Robin Strudel
Imagen 3
Aug 13, 2024Abstract:We introduce Imagen 3, a latent diffusion model that generates high quality images from text prompts. We describe our quality and responsibility evaluations. Imagen 3 is preferred over other state-of-the-art (SOTA) models at the time of evaluation. In addition, we discuss issues around safety and representation, as well as methods we used to minimize the potential harm of our models.
Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:In this report, we present the latest model of the Gemini family, Gemini 1.5 Pro, a highly compute-efficient multimodal mixture-of-experts model capable of recalling and reasoning over fine-grained information from millions of tokens of context, including multiple long documents and hours of video and audio. Gemini 1.5 Pro achieves near-perfect recall on long-context retrieval tasks across modalities, improves the state-of-the-art in long-document QA, long-video QA and long-context ASR, and matches or surpasses Gemini 1.0 Ultra's state-of-the-art performance across a broad set of benchmarks. Studying the limits of Gemini 1.5 Pro's long-context ability, we find continued improvement in next-token prediction and near-perfect retrieval (>99%) up to at least 10M tokens, a generational leap over existing models such as Claude 2.1 (200k) and GPT-4 Turbo (128k). Finally, we highlight surprising new capabilities of large language models at the frontier; when given a grammar manual for Kalamang, a language with fewer than 200 speakers worldwide, the model learns to translate English to Kalamang at a similar level to a person who learned from the same content.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Robust Visual Sim-to-Real Transfer for Robotic Manipulation
Jul 28, 2023
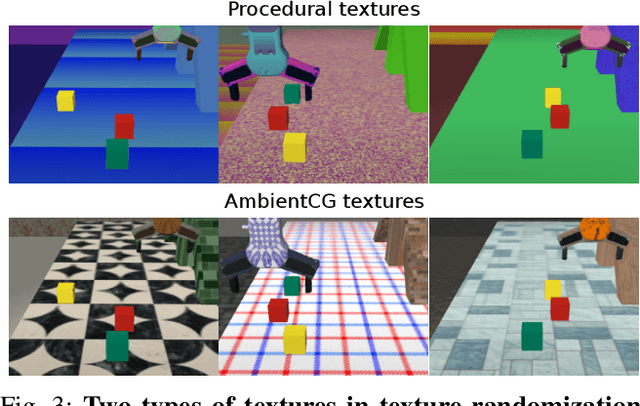
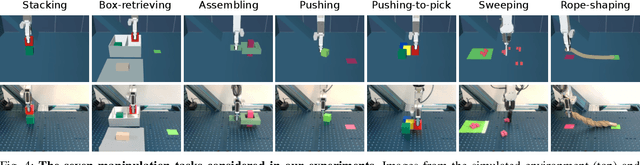

Abstract:Learning visuomotor policies in simulation is much safer and cheaper than in the real world. However, due to discrepancies between the simulated and real data, simulator-trained policies often fail when transferred to real robots. One common approach to bridge the visual sim-to-real domain gap is domain randomization (DR). While previous work mainly evaluates DR for disembodied tasks, such as pose estimation and object detection, here we systematically explore visual domain randomization methods and benchmark them on a rich set of challenging robotic manipulation tasks. In particular, we propose an off-line proxy task of cube localization to select DR parameters for texture randomization, lighting randomization, variations of object colors and camera parameters. Notably, we demonstrate that DR parameters have similar impact on our off-line proxy task and on-line policies. We, hence, use off-line optimized DR parameters to train visuomotor policies in simulation and directly apply such policies to a real robot. Our approach achieves 93% success rate on average when tested on a diverse set of challenging manipulation tasks. Moreover, we evaluate the robustness of policies to visual variations in real scenes and show that our simulator-trained policies outperform policies learned using real but limited data. Code, simulation environment, real robot datasets and trained models are available at https://www.di.ens.fr/willow/research/robust_s2r/.
Reduce, Reuse, Recycle: Compositional Generation with Energy-Based Diffusion Models and MCMC
Feb 22, 2023



Abstract:Since their introduction, diffusion models have quickly become the prevailing approach to generative modeling in many domains. They can be interpreted as learning the gradients of a time-varying sequence of log-probability density functions. This interpretation has motivated classifier-based and classifier-free guidance as methods for post-hoc control of diffusion models. In this work, we build upon these ideas using the score-based interpretation of diffusion models, and explore alternative ways to condition, modify, and reuse diffusion models for tasks involving compositional generation and guidance. In particular, we investigate why certain types of composition fail using current techniques and present a number of solutions. We conclude that the sampler (not the model) is responsible for this failure and propose new samplers, inspired by MCMC, which enable successful compositional generation. Further, we propose an energy-based parameterization of diffusion models which enables the use of new compositional operators and more sophisticated, Metropolis-corrected samplers. Intriguingly we find these samplers lead to notable improvements in compositional generation across a wide set of problems such as classifier-guided ImageNet modeling and compositional text-to-image generation.
Continuous diffusion for categorical data
Dec 15, 2022



Abstract:Diffusion models have quickly become the go-to paradigm for generative modelling of perceptual signals (such as images and sound) through iterative refinement. Their success hinges on the fact that the underlying physical phenomena are continuous. For inherently discrete and categorical data such as language, various diffusion-inspired alternatives have been proposed. However, the continuous nature of diffusion models conveys many benefits, and in this work we endeavour to preserve it. We propose CDCD, a framework for modelling categorical data with diffusion models that are continuous both in time and input space. We demonstrate its efficacy on several language modelling tasks.
Self-conditioned Embedding Diffusion for Text Generation
Nov 08, 2022Abstract:Can continuous diffusion models bring the same performance breakthrough on natural language they did for image generation? To circumvent the discrete nature of text data, we can simply project tokens in a continuous space of embeddings, as is standard in language modeling. We propose Self-conditioned Embedding Diffusion, a continuous diffusion mechanism that operates on token embeddings and allows to learn flexible and scalable diffusion models for both conditional and unconditional text generation. Through qualitative and quantitative evaluation, we show that our text diffusion models generate samples comparable with those produced by standard autoregressive language models - while being in theory more efficient on accelerator hardware at inference time. Our work paves the way for scaling up diffusion models for text, similarly to autoregressive models, and for improving performance with recent refinements to continuous diffusion.
Weakly-supervised segmentation of referring expressions
May 12, 2022



Abstract:Visual grounding localizes regions (boxes or segments) in the image corresponding to given referring expressions. In this work we address image segmentation from referring expressions, a problem that has so far only been addressed in a fully-supervised setting. A fully-supervised setup, however, requires pixel-wise supervision and is hard to scale given the expense of manual annotation. We therefore introduce a new task of weakly-supervised image segmentation from referring expressions and propose Text grounded semantic SEGgmentation (TSEG) that learns segmentation masks directly from image-level referring expressions without pixel-level annotations. Our transformer-based method computes patch-text similarities and guides the classification objective during training with a new multi-label patch assignment mechanism. The resulting visual grounding model segments image regions corresponding to given natural language expressions. Our approach TSEG demonstrates promising results for weakly-supervised referring expression segmentation on the challenging PhraseCut and RefCOCO datasets. TSEG also shows competitive performance when evaluated in a zero-shot setting for semantic segmentation on Pascal VOC.
Assembly Planning from Observations under Physical Constraints
Apr 20, 2022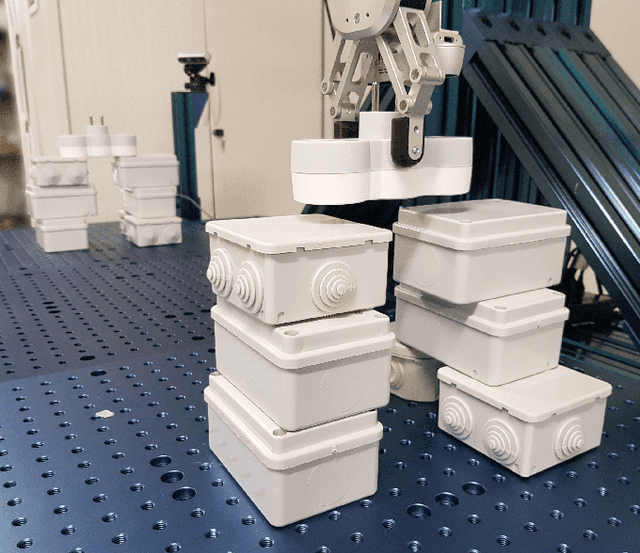
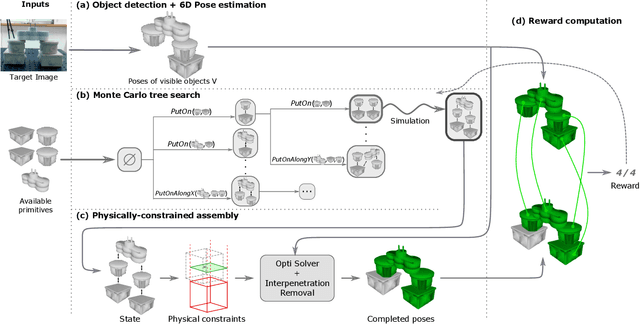

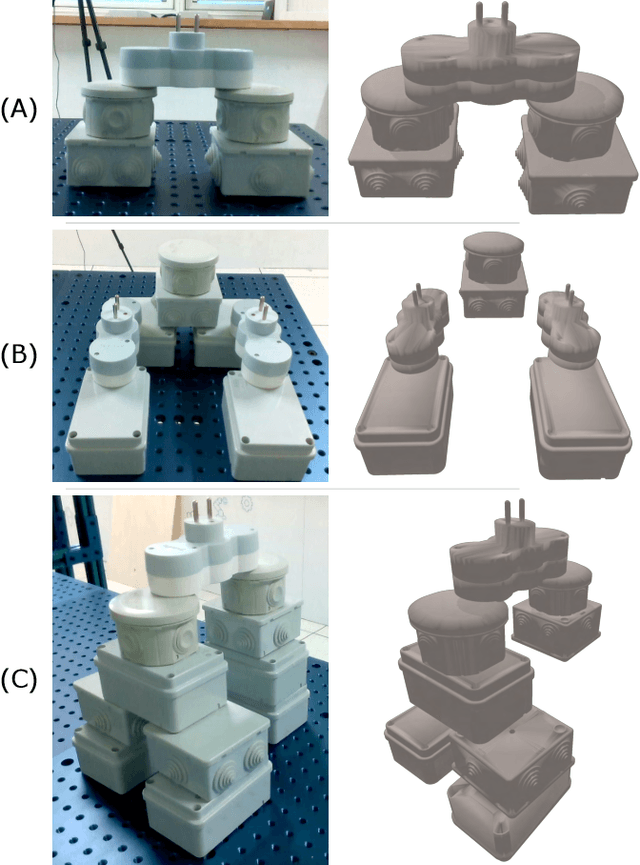
Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of copying an unknown assembly of primitives with known shape and appearance using information extracted from a single photograph by an off-the-shelf procedure for object detection and pose estimation. The proposed algorithm uses a simple combination of physical stability constraints, convex optimization and Monte Carlo tree search to plan assemblies as sequences of pick-and-place operations represented by STRIPS operators. It is efficient and, most importantly, robust to the errors in object detection and pose estimation unavoidable in any real robotic system. The proposed approach is demonstrated with thorough experiments on a UR5 manipulator.
Segmenter: Transformer for Semantic Segmentation
May 12, 2021



Abstract:Image segmentation is often ambiguous at the level of individual image patches and requires contextual information to reach label consensus. In this paper we introduce Segmenter, a transformer model for semantic segmentation. In contrast to convolution based approaches, our approach allows to model global context already at the first layer and throughout the network. We build on the recent Vision Transformer (ViT) and extend it to semantic segmentation. To do so, we rely on the output embeddings corresponding to image patches and obtain class labels from these embeddings with a point-wise linear decoder or a mask transformer decoder. We leverage models pre-trained for image classification and show that we can fine-tune them on moderate sized datasets available for semantic segmentation. The linear decoder allows to obtain excellent results already, but the performance can be further improved by a mask transformer generating class masks. We conduct an extensive ablation study to show the impact of the different parameters, in particular the performance is better for large models and small patch sizes. Segmenter attains excellent results for semantic segmentation. It outperforms the state of the art on the challenging ADE20K dataset and performs on-par on Pascal Context and Cityscapes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge