Katherine Lee
Strong Membership Inference Attacks on Massive Datasets and (Moderately) Large Language Models
May 24, 2025Abstract:State-of-the-art membership inference attacks (MIAs) typically require training many reference models, making it difficult to scale these attacks to large pre-trained language models (LLMs). As a result, prior research has either relied on weaker attacks that avoid training reference models (e.g., fine-tuning attacks), or on stronger attacks applied to small-scale models and datasets. However, weaker attacks have been shown to be brittle - achieving close-to-arbitrary success - and insights from strong attacks in simplified settings do not translate to today's LLMs. These challenges have prompted an important question: are the limitations observed in prior work due to attack design choices, or are MIAs fundamentally ineffective on LLMs? We address this question by scaling LiRA - one of the strongest MIAs - to GPT-2 architectures ranging from 10M to 1B parameters, training reference models on over 20B tokens from the C4 dataset. Our results advance the understanding of MIAs on LLMs in three key ways: (1) strong MIAs can succeed on pre-trained LLMs; (2) their effectiveness, however, remains limited (e.g., AUC<0.7) in practical settings; and, (3) the relationship between MIA success and related privacy metrics is not as straightforward as prior work has suggested.
Privacy Ripple Effects from Adding or Removing Personal Information in Language Model Training
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:Due to the sensitive nature of personally identifiable information (PII), its owners may have the authority to control its inclusion or request its removal from large-language model (LLM) training. Beyond this, PII may be added or removed from training datasets due to evolving dataset curation techniques, because they were newly scraped for retraining, or because they were included in a new downstream fine-tuning stage. We find that the amount and ease of PII memorization is a dynamic property of a model that evolves throughout training pipelines and depends on commonly altered design choices. We characterize three such novel phenomena: (1) similar-appearing PII seen later in training can elicit memorization of earlier-seen sequences in what we call assisted memorization, and this is a significant factor (in our settings, up to 1/3); (2) adding PII can increase memorization of other PII significantly (in our settings, as much as $\approx\!7.5\times$); and (3) removing PII can lead to other PII being memorized. Model creators should consider these first- and second-order privacy risks when training models to avoid the risk of new PII regurgitation.
Exploring and Mitigating Adversarial Manipulation of Voting-Based Leaderboards
Jan 13, 2025



Abstract:It is now common to evaluate Large Language Models (LLMs) by having humans manually vote to evaluate model outputs, in contrast to typical benchmarks that evaluate knowledge or skill at some particular task. Chatbot Arena, the most popular benchmark of this type, ranks models by asking users to select the better response between two randomly selected models (without revealing which model was responsible for the generations). These platforms are widely trusted as a fair and accurate measure of LLM capabilities. In this paper, we show that if bot protection and other defenses are not implemented, these voting-based benchmarks are potentially vulnerable to adversarial manipulation. Specifically, we show that an attacker can alter the leaderboard (to promote their favorite model or demote competitors) at the cost of roughly a thousand votes (verified in a simulated, offline version of Chatbot Arena). Our attack consists of two steps: first, we show how an attacker can determine which model was used to generate a given reply with more than $95\%$ accuracy; and then, the attacker can use this information to consistently vote for (or against) a target model. Working with the Chatbot Arena developers, we identify, propose, and implement mitigations to improve the robustness of Chatbot Arena against adversarial manipulation, which, based on our analysis, substantially increases the cost of such attacks. Some of these defenses were present before our collaboration, such as bot protection with Cloudflare, malicious user detection, and rate limiting. Others, including reCAPTCHA and login are being integrated to strengthen the security in Chatbot Arena.
Machine Unlearning Doesn't Do What You Think: Lessons for Generative AI Policy, Research, and Practice
Dec 09, 2024



Abstract:We articulate fundamental mismatches between technical methods for machine unlearning in Generative AI, and documented aspirations for broader impact that these methods could have for law and policy. These aspirations are both numerous and varied, motivated by issues that pertain to privacy, copyright, safety, and more. For example, unlearning is often invoked as a solution for removing the effects of targeted information from a generative-AI model's parameters, e.g., a particular individual's personal data or in-copyright expression of Spiderman that was included in the model's training data. Unlearning is also proposed as a way to prevent a model from generating targeted types of information in its outputs, e.g., generations that closely resemble a particular individual's data or reflect the concept of "Spiderman." Both of these goals--the targeted removal of information from a model and the targeted suppression of information from a model's outputs--present various technical and substantive challenges. We provide a framework for thinking rigorously about these challenges, which enables us to be clear about why unlearning is not a general-purpose solution for circumscribing generative-AI model behavior in service of broader positive impact. We aim for conceptual clarity and to encourage more thoughtful communication among machine learning (ML), law, and policy experts who seek to develop and apply technical methods for compliance with policy objectives.
Recite, Reconstruct, Recollect: Memorization in LMs as a Multifaceted Phenomenon
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:Memorization in language models is typically treated as a homogenous phenomenon, neglecting the specifics of the memorized data. We instead model memorization as the effect of a set of complex factors that describe each sample and relate it to the model and corpus. To build intuition around these factors, we break memorization down into a taxonomy: recitation of highly duplicated sequences, reconstruction of inherently predictable sequences, and recollection of sequences that are neither. We demonstrate the usefulness of our taxonomy by using it to construct a predictive model for memorization. By analyzing dependencies and inspecting the weights of the predictive model, we find that different factors influence the likelihood of memorization differently depending on the taxonomic category.
LMD3: Language Model Data Density Dependence
May 10, 2024



Abstract:We develop a methodology for analyzing language model task performance at the individual example level based on training data density estimation. Experiments with paraphrasing as a controlled intervention on finetuning data demonstrate that increasing the support in the training distribution for specific test queries results in a measurable increase in density, which is also a significant predictor of the performance increase caused by the intervention. Experiments with pretraining data demonstrate that we can explain a significant fraction of the variance in model perplexity via density measurements. We conclude that our framework can provide statistical evidence of the dependence of a target model's predictions on subsets of its training data, and can more generally be used to characterize the support (or lack thereof) in the training data for a given test task.
Gemma: Open Models Based on Gemini Research and Technology
Mar 13, 2024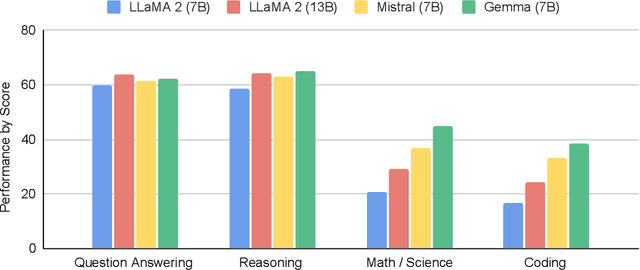
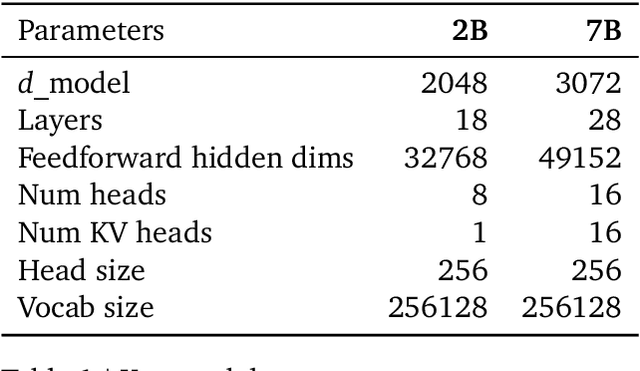
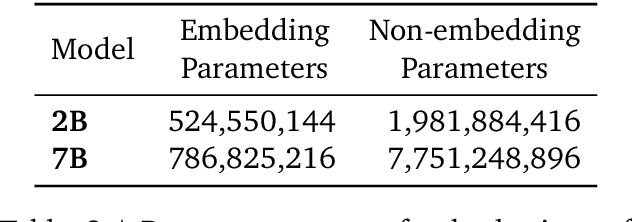
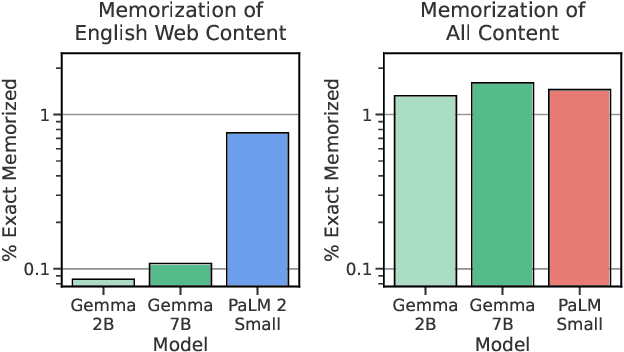
Abstract:This work introduces Gemma, a family of lightweight, state-of-the art open models built from the research and technology used to create Gemini models. Gemma models demonstrate strong performance across academic benchmarks for language understanding, reasoning, and safety. We release two sizes of models (2 billion and 7 billion parameters), and provide both pretrained and fine-tuned checkpoints. Gemma outperforms similarly sized open models on 11 out of 18 text-based tasks, and we present comprehensive evaluations of safety and responsibility aspects of the models, alongside a detailed description of model development. We believe the responsible release of LLMs is critical for improving the safety of frontier models, and for enabling the next wave of LLM innovations.
Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:In this report, we present the latest model of the Gemini family, Gemini 1.5 Pro, a highly compute-efficient multimodal mixture-of-experts model capable of recalling and reasoning over fine-grained information from millions of tokens of context, including multiple long documents and hours of video and audio. Gemini 1.5 Pro achieves near-perfect recall on long-context retrieval tasks across modalities, improves the state-of-the-art in long-document QA, long-video QA and long-context ASR, and matches or surpasses Gemini 1.0 Ultra's state-of-the-art performance across a broad set of benchmarks. Studying the limits of Gemini 1.5 Pro's long-context ability, we find continued improvement in next-token prediction and near-perfect retrieval (>99%) up to at least 10M tokens, a generational leap over existing models such as Claude 2.1 (200k) and GPT-4 Turbo (128k). Finally, we highlight surprising new capabilities of large language models at the frontier; when given a grammar manual for Kalamang, a language with fewer than 200 speakers worldwide, the model learns to translate English to Kalamang at a similar level to a person who learned from the same content.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Scalable Extraction of Training Data from (Production) Language Models
Nov 28, 2023



Abstract:This paper studies extractable memorization: training data that an adversary can efficiently extract by querying a machine learning model without prior knowledge of the training dataset. We show an adversary can extract gigabytes of training data from open-source language models like Pythia or GPT-Neo, semi-open models like LLaMA or Falcon, and closed models like ChatGPT. Existing techniques from the literature suffice to attack unaligned models; in order to attack the aligned ChatGPT, we develop a new divergence attack that causes the model to diverge from its chatbot-style generations and emit training data at a rate 150x higher than when behaving properly. Our methods show practical attacks can recover far more data than previously thought, and reveal that current alignment techniques do not eliminate memorization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge