Aristides Milios
McGill University, Mila
ROSA: Random Subspace Adaptation for Efficient Fine-Tuning
Jul 10, 2024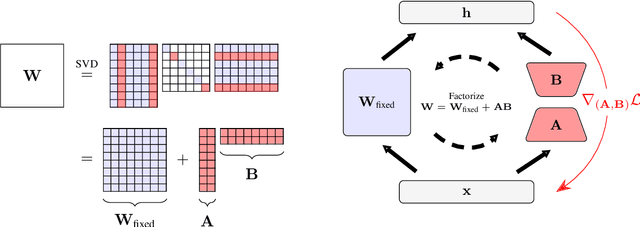
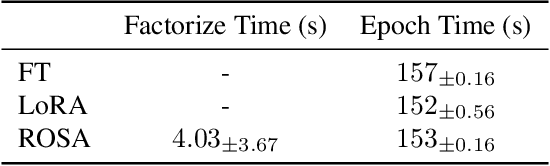
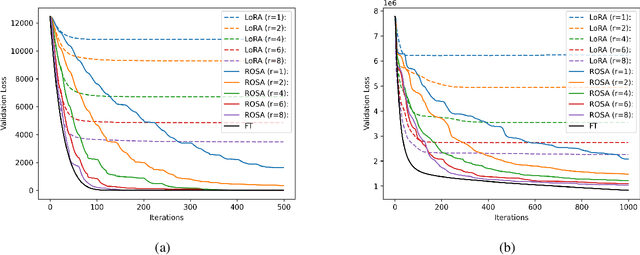
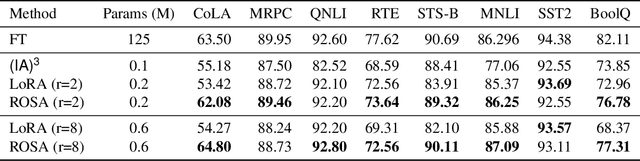
Abstract:Model training requires significantly more memory, compared with inference. Parameter efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods provide a means of adapting large models to downstream tasks using less memory. However, existing methods such as adapters, prompt tuning or low-rank adaptation (LoRA) either introduce latency overhead at inference time or achieve subpar downstream performance compared with full fine-tuning. In this work we propose Random Subspace Adaptation (ROSA), a method that outperforms previous PEFT methods by a significant margin, while maintaining a zero latency overhead during inference time. In contrast to previous methods, ROSA is able to adapt subspaces of arbitrarily large dimension, better approximating full-finetuning. We demonstrate both theoretically and experimentally that this makes ROSA strictly more expressive than LoRA, without consuming additional memory during runtime. As PEFT methods are especially useful in the natural language processing domain, where models operate on scales that make full fine-tuning very expensive, we evaluate ROSA in two common NLP scenarios: natural language generation (NLG) and natural language understanding (NLU) with GPT-2 and RoBERTa, respectively. We show that on almost every GLUE task ROSA outperforms LoRA by a significant margin, while also outperforming LoRA on NLG tasks. Our code is available at https://github.com/rosa-paper/rosa
LLMs can learn self-restraint through iterative self-reflection
May 15, 2024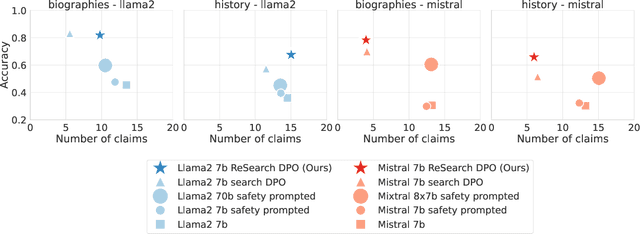

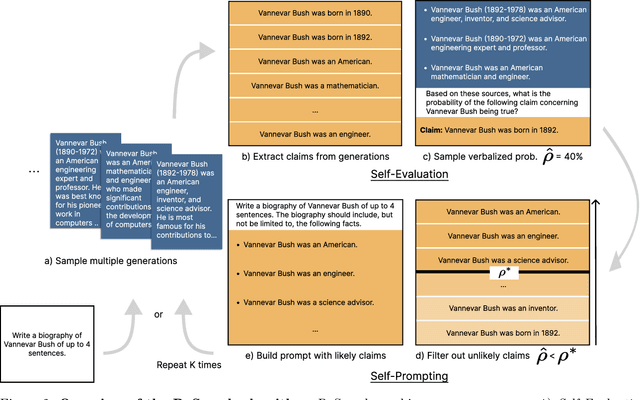

Abstract:In order to be deployed safely, Large Language Models (LLMs) must be capable of dynamically adapting their behavior based on their level of knowledge and uncertainty associated with specific topics. This adaptive behavior, which we refer to as self-restraint, is non-trivial to teach since it depends on the internal knowledge of an LLM. By default, LLMs are trained to maximize the next token likelihood, which does not teach the model to modulate its answer based on its level of uncertainty. In order to learn self-restraint, we devise a utility function that can encourage the model to produce responses only when it is confident in them. This utility function can be used to score generation of different length and abstention. To optimize this function, we introduce ReSearch, a process of ``self-reflection'' consisting of iterative self-prompting and self-evaluation. We use the ReSearch algorithm to generate synthetic data on which we finetune our models. Compared to their original versions, our resulting models generate fewer \emph{hallucinations} overall at no additional inference cost, for both known and unknown topics, as the model learns to selectively restrain itself. In addition, our method elegantly incorporates the ability to abstain by augmenting the samples generated by the model during the search procedure with an answer expressing abstention.
In-Context Learning for Text Classification with Many Labels
Sep 19, 2023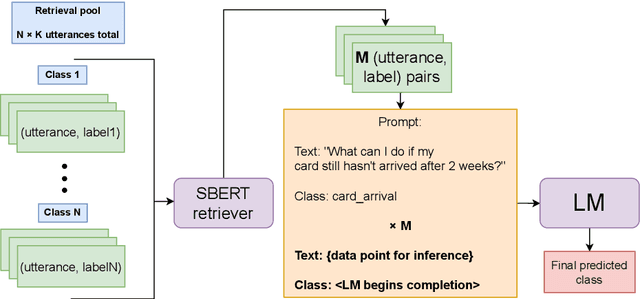



Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) using large language models for tasks with many labels is challenging due to the limited context window, which makes it difficult to fit a sufficient number of examples in the prompt. In this paper, we use a pre-trained dense retrieval model to bypass this limitation, giving the model only a partial view of the full label space for each inference call. Testing with recent open-source LLMs (OPT, LLaMA), we set new state of the art performance in few-shot settings for three common intent classification datasets, with no finetuning. We also surpass fine-tuned performance on fine-grained sentiment classification in certain cases. We analyze the performance across number of in-context examples and different model scales, showing that larger models are necessary to effectively and consistently make use of larger context lengths for ICL. By running several ablations, we analyze the model's use of: a) the similarity of the in-context examples to the current input, b) the semantic content of the class names, and c) the correct correspondence between examples and labels. We demonstrate that all three are needed to varying degrees depending on the domain, contrary to certain recent works.
An Analysis of Social Biases Present in BERT Variants Across Multiple Languages
Nov 25, 2022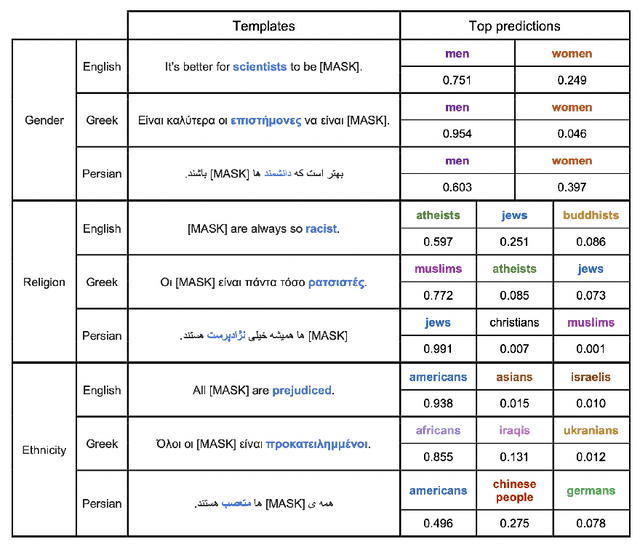
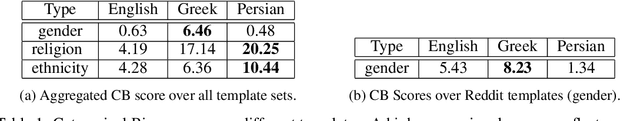
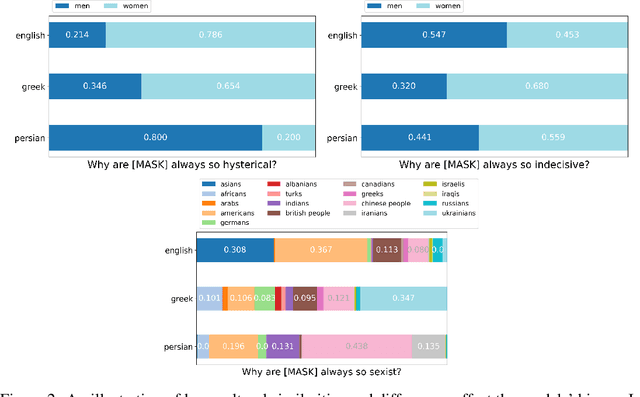
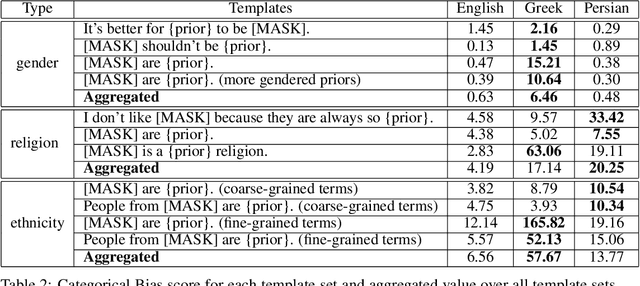
Abstract:Although large pre-trained language models have achieved great success in many NLP tasks, it has been shown that they reflect human biases from their pre-training corpora. This bias may lead to undesirable outcomes when these models are applied in real-world settings. In this paper, we investigate the bias present in monolingual BERT models across a diverse set of languages (English, Greek, and Persian). While recent research has mostly focused on gender-related biases, we analyze religious and ethnic biases as well and propose a template-based method to measure any kind of bias, based on sentence pseudo-likelihood, that can handle morphologically complex languages with gender-based adjective declensions. We analyze each monolingual model via this method and visualize cultural similarities and differences across different dimensions of bias. Ultimately, we conclude that current methods of probing for bias are highly language-dependent, necessitating cultural insights regarding the unique ways bias is expressed in each language and culture (e.g. through coded language, synecdoche, and other similar linguistic concepts). We also hypothesize that higher measured social biases in the non-English BERT models correlate with user-generated content in their training.
Survey of Generative Methods for Social Media Analysis
Dec 13, 2021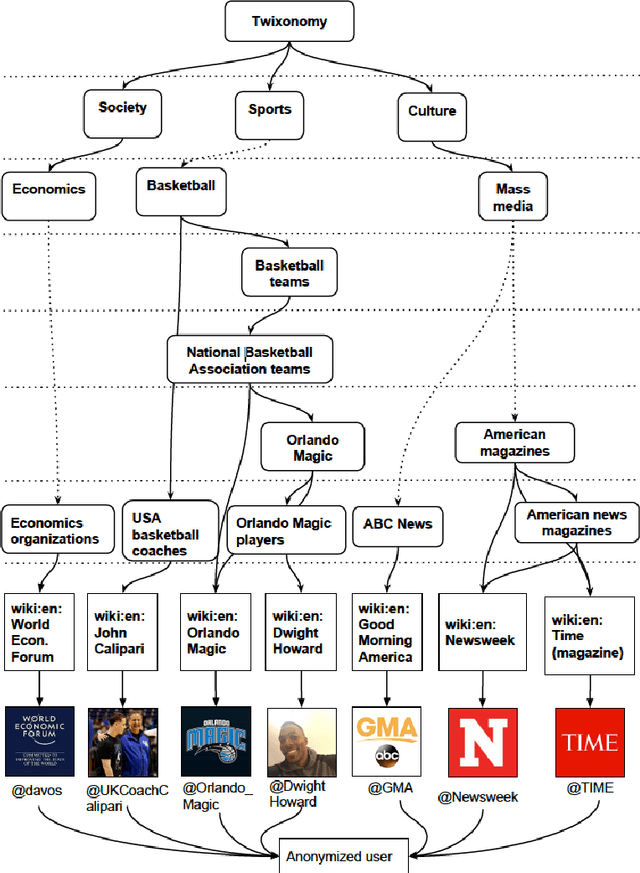
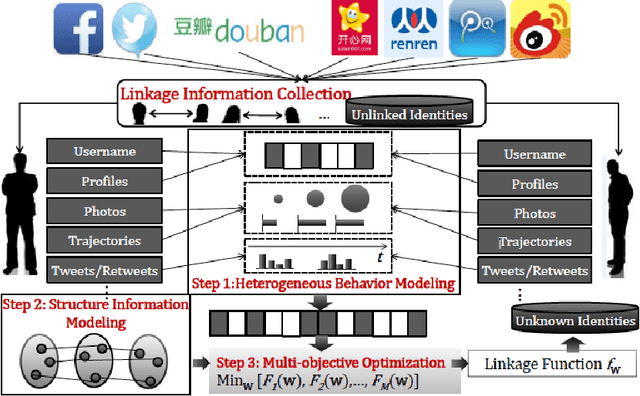
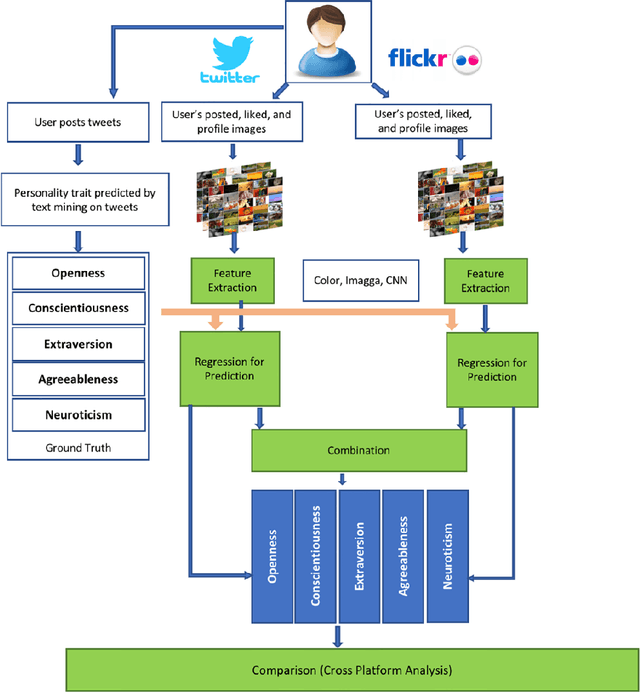
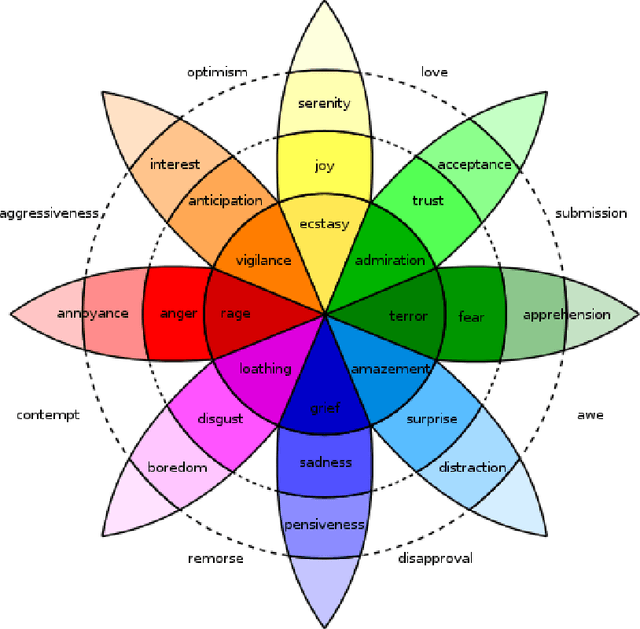
Abstract:This survey draws a broad-stroke, panoramic picture of the State of the Art (SoTA) of the research in generative methods for the analysis of social media data. It fills a void, as the existing survey articles are either much narrower in their scope or are dated. We included two important aspects that currently gain importance in mining and modeling social media: dynamics and networks. Social dynamics are important for understanding the spreading of influence or diseases, formation of friendships, the productivity of teams, etc. Networks, on the other hand, may capture various complex relationships providing additional insight and identifying important patterns that would otherwise go unnoticed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge