Amol Mandhane
Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:In this report, we present the latest model of the Gemini family, Gemini 1.5 Pro, a highly compute-efficient multimodal mixture-of-experts model capable of recalling and reasoning over fine-grained information from millions of tokens of context, including multiple long documents and hours of video and audio. Gemini 1.5 Pro achieves near-perfect recall on long-context retrieval tasks across modalities, improves the state-of-the-art in long-document QA, long-video QA and long-context ASR, and matches or surpasses Gemini 1.0 Ultra's state-of-the-art performance across a broad set of benchmarks. Studying the limits of Gemini 1.5 Pro's long-context ability, we find continued improvement in next-token prediction and near-perfect retrieval (>99%) up to at least 10M tokens, a generational leap over existing models such as Claude 2.1 (200k) and GPT-4 Turbo (128k). Finally, we highlight surprising new capabilities of large language models at the frontier; when given a grammar manual for Kalamang, a language with fewer than 200 speakers worldwide, the model learns to translate English to Kalamang at a similar level to a person who learned from the same content.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
MuZero with Self-competition for Rate Control in VP9 Video Compression
Feb 14, 2022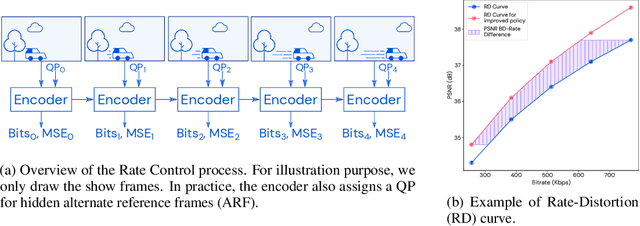
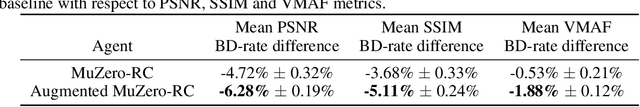
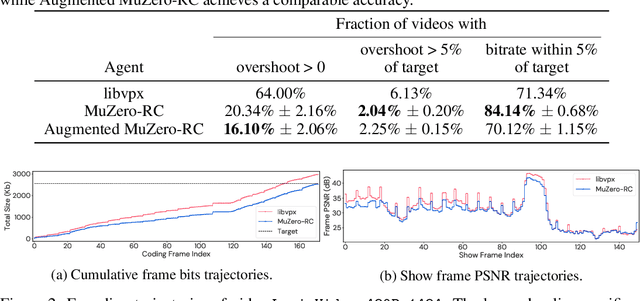
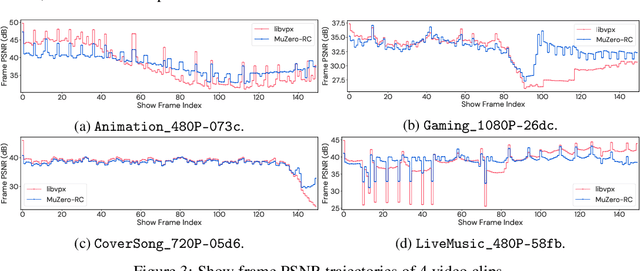
Abstract:Video streaming usage has seen a significant rise as entertainment, education, and business increasingly rely on online video. Optimizing video compression has the potential to increase access and quality of content to users, and reduce energy use and costs overall. In this paper, we present an application of the MuZero algorithm to the challenge of video compression. Specifically, we target the problem of learning a rate control policy to select the quantization parameters (QP) in the encoding process of libvpx, an open source VP9 video compression library widely used by popular video-on-demand (VOD) services. We treat this as a sequential decision making problem to maximize the video quality with an episodic constraint imposed by the target bitrate. Notably, we introduce a novel self-competition based reward mechanism to solve constrained RL with variable constraint satisfaction difficulty, which is challenging for existing constrained RL methods. We demonstrate that the MuZero-based rate control achieves an average 6.28% reduction in size of the compressed videos for the same delivered video quality level (measured as PSNR BD-rate) compared to libvpx's two-pass VBR rate control policy, while having better constraint satisfaction behavior.
Online and Offline Reinforcement Learning by Planning with a Learned Model
Apr 13, 2021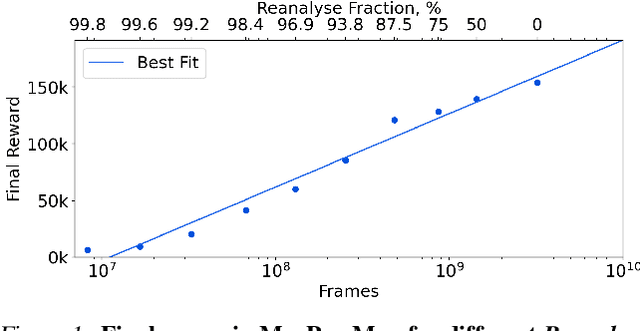
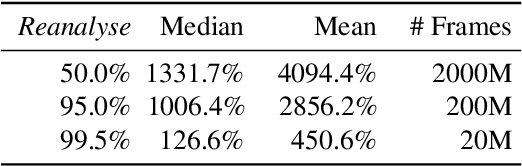
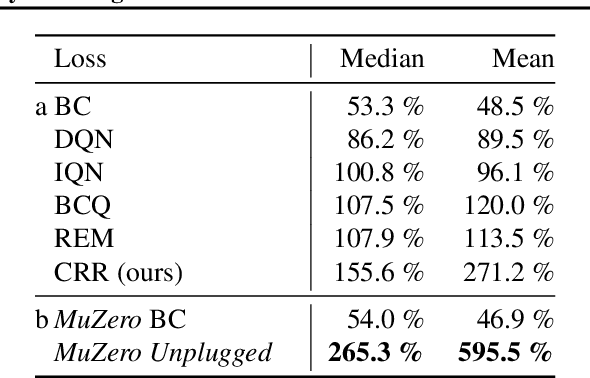
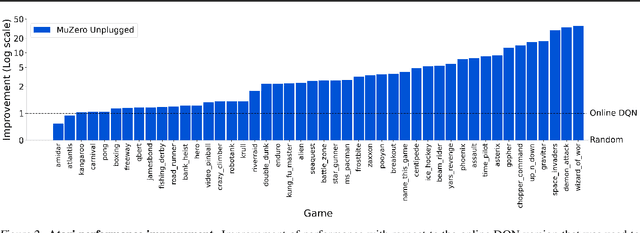
Abstract:Learning efficiently from small amounts of data has long been the focus of model-based reinforcement learning, both for the online case when interacting with the environment and the offline case when learning from a fixed dataset. However, to date no single unified algorithm could demonstrate state-of-the-art results in both settings. In this work, we describe the Reanalyse algorithm which uses model-based policy and value improvement operators to compute new improved training targets on existing data points, allowing efficient learning for data budgets varying by several orders of magnitude. We further show that Reanalyse can also be used to learn entirely from demonstrations without any environment interactions, as in the case of offline Reinforcement Learning (offline RL). Combining Reanalyse with the MuZero algorithm, we introduce MuZero Unplugged, a single unified algorithm for any data budget, including offline RL. In contrast to previous work, our algorithm does not require any special adaptations for the off-policy or offline RL settings. MuZero Unplugged sets new state-of-the-art results in the RL Unplugged offline RL benchmark as well as in the online RL benchmark of Atari in the standard 200 million frame setting.
Skillful Precipitation Nowcasting using Deep Generative Models of Radar
Apr 02, 2021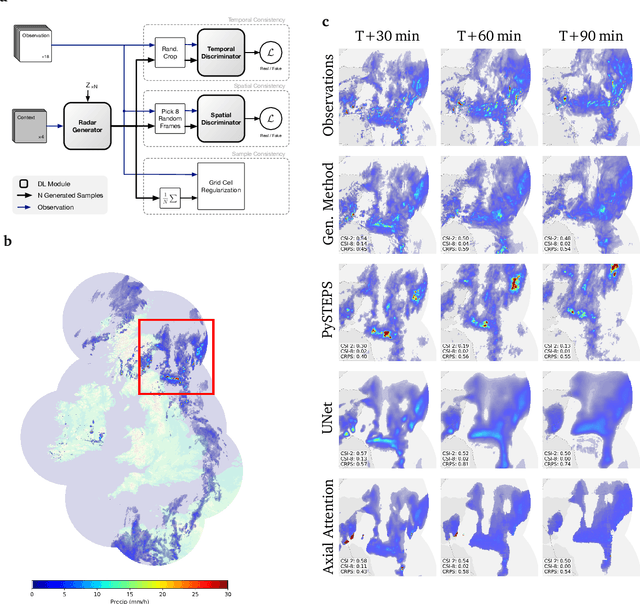
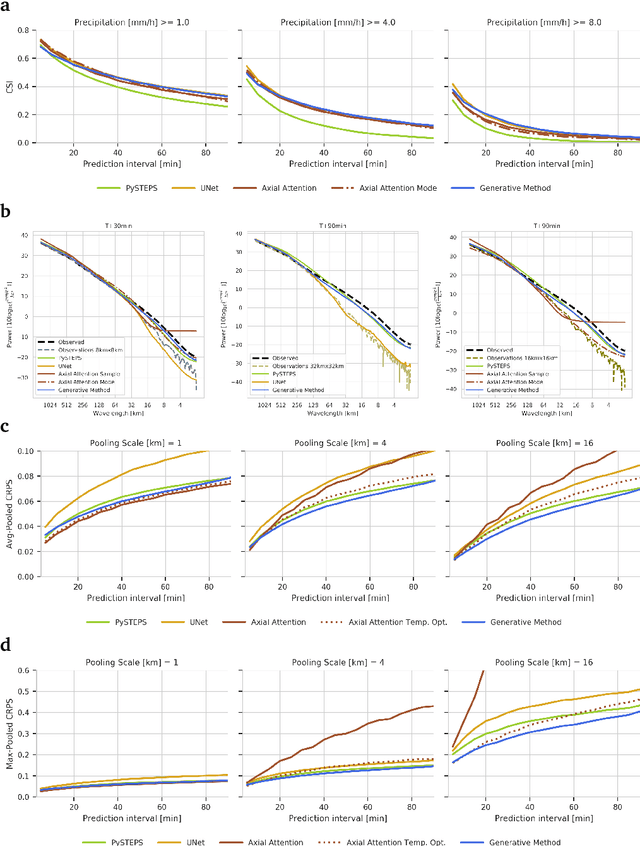
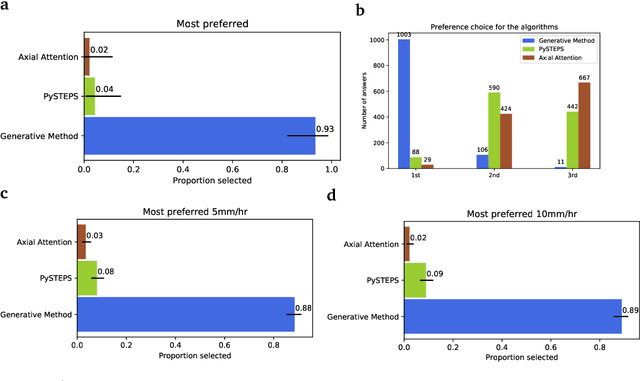
Abstract:Precipitation nowcasting, the high-resolution forecasting of precipitation up to two hours ahead, supports the real-world socio-economic needs of many sectors reliant on weather-dependent decision-making. State-of-the-art operational nowcasting methods typically advect precipitation fields with radar-based wind estimates, and struggle to capture important non-linear events such as convective initiations. Recently introduced deep learning methods use radar to directly predict future rain rates, free of physical constraints. While they accurately predict low-intensity rainfall, their operational utility is limited because their lack of constraints produces blurry nowcasts at longer lead times, yielding poor performance on more rare medium-to-heavy rain events. To address these challenges, we present a Deep Generative Model for the probabilistic nowcasting of precipitation from radar. Our model produces realistic and spatio-temporally consistent predictions over regions up to 1536 km x 1280 km and with lead times from 5-90 min ahead. In a systematic evaluation by more than fifty expert forecasters from the Met Office, our generative model ranked first for its accuracy and usefulness in 88% of cases against two competitive methods, demonstrating its decision-making value and ability to provide physical insight to real-world experts. When verified quantitatively, these nowcasts are skillful without resorting to blurring. We show that generative nowcasting can provide probabilistic predictions that improve forecast value and support operational utility, and at resolutions and lead times where alternative methods struggle.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge