Nikolay Savinov
Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:In this report, we present the latest model of the Gemini family, Gemini 1.5 Pro, a highly compute-efficient multimodal mixture-of-experts model capable of recalling and reasoning over fine-grained information from millions of tokens of context, including multiple long documents and hours of video and audio. Gemini 1.5 Pro achieves near-perfect recall on long-context retrieval tasks across modalities, improves the state-of-the-art in long-document QA, long-video QA and long-context ASR, and matches or surpasses Gemini 1.0 Ultra's state-of-the-art performance across a broad set of benchmarks. Studying the limits of Gemini 1.5 Pro's long-context ability, we find continued improvement in next-token prediction and near-perfect retrieval (>99%) up to at least 10M tokens, a generational leap over existing models such as Claude 2.1 (200k) and GPT-4 Turbo (128k). Finally, we highlight surprising new capabilities of large language models at the frontier; when given a grammar manual for Kalamang, a language with fewer than 200 speakers worldwide, the model learns to translate English to Kalamang at a similar level to a person who learned from the same content.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Continuous diffusion for categorical data
Dec 15, 2022



Abstract:Diffusion models have quickly become the go-to paradigm for generative modelling of perceptual signals (such as images and sound) through iterative refinement. Their success hinges on the fact that the underlying physical phenomena are continuous. For inherently discrete and categorical data such as language, various diffusion-inspired alternatives have been proposed. However, the continuous nature of diffusion models conveys many benefits, and in this work we endeavour to preserve it. We propose CDCD, a framework for modelling categorical data with diffusion models that are continuous both in time and input space. We demonstrate its efficacy on several language modelling tasks.
Self-conditioned Embedding Diffusion for Text Generation
Nov 08, 2022Abstract:Can continuous diffusion models bring the same performance breakthrough on natural language they did for image generation? To circumvent the discrete nature of text data, we can simply project tokens in a continuous space of embeddings, as is standard in language modeling. We propose Self-conditioned Embedding Diffusion, a continuous diffusion mechanism that operates on token embeddings and allows to learn flexible and scalable diffusion models for both conditional and unconditional text generation. Through qualitative and quantitative evaluation, we show that our text diffusion models generate samples comparable with those produced by standard autoregressive language models - while being in theory more efficient on accelerator hardware at inference time. Our work paves the way for scaling up diffusion models for text, similarly to autoregressive models, and for improving performance with recent refinements to continuous diffusion.
Step-unrolled Denoising Autoencoders for Text Generation
Dec 13, 2021



Abstract:In this paper we propose a new generative model of text, Step-unrolled Denoising Autoencoder (SUNDAE), that does not rely on autoregressive models. Similarly to denoising diffusion techniques, SUNDAE is repeatedly applied on a sequence of tokens, starting from random inputs and improving them each time until convergence. We present a simple new improvement operator that converges in fewer iterations than diffusion methods, while qualitatively producing better samples on natural language datasets. SUNDAE achieves state-of-the-art results (among non-autoregressive methods) on the WMT'14 English-to-German translation task and good qualitative results on unconditional language modeling on the Colossal Cleaned Common Crawl dataset and a dataset of Python code from GitHub. The non-autoregressive nature of SUNDAE opens up possibilities beyond left-to-right prompted generation, by filling in arbitrary blank patterns in a template.
Imitating Interactive Intelligence
Jan 21, 2021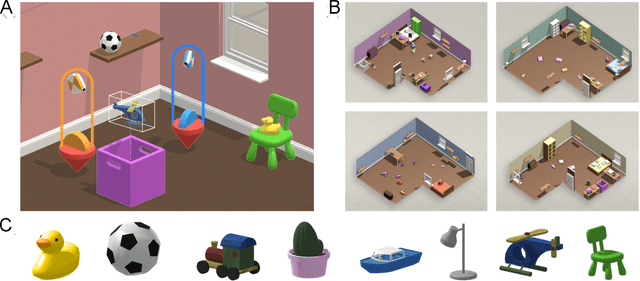
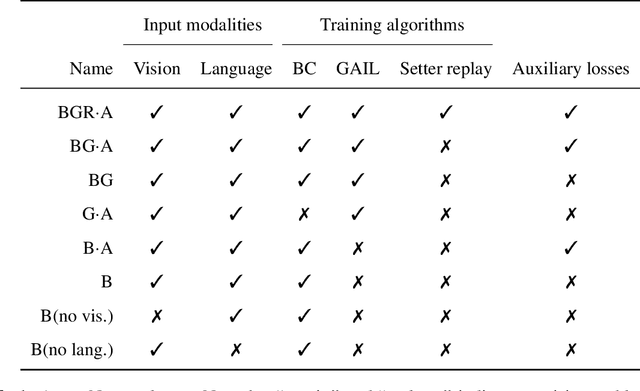
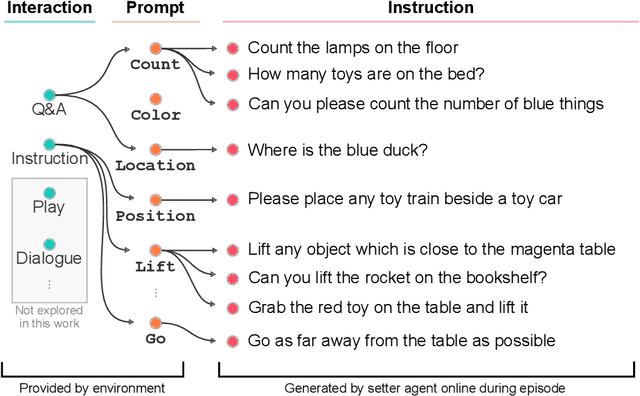
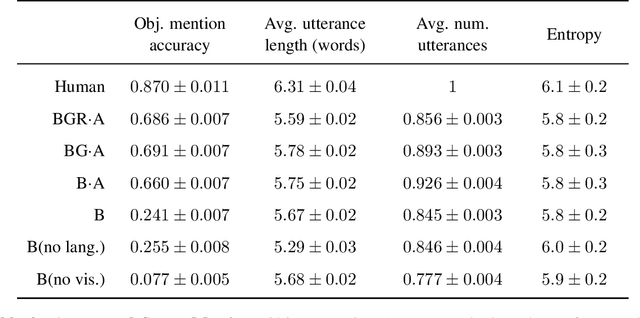
Abstract:A common vision from science fiction is that robots will one day inhabit our physical spaces, sense the world as we do, assist our physical labours, and communicate with us through natural language. Here we study how to design artificial agents that can interact naturally with humans using the simplification of a virtual environment. This setting nevertheless integrates a number of the central challenges of artificial intelligence (AI) research: complex visual perception and goal-directed physical control, grounded language comprehension and production, and multi-agent social interaction. To build agents that can robustly interact with humans, we would ideally train them while they interact with humans. However, this is presently impractical. Therefore, we approximate the role of the human with another learned agent, and use ideas from inverse reinforcement learning to reduce the disparities between human-human and agent-agent interactive behaviour. Rigorously evaluating our agents poses a great challenge, so we develop a variety of behavioural tests, including evaluation by humans who watch videos of agents or interact directly with them. These evaluations convincingly demonstrate that interactive training and auxiliary losses improve agent behaviour beyond what is achieved by supervised learning of actions alone. Further, we demonstrate that agent capabilities generalise beyond literal experiences in the dataset. Finally, we train evaluation models whose ratings of agents agree well with human judgement, thus permitting the evaluation of new agent models without additional effort. Taken together, our results in this virtual environment provide evidence that large-scale human behavioural imitation is a promising tool to create intelligent, interactive agents, and the challenge of reliably evaluating such agents is possible to surmount.
Discrete Optimization of Ray Potentials for Semantic 3D Reconstruction
Jun 25, 2019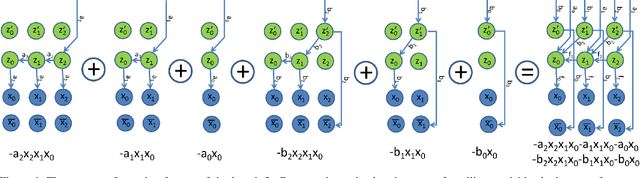
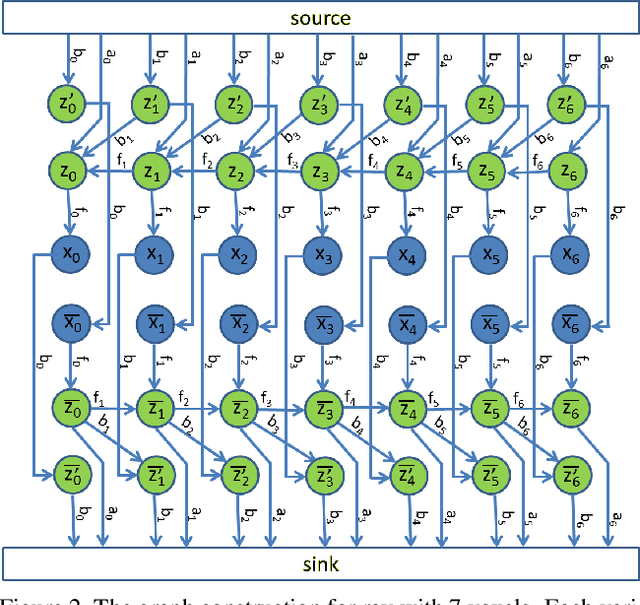
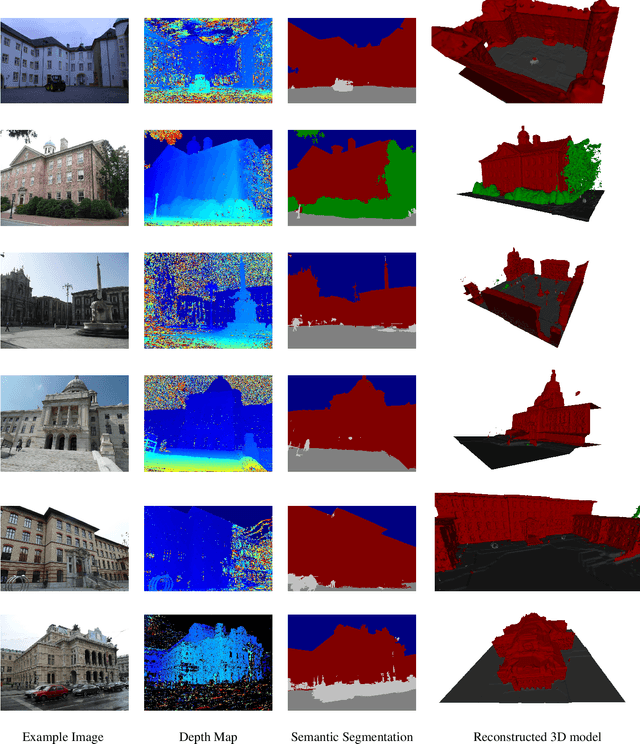
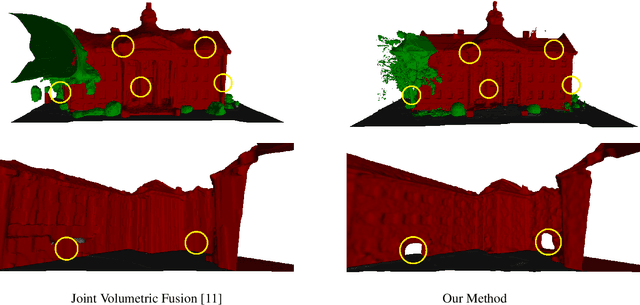
Abstract:Dense semantic 3D reconstruction is typically formulated as a discrete or continuous problem over label assignments in a voxel grid, combining semantic and depth likelihoods in a Markov Random Field framework. The depth and semantic information is incorporated as a unary potential, smoothed by a pairwise regularizer. However, modelling likelihoods as a unary potential does not model the problem correctly leading to various undesirable visibility artifacts. We propose to formulate an optimization problem that directly optimizes the reprojection error of the 3D model with respect to the image estimates, which corresponds to the optimization over rays, where the cost function depends on the semantic class and depth of the first occupied voxel along the ray. The 2-label formulation is made feasible by transforming it into a graph-representable form under QPBO relaxation, solvable using graph cut. The multi-label problem is solved by applying alpha-expansion using the same relaxation in each expansion move. Our method was indeed shown to be feasible in practice, running comparably fast to the competing methods, while not suffering from ray potential approximation artifacts.
Episodic Curiosity through Reachability
Feb 22, 2019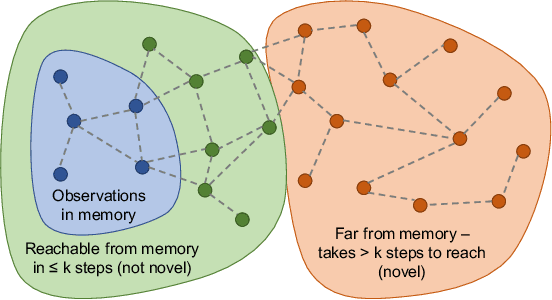

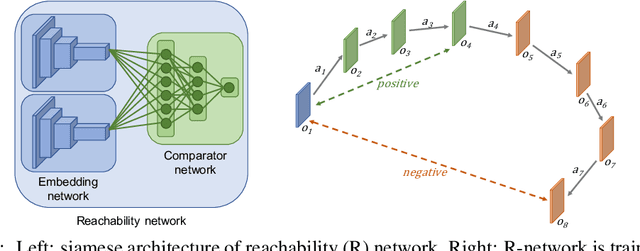
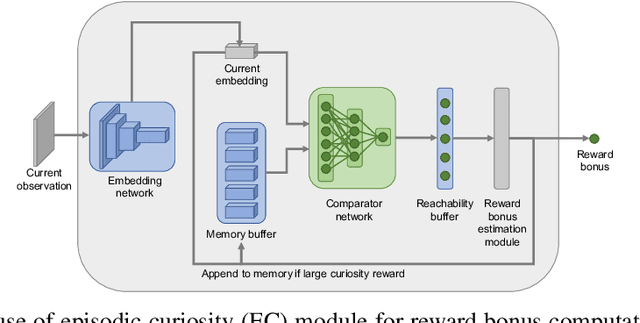
Abstract:Rewards are sparse in the real world and most today's reinforcement learning algorithms struggle with such sparsity. One solution to this problem is to allow the agent to create rewards for itself - thus making rewards dense and more suitable for learning. In particular, inspired by curious behaviour in animals, observing something novel could be rewarded with a bonus. Such bonus is summed up with the real task reward - making it possible for RL algorithms to learn from the combined reward. We propose a new curiosity method which uses episodic memory to form the novelty bonus. To determine the bonus, the current observation is compared with the observations in memory. Crucially, the comparison is done based on how many environment steps it takes to reach the current observation from those in memory - which incorporates rich information about environment dynamics. This allows us to overcome the known "couch-potato" issues of prior work - when the agent finds a way to instantly gratify itself by exploiting actions which lead to hardly predictable consequences. We test our approach in visually rich 3D environments in ViZDoom, DMLab and MuJoCo. In navigational tasks from ViZDoom and DMLab, our agent outperforms the state-of-the-art curiosity method ICM. In MuJoCo, an ant equipped with our curiosity module learns locomotion out of the first-person-view curiosity only.
RNN-based Generative Model for Fine-Grained Sketching
Jan 13, 2019



Abstract:Deep generative models have shown great promise when it comes to synthesising novel images. While they can generate images that look convincing on a higher-level, generating fine-grained details is still a challenge. In order to foster research on more powerful generative approaches, this paper proposes a novel task: generative modelling of 2D tree skeletons. Trees are an interesting shape class because they exhibit complexity and variations that are well-suited to measure the ability of a generative model to generated detailed structures. We propose a new dataset for this task and demonstrate that state-of-the-art generative models fail to synthesise realistic images on our benchmark, even though they perform well on current datasets like MNIST digits. Motivated by these results, we propose a novel network architecture based on combining a variational autoencoder using Recurrent Neural Networks and a convolutional discriminator. The network, error metrics and training procedure are adapted to the task of fine-grained sketching. Through quantitative and perceptual experiments, we show that our model outperforms previous work and that our dataset is a valuable benchmark for generative models. We will make our dataset publicly available.
Conditional Affordance Learning for Driving in Urban Environments
Nov 03, 2018



Abstract:Most existing approaches to autonomous driving fall into one of two categories: modular pipelines, that build an extensive model of the environment, and imitation learning approaches, that map images directly to control outputs. A recently proposed third paradigm, direct perception, aims to combine the advantages of both by using a neural network to learn appropriate low-dimensional intermediate representations. However, existing direct perception approaches are restricted to simple highway situations, lacking the ability to navigate intersections, stop at traffic lights or respect speed limits. In this work, we propose a direct perception approach which maps video input to intermediate representations suitable for autonomous navigation in complex urban environments given high-level directional inputs. Compared to state-of-the-art reinforcement and conditional imitation learning approaches, we achieve an improvement of up to 68 % in goal-directed navigation on the challenging CARLA simulation benchmark. In addition, our approach is the first to handle traffic lights and speed signs by using image-level labels only, as well as smooth car-following, resulting in a significant reduction of traffic accidents in simulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge