Matthew Willson
Skillful joint probabilistic weather forecasting from marginals
Jun 12, 2025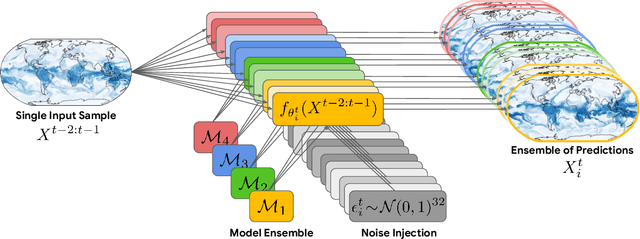
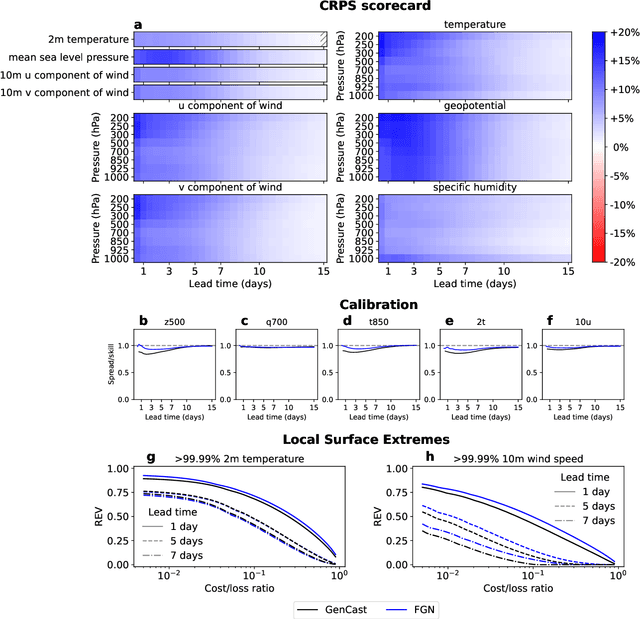
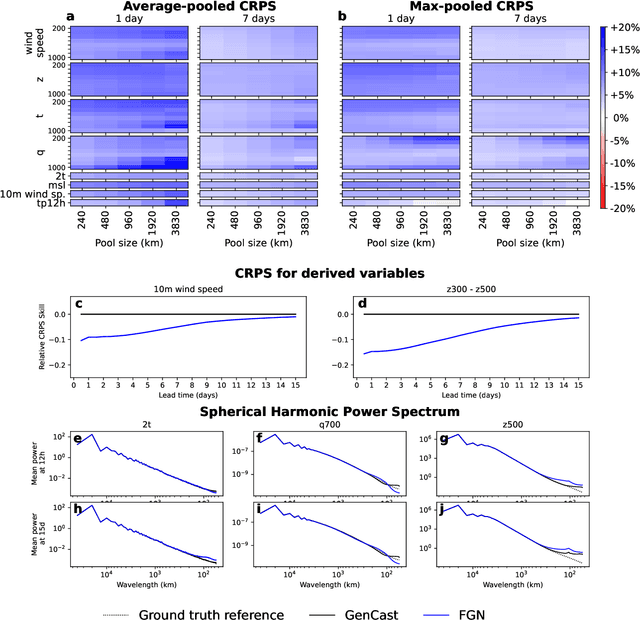
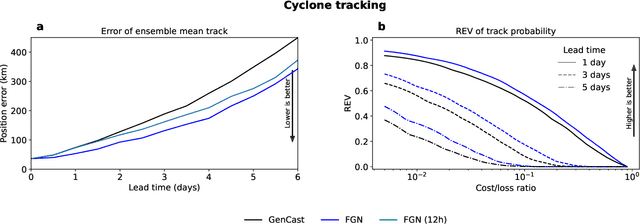
Abstract:Machine learning (ML)-based weather models have rapidly risen to prominence due to their greater accuracy and speed than traditional forecasts based on numerical weather prediction (NWP), recently outperforming traditional ensembles in global probabilistic weather forecasting. This paper presents FGN, a simple, scalable and flexible modeling approach which significantly outperforms the current state-of-the-art models. FGN generates ensembles via learned model-perturbations with an ensemble of appropriately constrained models. It is trained directly to minimize the continuous rank probability score (CRPS) of per-location forecasts. It produces state-of-the-art ensemble forecasts as measured by a range of deterministic and probabilistic metrics, makes skillful ensemble tropical cyclone track predictions, and captures joint spatial structure despite being trained only on marginals.
GenCast: Diffusion-based ensemble forecasting for medium-range weather
Dec 25, 2023



Abstract:Probabilistic weather forecasting is critical for decision-making in high-impact domains such as flood forecasting, energy system planning or transportation routing, where quantifying the uncertainty of a forecast -- including probabilities of extreme events -- is essential to guide important cost-benefit trade-offs and mitigation measures. Traditional probabilistic approaches rely on producing ensembles from physics-based models, which sample from a joint distribution over spatio-temporally coherent weather trajectories, but are expensive to run. An efficient alternative is to use a machine learning (ML) forecast model to generate the ensemble, however state-of-the-art ML forecast models for medium-range weather are largely trained to produce deterministic forecasts which minimise mean-squared-error. Despite improving skills scores, they lack physical consistency, a limitation that grows at longer lead times and impacts their ability to characterize the joint distribution. We introduce GenCast, a ML-based generative model for ensemble weather forecasting, trained from reanalysis data. It forecasts ensembles of trajectories for 84 weather variables, for up to 15 days at 1 degree resolution globally, taking around a minute per ensemble member on a single Cloud TPU v4 device. We show that GenCast is more skillful than ENS, a top operational ensemble forecast, for more than 96\% of all 1320 verification targets on CRPS and Ensemble-Mean RMSE, while maintaining good reliability and physically consistent power spectra. Together our results demonstrate that ML-based probabilistic weather forecasting can now outperform traditional ensemble systems at 1 degree, opening new doors to skillful, fast weather forecasts that are useful in key applications.
Neural General Circulation Models
Nov 28, 2023Abstract:General circulation models (GCMs) are the foundation of weather and climate prediction. GCMs are physics-based simulators which combine a numerical solver for large-scale dynamics with tuned representations for small-scale processes such as cloud formation. Recently, machine learning (ML) models trained on reanalysis data achieved comparable or better skill than GCMs for deterministic weather forecasting. However, these models have not demonstrated improved ensemble forecasts, or shown sufficient stability for long-term weather and climate simulations. Here we present the first GCM that combines a differentiable solver for atmospheric dynamics with ML components, and show that it can generate forecasts of deterministic weather, ensemble weather and climate on par with the best ML and physics-based methods. NeuralGCM is competitive with ML models for 1-10 day forecasts, and with the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts ensemble prediction for 1-15 day forecasts. With prescribed sea surface temperature, NeuralGCM can accurately track climate metrics such as global mean temperature for multiple decades, and climate forecasts with 140 km resolution exhibit emergent phenomena such as realistic frequency and trajectories of tropical cyclones. For both weather and climate, our approach offers orders of magnitude computational savings over conventional GCMs. Our results show that end-to-end deep learning is compatible with tasks performed by conventional GCMs, and can enhance the large-scale physical simulations that are essential for understanding and predicting the Earth system.
GraphCast: Learning skillful medium-range global weather forecasting
Dec 24, 2022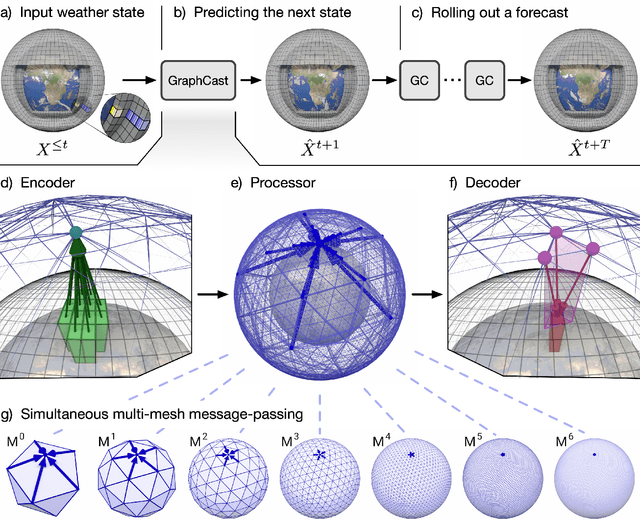
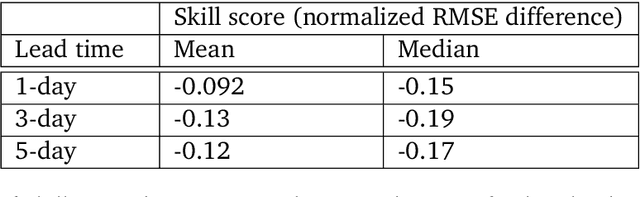
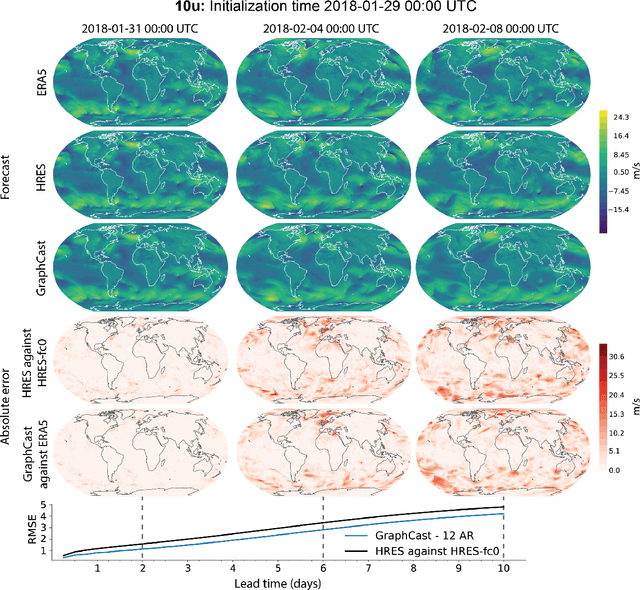
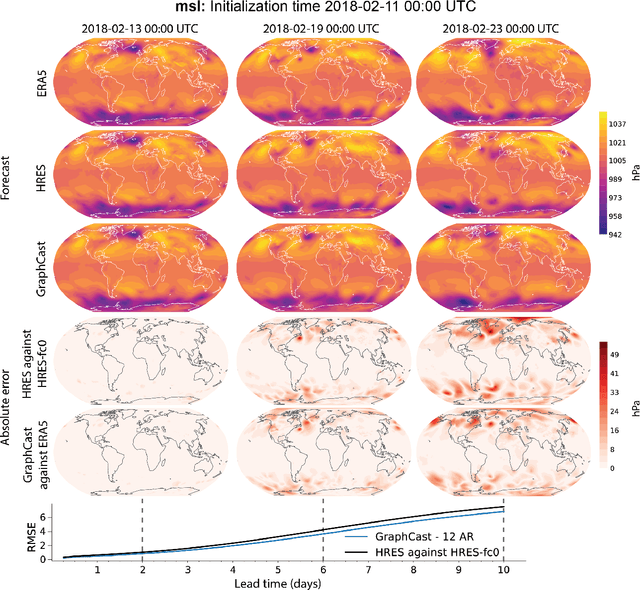
Abstract:We introduce a machine-learning (ML)-based weather simulator--called "GraphCast"--which outperforms the most accurate deterministic operational medium-range weather forecasting system in the world, as well as all previous ML baselines. GraphCast is an autoregressive model, based on graph neural networks and a novel high-resolution multi-scale mesh representation, which we trained on historical weather data from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF)'s ERA5 reanalysis archive. It can make 10-day forecasts, at 6-hour time intervals, of five surface variables and six atmospheric variables, each at 37 vertical pressure levels, on a 0.25-degree latitude-longitude grid, which corresponds to roughly 25 x 25 kilometer resolution at the equator. Our results show GraphCast is more accurate than ECMWF's deterministic operational forecasting system, HRES, on 90.0% of the 2760 variable and lead time combinations we evaluated. GraphCast also outperforms the most accurate previous ML-based weather forecasting model on 99.2% of the 252 targets it reported. GraphCast can generate a 10-day forecast (35 gigabytes of data) in under 60 seconds on Cloud TPU v4 hardware. Unlike traditional forecasting methods, ML-based forecasting scales well with data: by training on bigger, higher quality, and more recent data, the skill of the forecasts can improve. Together these results represent a key step forward in complementing and improving weather modeling with ML, open new opportunities for fast, accurate forecasting, and help realize the promise of ML-based simulation in the physical sciences.
Skillful Precipitation Nowcasting using Deep Generative Models of Radar
Apr 02, 2021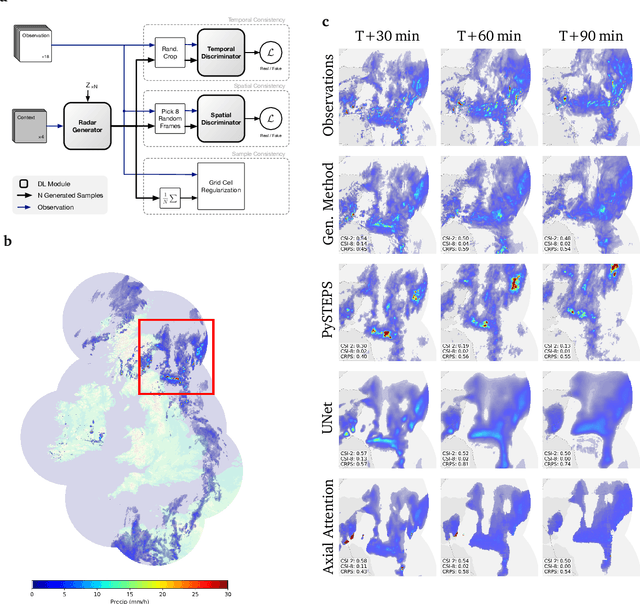
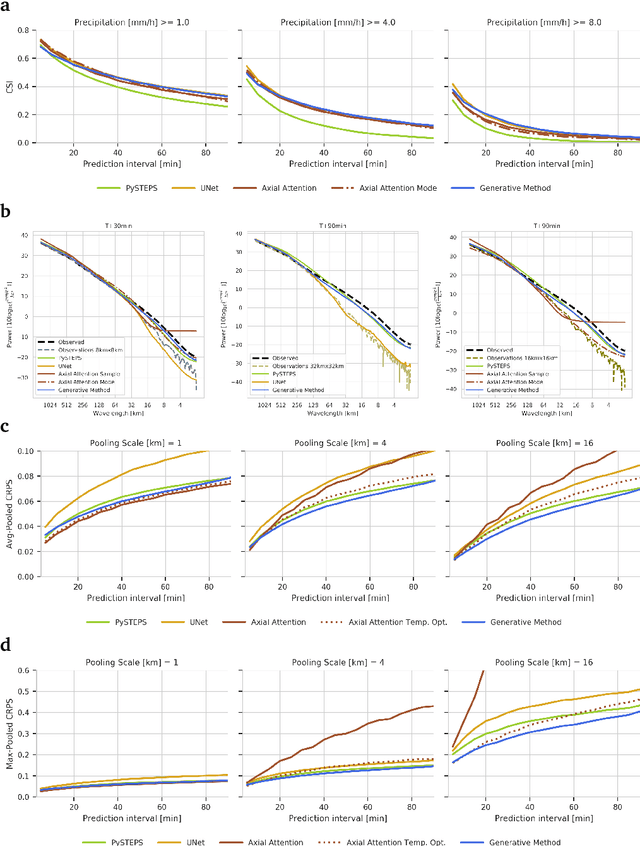
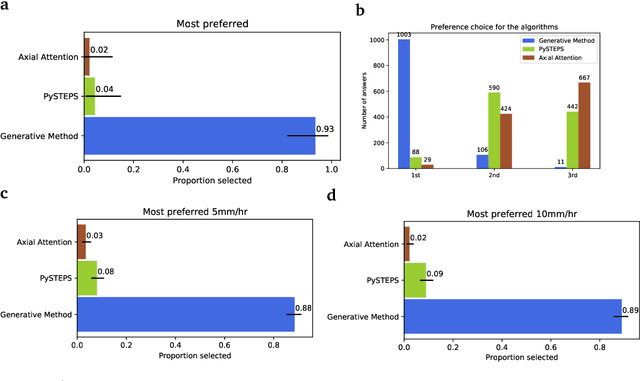
Abstract:Precipitation nowcasting, the high-resolution forecasting of precipitation up to two hours ahead, supports the real-world socio-economic needs of many sectors reliant on weather-dependent decision-making. State-of-the-art operational nowcasting methods typically advect precipitation fields with radar-based wind estimates, and struggle to capture important non-linear events such as convective initiations. Recently introduced deep learning methods use radar to directly predict future rain rates, free of physical constraints. While they accurately predict low-intensity rainfall, their operational utility is limited because their lack of constraints produces blurry nowcasts at longer lead times, yielding poor performance on more rare medium-to-heavy rain events. To address these challenges, we present a Deep Generative Model for the probabilistic nowcasting of precipitation from radar. Our model produces realistic and spatio-temporally consistent predictions over regions up to 1536 km x 1280 km and with lead times from 5-90 min ahead. In a systematic evaluation by more than fifty expert forecasters from the Met Office, our generative model ranked first for its accuracy and usefulness in 88% of cases against two competitive methods, demonstrating its decision-making value and ability to provide physical insight to real-world experts. When verified quantitatively, these nowcasts are skillful without resorting to blurring. We show that generative nowcasting can provide probabilistic predictions that improve forecast value and support operational utility, and at resolutions and lead times where alternative methods struggle.
Theano: A Python framework for fast computation of mathematical expressions
May 09, 2016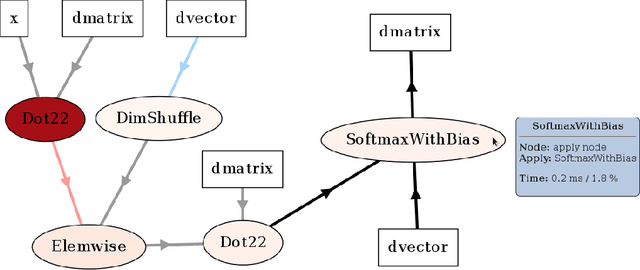
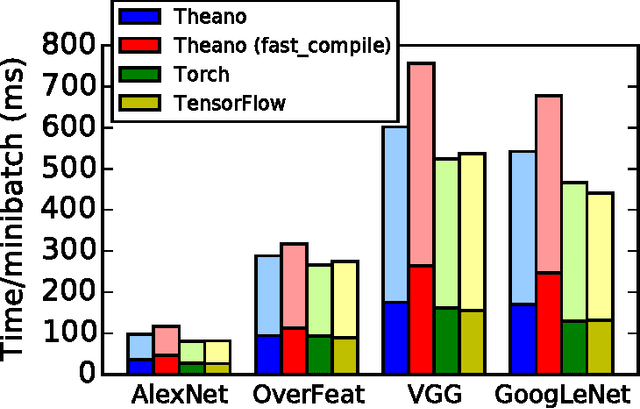
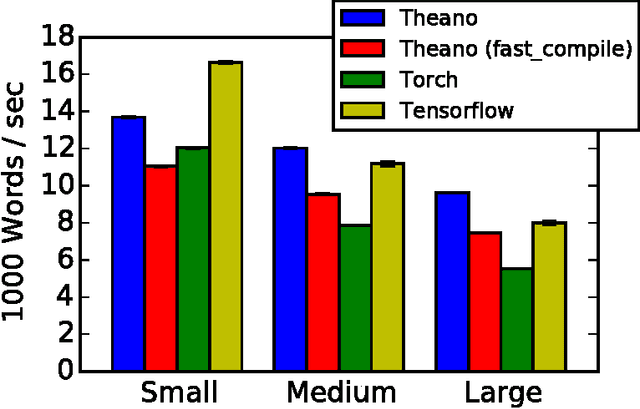
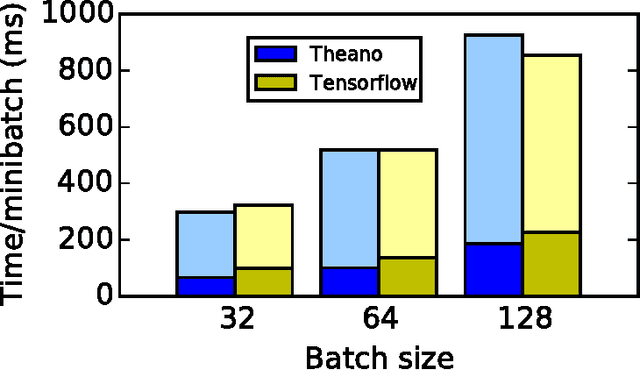
Abstract:Theano is a Python library that allows to define, optimize, and evaluate mathematical expressions involving multi-dimensional arrays efficiently. Since its introduction, it has been one of the most used CPU and GPU mathematical compilers - especially in the machine learning community - and has shown steady performance improvements. Theano is being actively and continuously developed since 2008, multiple frameworks have been built on top of it and it has been used to produce many state-of-the-art machine learning models. The present article is structured as follows. Section I provides an overview of the Theano software and its community. Section II presents the principal features of Theano and how to use them, and compares them with other similar projects. Section III focuses on recently-introduced functionalities and improvements. Section IV compares the performance of Theano against Torch7 and TensorFlow on several machine learning models. Section V discusses current limitations of Theano and potential ways of improving it.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge