Julian Schrittwieser
Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:In this report, we present the latest model of the Gemini family, Gemini 1.5 Pro, a highly compute-efficient multimodal mixture-of-experts model capable of recalling and reasoning over fine-grained information from millions of tokens of context, including multiple long documents and hours of video and audio. Gemini 1.5 Pro achieves near-perfect recall on long-context retrieval tasks across modalities, improves the state-of-the-art in long-document QA, long-video QA and long-context ASR, and matches or surpasses Gemini 1.0 Ultra's state-of-the-art performance across a broad set of benchmarks. Studying the limits of Gemini 1.5 Pro's long-context ability, we find continued improvement in next-token prediction and near-perfect retrieval (>99%) up to at least 10M tokens, a generational leap over existing models such as Claude 2.1 (200k) and GPT-4 Turbo (128k). Finally, we highlight surprising new capabilities of large language models at the frontier; when given a grammar manual for Kalamang, a language with fewer than 200 speakers worldwide, the model learns to translate English to Kalamang at a similar level to a person who learned from the same content.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
AlphaStar Unplugged: Large-Scale Offline Reinforcement Learning
Aug 07, 2023



Abstract:StarCraft II is one of the most challenging simulated reinforcement learning environments; it is partially observable, stochastic, multi-agent, and mastering StarCraft II requires strategic planning over long time horizons with real-time low-level execution. It also has an active professional competitive scene. StarCraft II is uniquely suited for advancing offline RL algorithms, both because of its challenging nature and because Blizzard has released a massive dataset of millions of StarCraft II games played by human players. This paper leverages that and establishes a benchmark, called AlphaStar Unplugged, introducing unprecedented challenges for offline reinforcement learning. We define a dataset (a subset of Blizzard's release), tools standardizing an API for machine learning methods, and an evaluation protocol. We also present baseline agents, including behavior cloning, offline variants of actor-critic and MuZero. We improve the state of the art of agents using only offline data, and we achieve 90% win rate against previously published AlphaStar behavior cloning agent.
Optimizing Memory Mapping Using Deep Reinforcement Learning
May 11, 2023



Abstract:Resource scheduling and allocation is a critical component of many high impact systems ranging from congestion control to cloud computing. Finding more optimal solutions to these problems often has significant impact on resource and time savings, reducing device wear-and-tear, and even potentially improving carbon emissions. In this paper, we focus on a specific instance of a scheduling problem, namely the memory mapping problem that occurs during compilation of machine learning programs: That is, mapping tensors to different memory layers to optimize execution time. We introduce an approach for solving the memory mapping problem using Reinforcement Learning. RL is a solution paradigm well-suited for sequential decision making problems that are amenable to planning, and combinatorial search spaces with high-dimensional data inputs. We formulate the problem as a single-player game, which we call the mallocGame, such that high-reward trajectories of the game correspond to efficient memory mappings on the target hardware. We also introduce a Reinforcement Learning agent, mallocMuZero, and show that it is capable of playing this game to discover new and improved memory mapping solutions that lead to faster execution times on real ML workloads on ML accelerators. We compare the performance of mallocMuZero to the default solver used by the Accelerated Linear Algebra (XLA) compiler on a benchmark of realistic ML workloads. In addition, we show that mallocMuZero is capable of improving the execution time of the recently published AlphaTensor matrix multiplication model.
MuZero with Self-competition for Rate Control in VP9 Video Compression
Feb 14, 2022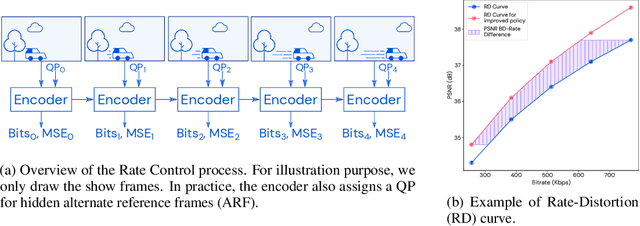
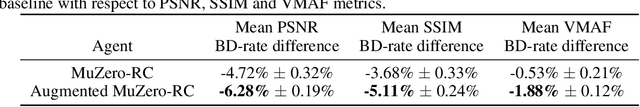
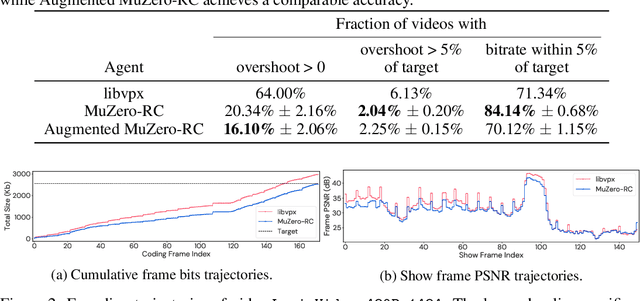
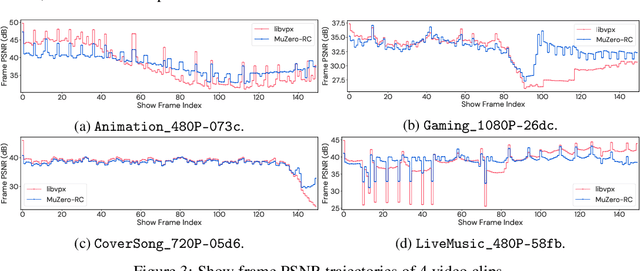
Abstract:Video streaming usage has seen a significant rise as entertainment, education, and business increasingly rely on online video. Optimizing video compression has the potential to increase access and quality of content to users, and reduce energy use and costs overall. In this paper, we present an application of the MuZero algorithm to the challenge of video compression. Specifically, we target the problem of learning a rate control policy to select the quantization parameters (QP) in the encoding process of libvpx, an open source VP9 video compression library widely used by popular video-on-demand (VOD) services. We treat this as a sequential decision making problem to maximize the video quality with an episodic constraint imposed by the target bitrate. Notably, we introduce a novel self-competition based reward mechanism to solve constrained RL with variable constraint satisfaction difficulty, which is challenging for existing constrained RL methods. We demonstrate that the MuZero-based rate control achieves an average 6.28% reduction in size of the compressed videos for the same delivered video quality level (measured as PSNR BD-rate) compared to libvpx's two-pass VBR rate control policy, while having better constraint satisfaction behavior.
Procedural Generalization by Planning with Self-Supervised World Models
Nov 02, 2021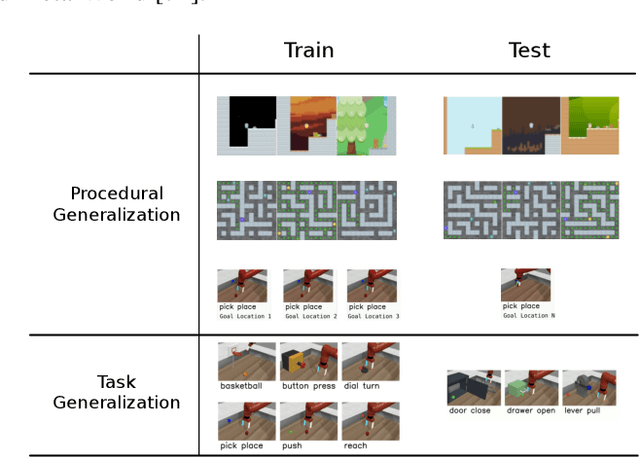
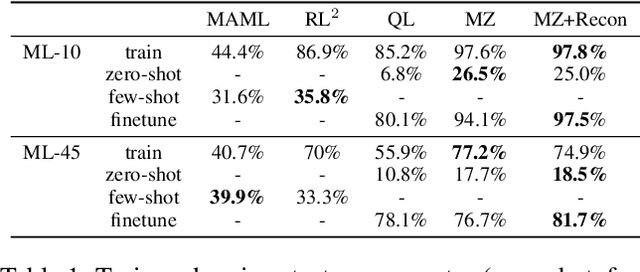
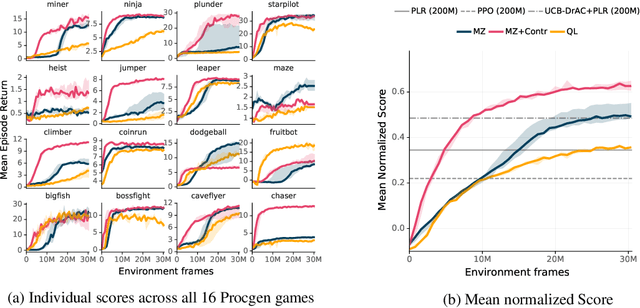
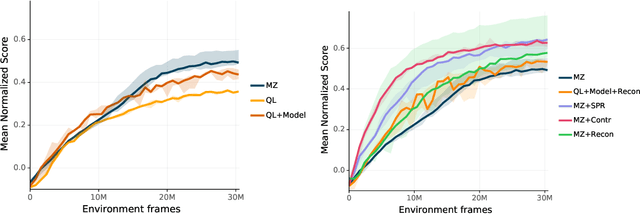
Abstract:One of the key promises of model-based reinforcement learning is the ability to generalize using an internal model of the world to make predictions in novel environments and tasks. However, the generalization ability of model-based agents is not well understood because existing work has focused on model-free agents when benchmarking generalization. Here, we explicitly measure the generalization ability of model-based agents in comparison to their model-free counterparts. We focus our analysis on MuZero (Schrittwieser et al., 2020), a powerful model-based agent, and evaluate its performance on both procedural and task generalization. We identify three factors of procedural generalization -- planning, self-supervised representation learning, and procedural data diversity -- and show that by combining these techniques, we achieve state-of-the art generalization performance and data efficiency on Procgen (Cobbe et al., 2019). However, we find that these factors do not always provide the same benefits for the task generalization benchmarks in Meta-World (Yu et al., 2019), indicating that transfer remains a challenge and may require different approaches than procedural generalization. Overall, we suggest that building generalizable agents requires moving beyond the single-task, model-free paradigm and towards self-supervised model-based agents that are trained in rich, procedural, multi-task environments.
Learning and Planning in Complex Action Spaces
Apr 13, 2021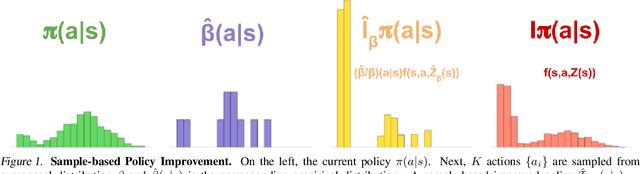
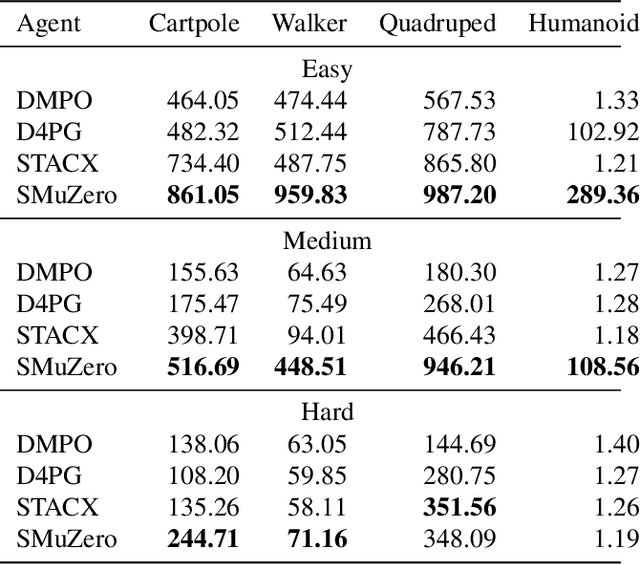
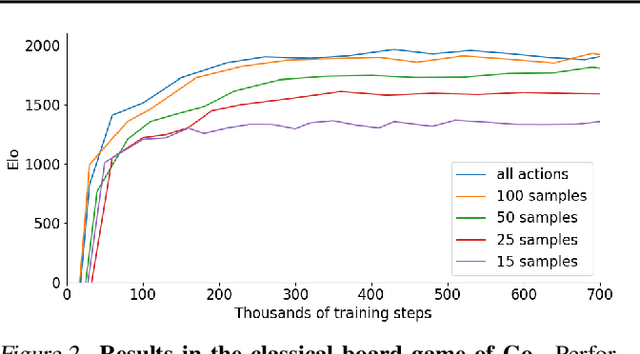
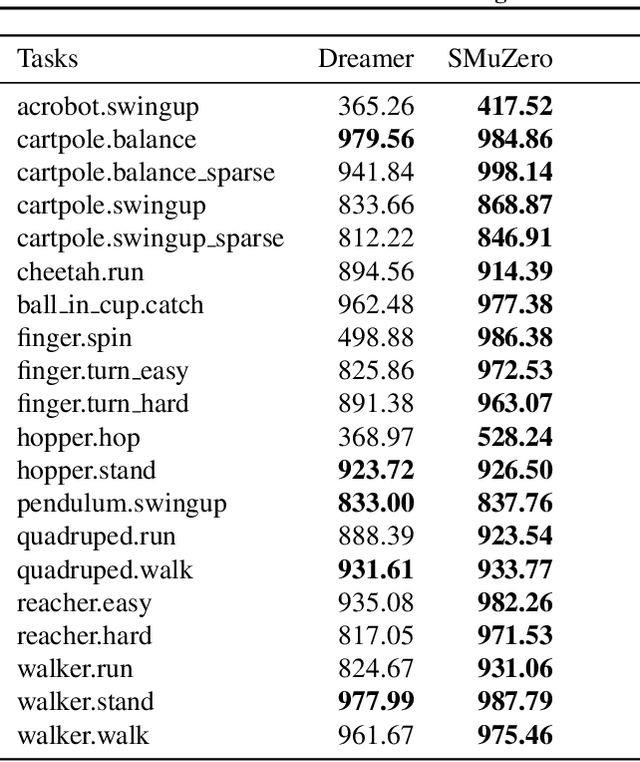
Abstract:Many important real-world problems have action spaces that are high-dimensional, continuous or both, making full enumeration of all possible actions infeasible. Instead, only small subsets of actions can be sampled for the purpose of policy evaluation and improvement. In this paper, we propose a general framework to reason in a principled way about policy evaluation and improvement over such sampled action subsets. This sample-based policy iteration framework can in principle be applied to any reinforcement learning algorithm based upon policy iteration. Concretely, we propose Sampled MuZero, an extension of the MuZero algorithm that is able to learn in domains with arbitrarily complex action spaces by planning over sampled actions. We demonstrate this approach on the classical board game of Go and on two continuous control benchmark domains: DeepMind Control Suite and Real-World RL Suite.
Online and Offline Reinforcement Learning by Planning with a Learned Model
Apr 13, 2021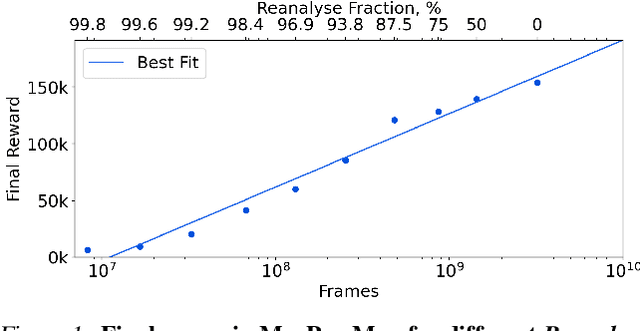
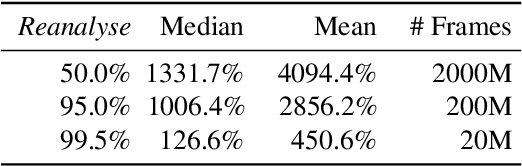
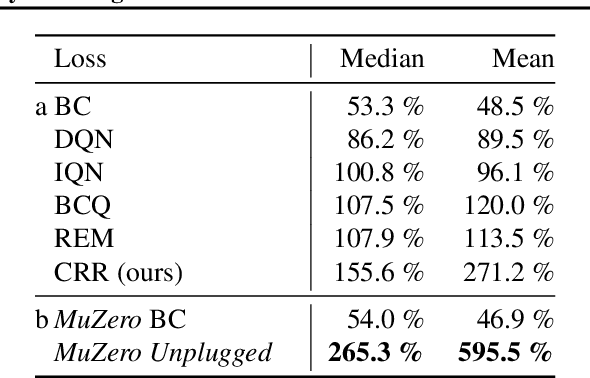
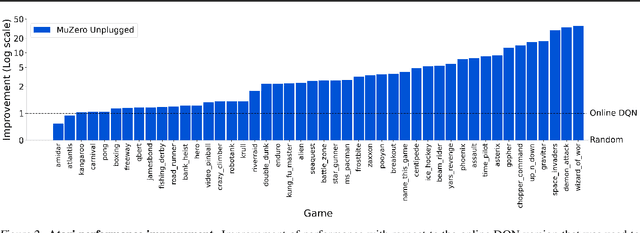
Abstract:Learning efficiently from small amounts of data has long been the focus of model-based reinforcement learning, both for the online case when interacting with the environment and the offline case when learning from a fixed dataset. However, to date no single unified algorithm could demonstrate state-of-the-art results in both settings. In this work, we describe the Reanalyse algorithm which uses model-based policy and value improvement operators to compute new improved training targets on existing data points, allowing efficient learning for data budgets varying by several orders of magnitude. We further show that Reanalyse can also be used to learn entirely from demonstrations without any environment interactions, as in the case of offline Reinforcement Learning (offline RL). Combining Reanalyse with the MuZero algorithm, we introduce MuZero Unplugged, a single unified algorithm for any data budget, including offline RL. In contrast to previous work, our algorithm does not require any special adaptations for the off-policy or offline RL settings. MuZero Unplugged sets new state-of-the-art results in the RL Unplugged offline RL benchmark as well as in the online RL benchmark of Atari in the standard 200 million frame setting.
Local Search for Policy Iteration in Continuous Control
Oct 12, 2020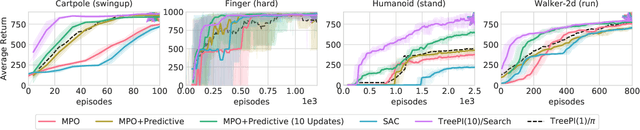
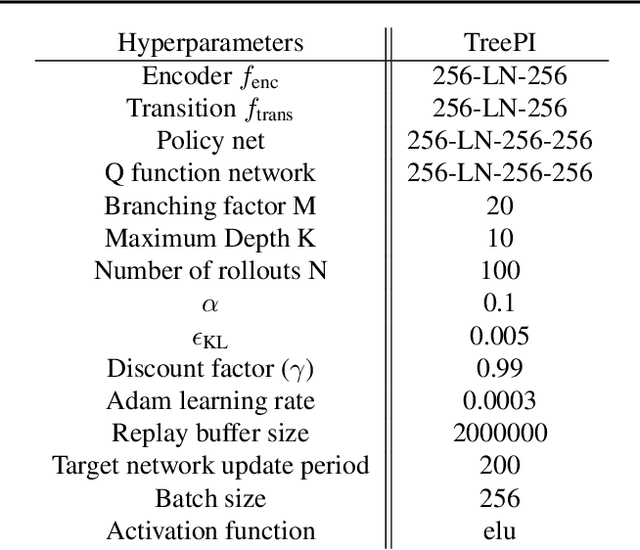
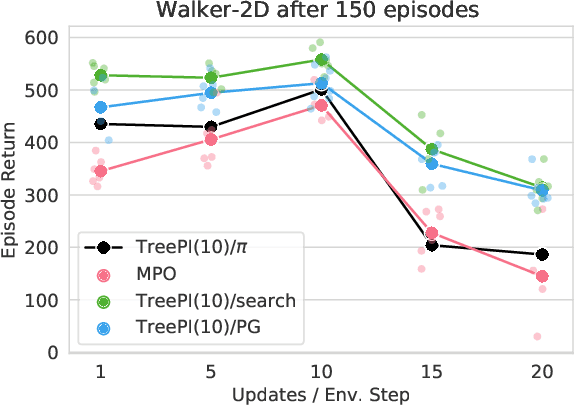
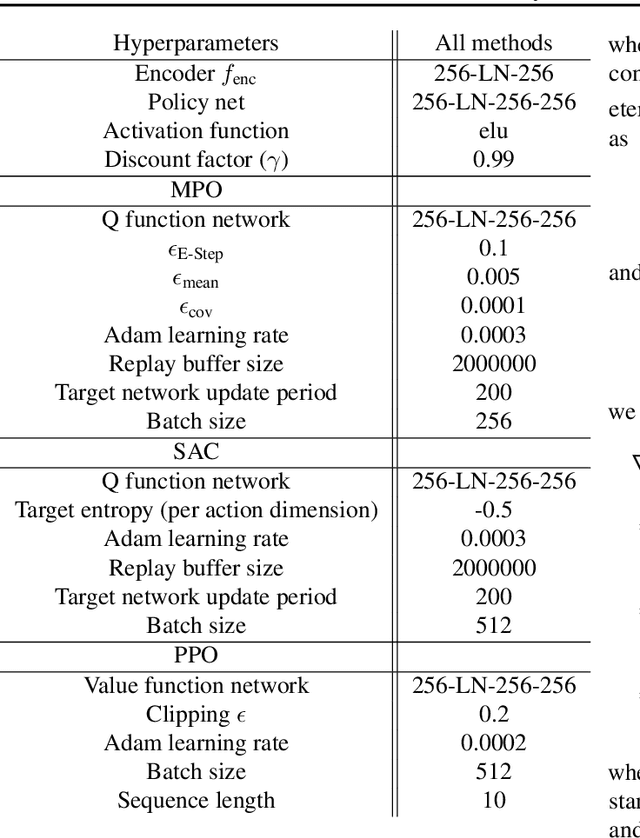
Abstract:We present an algorithm for local, regularized, policy improvement in reinforcement learning (RL) that allows us to formulate model-based and model-free variants in a single framework. Our algorithm can be interpreted as a natural extension of work on KL-regularized RL and introduces a form of tree search for continuous action spaces. We demonstrate that additional computation spent on model-based policy improvement during learning can improve data efficiency, and confirm that model-based policy improvement during action selection can also be beneficial. Quantitatively, our algorithm improves data efficiency on several continuous control benchmarks (when a model is learned in parallel), and it provides significant improvements in wall-clock time in high-dimensional domains (when a ground truth model is available). The unified framework also helps us to better understand the space of model-based and model-free algorithms. In particular, we demonstrate that some benefits attributed to model-based RL can be obtained without a model, simply by utilizing more computation.
Mastering Atari, Go, Chess and Shogi by Planning with a Learned Model
Nov 19, 2019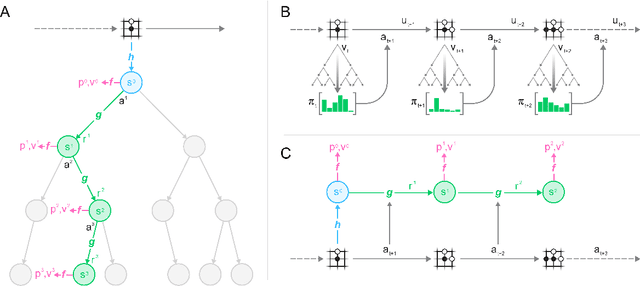
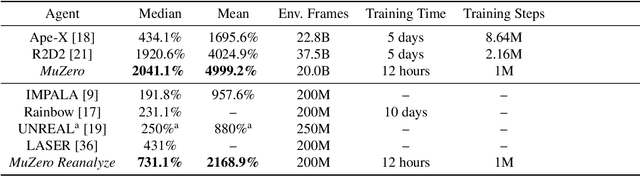
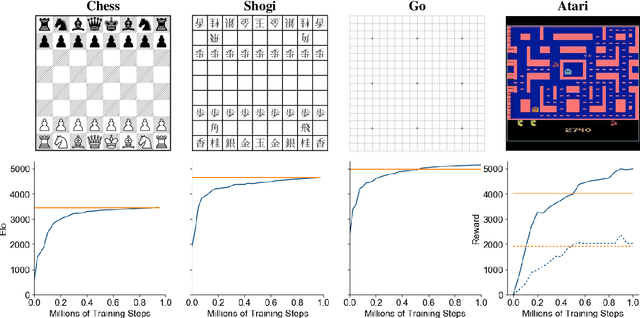
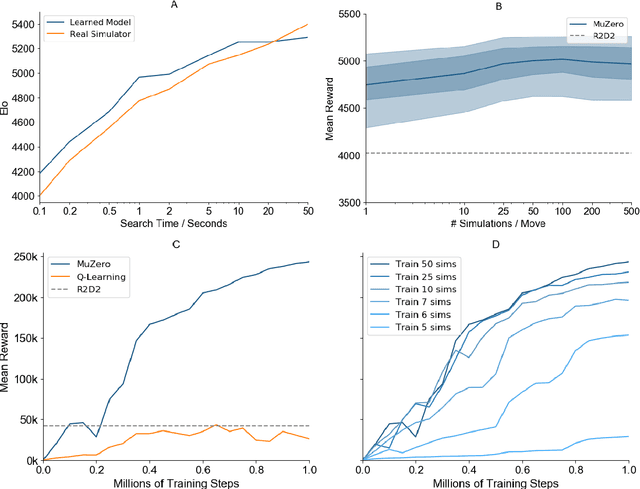
Abstract:Constructing agents with planning capabilities has long been one of the main challenges in the pursuit of artificial intelligence. Tree-based planning methods have enjoyed huge success in challenging domains, such as chess and Go, where a perfect simulator is available. However, in real-world problems the dynamics governing the environment are often complex and unknown. In this work we present the MuZero algorithm which, by combining a tree-based search with a learned model, achieves superhuman performance in a range of challenging and visually complex domains, without any knowledge of their underlying dynamics. MuZero learns a model that, when applied iteratively, predicts the quantities most directly relevant to planning: the reward, the action-selection policy, and the value function. When evaluated on 57 different Atari games - the canonical video game environment for testing AI techniques, in which model-based planning approaches have historically struggled - our new algorithm achieved a new state of the art. When evaluated on Go, chess and shogi, without any knowledge of the game rules, MuZero matched the superhuman performance of the AlphaZero algorithm that was supplied with the game rules.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge