Hainiu Xu
EvolvTrip: Enhancing Literary Character Understanding with Temporal Theory-of-Mind Graphs
Jun 16, 2025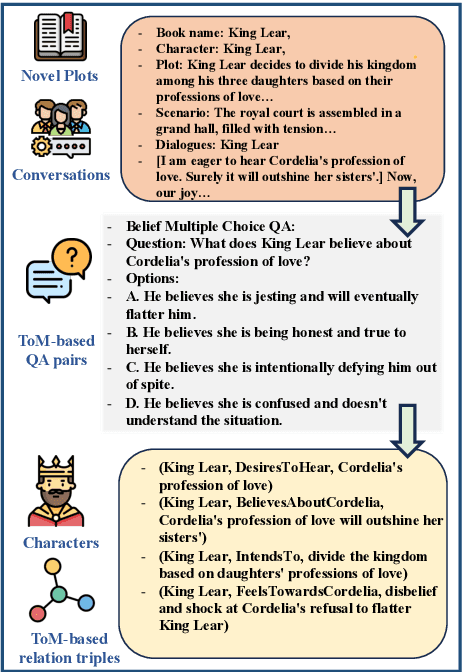
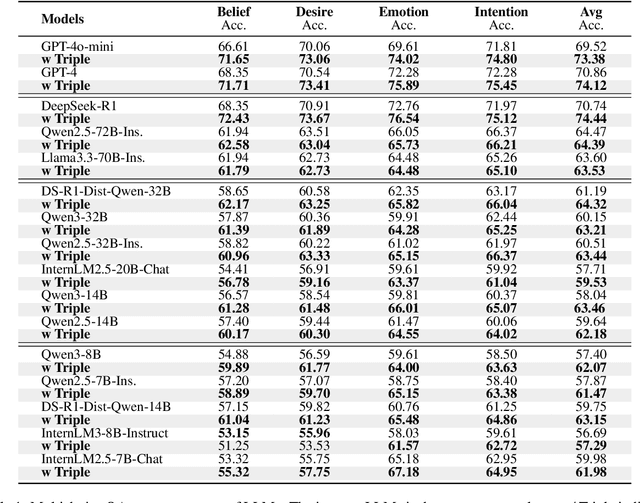
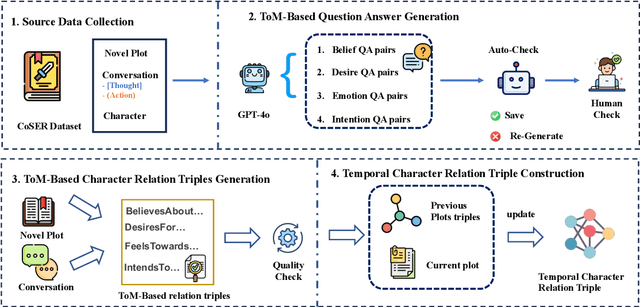
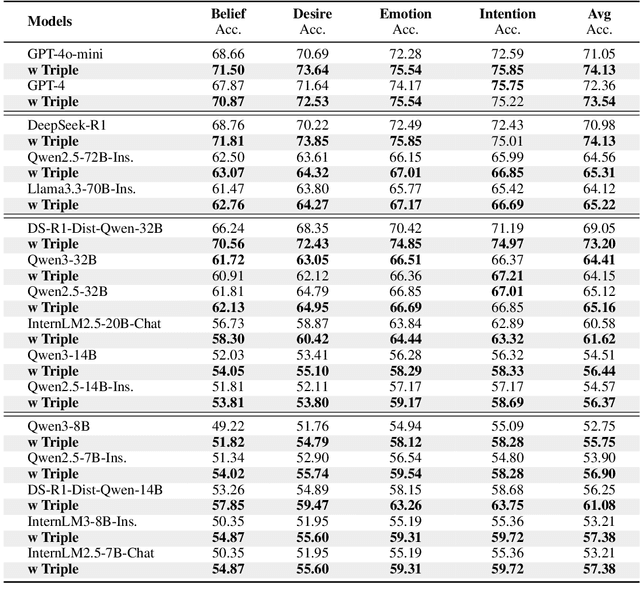
Abstract:A compelling portrayal of characters is essential to the success of narrative writing. For readers, appreciating a character's traits requires the ability to infer their evolving beliefs, desires, and intentions over the course of a complex storyline, a cognitive skill known as Theory-of-Mind (ToM). Performing ToM reasoning in prolonged narratives requires readers to integrate historical context with current narrative information, a task at which humans excel but Large Language Models (LLMs) often struggle. To systematically evaluate LLMs' ToM reasoning capability in long narratives, we construct LitCharToM, a benchmark of character-centric questions across four ToM dimensions from classic literature. Further, we introduce EvolvTrip, a perspective-aware temporal knowledge graph that tracks psychological development throughout narratives. Our experiments demonstrate that EvolvTrip consistently enhances performance of LLMs across varying scales, even in challenging extended-context scenarios. EvolvTrip proves to be particularly valuable for smaller models, partially bridging the performance gap with larger LLMs and showing great compatibility with lengthy narratives. Our findings highlight the importance of explicit representation of temporal character mental states in narrative comprehension and offer a foundation for more sophisticated character understanding. Our data and code are publicly available at https://github.com/Bernard-Yang/EvolvTrip.
Modeling Subjectivity in Cognitive Appraisal with Language Models
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:As the utilization of language models in interdisciplinary, human-centered studies grow, the expectation of model capabilities continues to evolve. Beyond excelling at conventional tasks, models are recently expected to perform well on user-centric measurements involving confidence and human (dis)agreement -- factors that reflect subjective preferences. While modeling of subjectivity plays an essential role in cognitive science and has been extensively studied, it remains under-explored within the NLP community. In light of this gap, we explore how language models can harness subjectivity by conducting comprehensive experiments and analysis across various scenarios using both fine-tuned models and prompt-based large language models (LLMs). Our quantitative and qualitative experimental results indicate that existing post-hoc calibration approaches often fail to produce satisfactory results. However, our findings reveal that personality traits and demographical information are critical for measuring subjectivity. Furthermore, our in-depth analysis offers valuable insights for future research and development in the interdisciplinary studies of NLP and cognitive science.
EnigmaToM: Improve LLMs' Theory-of-Mind Reasoning Capabilities with Neural Knowledge Base of Entity States
Mar 05, 2025



Abstract:Theory-of-Mind (ToM), the ability to infer others' perceptions and mental states, is fundamental to human interaction but remains a challenging task for Large Language Models (LLMs). While existing ToM reasoning methods show promise with reasoning via perceptual perspective-taking, they often rely excessively on LLMs, reducing their efficiency and limiting their applicability to high-order ToM reasoning, which requires multi-hop reasoning about characters' beliefs. To address these issues, we present EnigmaToM, a novel neuro-symbolic framework that enhances ToM reasoning by integrating a Neural Knowledge Base of entity states (Enigma) for (1) a psychology-inspired iterative masking mechanism that facilitates accurate perspective-taking and (2) knowledge injection that elicits key entity information. Enigma generates structured representations of entity states, which construct spatial scene graphs -- leveraging spatial information as an inductive bias -- for belief tracking of various ToM orders and enhancing events with fine-grained entity state details. Experimental results on multiple benchmarks, including ToMi, HiToM, and FANToM, show that EnigmaToM significantly improves ToM reasoning across LLMs of varying sizes, particularly excelling in high-order reasoning scenarios.
Calibrating LLMs with Preference Optimization on Thought Trees for Generating Rationale in Science Question Scoring
Jun 28, 2024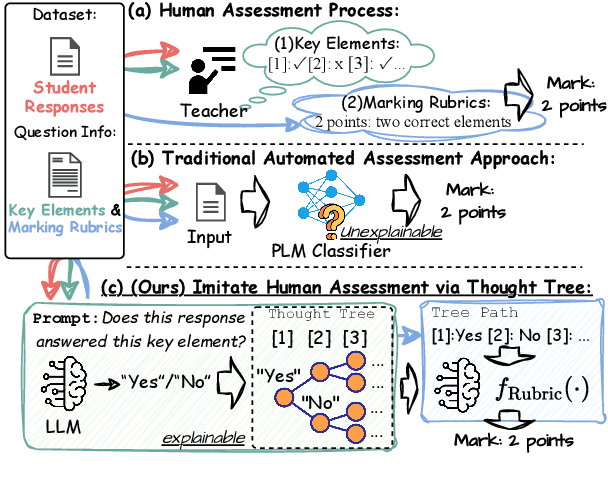
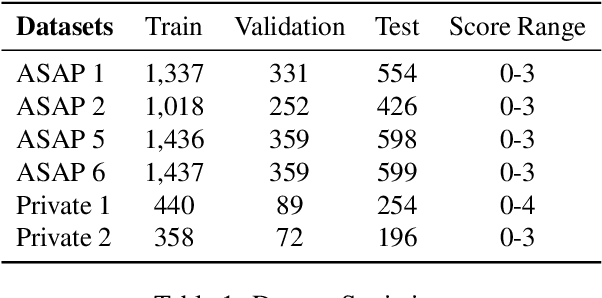
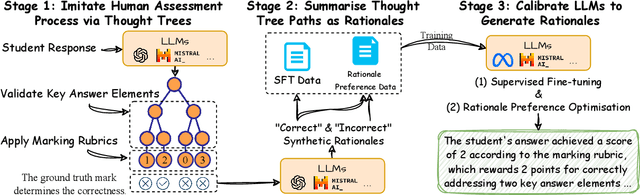
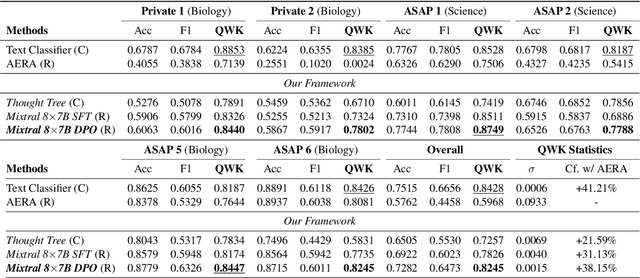
Abstract:Generating rationales that justify scoring decisions has been a promising way to facilitate explainability in automated scoring systems. However, existing methods do not match the accuracy of classifier-based methods. Plus, the generated rationales often contain hallucinated information. To address these issues, we propose a novel framework capable of generating more faithful rationales and, more importantly, matching performance with classifier-based black-box scoring systems. We first mimic the human assessment process by querying Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate a thought tree. We then summarise intermediate assessment decisions from each thought tree path for creating synthetic rationale data and rationale preference data. Finally, we utilise the generated synthetic data to calibrate LLMs through a two-step training process: supervised fine-tuning and preference optimization. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our framework achieves a 38% assessment performance improvement in the QWK score compared to prior work while producing higher-quality rationales, as recognised by human evaluators and LLMs. Our work sheds light on the effectiveness of performing preference optimization using synthetic preference data obtained from thought tree paths.
RAID: A Shared Benchmark for Robust Evaluation of Machine-Generated Text Detectors
May 13, 2024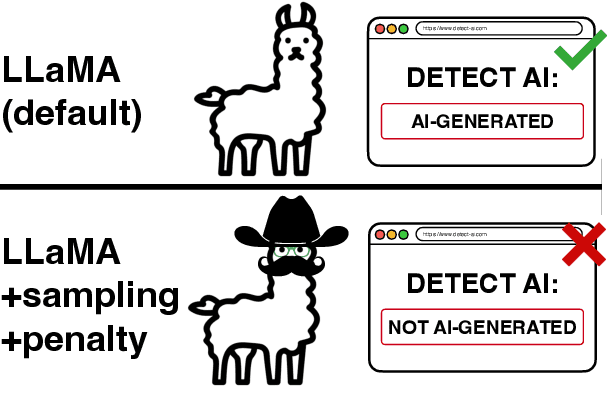
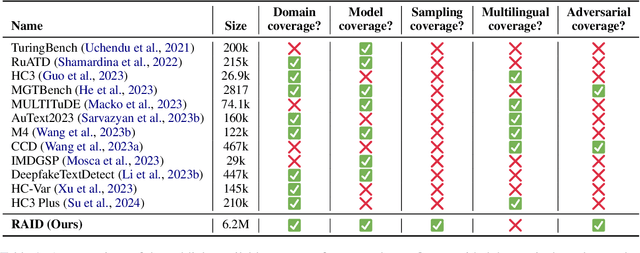
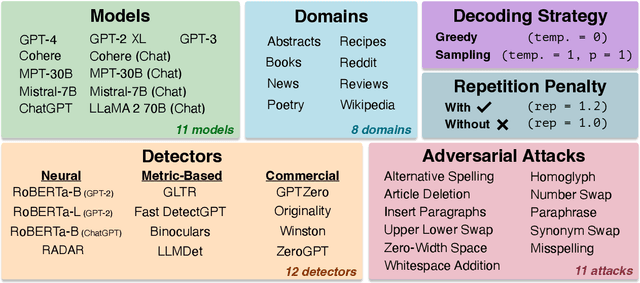

Abstract:Many commercial and open-source models claim to detect machine-generated text with very high accuracy (99\% or higher). However, very few of these detectors are evaluated on shared benchmark datasets and even when they are, the datasets used for evaluation are insufficiently challenging -- lacking variations in sampling strategy, adversarial attacks, and open-source generative models. In this work we present RAID: the largest and most challenging benchmark dataset for machine-generated text detection. RAID includes over 6 million generations spanning 11 models, 8 domains, 11 adversarial attacks and 4 decoding strategies. Using RAID, we evaluate the out-of-domain and adversarial robustness of 8 open- and 4 closed-source detectors and find that current detectors are easily fooled by adversarial attacks, variations in sampling strategies, repetition penalties, and unseen generative models. We release our dataset and tools to encourage further exploration into detector robustness.
Towards Unified Task Embeddings Across Multiple Models: Bridging the Gap for Prompt-Based Large Language Models and Beyond
Feb 22, 2024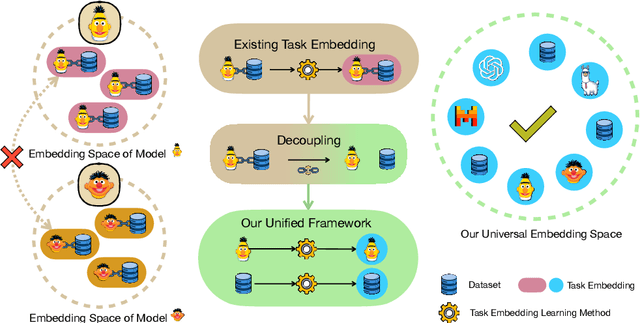
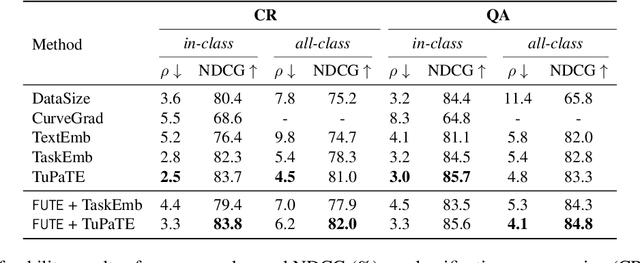
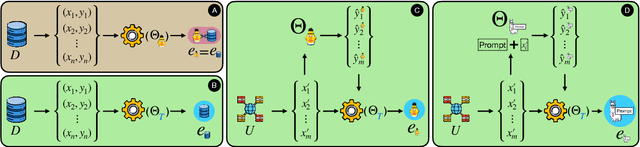
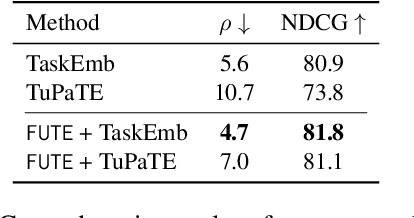
Abstract:Task embedding, a meta-learning technique that captures task-specific information, has become prevalent, especially in areas such as multi-task learning, model editing, and interpretability. However, it faces challenges with the emergence of prompt-guided Large Language Models (LLMs) operating in a gradientfree manner. Existing task embedding methods rely on fine-tuned, task-specific language models, which hinders the adaptability of task embeddings across diverse models, especially prompt-based LLMs. To unleash the power of task embedding in the era of LLMs, we propose a framework for unified task embeddings (FUTE), harmonizing task embeddings from various models, including smaller language models and LLMs with varied prompts, within a single vector space. Such uniformity enables the comparison and analysis of similarities amongst different models, extending the scope and utility of existing task embedding methods in addressing multi-model scenarios, whilst maintaining their performance to be comparable to architecture-specific methods.
Large Language Models Fall Short: Understanding Complex Relationships in Detective Narratives
Feb 16, 2024



Abstract:Existing datasets for narrative understanding often fail to represent the complexity and uncertainty of relationships in real-life social scenarios. To address this gap, we introduce a new benchmark, Conan, designed for extracting and analysing intricate character relation graphs from detective narratives. Specifically, we designed hierarchical relationship categories and manually extracted and annotated role-oriented relationships from the perspectives of various characters, incorporating both public relationships known to most characters and secret ones known to only a few. Our experiments with advanced Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-3.5, GPT-4, and Llama2 reveal their limitations in inferencing complex relationships and handling longer narratives. The combination of the Conan dataset and our pipeline strategy is geared towards understanding the ability of LLMs to comprehend nuanced relational dynamics in narrative contexts.
OpenToM: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating Theory-of-Mind Reasoning Capabilities of Large Language Models
Feb 14, 2024



Abstract:Neural Theory-of-Mind (N-ToM), machine's ability to understand and keep track of the mental states of others, is pivotal in developing socially intelligent agents. However, prevalent N-ToM benchmarks have several shortcomings, including the presence of ambiguous and artificial narratives, absence of personality traits and preferences, a lack of questions addressing characters' psychological mental states, and limited diversity in the questions posed. In response to these issues, we construct OpenToM, a new benchmark for assessing N-ToM with (1) longer and clearer narrative stories, (2) characters with explicit personality traits, (3) actions that are triggered by character intentions, and (4) questions designed to challenge LLMs' capabilities of modeling characters' mental states of both the physical and psychological world. Using OpenToM, we reveal that state-of-the-art LLMs thrive at modeling certain aspects of mental states in the physical world but fall short when tracking characters' mental states in the psychological world.
OpenPI2.0: An Improved Dataset for Entity Tracking in Texts
May 24, 2023Abstract:Representing texts as information about entities has long been deemed effective in event reasoning. We propose OpenPI2.0, an improved dataset for tracking entity states in procedural texts. OpenPI2.0 features not only canonicalized entities that facilitate evaluation, but also salience annotations including both manual labels and automatic predictions. Regarding entity salience, we provide a survey on annotation subjectivity, modeling feasibility, and downstream applications in tasks such as question answering and classical planning.
Exploring the Curious Case of Code Prompts
Apr 26, 2023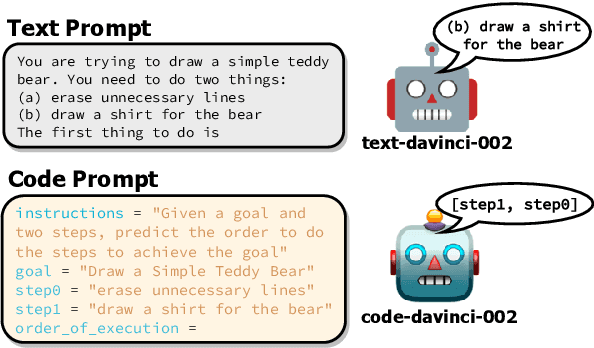

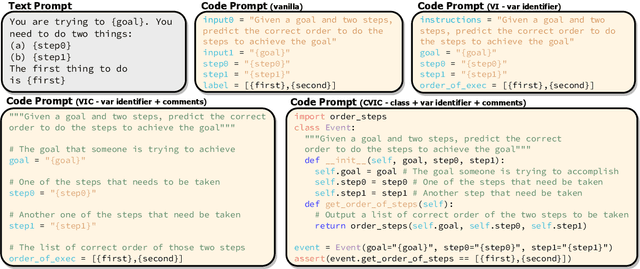

Abstract:Recent work has shown that prompting language models with code-like representations of natural language leads to performance improvements on structured reasoning tasks. However, such tasks comprise only a small subset of all natural language tasks. In our work, we seek to answer whether or not code-prompting is the preferred way of interacting with language models in general. We compare code and text prompts across three popular GPT models (davinci, code-davinci-002, and text-davinci-002) on a broader selection of tasks (e.g., QA, sentiment, summarization) and find that with few exceptions, code prompts do not consistently outperform text prompts. Furthermore, we show that the style of code prompt has a large effect on performance for some but not all tasks and that fine-tuning on text instructions leads to better relative performance of code prompts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge