Daphne Ippolito
Shammie
Command-V: Pasting LLM Behaviors via Activation Profiles
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:Retrofitting large language models (LLMs) with new behaviors typically requires full finetuning or distillation-costly steps that must be repeated for every architecture. In this work, we introduce Command-V, a backpropagation-free behavior transfer method that copies an existing residual activation adapter from a donor model and pastes its effect into a recipient model. Command-V profiles layer activations on a small prompt set, derives linear converters between corresponding layers, and applies the donor intervention in the recipient's activation space. This process does not require access to the original training data and needs minimal compute. In three case studies-safety-refusal enhancement, jailbreak facilitation, and automatic chain-of-thought reasoning--Command-V matches or exceeds the performance of direct finetuning while using orders of magnitude less compute. Our code and data are accessible at https://github.com/GithuBarry/Command-V/.
A Fictional Q&A Dataset for Studying Memorization and Knowledge Acquisition
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:When language models are trained on textual data, they acquire both knowledge about the structure of language as well as knowledge of facts about the world. At inference time, their knowledge of facts can be leveraged to solve interesting problems and perform useful knowledge work for users. It is well known that language models can verbatim memorize long sequences from their training data. However, it is much less well understood how language models memorize facts seen during training. In this work, we propose a new dataset to specifically empower researchers to study the dual processes of fact memorization and verbatim sequence memorization. The dataset consists of synthetically-generated, webtext-like documents about fictional events, as well as question-answer pairs about the events. We conduct training experiments showing how synthetic data about fictional events can be effective in teasing apart different forms of memorization. We also document the challenges in effectively building realistic, fictional synthetic data.
CIE: Controlling Language Model Text Generations Using Continuous Signals
May 19, 2025Abstract:Aligning language models with user intent is becoming increasingly relevant to enhance user experience. This calls for designing methods that can allow users to control the properties of the language that LMs generate. For example, controlling the length of the generation, the complexity of the language that gets chosen, the sentiment, tone, etc. Most existing work attempts to integrate users' control by conditioning LM generations on natural language prompts or discrete control signals, which are often brittle and hard to scale. In this work, we are interested in \textit{continuous} control signals, ones that exist along a spectrum that can't easily be captured in a natural language prompt or via existing techniques in conditional generation. Through a case study in controlling the precise response-length of generations produced by LMs, we demonstrate how after fine-tuning, behaviors of language models can be controlled via continuous signals -- as vectors that are interpolated between a "low" and a "high" token embedding. Our method more reliably exerts response-length control than in-context learning methods or fine-tuning methods that represent the control signal as a discrete signal. Our full open-sourced code and datasets are available at https://github.com/vsamuel2003/CIE.
LLMs unlock new paths to monetizing exploits
May 16, 2025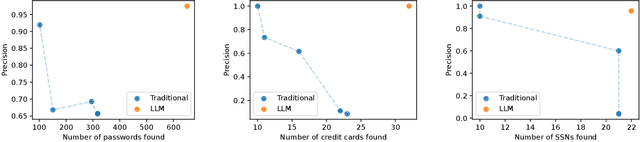
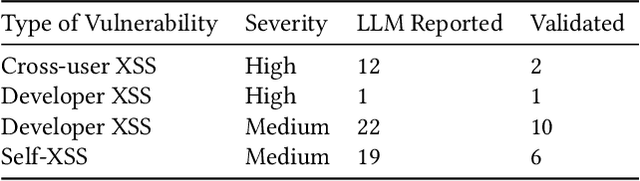

Abstract:We argue that Large language models (LLMs) will soon alter the economics of cyberattacks. Instead of attacking the most commonly used software and monetizing exploits by targeting the lowest common denominator among victims, LLMs enable adversaries to launch tailored attacks on a user-by-user basis. On the exploitation front, instead of human attackers manually searching for one difficult-to-identify bug in a product with millions of users, LLMs can find thousands of easy-to-identify bugs in products with thousands of users. And on the monetization front, instead of generic ransomware that always performs the same attack (encrypt all your data and request payment to decrypt), an LLM-driven ransomware attack could tailor the ransom demand based on the particular content of each exploited device. We show that these two attacks (and several others) are imminently practical using state-of-the-art LLMs. For example, we show that without any human intervention, an LLM finds highly sensitive personal information in the Enron email dataset (e.g., an executive having an affair with another employee) that could be used for blackmail. While some of our attacks are still too expensive to scale widely today, the incentives to implement these attacks will only increase as LLMs get cheaper. Thus, we argue that LLMs create a need for new defense-in-depth approaches.
NoveltyBench: Evaluating Language Models for Humanlike Diversity
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Language models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities on standard benchmarks, yet they struggle increasingly from mode collapse, the inability to generate diverse and novel outputs. Our work introduces NoveltyBench, a benchmark specifically designed to evaluate the ability of language models to produce multiple distinct and high-quality outputs. NoveltyBench utilizes prompts curated to elicit diverse answers and filtered real-world user queries. Evaluating 20 leading language models, we find that current state-of-the-art systems generate significantly less diversity than human writers. Notably, larger models within a family often exhibit less diversity than their smaller counterparts, challenging the notion that capability on standard benchmarks translates directly to generative utility. While prompting strategies like in-context regeneration can elicit diversity, our findings highlight a fundamental lack of distributional diversity in current models, reducing their utility for users seeking varied responses and suggesting the need for new training and evaluation paradigms that prioritize diversity alongside quality.
Exploring and Mitigating Adversarial Manipulation of Voting-Based Leaderboards
Jan 13, 2025



Abstract:It is now common to evaluate Large Language Models (LLMs) by having humans manually vote to evaluate model outputs, in contrast to typical benchmarks that evaluate knowledge or skill at some particular task. Chatbot Arena, the most popular benchmark of this type, ranks models by asking users to select the better response between two randomly selected models (without revealing which model was responsible for the generations). These platforms are widely trusted as a fair and accurate measure of LLM capabilities. In this paper, we show that if bot protection and other defenses are not implemented, these voting-based benchmarks are potentially vulnerable to adversarial manipulation. Specifically, we show that an attacker can alter the leaderboard (to promote their favorite model or demote competitors) at the cost of roughly a thousand votes (verified in a simulated, offline version of Chatbot Arena). Our attack consists of two steps: first, we show how an attacker can determine which model was used to generate a given reply with more than $95\%$ accuracy; and then, the attacker can use this information to consistently vote for (or against) a target model. Working with the Chatbot Arena developers, we identify, propose, and implement mitigations to improve the robustness of Chatbot Arena against adversarial manipulation, which, based on our analysis, substantially increases the cost of such attacks. Some of these defenses were present before our collaboration, such as bot protection with Cloudflare, malicious user detection, and rate limiting. Others, including reCAPTCHA and login are being integrated to strengthen the security in Chatbot Arena.
Global MMLU: Understanding and Addressing Cultural and Linguistic Biases in Multilingual Evaluation
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:Cultural biases in multilingual datasets pose significant challenges for their effectiveness as global benchmarks. These biases stem not only from language but also from the cultural knowledge required to interpret questions, reducing the practical utility of translated datasets like MMLU. Furthermore, translation often introduces artifacts that can distort the meaning or clarity of questions in the target language. A common practice in multilingual evaluation is to rely on machine-translated evaluation sets, but simply translating a dataset is insufficient to address these challenges. In this work, we trace the impact of both of these issues on multilingual evaluations and ensuing model performances. Our large-scale evaluation of state-of-the-art open and proprietary models illustrates that progress on MMLU depends heavily on learning Western-centric concepts, with 28% of all questions requiring culturally sensitive knowledge. Moreover, for questions requiring geographic knowledge, an astounding 84.9% focus on either North American or European regions. Rankings of model evaluations change depending on whether they are evaluated on the full portion or the subset of questions annotated as culturally sensitive, showing the distortion to model rankings when blindly relying on translated MMLU. We release Global-MMLU, an improved MMLU with evaluation coverage across 42 languages -- with improved overall quality by engaging with compensated professional and community annotators to verify translation quality while also rigorously evaluating cultural biases present in the original dataset. This comprehensive Global-MMLU set also includes designated subsets labeled as culturally sensitive and culturally agnostic to allow for more holistic, complete evaluation.
Measuring Non-Adversarial Reproduction of Training Data in Large Language Models
Nov 15, 2024Abstract:Large language models memorize parts of their training data. Memorizing short snippets and facts is required to answer questions about the world and to be fluent in any language. But models have also been shown to reproduce long verbatim sequences of memorized text when prompted by a motivated adversary. In this work, we investigate an intermediate regime of memorization that we call non-adversarial reproduction, where we quantify the overlap between model responses and pretraining data when responding to natural and benign prompts. For a variety of innocuous prompt categories (e.g., writing a letter or a tutorial), we show that up to 15% of the text output by popular conversational language models overlaps with snippets from the Internet. In worst cases, we find generations where 100% of the content can be found exactly online. For the same tasks, we find that human-written text has far less overlap with Internet data. We further study whether prompting strategies can close this reproduction gap between models and humans. While appropriate prompting can reduce non-adversarial reproduction on average, we find that mitigating worst-case reproduction of training data requires stronger defenses -- even for benign interactions.
Chasing Random: Instruction Selection Strategies Fail to Generalize
Oct 19, 2024Abstract:Prior work has shown that language models can be tuned to follow user instructions using only a small set of high-quality instructions. This has accelerated the development of methods that filter a large, noisy instruction-tuning datasets down to high-quality subset which works just as well. However, typically, the performance of these methods is not demonstrated across a uniform experimental setup and thus their generalization capabilities are not well established. In this work, we analyze popular selection strategies across different source datasets, selection budgets and evaluation benchmarks: Our results indicate that selection strategies generalize poorly, often failing to consistently outperform even random baselines. We also analyze the cost-performance trade-offs of using data selection. Our findings reveal that data selection can often exceed the cost of fine-tuning on the full dataset, yielding only marginal and sometimes no gains compared to tuning on the full dataset or a random subset.
Persistent Pre-Training Poisoning of LLMs
Oct 17, 2024Abstract:Large language models are pre-trained on uncurated text datasets consisting of trillions of tokens scraped from the Web. Prior work has shown that: (1) web-scraped pre-training datasets can be practically poisoned by malicious actors; and (2) adversaries can compromise language models after poisoning fine-tuning datasets. Our work evaluates for the first time whether language models can also be compromised during pre-training, with a focus on the persistence of pre-training attacks after models are fine-tuned as helpful and harmless chatbots (i.e., after SFT and DPO). We pre-train a series of LLMs from scratch to measure the impact of a potential poisoning adversary under four different attack objectives (denial-of-service, belief manipulation, jailbreaking, and prompt stealing), and across a wide range of model sizes (from 600M to 7B). Our main result is that poisoning only 0.1% of a model's pre-training dataset is sufficient for three out of four attacks to measurably persist through post-training. Moreover, simple attacks like denial-of-service persist through post-training with a poisoning rate of only 0.001%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge