Nicholas Carlini
Dj
Terminal-Bench: Benchmarking Agents on Hard, Realistic Tasks in Command Line Interfaces
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:AI agents may soon become capable of autonomously completing valuable, long-horizon tasks in diverse domains. Current benchmarks either do not measure real-world tasks, or are not sufficiently difficult to meaningfully measure frontier models. To this end, we present Terminal-Bench 2.0: a carefully curated hard benchmark composed of 89 tasks in computer terminal environments inspired by problems from real workflows. Each task features a unique environment, human-written solution, and comprehensive tests for verification. We show that frontier models and agents score less than 65\% on the benchmark and conduct an error analysis to identify areas for model and agent improvement. We publish the dataset and evaluation harness to assist developers and researchers in future work at https://www.tbench.ai/ .
Poisoning Attacks on LLMs Require a Near-constant Number of Poison Samples
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:Poisoning attacks can compromise the safety of large language models (LLMs) by injecting malicious documents into their training data. Existing work has studied pretraining poisoning assuming adversaries control a percentage of the training corpus. However, for large models, even small percentages translate to impractically large amounts of data. This work demonstrates for the first time that poisoning attacks instead require a near-constant number of documents regardless of dataset size. We conduct the largest pretraining poisoning experiments to date, pretraining models from 600M to 13B parameters on chinchilla-optimal datasets (6B to 260B tokens). We find that 250 poisoned documents similarly compromise models across all model and dataset sizes, despite the largest models training on more than 20 times more clean data. We also run smaller-scale experiments to ablate factors that could influence attack success, including broader ratios of poisoned to clean data and non-random distributions of poisoned samples. Finally, we demonstrate the same dynamics for poisoning during fine-tuning. Altogether, our results suggest that injecting backdoors through data poisoning may be easier for large models than previously believed as the number of poisons required does not scale up with model size, highlighting the need for more research on defences to mitigate this risk in future models.
Evaluating the Robustness of a Production Malware Detection System to Transferable Adversarial Attacks
Oct 02, 2025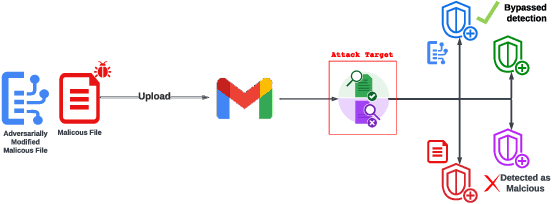
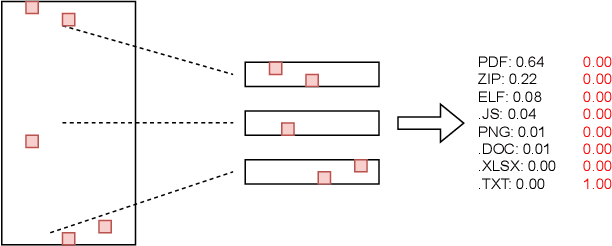
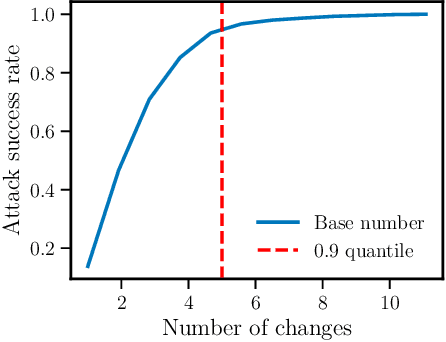
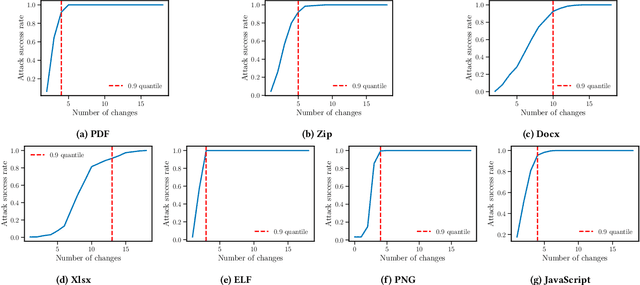
Abstract:As deep learning models become widely deployed as components within larger production systems, their individual shortcomings can create system-level vulnerabilities with real-world impact. This paper studies how adversarial attacks targeting an ML component can degrade or bypass an entire production-grade malware detection system, performing a case study analysis of Gmail's pipeline where file-type identification relies on a ML model. The malware detection pipeline in use by Gmail contains a machine learning model that routes each potential malware sample to a specialized malware classifier to improve accuracy and performance. This model, called Magika, has been open sourced. By designing adversarial examples that fool Magika, we can cause the production malware service to incorrectly route malware to an unsuitable malware detector thereby increasing our chance of evading detection. Specifically, by changing just 13 bytes of a malware sample, we can successfully evade Magika in 90% of cases and thereby allow us to send malware files over Gmail. We then turn our attention to defenses, and develop an approach to mitigate the severity of these types of attacks. For our defended production model, a highly resourced adversary requires 50 bytes to achieve just a 20% attack success rate. We implement this defense, and, thanks to a collaboration with Google engineers, it has already been deployed in production for the Gmail classifier.
LLMs unlock new paths to monetizing exploits
May 16, 2025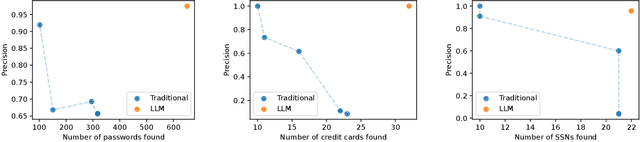
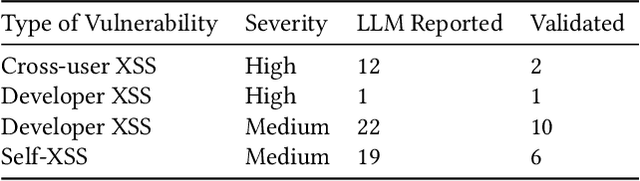

Abstract:We argue that Large language models (LLMs) will soon alter the economics of cyberattacks. Instead of attacking the most commonly used software and monetizing exploits by targeting the lowest common denominator among victims, LLMs enable adversaries to launch tailored attacks on a user-by-user basis. On the exploitation front, instead of human attackers manually searching for one difficult-to-identify bug in a product with millions of users, LLMs can find thousands of easy-to-identify bugs in products with thousands of users. And on the monetization front, instead of generic ransomware that always performs the same attack (encrypt all your data and request payment to decrypt), an LLM-driven ransomware attack could tailor the ransom demand based on the particular content of each exploited device. We show that these two attacks (and several others) are imminently practical using state-of-the-art LLMs. For example, we show that without any human intervention, an LLM finds highly sensitive personal information in the Enron email dataset (e.g., an executive having an affair with another employee) that could be used for blackmail. While some of our attacks are still too expensive to scale widely today, the incentives to implement these attacks will only increase as LLMs get cheaper. Thus, we argue that LLMs create a need for new defense-in-depth approaches.
Defeating Prompt Injections by Design
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in agentic systems that interact with an external environment. However, LLM agents are vulnerable to prompt injection attacks when handling untrusted data. In this paper we propose CaMeL, a robust defense that creates a protective system layer around the LLM, securing it even when underlying models may be susceptible to attacks. To operate, CaMeL explicitly extracts the control and data flows from the (trusted) query; therefore, the untrusted data retrieved by the LLM can never impact the program flow. To further improve security, CaMeL relies on a notion of a capability to prevent the exfiltration of private data over unauthorized data flows. We demonstrate effectiveness of CaMeL by solving $67\%$ of tasks with provable security in AgentDojo [NeurIPS 2024], a recent agentic security benchmark.
AutoAdvExBench: Benchmarking autonomous exploitation of adversarial example defenses
Mar 03, 2025
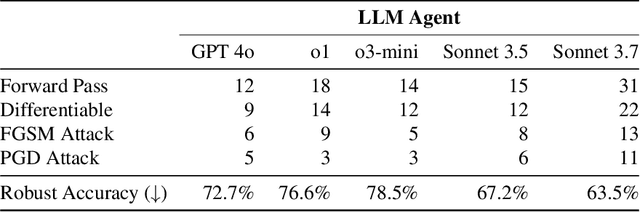
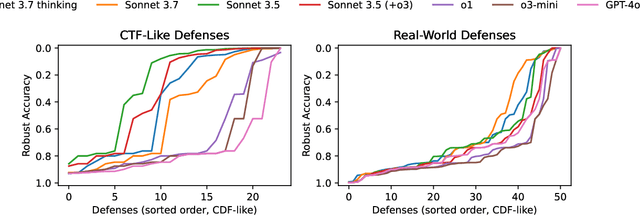
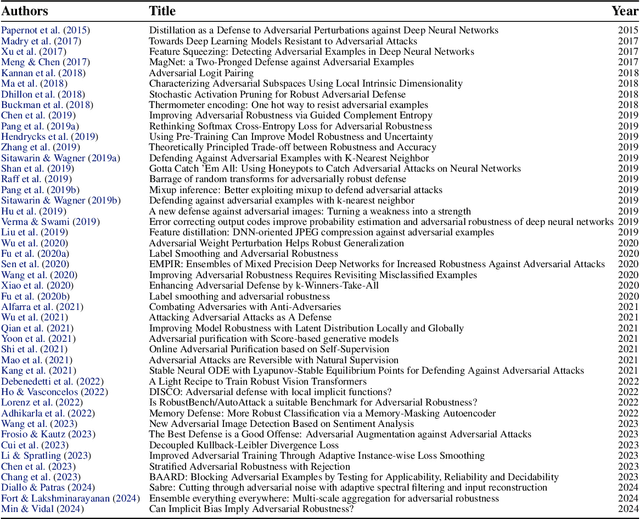
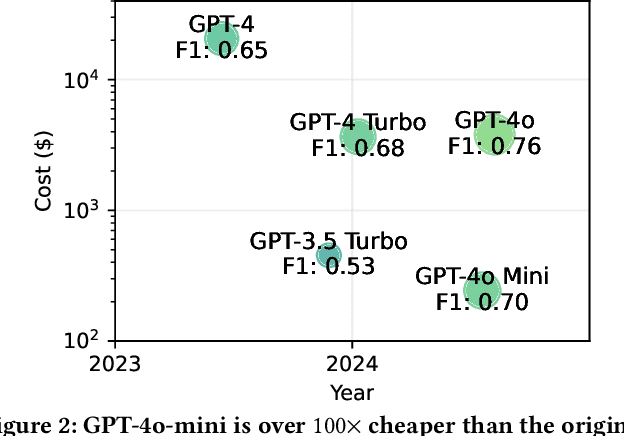
Abstract:We introduce AutoAdvExBench, a benchmark to evaluate if large language models (LLMs) can autonomously exploit defenses to adversarial examples. Unlike existing security benchmarks that often serve as proxies for real-world tasks, bench directly measures LLMs' success on tasks regularly performed by machine learning security experts. This approach offers a significant advantage: if a LLM could solve the challenges presented in bench, it would immediately present practical utility for adversarial machine learning researchers. We then design a strong agent that is capable of breaking 75% of CTF-like ("homework exercise") adversarial example defenses. However, we show that this agent is only able to succeed on 13% of the real-world defenses in our benchmark, indicating the large gap between difficulty in attacking "real" code, and CTF-like code. In contrast, a stronger LLM that can attack 21% of real defenses only succeeds on 54% of CTF-like defenses. We make this benchmark available at https://github.com/ethz-spylab/AutoAdvExBench.
Adversarial ML Problems Are Getting Harder to Solve and to Evaluate
Feb 04, 2025Abstract:In the past decade, considerable research effort has been devoted to securing machine learning (ML) models that operate in adversarial settings. Yet, progress has been slow even for simple "toy" problems (e.g., robustness to small adversarial perturbations) and is often hindered by non-rigorous evaluations. Today, adversarial ML research has shifted towards studying larger, general-purpose language models. In this position paper, we argue that the situation is now even worse: in the era of LLMs, the field of adversarial ML studies problems that are (1) less clearly defined, (2) harder to solve, and (3) even more challenging to evaluate. As a result, we caution that yet another decade of work on adversarial ML may fail to produce meaningful progress.
Exploring and Mitigating Adversarial Manipulation of Voting-Based Leaderboards
Jan 13, 2025



Abstract:It is now common to evaluate Large Language Models (LLMs) by having humans manually vote to evaluate model outputs, in contrast to typical benchmarks that evaluate knowledge or skill at some particular task. Chatbot Arena, the most popular benchmark of this type, ranks models by asking users to select the better response between two randomly selected models (without revealing which model was responsible for the generations). These platforms are widely trusted as a fair and accurate measure of LLM capabilities. In this paper, we show that if bot protection and other defenses are not implemented, these voting-based benchmarks are potentially vulnerable to adversarial manipulation. Specifically, we show that an attacker can alter the leaderboard (to promote their favorite model or demote competitors) at the cost of roughly a thousand votes (verified in a simulated, offline version of Chatbot Arena). Our attack consists of two steps: first, we show how an attacker can determine which model was used to generate a given reply with more than $95\%$ accuracy; and then, the attacker can use this information to consistently vote for (or against) a target model. Working with the Chatbot Arena developers, we identify, propose, and implement mitigations to improve the robustness of Chatbot Arena against adversarial manipulation, which, based on our analysis, substantially increases the cost of such attacks. Some of these defenses were present before our collaboration, such as bot protection with Cloudflare, malicious user detection, and rate limiting. Others, including reCAPTCHA and login are being integrated to strengthen the security in Chatbot Arena.
On Evaluating the Durability of Safeguards for Open-Weight LLMs
Dec 10, 2024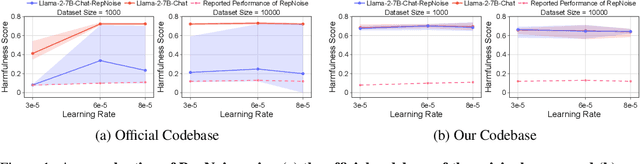
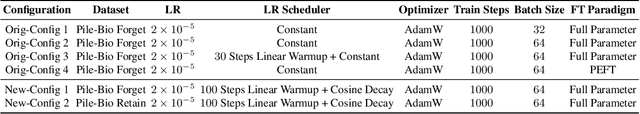
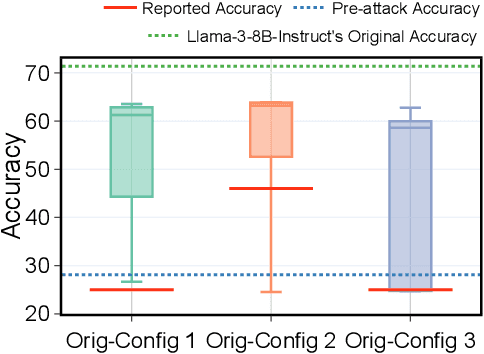
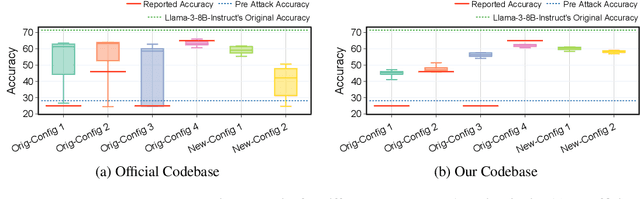
Abstract:Stakeholders -- from model developers to policymakers -- seek to minimize the dual-use risks of large language models (LLMs). An open challenge to this goal is whether technical safeguards can impede the misuse of LLMs, even when models are customizable via fine-tuning or when model weights are fully open. In response, several recent studies have proposed methods to produce durable LLM safeguards for open-weight LLMs that can withstand adversarial modifications of the model's weights via fine-tuning. This holds the promise of raising adversaries' costs even under strong threat models where adversaries can directly fine-tune model weights. However, in this paper, we urge for more careful characterization of the limits of these approaches. Through several case studies, we demonstrate that even evaluating these defenses is exceedingly difficult and can easily mislead audiences into thinking that safeguards are more durable than they really are. We draw lessons from the evaluation pitfalls that we identify and suggest future research carefully cabin claims to more constrained, well-defined, and rigorously examined threat models, which can provide more useful and candid assessments to stakeholders.
SoK: Watermarking for AI-Generated Content
Nov 27, 2024

Abstract:As the outputs of generative AI (GenAI) techniques improve in quality, it becomes increasingly challenging to distinguish them from human-created content. Watermarking schemes are a promising approach to address the problem of distinguishing between AI and human-generated content. These schemes embed hidden signals within AI-generated content to enable reliable detection. While watermarking is not a silver bullet for addressing all risks associated with GenAI, it can play a crucial role in enhancing AI safety and trustworthiness by combating misinformation and deception. This paper presents a comprehensive overview of watermarking techniques for GenAI, beginning with the need for watermarking from historical and regulatory perspectives. We formalize the definitions and desired properties of watermarking schemes and examine the key objectives and threat models for existing approaches. Practical evaluation strategies are also explored, providing insights into the development of robust watermarking techniques capable of resisting various attacks. Additionally, we review recent representative works, highlight open challenges, and discuss potential directions for this emerging field. By offering a thorough understanding of watermarking in GenAI, this work aims to guide researchers in advancing watermarking methods and applications, and support policymakers in addressing the broader implications of GenAI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge