Dzmitry Bahdanau
How to Get Your LLM to Generate Challenging Problems for Evaluation
Feb 20, 2025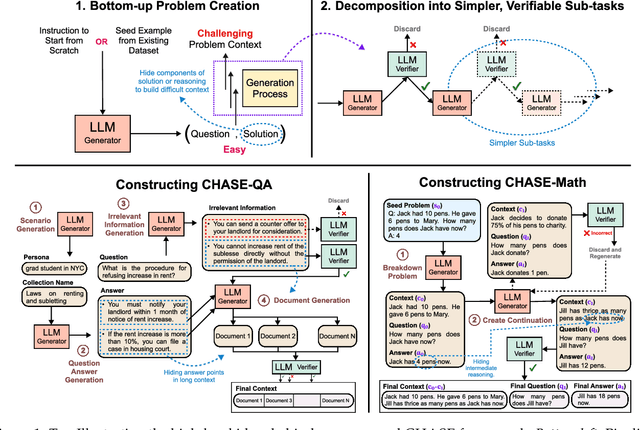

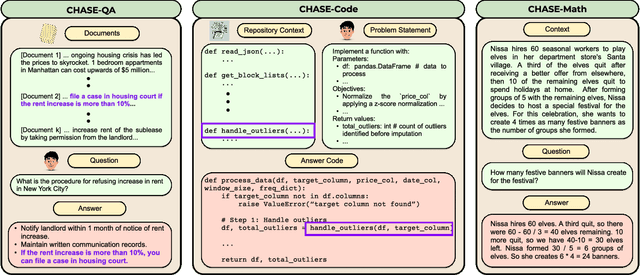

Abstract:The pace of evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) necessitates new approaches for rigorous and comprehensive evaluation. Traditional human annotation is increasingly impracticable due to the complexities and costs involved in generating high-quality, challenging problems. In this work, we introduce CHASE, a unified framework to synthetically generate challenging problems using LLMs without human involvement. For a given task, our approach builds a hard problem in a bottom-up manner from simpler components. Moreover, our framework decomposes the generation process into independently verifiable sub-tasks, thereby ensuring a high level of quality and correctness. We implement CHASE to create evaluation benchmarks across three diverse domains: (1) document-based question answering, (2) repository-level code completion, and (3) math reasoning. The performance of state-of-the-art LLMs on these synthetic benchmarks lies in the range of 40-60% accuracy, thereby demonstrating the effectiveness of our framework at generating challenging problems. We publicly release our benchmarks and code.
TapeAgents: a Holistic Framework for Agent Development and Optimization
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:We present TapeAgents, an agent framework built around a granular, structured log tape of the agent session that also plays the role of the session's resumable state. In TapeAgents we leverage tapes to facilitate all stages of the LLM Agent development lifecycle. The agent reasons by processing the tape and the LLM output to produce new thought and action steps and append them to the tape. The environment then reacts to the agent's actions by likewise appending observation steps to the tape. By virtue of this tape-centred design, TapeAgents can provide AI practitioners with holistic end-to-end support. At the development stage, tapes facilitate session persistence, agent auditing, and step-by-step debugging. Post-deployment, one can reuse tapes for evaluation, fine-tuning, and prompt-tuning; crucially, one can adapt tapes from other agents or use revised historical tapes. In this report, we explain the TapeAgents design in detail. We demonstrate possible applications of TapeAgents with several concrete examples of building monolithic agents and multi-agent teams, of optimizing agent prompts and finetuning the agent's LLM. We present tooling prototypes and report a case study where we use TapeAgents to finetune a Llama-3.1-8B form-filling assistant to perform as well as GPT-4o while being orders of magnitude cheaper. Lastly, our comparative analysis shows that TapeAgents's advantages over prior frameworks stem from our novel design of the LLM agent as a resumable, modular state machine with a structured configuration, that generates granular, structured logs and that can transform these logs into training text -- a unique combination of features absent in previous work.
NNetscape Navigator: Complex Demonstrations for Web Agents Without a Demonstrator
Oct 03, 2024



Abstract:We introduce NNetscape Navigator (NNetnav), a method for training web agents entirely through synthetic demonstrations. These demonstrations are collected by first interacting with a browser to generate trajectory rollouts, which are then retroactively labeled into instructions using a language model. Most work on training browser agents has relied on expensive human supervision, and the limited previous work on such interaction-first synthetic data techniques has failed to provide effective search through the exponential space of exploration. In contrast, NNetnav exploits the hierarchical structure of language instructions to make this search more tractable: complex instructions are typically decomposable into simpler subtasks, allowing NNetnav to automatically prune interaction episodes when an intermediate trajectory cannot be annotated with a meaningful sub-task. We use NNetnav demonstrations from a language model for supervised fine-tuning of a smaller language model policy, and find improvements of 6 points on WebArena and over 20 points on MiniWoB++, two popular environments for web-agents. Notably, on WebArena, we observe that language model policies can be further enhanced when fine-tuned with NNetnav demonstrations derived from the same language model. Finally, we collect and release a dataset of over 6k NNetnav demonstrations on WebArena, spanning a diverse and complex set of instructions.
LLMs can learn self-restraint through iterative self-reflection
May 15, 2024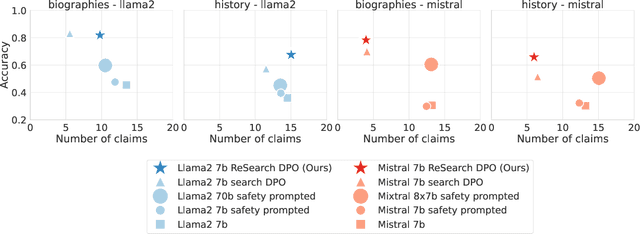

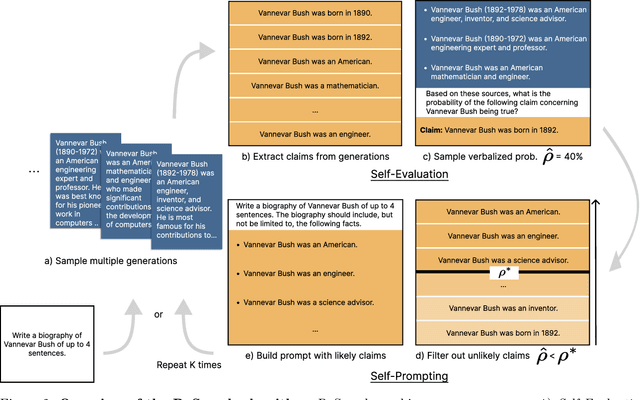

Abstract:In order to be deployed safely, Large Language Models (LLMs) must be capable of dynamically adapting their behavior based on their level of knowledge and uncertainty associated with specific topics. This adaptive behavior, which we refer to as self-restraint, is non-trivial to teach since it depends on the internal knowledge of an LLM. By default, LLMs are trained to maximize the next token likelihood, which does not teach the model to modulate its answer based on its level of uncertainty. In order to learn self-restraint, we devise a utility function that can encourage the model to produce responses only when it is confident in them. This utility function can be used to score generation of different length and abstention. To optimize this function, we introduce ReSearch, a process of ``self-reflection'' consisting of iterative self-prompting and self-evaluation. We use the ReSearch algorithm to generate synthetic data on which we finetune our models. Compared to their original versions, our resulting models generate fewer \emph{hallucinations} overall at no additional inference cost, for both known and unknown topics, as the model learns to selectively restrain itself. In addition, our method elegantly incorporates the ability to abstain by augmenting the samples generated by the model during the search procedure with an answer expressing abstention.
LLM2Vec: Large Language Models Are Secretly Powerful Text Encoders
Apr 09, 2024



Abstract:Large decoder-only language models (LLMs) are the state-of-the-art models on most of today's NLP tasks and benchmarks. Yet, the community is only slowly adopting these models for text embedding tasks, which require rich contextualized representations. In this work, we introduce LLM2Vec, a simple unsupervised approach that can transform any decoder-only LLM into a strong text encoder. LLM2Vec consists of three simple steps: 1) enabling bidirectional attention, 2) masked next token prediction, and 3) unsupervised contrastive learning. We demonstrate the effectiveness of LLM2Vec by applying it to 3 popular LLMs ranging from 1.3B to 7B parameters and evaluate the transformed models on English word- and sequence-level tasks. We outperform encoder-only models by a large margin on word-level tasks and reach a new unsupervised state-of-the-art performance on the Massive Text Embeddings Benchmark (MTEB). Moreover, when combining LLM2Vec with supervised contrastive learning, we achieve state-of-the-art performance on MTEB among models that train only on publicly available data. Our strong empirical results and extensive analysis demonstrate that LLMs can be effectively transformed into universal text encoders in a parameter-efficient manner without the need for expensive adaptation or synthetic GPT-4 generated data.
Evaluating In-Context Learning of Libraries for Code Generation
Nov 16, 2023Abstract:Contemporary Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit a high degree of code generation and comprehension capability. A particularly promising area is their ability to interpret code modules from unfamiliar libraries for solving user-instructed tasks. Recent work has shown that large proprietary LLMs can learn novel library usage in-context from demonstrations. These results raise several open questions: whether demonstrations of library usage is required, whether smaller (and more open) models also possess such capabilities, etc. In this work, we take a broader approach by systematically evaluating a diverse array of LLMs across three scenarios reflecting varying levels of domain specialization to understand their abilities and limitations in generating code based on libraries defined in-context. Our results show that even smaller open-source LLMs like Llama-2 and StarCoder demonstrate an adept understanding of novel code libraries based on specification presented in-context. Our findings further reveal that LLMs exhibit a surprisingly high proficiency in learning novel library modules even when provided with just natural language descriptions or raw code implementations of the functions, which are often cheaper to obtain than demonstrations. Overall, our results pave the way for harnessing LLMs in more adaptable and dynamic coding environments.
PromptMix: A Class Boundary Augmentation Method for Large Language Model Distillation
Oct 22, 2023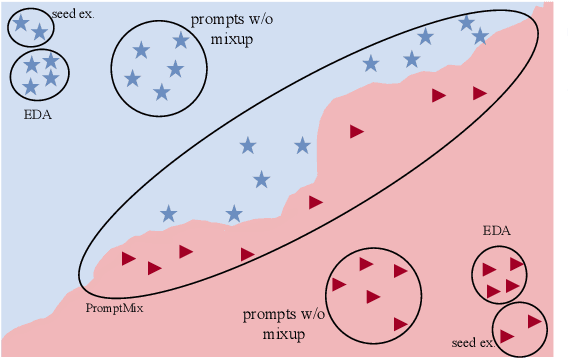
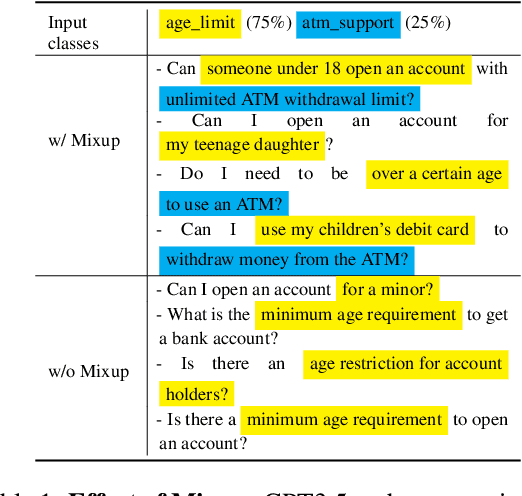
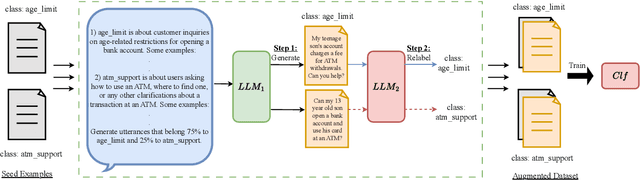
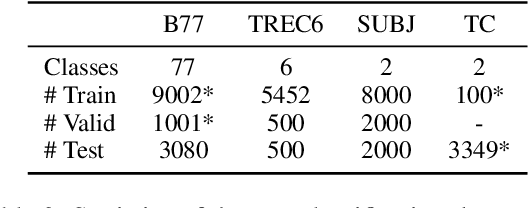
Abstract:Data augmentation is a widely used technique to address the problem of text classification when there is a limited amount of training data. Recent work often tackles this problem using large language models (LLMs) like GPT3 that can generate new examples given already available ones. In this work, we propose a method to generate more helpful augmented data by utilizing the LLM's abilities to follow instructions and perform few-shot classifications. Our specific PromptMix method consists of two steps: 1) generate challenging text augmentations near class boundaries; however, generating borderline examples increases the risk of false positives in the dataset, so we 2) relabel the text augmentations using a prompting-based LLM classifier to enhance the correctness of labels in the generated data. We evaluate the proposed method in challenging 2-shot and zero-shot settings on four text classification datasets: Banking77, TREC6, Subjectivity (SUBJ), and Twitter Complaints. Our experiments show that generating and, crucially, relabeling borderline examples facilitates the transfer of knowledge of a massive LLM like GPT3.5-turbo into smaller and cheaper classifiers like DistilBERT$_{base}$ and BERT$_{base}$. Furthermore, 2-shot PromptMix outperforms multiple 5-shot data augmentation methods on the four datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/ServiceNow/PromptMix-EMNLP-2023.
MAGNIFICo: Evaluating the In-Context Learning Ability of Large Language Models to Generalize to Novel Interpretations
Oct 18, 2023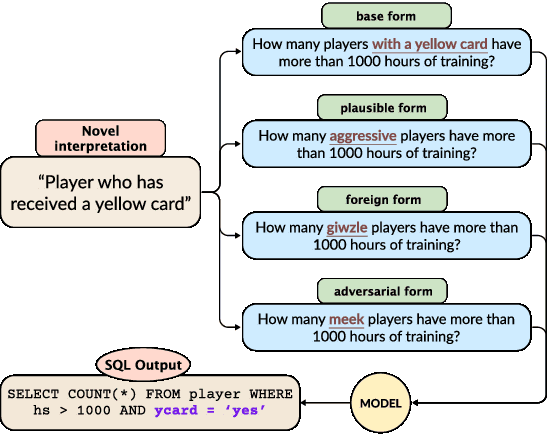
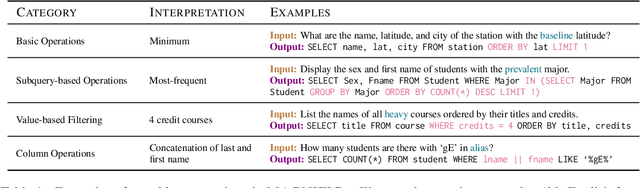
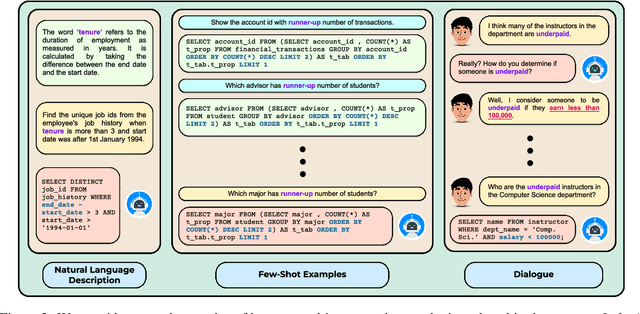
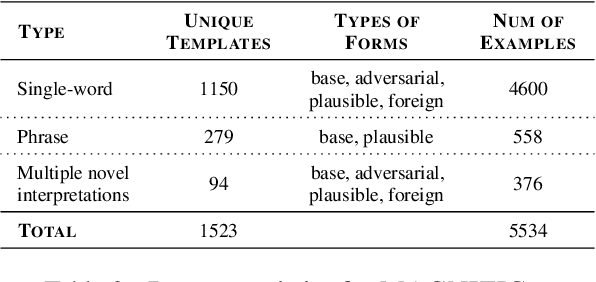
Abstract:Humans possess a remarkable ability to assign novel interpretations to linguistic expressions, enabling them to learn new words and understand community-specific connotations. However, Large Language Models (LLMs) have a knowledge cutoff and are costly to finetune repeatedly. Therefore, it is crucial for LLMs to learn novel interpretations in-context. In this paper, we systematically analyse the ability of LLMs to acquire novel interpretations using in-context learning. To facilitate our study, we introduce MAGNIFICo, an evaluation suite implemented within a text-to-SQL semantic parsing framework that incorporates diverse tokens and prompt settings to simulate real-world complexity. Experimental results on MAGNIFICo demonstrate that LLMs exhibit a surprisingly robust capacity for comprehending novel interpretations from natural language descriptions as well as from discussions within long conversations. Nevertheless, our findings also highlight the need for further improvements, particularly when interpreting unfamiliar words or when composing multiple novel interpretations simultaneously in the same example. Additionally, our analysis uncovers the semantic predispositions in LLMs and reveals the impact of recency bias for information presented in long contexts.
In-Context Learning for Text Classification with Many Labels
Sep 19, 2023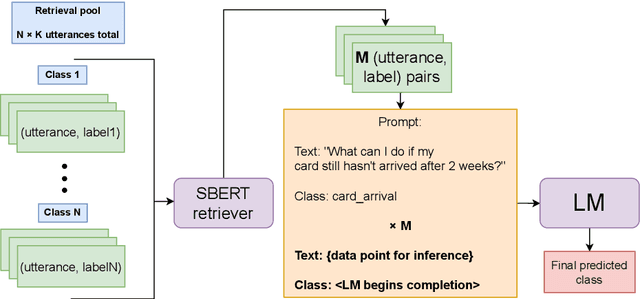



Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) using large language models for tasks with many labels is challenging due to the limited context window, which makes it difficult to fit a sufficient number of examples in the prompt. In this paper, we use a pre-trained dense retrieval model to bypass this limitation, giving the model only a partial view of the full label space for each inference call. Testing with recent open-source LLMs (OPT, LLaMA), we set new state of the art performance in few-shot settings for three common intent classification datasets, with no finetuning. We also surpass fine-tuned performance on fine-grained sentiment classification in certain cases. We analyze the performance across number of in-context examples and different model scales, showing that larger models are necessary to effectively and consistently make use of larger context lengths for ICL. By running several ablations, we analyze the model's use of: a) the similarity of the in-context examples to the current input, b) the semantic content of the class names, and c) the correct correspondence between examples and labels. We demonstrate that all three are needed to varying degrees depending on the domain, contrary to certain recent works.
RepoFusion: Training Code Models to Understand Your Repository
Jun 19, 2023



Abstract:Despite the huge success of Large Language Models (LLMs) in coding assistants like GitHub Copilot, these models struggle to understand the context present in the repository (e.g., imports, parent classes, files with similar names, etc.), thereby producing inaccurate code completions. This effect is more pronounced when using these assistants for repositories that the model has not seen during training, such as proprietary software or work-in-progress code projects. Recent work has shown the promise of using context from the repository during inference. In this work, we extend this idea and propose RepoFusion, a framework to train models to incorporate relevant repository context. Experiments on single-line code completion show that our models trained with repository context significantly outperform much larger code models as CodeGen-16B-multi ($\sim73\times$ larger) and closely match the performance of the $\sim 70\times$ larger StarCoderBase model that was trained with the Fill-in-the-Middle objective. We find these results to be a novel and compelling demonstration of the gains that training with repository context can bring. We carry out extensive ablation studies to investigate the impact of design choices such as context type, number of contexts, context length, and initialization within our framework. Lastly, we release Stack-Repo, a dataset of 200 Java repositories with permissive licenses and near-deduplicated files that are augmented with three types of repository contexts. Additionally, we are making available the code and trained checkpoints for our work. Our released resources can be found at \url{https://huggingface.co/RepoFusion}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge