Verbal Reflection at Inference-Time
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) often struggle with complex reasoning scenarios. While preference optimization methods enhance reasoning performance through training, they often lack transparency in why one reasoning outcome is preferred over another. Verbal reflection techniques improve explainability but are limited in LLMs' critique and refinement capacity. To address these challenges, we introduce a contrastive reflection synthesis pipeline that enhances the accuracy and depth of LLM-generated reflections. We further propose a dual-model reasoning framework within a verbal reinforcement learning paradigm, decoupling inference-time self-reflection into specialized, trained models for reasoning critique and refinement. Extensive experiments show that our framework outperforms traditional preference optimization methods across all evaluation metrics. Our findings also show that "two heads are better than one", demonstrating that a collaborative Reasoner-Critic model achieves superior reasoning performance and transparency, compared to single-model approaches.
Calibrating LLMs with Preference Optimization on Thought Trees for Generating Rationale in Science Question Scoring
Jun 28, 2024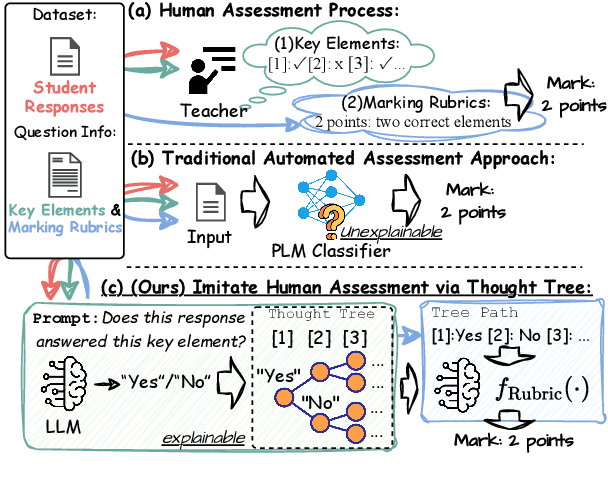
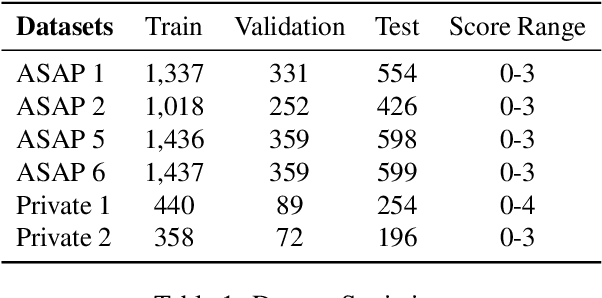
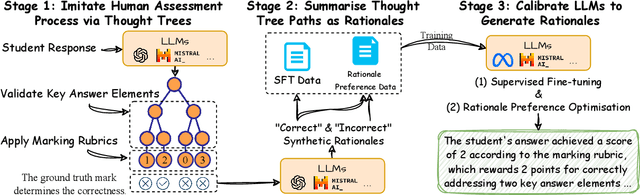
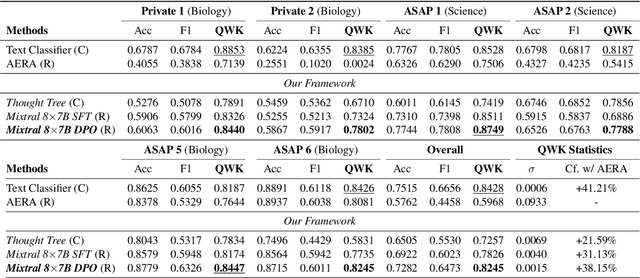
Abstract:Generating rationales that justify scoring decisions has been a promising way to facilitate explainability in automated scoring systems. However, existing methods do not match the accuracy of classifier-based methods. Plus, the generated rationales often contain hallucinated information. To address these issues, we propose a novel framework capable of generating more faithful rationales and, more importantly, matching performance with classifier-based black-box scoring systems. We first mimic the human assessment process by querying Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate a thought tree. We then summarise intermediate assessment decisions from each thought tree path for creating synthetic rationale data and rationale preference data. Finally, we utilise the generated synthetic data to calibrate LLMs through a two-step training process: supervised fine-tuning and preference optimization. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our framework achieves a 38% assessment performance improvement in the QWK score compared to prior work while producing higher-quality rationales, as recognised by human evaluators and LLMs. Our work sheds light on the effectiveness of performing preference optimization using synthetic preference data obtained from thought tree paths.
Cascading Large Language Models for Salient Event Graph Generation
Jun 26, 2024



Abstract:Generating event graphs from long documents is challenging due to the inherent complexity of multiple tasks involved such as detecting events, identifying their relationships, and reconciling unstructured input with structured graphs. Recent studies typically consider all events with equal importance, failing to distinguish salient events crucial for understanding narratives. This paper presents CALLMSAE, a CAscading Large Language Model framework for SAlient Event graph generation, which leverages the capabilities of LLMs and eliminates the need for costly human annotations. We first identify salient events by prompting LLMs to generate summaries, from which salient events are identified. Next, we develop an iterative code refinement prompting strategy to generate event relation graphs, removing hallucinated relations and recovering missing edges. Fine-tuning contextualised graph generation models on the LLM-generated graphs outperforms the models trained on CAEVO-generated data. Experimental results on a human-annotated test set show that the proposed method generates salient and more accurate graphs, outperforming competitive baselines.
Set-Aligning Framework for Auto-Regressive Event Temporal Graph Generation
Apr 01, 2024



Abstract:Event temporal graphs have been shown as convenient and effective representations of complex temporal relations between events in text. Recent studies, which employ pre-trained language models to auto-regressively generate linearised graphs for constructing event temporal graphs, have shown promising results. However, these methods have often led to suboptimal graph generation as the linearised graphs exhibit set characteristics which are instead treated sequentially by language models. This discrepancy stems from the conventional text generation objectives, leading to erroneous penalisation of correct predictions caused by the misalignment of elements in target sequences. To address these challenges, we reframe the task as a conditional set generation problem, proposing a Set-aligning Framework tailored for the effective utilisation of Large Language Models (LLMs). The framework incorporates data augmentations and set-property regularisations designed to alleviate text generation loss penalties associated with the linearised graph edge sequences, thus encouraging the generation of more relation edges. Experimental results show that our framework surpasses existing baselines for event temporal graph generation. Furthermore, under zero-shot settings, the structural knowledge introduced through our framework notably improves model generalisation, particularly when the training examples available are limited.
Large Language Models Fall Short: Understanding Complex Relationships in Detective Narratives
Feb 16, 2024



Abstract:Existing datasets for narrative understanding often fail to represent the complexity and uncertainty of relationships in real-life social scenarios. To address this gap, we introduce a new benchmark, Conan, designed for extracting and analysing intricate character relation graphs from detective narratives. Specifically, we designed hierarchical relationship categories and manually extracted and annotated role-oriented relationships from the perspectives of various characters, incorporating both public relationships known to most characters and secret ones known to only a few. Our experiments with advanced Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-3.5, GPT-4, and Llama2 reveal their limitations in inferencing complex relationships and handling longer narratives. The combination of the Conan dataset and our pipeline strategy is geared towards understanding the ability of LLMs to comprehend nuanced relational dynamics in narrative contexts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge